SLIMbus: Difference between revisions
→Subframe: Explained size limits. |
m Task 18 (cosmetic): eval 8 templates: hyphenate params (7×); |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{multiple issues| |
{{multiple issues|{{more footnotes|date=January 2013}} |
||
{{more citations needed|date=January 2013}}}} |
|||
The '''Serial Low-power Inter-chip Media Bus (SLIMbus℠)''' is a standard interface between baseband or application processors and peripheral components in mobile terminals. It was developed within the [[Mobile Industry Processor Interface|MIPI® Alliance]], founded by ARM, Nokia, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments.<ref name=merritt>{{cite web|last=Merritt|first=Rick|title=Mobile chip interface gets real|url=http://eetimes.com/electronics-news/4058490/Mobile-chip-interface-gets-real|work=EETimes|accessdate=17 January 2013|date=13 February 2006}}</ref> The interface supports many digital audio components simultaneously, and carries multiple digital audio data streams at differing sample rates and bit widths. |
|||
The '''Serial Low-power Inter-chip Media Bus''' ('''SLIMbus''') is a standard interface between baseband or application processors and peripheral components in mobile terminals. It was developed within the [[MIPI Alliance]], founded by [[Arm Holdings|ARM]], [[Nokia]], [[STMicroelectronics]] and [[Texas Instruments]].<ref name=merritt>{{cite web|last=Merritt|first=Rick|title=Mobile chip interface gets real|url=http://eetimes.com/electronics-news/4058490/Mobile-chip-interface-gets-real|work=EETimes|access-date=17 January 2013|date=13 February 2006}}</ref> The interface supports many [[digital audio]] components simultaneously, and carries multiple digital audio data streams at differing sample rates and bit widths. |
|||
SLIMbus is implemented as a synchronous 2-wire, configurable Time Division Multiplexed (TDM) frame structure. It has supporting bus arbitration mechanisms and message structures which permit re-configuring the bus operational characteristics to system application needs at runtime. Physically, the data line (DATA) and the clock line (CLK) interconnect multiple SLIMbus components in a multi-drop bus topology. SLIMbus devices may dynamically “drop off” the bus and “reconnect” to the bus as required by using appropriate protocols outlined in the SLIMbus specification. |
|||
When used in a mobile terminal or portable product, SLIMbus may replace legacy digital audio interfaces such as PCM, I<sup>2</sup>S,<ref>{{cite web|title=I2S bus specification|url=http://www.classic.nxp.com/acrobat_download2/various/I2SBUS.pdf|publisher=Philips Semiconductors|accessdate=17 January 2013}}</ref> and SSI (Synchronous Serial Interface for digital audio), as well as some instances of many digital control buses such as I<sup>2</sup>C,<ref>{{cite web|title=The I2C-Bus Specification|url=http://www.classic.nxp.com/acrobat_download2/literature/9398/39340011.pdf|publisher=Philips Semiconductors|accessdate=17 January 2013|month=January|year=2000}}</ref> SPI, microWire,<ref>{{cite web|title=AN-452 MICROWIRE Serial Interface|url=http://www.ti.com/lit/an/snoa743/snoa743.pdf|publisher=Texas Instruments|accessdate=17 January 2013}}</ref> UART, or GPIO pins on the digital audio components. |
|||
SLIMbus is implemented as a synchronous 2-wire, configurable [[Time-division multiplexing|Time Division Multiplexed]] (TDM) frame structure. It has supporting bus arbitration mechanisms and message structures which permit re-configuring the bus operational characteristics to system application needs at runtime. Physically, the data line (DATA) and the clock line (CLK) interconnect multiple SLIMbus components in a [[Multidrop bus|multi-drop bus]] topology. SLIMbus devices may dynamically “drop off” the bus and “reconnect” to the bus as required by using appropriate protocols outlined in the SLIMbus specification. When used in a mobile terminal or portable product, SLIMbus may replace legacy digital audio interfaces such as [[Pulse-code modulation|PCM]], [[I²S|I<sup>2</sup>S]],<ref>{{cite web|title=I2S bus specification|url=http://www.classic.nxp.com/acrobat_download2/various/I2SBUS.pdf|publisher=Philips Semiconductors|access-date=17 January 2013}}</ref> and [[Synchronous Serial Interface|SSI]] (Synchronous Serial Interface for digital audio), as well as some instances of many digital control buses such as I<sup>2</sup>C,<ref>{{cite web|title=The I2C-Bus Specification|url=http://www.classic.nxp.com/acrobat_download2/literature/9398/39340011.pdf|publisher=Philips Semiconductors|access-date=17 January 2013|date=January 2000}}</ref> SPI, [[Serial Peripheral Interface|microWire]],<ref>{{cite web|title=AN-452 MICROWIRE Serial Interface|url=http://www.ti.com/lit/an/snoa743/snoa743.pdf|publisher=Texas Instruments|access-date=17 January 2013}}</ref> [[Universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter|UART]], or [[General-purpose input/output|GPIO]] pins on the digital audio components. |
|||
== History == |
== History == |
||
*The MIPI Alliance was formed in fall of 2003. |
*The [[MIPI Alliance]] was formed in fall of 2003. |
||
* Interface architecture including a low speed media link bus (LowML) presented at the F2F meeting of MIPI Alliance in Sophia Antipolis, France in March, 2004. |
* Interface architecture including a low speed media link bus (LowML) presented at the F2F meeting of MIPI Alliance in [[Sophia Antipolis]], France in March, 2004. |
||
* LML Investigation Group (LML-IG) created in July 2004 by the MIPI Alliance. |
* LML Investigation Group (LML-IG) created in July 2004 by the MIPI Alliance. First meeting was a teleconference on August 3, 2004. |
||
* LML Working Group (LML-WG) created in Q4 2004. LML WG Charter submitted to the MIPI Board in December, 2004. |
* LML Working Group (LML-WG) created in Q4 2004. LML WG Charter submitted to the MIPI Board in December, 2004. |
||
*First meeting as a full Working Group on |
*First meeting as a full Working Group on April 12, 2005. |
||
* LML-WG released first draft of SLIMbus with text in all chapters (v0.55) on |
* LML-WG released first draft of SLIMbus with text in all chapters (v0.55) on October 18, 2005. |
||
* SLIMbus specification v1.00 was released to adopters on |
* SLIMbus specification v1.00 was released to adopters on May 16, 2007. |
||
* From June 2007 to June 2008, SLIMbus specification improvement (ambiguities, typos & bugs fixed) based on implementer feed-back. |
* From June 2007 to June 2008, SLIMbus specification improvement (ambiguities, typos & bugs fixed) based on implementer feed-back. |
||
* SLIMbus specification V1.01 was released to adopters on |
* SLIMbus specification V1.01 was released to adopters on December 3, 2008 and is recommended for implementation. |
||
== SLIMbus Devices and Device Classes == |
== SLIMbus Devices and Device Classes == |
||
SLIMbus Device Class definitions are those which specify the minimum requirements for Device control data, Device behavior, and data Transport Protocol support. |
SLIMbus Device Class definitions are those which specify the minimum requirements for Device control data, Device behavior, and data Transport Protocol support. There are four SLIMbus Device Classes defined at the release of Version 1.01 of the SLIMbus specification: Manager, Framer, Interface, and Generic. Complete SLIMbus systems can be implemented without any additional Device Classes. |
||
There are four SLIMbus Device Classes defined at the release of Version 1.01 of the SLIMbus specification: Manager, Framer, Interface, and Generic. Complete SLIMbus systems can be implemented without any additional Device Classes. |
|||
===Manager Device=== |
===Manager Device=== |
||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
===Framer Device=== |
===Framer Device=== |
||
The Framer delivers a clock signal on the CLK line to all SLIMbus Components, and also contains logic to transmit the Frame Sync and Framing Information channels on the DATA line. |
The Framer delivers a [[clock signal]] on the CLK line to all SLIMbus Components, and also contains logic to transmit the Frame Sync and Framing Information channels on the DATA line. |
||
===Interface Device=== |
===Interface Device=== |
||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
The Interface Device provides bus management services, monitors the Physical Layer for errors, reports information about the status of a SLIMbus Component, and otherwise manages the Component such that the Devices within it will function properly on the bus. |
The Interface Device provides bus management services, monitors the Physical Layer for errors, reports information about the status of a SLIMbus Component, and otherwise manages the Component such that the Devices within it will function properly on the bus. |
||
To implement a functional SLIMbus component always requires the use of a SLIMbus Interface Device, plus the function to be performed, such as DAC, ADC, digital amplifier, and so on. |
To implement a functional SLIMbus component always requires the use of a SLIMbus Interface Device, plus the function to be performed, such as DAC, ADC, [[Class-D amplifier|digital amplifier]], and so on. |
||
===Generic Device (Function)=== |
===Generic Device (Function)=== |
||
A Generic Device is a Device other than a Manager, Framer, or Interface. |
A Generic Device is a Device other than a Manager, Framer, or Interface. A Generic Device is generally considered to be the device to provide certain application functionality, for example, conversion from digital audio to analog (DAC) and vice versa (ADC). |
||
== SLIMbus Component == |
== SLIMbus Component == |
||
A SLIMbus Component contains two or more SLIMbus Devices. |
A SLIMbus Component contains two or more SLIMbus Devices. A SLIMbus Component will have only one SLIMbus Interface Device (INTERFACE), and may have one or more other types of SLIMbus devices which perform a particular function (FUNCTION). |
||
A SLIMbus Port (P) provides the connection path for data flow between Devices. SLIMbus Ports are normally used for digital audio data flow, but may also be used for other digital data flow. |
A SLIMbus Port (P) provides the connection path for data flow between Devices. SLIMbus Ports are normally used for digital audio data flow, but may also be used for other digital data flow. |
||
Port capabilities vary depending upon the Device and are to be specified in the Component data sheet. Typical Port attributes include data direction, i.e. input-only (sink), output-only (source) or both input and output, supported Transport Protocols, and data width. |
Port capabilities vary depending upon the Device and are to be specified in the Component data sheet. Typical Port attributes include data direction, i.e. input-only (sink), output-only (source) or both input and output, supported Transport Protocols, and data width. |
||
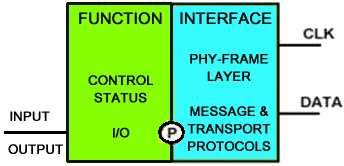
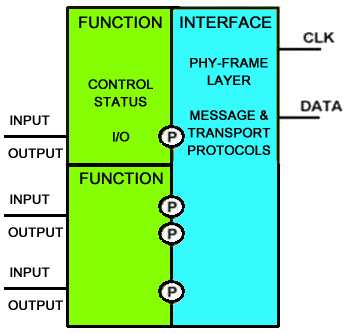
A simple SLIMbus Component example is shown in Figure 1 below, and a complex SLIMbus Component example is shown in Figure 2 below. |
A simple SLIMbus Component example is shown in Figure 1 below, and a complex SLIMbus Component example is shown in Figure 2 below. |
||
{{center| |
|||
[[ |
[[File:SLIMbusSimpleComponent.jpg|Simple SLIMbus Component]] |
||
{{center|Figure 1: Simple SLIMbus Component}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{center| |
|||
Figure 1: Simple SLIMbus Component |
|||
[[File:SLIMbusComplexComponent.jpg|Complex SLIMbus Component]] |
|||
{{center|Figure 2: Complex SLIMbus Component}} |
|||
}} |
|||
Figure 2: Complex SLIMbus Component |
|||
</center> |
|||
== SLIMbus DATA and CLK== |
== SLIMbus DATA and CLK== |
||
All SLIMbus Devices use DATA and CLK to synchronize with the bus configuration in use, to receive or transmit messages and data, and to implement bus arbitration, collision detection, and contention resolution between devices. |
All SLIMbus Devices use DATA and CLK to synchronize with the bus configuration in use, to receive or transmit messages and data, and to implement bus arbitration, [[collision detection]], and contention resolution between devices. |
||
For all SLIMbus Components (except one containing a Framer Device), the CLK terminal is input only. |
For all SLIMbus Components (except one containing a Framer Device), the CLK terminal is input only. If a SLIMbus Component is the Framer Device, or contains a Framer Device, the CLK signal is bi-directional. |
||
For all SLIMbus Components, the DATA line is bidirectional, and carries all information sent or received on the bus using Non-Return-to-Zero Inverted (NRZI) encoding. |
For all SLIMbus Components, the DATA line is bidirectional, and carries all information sent or received on the bus using [[Non-return-to-zero|Non-Return-to-Zero Inverted]] (NRZI) encoding. |
||
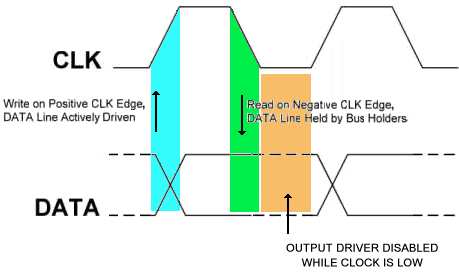
The DATA line is driven on the positive edge and read on the negative edge of the CLK line. The DATA line can be driven high, driven low, or held at the high or low level by an internal [[bus-holder]] circuit, depending upon the particular operational mode of a SLIMbus Device. |
The DATA line is driven on the positive edge and read on the negative edge of the CLK line. The DATA line can be driven high, driven low, or held at the high or low level by an internal [[bus-holder]] circuit, depending upon the particular operational mode of a SLIMbus Device. |
||
The SLIMbus interface DATA and CLK lines use CMOS-like single-ended, ground referenced, rail-to-rail, voltage mode signals, and signaling voltages are specified with respect to the interface supply voltage (+1.8Vdd or +1.2Vdd are permitted). |
The SLIMbus interface DATA and CLK lines use [[CMOS]]-like single-ended, ground referenced, rail-to-rail, voltage mode signals, and signaling voltages are specified with respect to the interface supply voltage (+1.8Vdd or +1.2Vdd are permitted). For EMI performance reasons, slew rate limits have been specified for SLIMbus. |
||
===SLIMbus Clock Frequencies and Gears=== |
===SLIMbus Clock Frequencies and Gears=== |
||
The SLIMbus CLK line frequency is determined by a range of "Root" clock frequencies up to 28 MHz, and 10 Clock Gears for altering the clock frequency by powers of 2 over a span of 512x from lowest to highest Gear. |
The SLIMbus CLK line frequency is determined by a range of "Root" clock frequencies up to 28 MHz, and 10 Clock Gears for altering the clock frequency by powers of 2 over a span of 512x from lowest to highest Gear. The Root Frequency is defined as 2<sup>(10-G)</sup> times the frequency of the CLK line. For G=10, the CLK line frequency and Root Frequency are equal. |
||
The SLIMbus CLK may also be stopped and restarted. |
The SLIMbus CLK may also be stopped and restarted. |
||
| Line 89: | Line 88: | ||
A Cell is defined as a region of the DATA signal that is bounded by two consecutive positive edges of the CLK line and holds a single bit of information. |
A Cell is defined as a region of the DATA signal that is bounded by two consecutive positive edges of the CLK line and holds a single bit of information. |
||
{{center| |
|||
[[ |
[[File:SLIMbusCell.jpg|Cell Structure]] |
||
{{center|Figure 3: Cell Structure}} |
|||
}} |
|||
Figure 3: Cell Structure |
|||
</center> |
|||
===Slot=== |
===Slot=== |
||
A Slot is defined as four contiguous Cells (4-bits transmitted in MSB to LSB order). |
A Slot is defined as four contiguous Cells (4-bits transmitted in MSB to LSB order). Bandwidth allocation for various data organizations, from 4-bits to 32-bits or more, can be done by grouping 4-bit Slots. |
||
===Frame=== |
===Frame=== |
||
A Frame is defined as 192 (0 through 191) contiguous Slots and are transmitted as S0, followed by S1, S2 |
A Frame is defined as 192 (0 through 191) contiguous Slots and are transmitted as S0, followed by S1, S2 ... S191 in that order. The first Slot (Slot 0) of each Frame is a Control Space slot which contains the four (4) bit Frame Sync symbol. Slot S96 of each Frame is also a Control Space slot which contains four (4) bits of Framing Information. |
||
The active Framer writes all Framing Information to the Data line at the appropriate time. |
The active Framer writes all Framing Information to the Data line at the appropriate time. |
||
| Line 107: | Line 105: | ||
===Subframe=== |
===Subframe=== |
||
A Subframe is defined as the division of the Frame Structure at which Control Space and Data Space are interleaved. |
A Subframe is defined as the division of the Frame Structure at which Control Space and Data Space are [[Forward error correction|interleaved]]. A Subframe is partitioned into 1 or more slots of Control Space, followed by 0 or more slots of Data Space. |
||
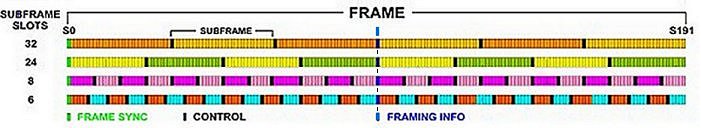
As shown in Figure 4 below, the Subframe length is programmable to 6, 8, 24 or 32 contiguous Slots (24, 32, 96 or 128 Cells). The number of possible Subframes per Frame is therefore 32, 24, 8, or 6 respectively. |
As shown in Figure 4 below, the Subframe length is programmable to 6, 8, 24 or 32 contiguous Slots (24, 32, 96 or 128 Cells). The number of possible Subframes per Frame is therefore 32, 24, 8, or 6 respectively. The Subframe configuration used can be dynamically changed depending upon the data flow requirements of the applications being supported at the time. |
||
{{center| |
|||
[[ |
[[File:SLIMbusCellSlotFrameStructure.jpg|Cell, Slot, Subframe, Frame Structure]] |
||
{{center|Figure 4: Cell, Slot, Subframe, Frame Structure}} |
|||
}} |
|||
4 of the Control space slots are reserved for a frame sync symbol, 4 bits if a Framing Information word, and 8 bits of Guide Byte. The remainder is available for more general control messages. |
|||
Figure 4: Cell, Slot, Subframe, Frame Structure |
|||
</center> |
|||
4 of the Control space slots are reserved for a frame sync symbol, 4 bits if a Framing Information word, and 8 bits of Guide Byte. The remainder is available for more general control messages. |
|||
Any Slots not allocated to Control Space are considered Data Space. |
Any Slots not allocated to Control Space are considered Data Space. |
||
| Line 125: | Line 122: | ||
A Superframe is defined as eight contiguous Frames (1536 Slots). Frames within a Superframe are labeled Frame 0 through Frame 7. |
A Superframe is defined as eight contiguous Frames (1536 Slots). Frames within a Superframe are labeled Frame 0 through Frame 7. |
||
The duration of a Superframe is fixed in terms of Slots (and, therefore, Cells), but not in terms of time. |
The duration of a Superframe is fixed in terms of Slots (and, therefore, Cells), but not in terms of time. The Superframe rate can be dynamically changed on SLIMbus to suit the particular application by changing either SLIMbus Root Frequency or Clock Gear, or both. |
||
== Channels == |
== Channels == |
||
Information on the SLIMbus DATA line is allocated to Control Space and Data Space channels. |
Information on the SLIMbus DATA line is allocated to Control Space and Data Space channels. |
||
The Control Space carries bus configuration and synchronization information as well as inter-Device Message communication. |
The Control Space carries bus configuration and synchronization information as well as inter-Device Message communication. The Control Space may be dynamically programmed to take as much of the SLIMbus bandwidth as required, even up to 100% at times. |
||
Data Space, when present, carries application-specific information such as isochronous |
Data Space, when present, carries application-specific information such as [[Isochronous timing|isochronous]] and [[Data transmission|asynchronous data]] streams. |
||
SLIMbus Components convey control and data information between each other using Control and Data Channels with Transport Protocols to achieve the required system operation. |
SLIMbus Components convey control and data information between each other using Control and Data Channels with Transport Protocols to achieve the required system operation. Messages are used for Control functions. |
||
Channels can be established between a pair of Devices (inter-Device communication), or between one Device and many Devices (broadcast communication), or in the case of the Message Channel, from all devices to all other devices (shared). |
Channels can be established between a pair of Devices (inter-Device communication), or between one Device and many Devices (broadcast communication), or in the case of the Message Channel, from all devices to all other devices (shared). |
||
| Line 141: | Line 138: | ||
===Control Channels=== |
===Control Channels=== |
||
Control Space is divided into three types of channels: Framing, Guide, and Message. |
|||
*The Framing Channel carries a Frame Sync symbol and Framing Information (bus configuration parameters) in two (2) Slots (fixed channel width) of each Frame. |
|||
The Framing Channel occupies Slots 0 and 96 of each Frame. (Since all Subframe lengths divide 96, these Slots are always available for the purpose.) Slot 0 holds a fixed Frame Sync symbol (1011<sub>2</sub>), while Slot 96 holds 4 bits of a Framing Information word. Over the course of a Superframe, 32 bits of Framing Information are available. Some of these hold a fixed bit pattern used to acquire Superframe synchronization (0''x''011''xxx''<sub>2</sub>), while the others hold other critical configuration information. |
|||
*The Guide Channel is carried in the first two (2) Slots (fixed channel width) allocated to Control Channels and displaces the Message Channel, and is used to acquire and verify Message synchronization in the Message Channel. |
|||
The Guide Channel consists of the first 2 non-Framing control Slots in each Superframe. This "guide byte" is normally 0, but if a control message straddles a Superframe boundary, it indicates the number of bytes until the end of that message. |
|||
*The Message Channel is a programmable width channel that carries various types of information including bus configuration announcements, Device control and Device status. |
|||
The Message Channel consists of all remaining Slots. It carries various types of information including bus configuration announcements, Device control and Device status. |
|||
The format of Control Space is determined by a 5-bit Subframe mode identifier transmitted in the Framing Information word. This communicates the Subframe length and the number of control Slots. The number of control Slots is limited to the choices of 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, or 24. Adding the limitations that the number of control Slots must be less than the Subframe length produces 26 valid combinations. A special encoding for "100% Control Space", in which case the Subframe length is unimportant, produces 27 valid modes. (Modes 1–3, 20 and 30 are not valid.) |
|||
===Data Channels=== |
===Data Channels=== |
||
Data Channels are one or more contiguous Data Slots (Segments) and are dynamically created by the active Manager depending on the application and size of Data Space available. A Data Channel, and therefore the structure of a Segment, is defined by parameters such as Data rate, type, field length, and required Transport Protocol. |
Data Channels are one or more contiguous Data Slots (Segments) and are dynamically created by the active Manager depending on the application and size of Data Space available. A Data Channel, and therefore the structure of a Segment, is defined by parameters such as Data rate, type, field length, and required Transport Protocol. |
||
Segments repeat at known intervals and behave as virtual bus's with their own bandwidth guarantee and latency. |
|||
Segments repeat at known intervals and behave as virtual bus's with their own bandwidth guarantee and latency. |
|||
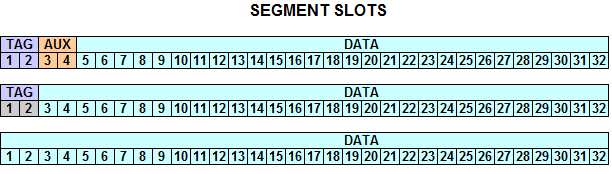
A Segment, shown below in Figure 5, has TAG (2 Slots), AUX (2 Slots), and DATA fields. The TAG and AUX fields are optional. If used, the TAG bits carry flow control information for the data channel, while the auxiliary (AUX) bits carry side information relating to the content of the DATA field. The data payload may or may not fill the entire allotted DATA field. |
A Segment, shown below in Figure 5, has TAG (2 Slots), AUX (2 Slots), and DATA fields. The TAG and AUX fields are optional. If used, the TAG bits carry flow control information for the data channel, while the auxiliary (AUX) bits carry side information relating to the content of the DATA field. The data payload may or may not fill the entire allotted DATA field. |
||
<center> |
|||
{{center| |
|||
[[Image:SLIMbusSegmentOrganization.jpg|Segment Organization]] |
|||
[[File:SLIMbusSegmentOrganization.jpg|Segment Organization]] |
|||
{{center|Figure 5: Segment Organization}} |
|||
</center> |
|||
}} |
|||
== Data Channel Transport Protocols and Flow Control== |
== Data Channel Transport Protocols and Flow Control== |
||
A Data Channel has exactly one data source at a time and may have one or more data sinks depending upon the Transport Protocol used in the channel. |
A Data Channel has exactly one data source at a time and may have one or more data sinks depending upon the Transport Protocol used in the channel. |
||
Flow Control in the Channel, if needed, depends on the Devices and the type of Data involved. |
Flow Control in the Channel, if needed, depends on the Devices and the type of Data involved. TAG bits are used to carry the flow control information. |
||
SLIMbus Device Ports are associated with Data Channels using appropriate channel connection and dis-connection Messages. For data flow between Ports attached to Channels, SLIMbus supports a small group of frequently used Transport Protocols (including a User Defined Transport Protocol) which define data flow type, flow control mechanism, and a side-channel (if any) for any additional application-specific information. |
SLIMbus Device Ports are associated with Data Channels using appropriate channel connection and dis-connection Messages. For data flow between Ports attached to Channels, SLIMbus supports a small group of frequently used Transport Protocols (including a User Defined Transport Protocol) which define data flow type, flow control mechanism, and a side-channel (if any) for any additional application-specific information. A summary of the Transport Protocols is shown in Table 1. |
||
<div style="float:left; position:relative; left:50%"><div style="float:left; position:relative; left:-50%"> |
|||
<center> |
|||
{| class="wikitable |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! |TP |
|||
| row 1, cell 1 |<center>TP</center> |
|||
! |Protocol Name |
|||
! |Type |
|||
| row 1, cell 3 |<center>Type</center> |
|||
! |# of TAG field Slots |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |0 |
||
| |
| |Isochronous |
||
| |
| |Multicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |0 |
|||
| row 2, cell 4 |<center>0</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |1 |
||
| |
| |Pushed |
||
| |
| |Multicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |1 |
|||
| row 3, cell 4 |<center>1</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |2 |
||
| |
| |Pulled |
||
| |
| |Unicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |1 |
|||
| row 4, cell 4 |<center>1</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |3 |
||
| |
| |Locked |
||
| |
| |Multicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |0 |
|||
| row 5, cell 4 |<center>0</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |4 |
||
| |
| |Asynchronous – Simplex |
||
| |
| |Unicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |1 |
|||
| row 6, cell 4 |<center>1</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |5 |
||
| |
| |Asynchronous – Half-duplex |
||
| |
| |Unicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |1 |
|||
| row 7, cell 4 |<center>1</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |6 |
||
| |
| |Extended Asynchronous – Simplex |
||
| |
| |Unicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |2 |
|||
| row 8, cell 4 |<center>2</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |7 |
||
| |
| |Extended Asynchronous – Half duplex |
||
| |
| |Unicast |
||
| style="text-align:center" |2 |
|||
| row 9, cell 4 |<center>2</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |8 to 13 |
||
| |
| |Reserved |
||
| style="text-align:center" |- |
|||
| row 10, cell 3 |<center> - </center> |
|||
| style="text-align:center" |- |
|||
| row 10, cell 4 |<center> - </center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |14 |
||
| |
| |User Defined 1 |
||
| style="text-align:center" |- |
|||
| row 11, cell 3 |<center> - </center> |
|||
| style="text-align:center" |1 |
|||
| row 11, cell 4 |<center>1</center> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| |15 |
||
| |
| |User Defined 2 |
||
| style="text-align:center" |- |
|||
| row 12, cell 3 |<center> - </center> |
|||
| style="text-align:center" |2 |
|||
| row 12, cell 4 |<center>2</center> |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
{{center|Table 1: SLIMbus Supported Transport Protocols}} |
|||
</div></div> |
|||
TABLE 1: SLIMbus Supported Transport Protocols |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
</center> |
|||
User 1 & 2 protocols are used to extend SLIMbus's data transmission mechanisms and it is assumed that a Device connected to a User Protocol Data Channel knows the definition of the TAG and AUX bits and how they are used. |
User 1 & 2 protocols are used to extend SLIMbus's data transmission mechanisms and it is assumed that a Device connected to a User Protocol Data Channel knows the definition of the TAG and AUX bits and how they are used. |
||
| Line 237: | Line 240: | ||
== SLIMbus System == |
== SLIMbus System == |
||
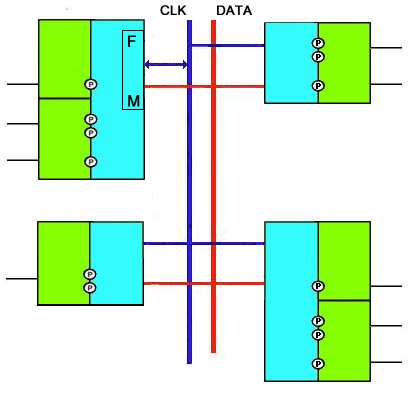
A SLIMbus system for illustrative purposes only is shown in Figure 7 below. |
A SLIMbus system for illustrative purposes only is shown in Figure 7 below. All of the Components are different from each other. Note that the upper left SLIMbus Component in this example contains a Framer Device (F), and therefore the CLK signal for this component is bidirectional. |
||
The upper left SLIMbus Component also contains a Manager Device (M). |
The upper left SLIMbus Component also contains a Manager Device (M). However, there is no requirement that the Manager and the Framer Devices be in the same SLIMbus Component. |
||
{{center| |
|||
[[ |
[[File:SLIMbusSystem.jpg|An Illustrative SLIMbus System]] |
||
{{center|Figure 7: An Illustrative SLIMbus System}} |
|||
}} |
|||
Figure 7: An Illustrative SLIMbus System |
|||
</center> |
|||
The Manager and/or Framer Device shown in the upper left SLIMbus Component can also be incorporated into baseband and/or applications processors typically used to build mobile terminals. |
The Manager and/or Framer Device shown in the upper left SLIMbus Component can also be incorporated into baseband and/or applications processors typically used to build mobile terminals. |
||
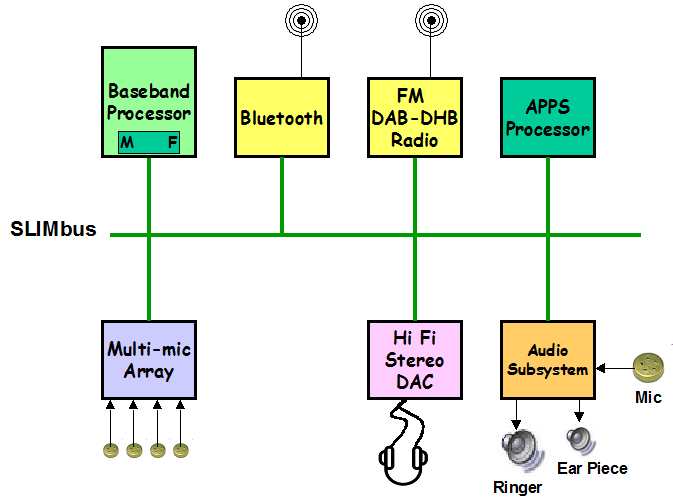
Figure 8 below shows a conceptual view of a possible real world SLIMbus system. The "M" and "F" represents the Manager and Framer Devices respectively. |
Figure 8 below shows a conceptual view of a possible real world SLIMbus system. The "M" and "F" represents the Manager and Framer Devices respectively. Alternatively, the multi-mic array could replace the single mic in the system. Any mixture of audio related blocks could be attached. |
||
<center> |
|||
[[Image:SLIMbusConceptualSystem.jpg|SLIMbus System]] |
|||
{{center| |
|||
Figure 8: Conceptual SLIMbus System |
|||
[[File:SLIMbusConceptualSystem.jpg|SLIMbus System]] |
|||
</center> |
|||
{{center|Figure 8: Conceptual SLIMbus System}} |
|||
}} |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 267: | Line 268: | ||
===Press coverage=== |
===Press coverage=== |
||
*{{cite web|title=MIPI Alliance Rolls Out SLIMbus®|url=http://www.mipi.org/content/mipi-alliance-rolls-out-slimbus%C2%AE|work=MIPI Alliance|publisher=MIPI Alliance, Inc.| |
*{{cite web|title=MIPI Alliance Rolls Out SLIMbus®|url=http://www.mipi.org/content/mipi-alliance-rolls-out-slimbus%C2%AE|work=MIPI Alliance|publisher=MIPI Alliance, Inc.|access-date=17 January 2013|date=9 July 2007}} |
||
*{{cite conference|last=Backman|first=Juha| |
*{{cite conference|last=Backman|first=Juha |author2=Boyce, Kenneth |author3=Kavanagh, Peter |author4=Lambrecht, Xavier |author5=Schuessler, James |author6=Travis, Chris |author7=van Vlimmeren, Bernard |author8=Vansteeg, Genevieve |title=Slimbus: An Audio, Data And Control Interface For Mobile Devices|conference=29th International Conference: Audio for Mobile and Handheld Devices|date=September 2006|url=http://www.aes.org/e-lib/browse.cfm?elib=13869}} |
||
*{{cite |
*{{cite web |last=Lee|first=Yong-Hwan |author2=Hoon-Ju Chung |author3=Chang-Gu Rho |title=Design of Clock Gears for Low-power Media Bis |work=The 23rd International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications|year=2008|url=http://www.ieice.org/proceedings/ITC-CSCC2008/pdf/p1089_P1-22.pdf|access-date=17 January 2013}} |
||
*{{cite news|title=MIPI® Alliance Delivers Seven Vital Mobile Device Interface Specifications in 2008|url=http://www.businesswire.com/portal/site/home/permalink/?ndmViewId=news_view&newsId=20090209005179&newsLang=en| |
*{{cite news|title=MIPI® Alliance Delivers Seven Vital Mobile Device Interface Specifications in 2008|url=http://www.businesswire.com/portal/site/home/permalink/?ndmViewId=news_view&newsId=20090209005179&newsLang=en|access-date=17 January 2013|newspaper=Business Wire|date=9 February 2009}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Slimbus}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Slimbus}} |
||
[[Category:Computer buses]] |
[[Category:Computer buses]] |
||
[[Category:MIPI standards]] |
[[Category:MIPI Alliance standards]] |
||
Latest revision as of 19:47, 27 January 2021
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
The Serial Low-power Inter-chip Media Bus (SLIMbus) is a standard interface between baseband or application processors and peripheral components in mobile terminals. It was developed within the MIPI Alliance, founded by ARM, Nokia, STMicroelectronics and Texas Instruments.[1] The interface supports many digital audio components simultaneously, and carries multiple digital audio data streams at differing sample rates and bit widths.
SLIMbus is implemented as a synchronous 2-wire, configurable Time Division Multiplexed (TDM) frame structure. It has supporting bus arbitration mechanisms and message structures which permit re-configuring the bus operational characteristics to system application needs at runtime. Physically, the data line (DATA) and the clock line (CLK) interconnect multiple SLIMbus components in a multi-drop bus topology. SLIMbus devices may dynamically “drop off” the bus and “reconnect” to the bus as required by using appropriate protocols outlined in the SLIMbus specification. When used in a mobile terminal or portable product, SLIMbus may replace legacy digital audio interfaces such as PCM, I2S,[2] and SSI (Synchronous Serial Interface for digital audio), as well as some instances of many digital control buses such as I2C,[3] SPI, microWire,[4] UART, or GPIO pins on the digital audio components.
History
[edit]- The MIPI Alliance was formed in fall of 2003.
- Interface architecture including a low speed media link bus (LowML) presented at the F2F meeting of MIPI Alliance in Sophia Antipolis, France in March, 2004.
- LML Investigation Group (LML-IG) created in July 2004 by the MIPI Alliance. First meeting was a teleconference on August 3, 2004.
- LML Working Group (LML-WG) created in Q4 2004. LML WG Charter submitted to the MIPI Board in December, 2004.
- First meeting as a full Working Group on April 12, 2005.
- LML-WG released first draft of SLIMbus with text in all chapters (v0.55) on October 18, 2005.
- SLIMbus specification v1.00 was released to adopters on May 16, 2007.
- From June 2007 to June 2008, SLIMbus specification improvement (ambiguities, typos & bugs fixed) based on implementer feed-back.
- SLIMbus specification V1.01 was released to adopters on December 3, 2008 and is recommended for implementation.
SLIMbus Devices and Device Classes
[edit]SLIMbus Device Class definitions are those which specify the minimum requirements for Device control data, Device behavior, and data Transport Protocol support. There are four SLIMbus Device Classes defined at the release of Version 1.01 of the SLIMbus specification: Manager, Framer, Interface, and Generic. Complete SLIMbus systems can be implemented without any additional Device Classes.
Manager Device
[edit]The Manager Device is responsible for configuring SLIMbus, and performs bus administration (administration of Components and Devices, bus configuration, and dynamic channel allocation) and is typically located in a baseband or application processor rather than in a peripheral component.
Framer Device
[edit]The Framer delivers a clock signal on the CLK line to all SLIMbus Components, and also contains logic to transmit the Frame Sync and Framing Information channels on the DATA line.
Interface Device
[edit]The Interface Device provides bus management services, monitors the Physical Layer for errors, reports information about the status of a SLIMbus Component, and otherwise manages the Component such that the Devices within it will function properly on the bus.
To implement a functional SLIMbus component always requires the use of a SLIMbus Interface Device, plus the function to be performed, such as DAC, ADC, digital amplifier, and so on.
Generic Device (Function)
[edit]A Generic Device is a Device other than a Manager, Framer, or Interface. A Generic Device is generally considered to be the device to provide certain application functionality, for example, conversion from digital audio to analog (DAC) and vice versa (ADC).
SLIMbus Component
[edit]A SLIMbus Component contains two or more SLIMbus Devices. A SLIMbus Component will have only one SLIMbus Interface Device (INTERFACE), and may have one or more other types of SLIMbus devices which perform a particular function (FUNCTION).
A SLIMbus Port (P) provides the connection path for data flow between Devices. SLIMbus Ports are normally used for digital audio data flow, but may also be used for other digital data flow.
Port capabilities vary depending upon the Device and are to be specified in the Component data sheet. Typical Port attributes include data direction, i.e. input-only (sink), output-only (source) or both input and output, supported Transport Protocols, and data width.
A simple SLIMbus Component example is shown in Figure 1 below, and a complex SLIMbus Component example is shown in Figure 2 below.
SLIMbus DATA and CLK
[edit]All SLIMbus Devices use DATA and CLK to synchronize with the bus configuration in use, to receive or transmit messages and data, and to implement bus arbitration, collision detection, and contention resolution between devices.
For all SLIMbus Components (except one containing a Framer Device), the CLK terminal is input only. If a SLIMbus Component is the Framer Device, or contains a Framer Device, the CLK signal is bi-directional.
For all SLIMbus Components, the DATA line is bidirectional, and carries all information sent or received on the bus using Non-Return-to-Zero Inverted (NRZI) encoding.
The DATA line is driven on the positive edge and read on the negative edge of the CLK line. The DATA line can be driven high, driven low, or held at the high or low level by an internal bus-holder circuit, depending upon the particular operational mode of a SLIMbus Device.
The SLIMbus interface DATA and CLK lines use CMOS-like single-ended, ground referenced, rail-to-rail, voltage mode signals, and signaling voltages are specified with respect to the interface supply voltage (+1.8Vdd or +1.2Vdd are permitted). For EMI performance reasons, slew rate limits have been specified for SLIMbus.
SLIMbus Clock Frequencies and Gears
[edit]The SLIMbus CLK line frequency is determined by a range of "Root" clock frequencies up to 28 MHz, and 10 Clock Gears for altering the clock frequency by powers of 2 over a span of 512x from lowest to highest Gear. The Root Frequency is defined as 2(10-G) times the frequency of the CLK line. For G=10, the CLK line frequency and Root Frequency are equal.
The SLIMbus CLK may also be stopped and restarted.
SLIMbus CLK frequencies and data transport protocols will support all common digital audio converter over-sampling frequencies and associated sample rates.
Cells, Slots, Subframes, Frames, and Superframes
[edit]The SLIMbus Frame Structure has five building blocks: Cells, Slots, Frames, Subframes, and Superframes.
Cell
[edit]A Cell is defined as a region of the DATA signal that is bounded by two consecutive positive edges of the CLK line and holds a single bit of information.
Slot
[edit]A Slot is defined as four contiguous Cells (4-bits transmitted in MSB to LSB order). Bandwidth allocation for various data organizations, from 4-bits to 32-bits or more, can be done by grouping 4-bit Slots.
Frame
[edit]A Frame is defined as 192 (0 through 191) contiguous Slots and are transmitted as S0, followed by S1, S2 ... S191 in that order. The first Slot (Slot 0) of each Frame is a Control Space slot which contains the four (4) bit Frame Sync symbol. Slot S96 of each Frame is also a Control Space slot which contains four (4) bits of Framing Information.
The active Framer writes all Framing Information to the Data line at the appropriate time.
Subframe
[edit]A Subframe is defined as the division of the Frame Structure at which Control Space and Data Space are interleaved. A Subframe is partitioned into 1 or more slots of Control Space, followed by 0 or more slots of Data Space.
As shown in Figure 4 below, the Subframe length is programmable to 6, 8, 24 or 32 contiguous Slots (24, 32, 96 or 128 Cells). The number of possible Subframes per Frame is therefore 32, 24, 8, or 6 respectively. The Subframe configuration used can be dynamically changed depending upon the data flow requirements of the applications being supported at the time.
4 of the Control space slots are reserved for a frame sync symbol, 4 bits if a Framing Information word, and 8 bits of Guide Byte. The remainder is available for more general control messages.
Any Slots not allocated to Control Space are considered Data Space.
Superframe
[edit]A Superframe is defined as eight contiguous Frames (1536 Slots). Frames within a Superframe are labeled Frame 0 through Frame 7.
The duration of a Superframe is fixed in terms of Slots (and, therefore, Cells), but not in terms of time. The Superframe rate can be dynamically changed on SLIMbus to suit the particular application by changing either SLIMbus Root Frequency or Clock Gear, or both.
Channels
[edit]Information on the SLIMbus DATA line is allocated to Control Space and Data Space channels.
The Control Space carries bus configuration and synchronization information as well as inter-Device Message communication. The Control Space may be dynamically programmed to take as much of the SLIMbus bandwidth as required, even up to 100% at times.
Data Space, when present, carries application-specific information such as isochronous and asynchronous data streams.
SLIMbus Components convey control and data information between each other using Control and Data Channels with Transport Protocols to achieve the required system operation. Messages are used for Control functions.
Channels can be established between a pair of Devices (inter-Device communication), or between one Device and many Devices (broadcast communication), or in the case of the Message Channel, from all devices to all other devices (shared).
Control Channels
[edit]Control Space is divided into three types of channels: Framing, Guide, and Message.
The Framing Channel occupies Slots 0 and 96 of each Frame. (Since all Subframe lengths divide 96, these Slots are always available for the purpose.) Slot 0 holds a fixed Frame Sync symbol (10112), while Slot 96 holds 4 bits of a Framing Information word. Over the course of a Superframe, 32 bits of Framing Information are available. Some of these hold a fixed bit pattern used to acquire Superframe synchronization (0x011xxx2), while the others hold other critical configuration information.
The Guide Channel consists of the first 2 non-Framing control Slots in each Superframe. This "guide byte" is normally 0, but if a control message straddles a Superframe boundary, it indicates the number of bytes until the end of that message.
The Message Channel consists of all remaining Slots. It carries various types of information including bus configuration announcements, Device control and Device status.
The format of Control Space is determined by a 5-bit Subframe mode identifier transmitted in the Framing Information word. This communicates the Subframe length and the number of control Slots. The number of control Slots is limited to the choices of 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, or 24. Adding the limitations that the number of control Slots must be less than the Subframe length produces 26 valid combinations. A special encoding for "100% Control Space", in which case the Subframe length is unimportant, produces 27 valid modes. (Modes 1–3, 20 and 30 are not valid.)
Data Channels
[edit]Data Channels are one or more contiguous Data Slots (Segments) and are dynamically created by the active Manager depending on the application and size of Data Space available. A Data Channel, and therefore the structure of a Segment, is defined by parameters such as Data rate, type, field length, and required Transport Protocol.
Segments repeat at known intervals and behave as virtual bus's with their own bandwidth guarantee and latency.
A Segment, shown below in Figure 5, has TAG (2 Slots), AUX (2 Slots), and DATA fields. The TAG and AUX fields are optional. If used, the TAG bits carry flow control information for the data channel, while the auxiliary (AUX) bits carry side information relating to the content of the DATA field. The data payload may or may not fill the entire allotted DATA field.
Data Channel Transport Protocols and Flow Control
[edit]A Data Channel has exactly one data source at a time and may have one or more data sinks depending upon the Transport Protocol used in the channel.
Flow Control in the Channel, if needed, depends on the Devices and the type of Data involved. TAG bits are used to carry the flow control information.
SLIMbus Device Ports are associated with Data Channels using appropriate channel connection and dis-connection Messages. For data flow between Ports attached to Channels, SLIMbus supports a small group of frequently used Transport Protocols (including a User Defined Transport Protocol) which define data flow type, flow control mechanism, and a side-channel (if any) for any additional application-specific information. A summary of the Transport Protocols is shown in Table 1.
| TP | Protocol Name | Type | # of TAG field Slots |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Isochronous | Multicast | 0 |
| 1 | Pushed | Multicast | 1 |
| 2 | Pulled | Unicast | 1 |
| 3 | Locked | Multicast | 0 |
| 4 | Asynchronous – Simplex | Unicast | 1 |
| 5 | Asynchronous – Half-duplex | Unicast | 1 |
| 6 | Extended Asynchronous – Simplex | Unicast | 2 |
| 7 | Extended Asynchronous – Half duplex | Unicast | 2 |
| 8 to 13 | Reserved | - | - |
| 14 | User Defined 1 | - | 1 |
| 15 | User Defined 2 | - | 2 |
User 1 & 2 protocols are used to extend SLIMbus's data transmission mechanisms and it is assumed that a Device connected to a User Protocol Data Channel knows the definition of the TAG and AUX bits and how they are used.
SLIMbus System
[edit]A SLIMbus system for illustrative purposes only is shown in Figure 7 below. All of the Components are different from each other. Note that the upper left SLIMbus Component in this example contains a Framer Device (F), and therefore the CLK signal for this component is bidirectional.
The upper left SLIMbus Component also contains a Manager Device (M). However, there is no requirement that the Manager and the Framer Devices be in the same SLIMbus Component.
The Manager and/or Framer Device shown in the upper left SLIMbus Component can also be incorporated into baseband and/or applications processors typically used to build mobile terminals.
Figure 8 below shows a conceptual view of a possible real world SLIMbus system. The "M" and "F" represents the Manager and Framer Devices respectively. Alternatively, the multi-mic array could replace the single mic in the system. Any mixture of audio related blocks could be attached.
References
[edit]- ^ Merritt, Rick (13 February 2006). "Mobile chip interface gets real". EETimes. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "I2S bus specification" (PDF). Philips Semiconductors. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "The I2C-Bus Specification" (PDF). Philips Semiconductors. January 2000. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- ^ "AN-452 MICROWIRE Serial Interface" (PDF). Texas Instruments. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
External links
[edit]A partial list of SLIMbus implementer information can be found at the following:
Press coverage
[edit]- "MIPI Alliance Rolls Out SLIMbus®". MIPI Alliance. MIPI Alliance, Inc. 9 July 2007. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- Backman, Juha; Boyce, Kenneth; Kavanagh, Peter; Lambrecht, Xavier; Schuessler, James; Travis, Chris; van Vlimmeren, Bernard; Vansteeg, Genevieve (September 2006). Slimbus: An Audio, Data And Control Interface For Mobile Devices. 29th International Conference: Audio for Mobile and Handheld Devices.
- Lee, Yong-Hwan; Hoon-Ju Chung; Chang-Gu Rho (2008). "Design of Clock Gears for Low-power Media Bis" (PDF). The 23rd International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers and Communications. Retrieved 17 January 2013.
- "MIPI® Alliance Delivers Seven Vital Mobile Device Interface Specifications in 2008". Business Wire. 9 February 2009. Retrieved 17 January 2013.