Wesergebirge: Difference between revisions
Bermicourt (talk | contribs) m Removed category Mountains of Lower Saxony; Quick-adding category Hills of Lower Saxony (using HotCat) |
No edit summary |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox mountain |
|||
{{Geobox |
|||
|name=Weser Hills<br />(''Wesergebirge'') |
|||
| Range |
|||
| |
|photo=Blick zum Wesergebirge und zum Jakobsberg mit Fernsehturm.JPG |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|image=Blick zum Wesergebirge und zum Jakobsberg mit Fernsehturm.JPG |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|country = Germany |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
|highest=Möncheberg |
||
| |
|elevation_m=326.1 |
||
|MAX-HÖHE-BEZUG=DE-NN |
|||
|region=[[North Rhine-Westphalia]], [[Lower Saxony]] |
|region=[[North Rhine-Westphalia]], [[Lower Saxony]] |
||
|coordinates = {{coord|52|13|N|9|5|E|type:mountain|format=dms|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|highest_lat_d=52.216667 |
|||
|range_coordinates = |
|||
|highest_long_d=9.083333 |
|||
|length_km=100 |
|||
|REGION-ISO=DE-NW/DE-NI |
|||
|length=100 |
|||
|BESONDERHEITEN= |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:Wesergeb34.jpg|190px|thumb|The |
[[File:Wesergeb34.jpg|190px|thumb|The Weser Hills seen from the west. In the left foreground [[Bad Eilsen]] and behind that the [[Bückeberge]]; in the right foreground [[Rinteln]] with a few meanders of the Weser river (right margin). The background shows a few more forested elevations of the [[Weser Uplands]].]] |
||
The ''' |
The '''Weser Hills''' ('''''Wesergebirge'''''), also known in German as the ''Weserkette'' ("Weser Chain"),<ref>"Ein anderes Bild als die Bergländer der oberen Weser bieten die ''Weserkette'', das ''Wiehengebirge'' und der ''Teutoburger Wald'', see Christian Degn, et al. (ed.) Seydlitz, 1st Part, ''das deutsche Vaterland, wir und die Welt'', 7th ed., Kiel, Hanover, 1954, p. 50</ref> form a low [[hill chain]], up to {{Höhe|326.1|DE-NN|link=true}},<ref name=NI-Nav>[http://www.niedersachsennavigator.niedersachsen.de Niedersachsennavigator]</ref> in the [[Weser Uplands]] in the German states of [[North Rhine-Westphalia]] and [[Lower Saxony]]. |
||
The thickly wooded |
The thickly wooded Weser ridge is one of the northern outliers of the German [[Central Uplands]] on the southern edge of the [[North German Plain]] and forms part of the [[TERRA.vita Nature Park]] in the west and Weser Uplands Schaumburg-Hameln Nature Park in the east. |
||
The |
The Weser Hills are widely known because of [[Schaumburg Castle, Lower Saxony|Schaumburg Castle]] which stands on the [[Nesselberg]] (c. {{Höhe|225|DE-NN}}) in the Schaumburg district of the town of [[Rinteln]], and is the emblem of [[Schaumburg Land]]. |
||
== Geography == |
|||
The Weser Hills cross the counties of [[Minden-Lübbecke]], [[Landkreis Schaumburg|Schaumburg]] and [[Landkreis Hameln-Pyrmont|Hameln-Pyrmont]] in a roughly east–west direction, from the town of [[Porta Westfalica]] and the [[Westphalian Gap]] in the west past [[Rinteln]] to [[Hessisch Oldendorf]] in the east, where they transition seamlessly to the [[Süntel]], a ridge of similar height running from northwest to southeast. They form part of the perimeter of the [[Weser Uplands]] and thus also the German [[Central Uplands]] which lie south of the [[North German Plain]]. |
|||
North of the Weser Hills there are only a few hills of the [[Calenberg Uplands]], such as the nearby ridges of [[Harrl]] and [[Bückeberge]]. To the west, on the other side of the Porta Westfalica, the chain continues as the [[Wiehen Hills]], geologically of similar formation, reaching [[Bramsche]] (northwest of [[Osnabrück]]). |
|||
Südlich des Wesergebirges und in etwa parallel zu ihm fließt die Weser von Hessisch-Oldendorf im Osten über Rinteln in Richtung [[Vlotho]] im Westen, um dann in Richtung Nordosten bzw. zur Stadt Porta Westfalica abzuknicken. Diese dem Gebirge südlich vorgelagerten nördlichen Bereiche des [[Oberes Wesertal|Oberen Wesertals]] sind ein alter Besiedlungsraum, der durch die auf dem Nesselberg stehende [[Schaumburg_(Burg)|Schaumburg]] markiert wird. Ab dem Durchbruchstal Porta Westfalica wendet sich der Fluss nach Norden, um in die südlichen Bereiche der Norddeutschen Tiefebene einzufließen. Nördlich des Gebirges erstreckt sich das Oberlauftal der in etwa in Ost-West-Richtung verlaufenden [[Aue (Weser)|Aue]] („Bückeburger Aue“). |
|||
South of the Weser Hills, and roughly parallel to them, flows the River Weser, from Hessisch-Oldendorf in the east, through Rinteln, towards [[Vlotho]] in the west, before turning northeast to the town of Porta Westfalica. These northern areas around the [[Upper Weser Valley]], south of the hills are an old area of settlement, which was protected by [[Schaumburg Castle, Lower Saxony|Schaumburg Castle]] on the hill of [[Nesselberg]]. From the water gap at Porta Westfalica - the Westphalian Gap - the river swings north in order to reach the southern part of the North German Plain. North of the hills are the upper reaches of the [[Aue (Weser)|Aue]] (also called the ''Bückeburger Aue'') that run roughly east to west. |
|||
<!-- |
|||
== Geologie == |
== Geologie == |
||
Während das [[Gebirgskamm|kammartige]] Wesergebirge, das aus [[Kalksandstein]] ([[Korallenoolith]]) aufgebaut ist und als ein bedeutendes Kalksteingebiet Niedersachsens gilt, an seiner Südabdachung steile Gebirgsflanken aufweist, fällt seine Nordabdachung eher allmählich ab. Geologisch und naturräumlich zählt auch der landschaftlich eher dem [[Süntel]] zugehörige [[Hohenstein (Süntel)|Hohenstein]] ({{Höhe|340.5|DE-NN}}) mit der [[Teufelskanzel]] noch zum Wesergebirge. |
Während das [[Gebirgskamm|kammartige]] Wesergebirge, das aus [[Kalksandstein]] ([[Korallenoolith]]) aufgebaut ist und als ein bedeutendes Kalksteingebiet Niedersachsens gilt, an seiner Südabdachung steile Gebirgsflanken aufweist, fällt seine Nordabdachung eher allmählich ab. Geologisch und naturräumlich zählt auch der landschaftlich eher dem [[Süntel]] zugehörige [[Hohenstein (Süntel)|Hohenstein]] ({{Höhe|340.5|DE-NN}}) mit der [[Teufelskanzel]] noch zum Wesergebirge. |
||
== Geschichte == |
== Geschichte == |
||
Nördlich des Bergs Roter Brink, der sich süd-südwestlich von [[Nammen]] befindet, liegt im Wesergebirge in einer Vertiefung der Bereich des [[Nammer Lager]]s, das früher bei kritischen und kriegerischen Lagen im Rahmen einer Burganlage eine Rückzugsmöglichkeit für die Bevölkerung der Umgebung darstellt. |
Nördlich des Bergs Roter Brink, der sich süd-südwestlich von [[Nammen]] befindet, liegt im Wesergebirge in einer Vertiefung der Bereich des [[Nammer Lager]]s, das früher bei kritischen und kriegerischen Lagen im Rahmen einer Burganlage eine Rückzugsmöglichkeit für die Bevölkerung der Umgebung darstellt. |
||
== Flora und Fauna == |
== Flora und Fauna == |
||
Das [[wald]] |
Das [[wald]]reiche Wesergebirge ist ein bedeutendes [[Buchen]]waldgebiet in Niedersachsen. |
||
== Naturschutz und -parke == |
== Naturschutz und -parke == |
||
Teile des Wesergebirges stehen im Bereich des Hohensteins unter [[Naturschutz]]. Nur die Südhänge der bewaldeten Bergzüge mit teilweise seltenen Pflanzengesellschaften sind [[Landschaftsschutzgebiet]]e. |
Teile des Wesergebirges stehen im Bereich des Hohensteins unter [[Naturschutz]]. Nur die Südhänge der bewaldeten Bergzüge mit teilweise seltenen Pflanzengesellschaften sind [[Landschaftsschutzgebiet]]e. |
||
Während sein äußerster Westteil (südwestlich von Bückeburg) noch zum [[Naturpark TERRA.vita]] gerechnet wird, gehören die mit Abstand größeren Mittel- und Ostteile zum [[Naturpark Weserbergland Schaumburg-Hameln]]. --> |
Während sein äußerster Westteil (südwestlich von Bückeburg) noch zum [[Naturpark TERRA.vita]] gerechnet wird, gehören die mit Abstand größeren Mittel- und Ostteile zum [[Naturpark Weserbergland Schaumburg-Hameln]]. --> |
||
| Line 47: | Line 44: | ||
<!-- |
<!-- |
||
== Aktionsgemeinschaft „Rettet die Weserberge“ == |
== Aktionsgemeinschaft „Rettet die Weserberge“ == |
||
Eine unabhängig und überparteilich organisierte Interessengemeinschaft, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, das Wesergebirge und den [[Süntel]] vor einer vollständigen Zerstörung durch Gesteinsabbau zu bewahren, ist die Aktionsgemeinschaft „Rettet die Weserberge“. --> |
Eine unabhängig und überparteilich organisierte Interessengemeinschaft, die es sich zum Ziel gesetzt hat, das Wesergebirge und den [[Süntel]] vor einer vollständigen Zerstörung durch Gesteinsabbau zu bewahren, ist die Aktionsgemeinschaft „Rettet die Weserberge“. --> |
||
== Hills == |
== Hills == |
||
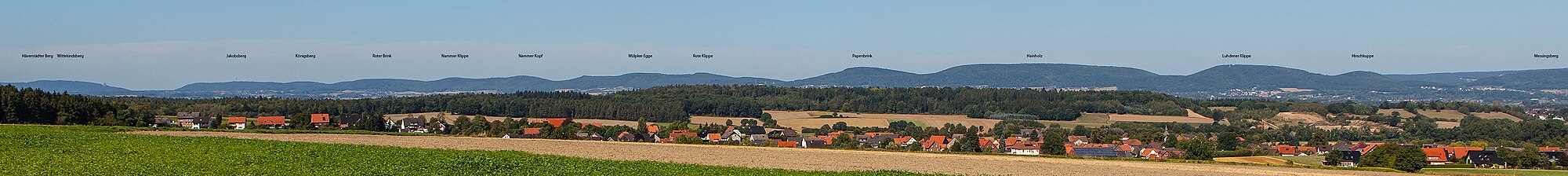
The Wesergebirge is a chain of about two dozen hills that are arranged one after another in a ridge and which reach a height of {{Höhe|326.1|DE-NN}} at the Möncheberg in the east. In its centre section, west of the [[Bundesautobahn 2|A 2 motorway]], they reach a maximum height of |
The ''Wesergebirge'' is a chain of about two dozen hills that are arranged one after another in a ridge and which reach a height of {{Höhe|326.1|DE-NN}} at the Möncheberg in the east. In its centre section, west of the [[Bundesautobahn 2|A 2 motorway]], they reach a maximum height of 278 m at the Wülpker Egge and a height of 235.2 m at the westernmost hill of the Weser chain, the [[Jakobsberg (Porta Westfalica)|Jakobsberg]], which is located east of Porta Westfalica and on which the ''Jakobsberg transmission tower'' stands. |
||
The hills and elevations of the Wesergebirge, as seen from west to east, are given below together with their heights in metres above [[Normalnull]] (NN)<ref name="NI-Nav"/> |
The hills and elevations of the Wesergebirge, as seen from west to east, are given below together with their heights in metres above [[Normalnull]] (NN)<ref name="NI-Nav"/> |
||
''':''' |
''':''' |
||
* [[Jakobsberg (Porta Westfalica)|Jakobsberg]] (235,2 m), with ''[[Jakobsberg Telecommunication Tower]]'', ''Schlageter Monument'' and ''Porta Kanzel''; north-northeast of the town of [[Porta Westfalica]] by the Porta Westfalica gorge |
* [[Jakobsberg (Porta Westfalica)|Jakobsberg]] (235,2 m), with ''[[Jakobsberg Telecommunication Tower]]'', ''Schlageter Monument'' and ''Porta Kanzel''; north-northeast of the town of [[Porta Westfalica]] by the Porta Westfalica gorge |
||
* Königsberg ( |
* Königsberg (c. 225 m<!--; with ???-->); northeast of Porta Westfalica |
||
* Roter Brink ( |
* Roter Brink (c. 225 m), and [[Nammer Lager]]; south-southwest of [[Nammen]] |
||
* Lohfelder Berg (215,2 m<!--; with ???-->); northeast of [[Lohfeld (Porta Westfalica)|Lohfeld]] |
* Lohfelder Berg (215,2 m<!--; with ???-->); northeast of [[Lohfeld (Porta Westfalica)|Lohfeld]] |
||
* Nammer Klippe (248,8 m<!--; with ???-->); nature reserve; south of Nammen |
* Nammer Klippe (248,8 m<!--; with ???-->); nature reserve; south of Nammen |
||
* Nammer Kopf (266,3 m), |
* Nammer Kopf (266,3 m), and the ''Nammer Klippe'', nature reserve; south-southeast of Nammen |
||
* Wülpker Egge ( |
* Wülpker Egge (c. 278 m), with a quarry; south of [[Wülpke]] |
||
* Rote Klippe ( |
* Rote Klippe (c. 220 m), with a quarry; south of [[Kleinenbremen]] |
||
* Papenbrink (303 m), with transmission facility and a quarry; north-northwest of [[Todenmann]] |
* Papenbrink (303 m), with transmission facility and a quarry; north-northwest of [[Todenmann]] |
||
* Lange Wand (320,1 m)<!--, with ???-->; in the Hainholz State Forest northeast of Todenmann |
* Lange Wand (320,1 m)<!--, with ???-->; in the Hainholz State Forest northeast of Todenmann |
||
* Frankenburg-Berg ( |
* Frankenburg-Berg (c. 235 m), and ruins of the [[Frankenburg (Wesergebirge)|Frankenburg]]; spur of the Langen Wand north of [[Rinteln]]-Todenmann |
||
* Luhdener Klippe ( |
* Luhdener Klippe (c. 300 m), and the 19.8 m high [[Klippe Tower]]; north-northeast of Rinteln |
||
* Hirschkuppe (250,1 m)<!--, with ???-->; northeast of Rinteln |
* Hirschkuppe (250,1 m)<!--, with ???-->; northeast of Rinteln |
||
* Messingsberg (270,1 m), with a quarry; north-northeast of Rinteln-Steinbergen |
* Messingsberg (270,1 m), with a quarry; north-northeast of Rinteln-Steinbergen |
||
* Westendorfer Egge ( |
* Westendorfer Egge (c. 295 m), with a quarry; north-northeast of Rinteln-Westendorf |
||
* Oberberg (325,2 m), |
* Oberberg (325,2 m), and the ''Springsteinen''; north of Rinteln-Schaumburg |
||
* Heutzeberg (225,5 m)<!--,mit ???-->; spur of the Oberberg north of Schaumburg |
* Heutzeberg (225,5 m)<!--,mit ???-->; spur of the Oberberg north of Schaumburg |
||
* [[Nesselberg]] ( |
* [[Nesselberg]] (c. 225 m), and [[Schaumburg Castle, Lower Saxony|Schaumburg Castle]] on a spur of the Möncheberg east of Schaumburg |
||
* Möncheberg (326,1 m), |
* Möncheberg (326,1 m), and the ''Paschenburg Guest House'' between Schaumburg and [[Hessisch Oldendorf]]-Rohdental |
||
==Panorama== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{wide image|Weserbergland-Panorama.jpg|2000px}} |
|||
| ⚫ | <!-- Zu den Ortschaften in the bzw. am Wesergebirge gehören die Stadt [[Porta Westfalica]], die sich westlich des Gebirges bzw. southeast of der Porta Westfalica (am Übergang zum [[Wiehengebirge]]) befindet, and die Stadt [[Minden]], die etwas north of dieses Durchbruchtals liegt. Nördlich vom Mittelteil des Wesergebirges befindet sich die Stadt [[Bückeburg]], south of davon die Stadt [[Rinteln]], and southwest of des Gebirges liegt die Stadt [[Vlotho]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | <!-- Zu den Ortschaften in the bzw. am Wesergebirge gehören die Stadt [[Porta Westfalica]], die sich westlich des Gebirges bzw. southeast of der Porta Westfalica (am Übergang zum [[Wiehengebirge]]) befindet, and die Stadt [[Minden]], die etwas north of dieses Durchbruchtals liegt. Nördlich vom Mittelteil des Wesergebirges befindet sich die Stadt [[Bückeburg]], south of davon die Stadt [[Rinteln]], and southwest of des Gebirges liegt die Stadt [[Vlotho]]. |
||
{| |
|||
| width = "250" valign=top | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| width = "250" valign=top | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| valign=top | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{div col|colwidth=18em}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{div col end}} |
|||
<!-- == Sehenswürdigkeiten == |
<!-- == Sehenswürdigkeiten == |
||
* An der Südabdachung des Wesergebirges steht auf dem Nesselberg östlich von Rinteln die [[Schaumburg (Burg)|Schaumburg]]. |
* An der Südabdachung des Wesergebirges steht auf dem Nesselberg östlich von Rinteln die [[Schaumburg (Burg)|Schaumburg]]. |
||
* An der Nordabdachung des Wesergebirges steht zwischen [[Buchholz (bei Stadthagen)|Buchholz]] und [[Rinteln]]-Steinbergen das [[Schloß Arensburg]]. |
* An der Nordabdachung des Wesergebirges steht zwischen [[Buchholz (bei Stadthagen)|Buchholz]] und [[Rinteln]]-Steinbergen das [[Schloß Arensburg]]. |
||
* An der Nordabdachung des Wesergebirges befindet sich in Kleinenbremen das [[Besucherbergwerk Kleinenbremen]] . |
* An der Nordabdachung des Wesergebirges befindet sich in Kleinenbremen das [[Besucherbergwerk Kleinenbremen]] . |
||
Das Wesergebirge wird südwestlich von Bad Eilsen zwischen [[Todenmann]] und Schermbeck bzw. den Bergen Papenbrink und Lange Wand(Hainholz) im „Schermbecker Paß“ ( |
Das Wesergebirge wird südwestlich von Bad Eilsen zwischen [[Todenmann]] und Schermbeck bzw. den Bergen Papenbrink und Lange Wand(Hainholz) im „Schermbecker Paß“ (c. {{Höhe|220|DE-NN}} in Südwest-Nordost-Richtung von der [[Bundesautobahn 2]] durchschnitten. Die Autobahn ist in diesem Bereich sechsspurig ausgebaut, was eine starke bauliche Einschneidung in die Wald- und Gebirgslandschaft darstellt, die es erdgebundenen Tieren kaum möglich macht, diese Barriere zu passieren. Wo die Autobahn nicht durch [[Lärmschutzwand|Lärmschutzwände]] umbaut ist, ist die Lärmbelastung für Mensch und Tier enorm hoch. |
||
Das Wesergebirge wird von Abschnitten einiger Bundesstraßen passiert oder durchschnitten: An der westlich des Gebirges gelegenen Porta Westfalica wird es von den Bundesstraßen [[Bundesstraße 61|61]] und [[Bundesstraße 482|482]] und nördlich des Gebirges von der [[Bundesstraße 65|B 65]] passiert. Durch den Mittelteil dieses Gebirges führt die [[Bundesstraße 83|B 83]], auf die bei Steinbergen die [[Bundesstraße 238|B 238]] stößt. Über die B 83, B 238 und B 482 besteht jeweils Anschluss an die A 2. --> |
Das Wesergebirge wird von Abschnitten einiger Bundesstraßen passiert oder durchschnitten: An der westlich des Gebirges gelegenen Porta Westfalica wird es von den Bundesstraßen [[Bundesstraße 61|61]] und [[Bundesstraße 482|482]] und nördlich des Gebirges von der [[Bundesstraße 65|B 65]] passiert. Durch den Mittelteil dieses Gebirges führt die [[Bundesstraße 83|B 83]], auf die bei Steinbergen die [[Bundesstraße 238|B 238]] stößt. Über die B 83, B 238 und B 482 besteht jeweils Anschluss an die A 2. --> |
||
| Line 106: | Line 102: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
*Aerial photograph of the western |
*Aerial photograph of the western Weser Hills at Google Maps [http://maps.google.de/maps?q=rinteln+germany&ie=UTF8&oe=utf-8&client=firefox-a&t=k&ll=52.225066,9.025955&spn=0.061725,0.247192&z=13] |
||
*Aktionsgemeinschaft Weserbergland [http://www.weserberge.de] |
*Aktionsgemeinschaft Weserbergland [http://www.weserberge.de] |
||
| Line 113: | Line 109: | ||
{{German Central Uplands}} |
{{German Central Uplands}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Central Uplands]] |
[[Category:Central Uplands]] |
||
[[Category:Mountains and hills of North Rhine-Westphalia]] |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Hill ranges of Lower Saxony]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Weser Uplands]] |
||
[[Category:Natural regions of the Weser-Leine Uplands]] |
|||
[[de:Wesergebirge]] |
|||
[[nl:Wezergebergte]] |
|||
[[sv:Wesergebirge]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:28, 30 May 2021
| Weser Hills (Wesergebirge) | |
|---|---|
 View from the Kaiser Wilhelm Monument (Wittekindsberg, Wiehen Hills) over Porta Westfalica to the Jakobsberg (Wesergebirge) | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Möncheberg |
| Elevation | 326.1 m (1,070 ft) |
| Coordinates | 52°13′N 9°5′E / 52.217°N 9.083°E |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 100 km (62 mi) |
| Geography | |
| Country | Germany |
| Region(s) | North Rhine-Westphalia, Lower Saxony |

The Weser Hills (Wesergebirge), also known in German as the Weserkette ("Weser Chain"),[1] form a low hill chain, up to 326.1 m above sea level (NN),[2] in the Weser Uplands in the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Lower Saxony.
The thickly wooded Weser ridge is one of the northern outliers of the German Central Uplands on the southern edge of the North German Plain and forms part of the TERRA.vita Nature Park in the west and Weser Uplands Schaumburg-Hameln Nature Park in the east.
The Weser Hills are widely known because of Schaumburg Castle which stands on the Nesselberg (c. 225 m above NN) in the Schaumburg district of the town of Rinteln, and is the emblem of Schaumburg Land.
Geography
[edit]The Weser Hills cross the counties of Minden-Lübbecke, Schaumburg and Hameln-Pyrmont in a roughly east–west direction, from the town of Porta Westfalica and the Westphalian Gap in the west past Rinteln to Hessisch Oldendorf in the east, where they transition seamlessly to the Süntel, a ridge of similar height running from northwest to southeast. They form part of the perimeter of the Weser Uplands and thus also the German Central Uplands which lie south of the North German Plain.
North of the Weser Hills there are only a few hills of the Calenberg Uplands, such as the nearby ridges of Harrl and Bückeberge. To the west, on the other side of the Porta Westfalica, the chain continues as the Wiehen Hills, geologically of similar formation, reaching Bramsche (northwest of Osnabrück).
South of the Weser Hills, and roughly parallel to them, flows the River Weser, from Hessisch-Oldendorf in the east, through Rinteln, towards Vlotho in the west, before turning northeast to the town of Porta Westfalica. These northern areas around the Upper Weser Valley, south of the hills are an old area of settlement, which was protected by Schaumburg Castle on the hill of Nesselberg. From the water gap at Porta Westfalica - the Westphalian Gap - the river swings north in order to reach the southern part of the North German Plain. North of the hills are the upper reaches of the Aue (also called the Bückeburger Aue) that run roughly east to west.
Hills
[edit]The Wesergebirge is a chain of about two dozen hills that are arranged one after another in a ridge and which reach a height of 326.1 m above NN at the Möncheberg in the east. In its centre section, west of the A 2 motorway, they reach a maximum height of 278 m at the Wülpker Egge and a height of 235.2 m at the westernmost hill of the Weser chain, the Jakobsberg, which is located east of Porta Westfalica and on which the Jakobsberg transmission tower stands.
The hills and elevations of the Wesergebirge, as seen from west to east, are given below together with their heights in metres above Normalnull (NN)[2] :
- Jakobsberg (235,2 m), with Jakobsberg Telecommunication Tower, Schlageter Monument and Porta Kanzel; north-northeast of the town of Porta Westfalica by the Porta Westfalica gorge
- Königsberg (c. 225 m); northeast of Porta Westfalica
- Roter Brink (c. 225 m), and Nammer Lager; south-southwest of Nammen
- Lohfelder Berg (215,2 m); northeast of Lohfeld
- Nammer Klippe (248,8 m); nature reserve; south of Nammen
- Nammer Kopf (266,3 m), and the Nammer Klippe, nature reserve; south-southeast of Nammen
- Wülpker Egge (c. 278 m), with a quarry; south of Wülpke
- Rote Klippe (c. 220 m), with a quarry; south of Kleinenbremen
- Papenbrink (303 m), with transmission facility and a quarry; north-northwest of Todenmann
- Lange Wand (320,1 m); in the Hainholz State Forest northeast of Todenmann
- Frankenburg-Berg (c. 235 m), and ruins of the Frankenburg; spur of the Langen Wand north of Rinteln-Todenmann
- Luhdener Klippe (c. 300 m), and the 19.8 m high Klippe Tower; north-northeast of Rinteln
- Hirschkuppe (250,1 m); northeast of Rinteln
- Messingsberg (270,1 m), with a quarry; north-northeast of Rinteln-Steinbergen
- Westendorfer Egge (c. 295 m), with a quarry; north-northeast of Rinteln-Westendorf
- Oberberg (325,2 m), and the Springsteinen; north of Rinteln-Schaumburg
- Heutzeberg (225,5 m); spur of the Oberberg north of Schaumburg
- Nesselberg (c. 225 m), and Schaumburg Castle on a spur of the Möncheberg east of Schaumburg
- Möncheberg (326,1 m), and the Paschenburg Guest House between Schaumburg and Hessisch Oldendorf-Rohdental
Panorama
[edit]Towns and villages
[edit]- Auetal (north)
- Bad Eilsen (north)
- Bückeburg (north)
- Heeßen (north)
- Hessisch Oldendorf (south)
- Minden (north)
- Porta Westfalica (south, west and north)
- Rinteln (south)
- Vlotho (southwest)
Literature
[edit]Bundesanstalt für Landeskunde und Raumforschung: Geographische Landesaufnahme 1:200000. Naturräumliche Gliederung Deutschlands. Die naturräumlichen Einheiten auf Blatt 85 Minden. Bad Godesberg 1959
External links
[edit]- Aerial photograph of the western Weser Hills at Google Maps [1]
- Aktionsgemeinschaft Weserbergland [2]
References
[edit]- ^ "Ein anderes Bild als die Bergländer der oberen Weser bieten die Weserkette, das Wiehengebirge und der Teutoburger Wald, see Christian Degn, et al. (ed.) Seydlitz, 1st Part, das deutsche Vaterland, wir und die Welt, 7th ed., Kiel, Hanover, 1954, p. 50