Rubidium sulfide: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
m Bot: link syntax and minor changes |
Reverting edit(s) by 80.37.191.82 (talk) to rev. 1067821127 by Manticore: Vandalism (RW 16.1) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| Appearance = white crystal |
| Appearance = white crystal |
||
| Density = 2.912 g/cm<sup>3</sup><ref name='Lax' /> |
| Density = 2.912 g/cm<sup>3</sup><ref name='Lax' /> |
||
| Solubility = hydrolyses to [[rubidium bisulfide]]<ref name='Lax'>Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: ''Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker. 3. Elemente, anorganische Verbindungen und Materialien, Minerale, Band 3.'' 4. Auflage, Springer, 1997, ISBN |
| Solubility = hydrolyses to [[rubidium bisulfide]]<ref name='Lax'>Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: ''Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker. 3. Elemente, anorganische Verbindungen und Materialien, Minerale, Band 3.'' 4. Auflage, Springer, 1997, {{ISBN|978-3-5406-0035-0}}, S. 692 ({{Google books|||page=692}}).</ref> |
||
| Solvent = [[ethanol]] and [[glycerol]] |
| Solvent = [[ethanol]] and [[glycerol]] |
||
| SolubleOther = soluble |
| SolubleOther = soluble |
||
| MeltingPt = 530 °C<ref name='Perry'>Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: ''Handbook of inorganic compounds''. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN |
| MeltingPt = 530 °C<ref name='Perry'>Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: ''Handbook of inorganic compounds''. CRC Press, 1995, {{ISBN|978-0-8493-8671-8}}, S. 336 ({{Google books|0fT4wfhF1AsC||page=336}}).</ref> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section3 = {{Chembox Structure |
| Section3 = {{Chembox Structure |
||
| CrystalStruct = [[cubic]]:anti-[[fluorite]] |
| CrystalStruct = [[Cubic crystal system|cubic]]:anti-[[fluorite]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards |
| Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related |
||
| OtherCations = [[ |
| OtherCations = [[Lithium sulfide]]<br>[[Sodium sulfide]]<br>[[Potassium sulfide]]<br>[[Caesium sulfide]]<br>[[Francium sulfide]] |
||
| OtherAnions = [[ |
| OtherAnions = [[Rubidium oxide]]<br />[[Rubidium selenide]]<br />[[Rubidium telluride]]<br />[[Rubidium polonide]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Rubidium sulfide''' is an [[inorganic compound]] and a [[salt]] with the [[chemical formula]] Rb<sub>2</sub>S. It is a white solid with similar properties to other [[alkali metal]] [[sulfides]]. |
'''Rubidium sulfide''' is an [[inorganic compound]] and a [[salt (chemistry)|salt]] with the [[chemical formula]] Rb<sub>2</sub>S. It is a white solid with similar properties to other [[alkali metal]] [[sulfides]]. |
||
== Production == |
== Production == |
||
By dissolving [[hydrogen sulfide]] into [[rubidium hydroxide]] solution, it will produce [[rubidium bisulfide]], |
By dissolving [[hydrogen sulfide]] into [[rubidium hydroxide]] solution, it will produce [[rubidium bisulfide]], followed by rubidium sulfide.<ref name="Blitz">Wilhelm Blitz, Ernst Wilke-Dörfurt: "Über Sulfide des Rubidiums und Cäsiums" in ''Zeitschr. f. anorg. Chem.'' '''1906'''. ''48'', S. 297–317. [http://www.archive.org/stream/zeitschriftfura45unkngoog#page/n310/mode/1up Volltext]</ref><ref name='Abegg'>R. Abegg, F. Auerbach: 'Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie'. Verlag S. Hirzel, Bd. 2, 1908. S. 430.[http://www.archive.org/stream/handbuchderanor09koppgoog#page/n449/mode/2up Volltext]</ref> |
||
: <math>\mathrm{ RbOH + H_2S \longrightarrow RbHS + H_2O }</math> |
: <math>\mathrm{ RbOH + H_2S \longrightarrow RbHS + H_2O }</math> |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
== Properties == |
== Properties == |
||
=== Physical properties === |
=== Physical properties === |
||
Rubidium sulfide has a cubic crystal similar to [[lithium sulfide]], [[sodium sulfide]] and [[potassium sulfide]], |
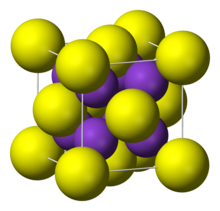
Rubidium sulfide has a cubic crystal similar to [[lithium sulfide]], [[sodium sulfide]] and [[potassium sulfide]], known as the [[Antifluorite|anti-fluorite]] structure. Their [[space group]]s are <math>Fm\bar{3}m</math>. Rubidium sulfide has a crystal lattice unit cell dimension of = 765.0 [[picometer|pm]].<ref name="Lax"/> |
||
=== Chemical properties === |
=== Chemical properties === |
||
Rubidium sulfide reacts with [[sulfur]] in [[hydrogen gas]] to form [[rubidium pentasulfide]] |
Rubidium sulfide reacts with [[sulfur]] in [[hydrogen gas]] to form [[rubidium pentasulfide]], Rb<sub>2</sub>S<sub>5</sub>.<ref name="Abegg"/><ref name="Blitz2">Wilhelm Blitz, Ernst Wilke-Dörfurt: ''Ueber die Pentasulfide des Rubidiums und Cäsiums.'' In ''Ber. d. dt. chem. Ges.'' 1905, 38, 1, S. 123–130, {{doi|10.1002/cber.19050380114}}.</ref> |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
[[Category:Rubidium compounds]] |
[[Category:Rubidium compounds]] |
||
[[Category:Sulfides]] |
[[Category:Sulfides]] |
||
[[Category:Fluorite crystal structure]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 12:47, 25 January 2022
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Rubidium sulfide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Rb2S | |
| Molar mass | 203.00 |
| Appearance | white crystal |
| Density | 2.912 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 530 °C[2] |
| hydrolyses to rubidium bisulfide[1] | |
| Solubility in ethanol and glycerol | soluble |
| Structure | |
| cubic:anti-fluorite | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H314, H400 | |
| P260, P264, P273, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Rubidium oxide Rubidium selenide Rubidium telluride Rubidium polonide |
Other cations
|
Lithium sulfide Sodium sulfide Potassium sulfide Caesium sulfide Francium sulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Rubidium sulfide is an inorganic compound and a salt with the chemical formula Rb2S. It is a white solid with similar properties to other alkali metal sulfides.
Production
[edit]By dissolving hydrogen sulfide into rubidium hydroxide solution, it will produce rubidium bisulfide, followed by rubidium sulfide.[3][4]
Properties
[edit]Physical properties
[edit]Rubidium sulfide has a cubic crystal similar to lithium sulfide, sodium sulfide and potassium sulfide, known as the anti-fluorite structure. Their space groups are . Rubidium sulfide has a crystal lattice unit cell dimension of = 765.0 pm.[1]
Chemical properties
[edit]Rubidium sulfide reacts with sulfur in hydrogen gas to form rubidium pentasulfide, Rb2S5.[4][5]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker. 3. Elemente, anorganische Verbindungen und Materialien, Minerale, Band 3. 4. Auflage, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-5406-0035-0, S. 692 ([1], p. 692, at Google Books).
- ^ Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of inorganic compounds. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8, S. 336 ([2], p. 336, at Google Books).
- ^ Wilhelm Blitz, Ernst Wilke-Dörfurt: "Über Sulfide des Rubidiums und Cäsiums" in Zeitschr. f. anorg. Chem. 1906. 48, S. 297–317. Volltext
- ^ a b R. Abegg, F. Auerbach: 'Handbuch der anorganischen Chemie'. Verlag S. Hirzel, Bd. 2, 1908. S. 430.Volltext
- ^ Wilhelm Blitz, Ernst Wilke-Dörfurt: Ueber die Pentasulfide des Rubidiums und Cäsiums. In Ber. d. dt. chem. Ges. 1905, 38, 1, S. 123–130, doi:10.1002/cber.19050380114.



