17α-Hydroxypregnenolone: Difference between revisions
New Page |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: s2cid. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:Pregnanes | #UCB_Category 96/278 |
||
| (87 intermediate revisions by 45 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Chemical compound}} |
|||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" width="250px" align="right" style="border-collapse:collapse;" |
|||
{{Drugbox |
|||
|- |
|||
| Verifiedfields = changed |
|||
|bgcolor="#ffffff" align="center" colspan=2|Chemical structure of 17-hydroxypregnenolone]]<br><small>17-alpha hydroxypregnenolone</small> |
|||
| verifiedrevid = 477209164 |
|||
|- |
|||
| IUPAC_name = 3β,17α-dihydroxypregn-5-en-20-one |
|||
|align="center" colspan=2 |<font size="-1">'' pregn-5-en-20-one, 3,17-dihydroxy-, (3beta)-''</font> |
|||
| image = 17-Hydroxypregnenolone.svg |
|||
|- align="center" style="border-bottom: 3px solid gray" |
|||
| width = 250 |
|||
| '''[[CAS number]]''' <br/> [387-79-1] |
|||
| image2 = 17-Hidroxipregnenolona3D.png |
|||
|- |
|||
| width2 = 250 |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|Empirical formula |
|||
<!--Clinical data--> |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"|C<sub>21</sub>H<sub>32</sub>O<sub>3</sub> |
|||
| tradename = |
|||
|- |
|||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|[[Molecular weight]] |
|||
| pregnancy_US = <!-- A / B / C / D / X --> |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"|332.48 |
|||
| pregnancy_category = |
|||
|- |
|||
| legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S3 / S4 / S8 --> |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|Bioavailability |
|||
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"| |
|||
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only --> |
|||
|- |
|||
| legal_status = |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|Metabolism |
|||
| routes_of_administration = |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"|[[Adrenal]][[Gonad]]s |
|||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> |
|||
|- |
|||
| bioavailability = |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|[[half life|Elimination half life]] |
|||
| protein_bound = |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"| |
|||
| metabolism = [[Adrenal]], [[Gonad]]s |
|||
|- |
|||
| elimination_half-life = |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|[[Excretion]] |
|||
| excretion = |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"| |
|||
<!--Identifiers--> |
|||
|- |
|||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}} |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|[[Pregnancy category (pharmaceutical) | Pregnancy category]] |
|||
| CAS_number = 387-79-1 |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"| |
|||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| UNII = 77ME40334S |
|||
| align="center" colspan=2 | '''Physical properties''' |
|||
| ATC_prefix = |
|||
|- |
|||
| ATC_suffix = |
|||
|bgcolor="#efefef"|[[Melting point]] |
|||
| PubChem = 3032570 |
|||
|bgcolor="#dfefff"|268°C |
|||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} |
|||
|- |
|||
| DrugBank = |
|||
|} |
|||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| ChemSpiderID = 17215939 |
|||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEBI = 28750 |
|||
<!--Chemical data--> |
|||
| C=21 | H=32 |
|||
| O=3 |
|||
| smiles = CC[C@@]2(O)CC[C@H]1[C@@H]3CCC4CC(O)C(=O)C[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]12C |
|||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChI = 1S/C21H34O3/c1-4-21(24)10-8-16-14-6-5-13-11-17(22)18(23)12-19(13,2)15(14)7-9-20(16,21)3/h13-17,22,24H,4-12H2,1-3H3/t13?,14-,15+,16+,17?,19+,20+,21-/m1/s1 |
|||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
|||
| StdInChIKey = QPLFSAZMHUAMKE-FOCOMJRBSA-N |
|||
| melting_point = 268 |
|||
}} |
|||
''' |
'''17α-Hydroxypregnenolone''' is a [[pregnane]] (C21) [[steroid]] that is obtained by [[hydroxylation]] of [[pregnenolone]] at the C17α position. This step is performed by the [[mitochondria]]l [[cytochrome P450 oxidase|cytochrome P450 enzyme]] 17α-hydroxylase ([[CYP17A1]]) that is present in the [[adrenal]] and [[gonad]]s. Peak levels are reached in humans at the end of [[puberty]] and then decline.<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Hill M, Lukác D, Lapcík O, Sulcová J, Hampl R, Pouzar V, Stárka L | title = Age relationships and sex differences in serum levels of pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in healthy subjects | journal = Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine | volume = 37 | issue = 4 | pages = 439–47 | date = April 1999 | pmid = 10369116 | doi = 10.1515/CCLM.1999.072 | s2cid = 41315909 }}</ref> High levels are also achieved during [[pregnancy]]. It is also a known [[Neuromodulation|neuromodulator]]. |
||
==Prohormone== |
==Prohormone== |
||
17α-Hydroxypregnenolone is considered a [[prohormone]] in the formation of [[dehydroepiandrosterone]] (DHEA), itself a prohormone of the [[sex steroid]]s. |
|||
This conversion is mediated by the enzyme 17,20 lyase . As such 17-OH-pregenolone represents an intermediary in the delta-5-pathway that leads from pregnenolone to DHEA. 17-hydroxypregneolone is also be converted to [[17-hydroxyprogesterone]], a prohomone for the [[glucocorticosteroid]]s and [[androstenedione]], through the activity of 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. |
|||
This conversion is mediated by the enzyme 17,20 lyase. As such 17α-hydroxypregenolone represents an intermediary in the Δ<sup>5</sup> pathway that leads from pregnenolone to DHEA. 17α-Hydroxypregneolone is also converted to [[17α-hydroxyprogesterone]], a prohormone for [[glucocorticosteroid]]s and [[androstenedione]] through the activity of [[3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase]]. |
|||
==Neurohormone== |
|||
There is some evidence that 17-OH-pregnenolone may have activity as a [[neurohormone]].<ref>Matsunaga M, Ukena K, Baulieu EE, Tsutsui K |
|||
7alpha-Hydroxypregnenolone acts as a neuronal activator to stimulate locomotor activity of breeding newts by means of the dopaminergic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17282-7. PMID 15569930</ref> |
|||
==Clinical use== |
==Clinical use== |
||
Measurements of |
Measurements of 17α-hydroxypregnenolone are useful in the diagnosis of certain forms of [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Riepe FG, Mahler P, Sippell WG, Partsch CJ | title = Longitudinal study of plasma pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in full-term and preterm neonates at birth and during the early neonatal period | journal = The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism | volume = 87 | issue = 9 | pages = 4301–6 | date = September 2002 | pmid = 12213889 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2002-020452 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
||
In patients with [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency]] 17α-hydroxypregnenolone is increased, while in patients with [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency]] levels are low to absent. |
|||
[http://jcem.endojournals.org/cgi/content/full/87/9/4301]</ref> |
|||
In patients with [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency]] 17-OH-pregnenolone is increased, while in patients with [[congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency]] levels are low to absent. |
|||
== Neurosteroid == |
|||
17α-hydroxypregnenolone is a known neuromodulator as its acts in the [[central nervous system]]. Specifically, it is known to modulate [[Animal locomotion|locomotion]].<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Tsutsui K, Haraguchi S, Vaudry H | title = 7α-Hydroxypregnenolone regulating locomotor behavior identified in the brain and pineal gland across vertebrates | journal = General and Comparative Endocrinology | volume = 265 | pages = 97–105 | date = September 2018 | pmid = 28919448 | doi = 10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.09.014 | s2cid = 5636071 }}</ref> |
|||
== See also == |
|||
* [[Congenital adrenal hyperplasia]] |
|||
* [[Narave pig]], intersex pigs that have low levels of 17α-Hydroxypregnenolone |
|||
==Additional images== |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
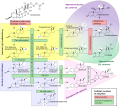
File:Steroidogenesis.svg|[[Steroidogenesis]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
{{Endogenous steroids}} |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators}} |
|||
[[Congenital adrenal hyperplasia]] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hydroxypregnenolone, 17α-}} |
|||
==References== |
|||
<references/> |
|||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Pregnane X receptor agonists]] |
||
[[Category:Pregnanes]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 19:10, 8 March 2023
 | |
 | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Adrenal, Gonads |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.239 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 332.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 268 °C (514 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
17α-Hydroxypregnenolone is a pregnane (C21) steroid that is obtained by hydroxylation of pregnenolone at the C17α position. This step is performed by the mitochondrial cytochrome P450 enzyme 17α-hydroxylase (CYP17A1) that is present in the adrenal and gonads. Peak levels are reached in humans at the end of puberty and then decline.[1] High levels are also achieved during pregnancy. It is also a known neuromodulator.
Prohormone
[edit]17α-Hydroxypregnenolone is considered a prohormone in the formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), itself a prohormone of the sex steroids.
This conversion is mediated by the enzyme 17,20 lyase. As such 17α-hydroxypregenolone represents an intermediary in the Δ5 pathway that leads from pregnenolone to DHEA. 17α-Hydroxypregneolone is also converted to 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, a prohormone for glucocorticosteroids and androstenedione through the activity of 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
Clinical use
[edit]Measurements of 17α-hydroxypregnenolone are useful in the diagnosis of certain forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.[2] In patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency 17α-hydroxypregnenolone is increased, while in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency levels are low to absent.
Neurosteroid
[edit]17α-hydroxypregnenolone is a known neuromodulator as its acts in the central nervous system. Specifically, it is known to modulate locomotion.[3]
See also
[edit]- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Narave pig, intersex pigs that have low levels of 17α-Hydroxypregnenolone
Additional images
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Hill M, Lukác D, Lapcík O, Sulcová J, Hampl R, Pouzar V, Stárka L (April 1999). "Age relationships and sex differences in serum levels of pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in healthy subjects". Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. 37 (4): 439–47. doi:10.1515/CCLM.1999.072. PMID 10369116. S2CID 41315909.
- ^ Riepe FG, Mahler P, Sippell WG, Partsch CJ (September 2002). "Longitudinal study of plasma pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in full-term and preterm neonates at birth and during the early neonatal period". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 87 (9): 4301–6. doi:10.1210/jc.2002-020452. PMID 12213889.
- ^ Tsutsui K, Haraguchi S, Vaudry H (September 2018). "7α-Hydroxypregnenolone regulating locomotor behavior identified in the brain and pineal gland across vertebrates". General and Comparative Endocrinology. 265: 97–105. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.09.014. PMID 28919448. S2CID 5636071.