Rückweiler: Difference between revisions
Niceguyedc (talk | contribs) |
m Disambiguating links to Ortsgemeinde (link changed to Ortsgemeinde (Germany)) using DisamAssist. |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox German location |
{{Infobox German location |
||
| |
|name = Rückweiler |
||
| |
|type = |
||
|Art = |
|||
|image_photo = |
|image_photo = |
||
|imagesize = |
|imagesize = |
||
|image_caption = |
|image_caption = |
||
| |
|image_coa = Wappen Rueckweiler.svg |
||
|coordinates = {{coord|49|34|57|N|07|14|21|E|format=dms|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|lat_deg = 49 |lat_min = 34 |lat_sec = 57 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|lon_deg = 07 |lon_min = 14 |lon_sec = 21 |
|||
|state = Rheinland-Pfalz |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| |
|district = Birkenfeld |
||
|Landkreis = Birkenfeld |
|||
|Verbandsgemeinde = Baumholder |
|Verbandsgemeinde = Baumholder |
||
| |
|elevation = 500 |
||
| |
|area = 2.75 |
||
| |
|postal_code = 55776 |
||
| |
|area_code = 06789 |
||
| |
|licence = BIR |
||
|Vorwahl = 06789 |
|||
|Kfz = BIR |
|||
|Gemeindeschlüssel = 07 1 34 074 |
|Gemeindeschlüssel = 07 1 34 074 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|Adresse-Verband = Am Weiherdamm 1<br />55774 Baumholder |
|||
|mayor = Lutz Altekrüger<ref name=mayor>[https://www.wahlen.rlp.de/de/kw/wahlen/kd/gebiete/1340000000000.html Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Birkenfeld], Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 10 August 2021.</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|leader_term = 2019–24 |
|||
|Bürgermeister = Leo Werle |
|||
|Bürgermeistertitel = Ortsbürgermeister |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
| ⚫ | '''Rückweiler''' is an ''[[Ortsgemeinde (Germany)|Ortsgemeinde]]'' – a [[Municipalities of Germany|municipality]] belonging to a ''[[Verbandsgemeinde]]'', a kind of collective municipality – in the [[Birkenfeld (district)|Birkenfeld]] [[Districts of Germany|district]] in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]], [[Germany]]. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of [[Baumholder (Verbandsgemeinde)|Baumholder]], whose seat is in the [[Baumholder|like-named town]]. |
||
<!-- |
|||
************************************************************************* |
|||
************************************************************************* |
|||
** THIS ARTICLE IS WRITTEN IN COMMONWEALTH SPELLING (CANADIAN VARIANT).** |
|||
** PLEASE DO NOT “CORRECT” SPELLINGS TO THEIR U.S. VERSIONS! ** |
|||
************************************************************************* |
|||
************************************************************************* |
|||
--> |
|||
| ⚫ | '''Rückweiler''' is an ''[[Ortsgemeinde]]'' – a [[Municipalities of Germany|municipality]] belonging to a ''[[Verbandsgemeinde]]'', a kind of collective municipality – in the [[Birkenfeld (district)|Birkenfeld]] [[Districts of Germany|district]] in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]], [[Germany]]. It belongs to the [[Baumholder (Verbandsgemeinde)| |
||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
===Location=== |
===Location=== |
||
The municipality lies in the [[Hunsrück]], at Rhineland- |
The municipality lies in the [[Hunsrück]], at Rhineland-Palatinate's boundary with the [[Saarland]]. The municipal area measures roughly 274 ha, and the elevation is 524 m above [[sea level]]. |
||
===Neighbouring municipalities=== |
===Neighbouring municipalities=== |
||
| Line 44: | Line 32: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
Bearing witness to early habitation in the Rückweiler area are [[grave goods]] from the [[Iron Age]] going back as far as the 6th century BC. The people of the Hunsrück-Eifel |
Bearing witness to early habitation in the Rückweiler area are [[grave goods]] from the [[Iron Age]] going back as far as the 6th century BC. The people of the [[Hunsrück-Eifel culture]] were [[Celts|Celtic]], raised livestock, and were also already raising crops. They burnt their dead and buried them with their belongings. Their “princes”, however, were buried in great mounds under hefty stones. An extensive burying ground was discovered near Rückweiler on the western slope of the Rückeberg. This discovery and other burying grounds in Freisen and near [[Hoppstädten-Weiersbach]] show that the region was already attracting settlers then. |
||
The Rückweiler burying ground comprised 12 graves sunk into the rock within an area of 3 000 m² at a sport field, which now no longer exists. Brought to light from these graves were handmade and [[Potter's wheel|thrown]] pots of various shapes. The way that the graves were laid out as a group suggested that the burying ground was a family plot, or perhaps one used by an estate. The graves were either [[Ellipse|elliptical]] or [[Rectangle|rectangular]] and more than a metre long. They lay as far down as 90 cm below the ground and were filled with dark earth coloured by [[charcoal]] remnants. The number of pots found in each grave varied from one to ten. For the voyage to the hereafter, some pots contained food, jewellery, items of clothing and other belongings. One peculiarity was the graves’ superstructures, which had, of course, long since vanished. However, the upright posts of these structures had left dark soil where they had once been sunk into the earth. The superstructure remnants at two of the graves suggested that the superstructures might have been replicas of the |
The Rückweiler burying ground comprised 12 graves sunk into the rock within an area of 3 000 m² at a sport field, which now no longer exists. Brought to light from these graves were handmade and [[Potter's wheel|thrown]] pots of various shapes. The way that the graves were laid out as a group suggested that the burying ground was a family plot, or perhaps one used by an estate. The graves were either [[Ellipse|elliptical]] or [[Rectangle|rectangular]] and more than a metre long. They lay as far down as 90 cm below the ground and were filled with dark earth coloured by [[charcoal]] remnants. The number of pots found in each grave varied from one to ten. For the voyage to the hereafter, some pots contained food, jewellery, items of clothing and other belongings. One peculiarity was the graves’ superstructures, which had, of course, long since vanished. However, the upright posts of these structures had left dark soil where they had once been sunk into the earth. The superstructure remnants at two of the graves suggested that the superstructures might have been replicas of the dead's houses, further suggesting a Mediterranean influence from [[La Tène culture|La Tène times]]. The superstructures served as remembrance to the dead and also were important in the care of the departed souls, for the builders believed that without such care, the dead were left to wander about without peace, bringing the living bad luck and harm. To ward off any such outcome, the dead were given food, drink and sacrifices. |
||
According to old documents, the Rückweiler area belonged in the 12th century to the Bishop of Verdun. Even the [[County of Veldenz|Counts of Veldenz]], who as fiefholders ruled the land, named the Bishop as the actual landowner. Given this, it can easily be concluded that the whole area once belonged to a greater landhold, Tholey, which Deacon Adelgisel, known as Grimo, a great [[Merovingian dynasty|Merovingian]] landholder, donated to the Church of Verdun on 30 December 634. |
According to old documents, the Rückweiler area belonged in the 12th century to the Bishop of Verdun. Even the [[County of Veldenz|Counts of Veldenz]], who as fiefholders ruled the land, named the Bishop as the actual landowner. Given this, it can easily be concluded that the whole area once belonged to a greater landhold, Tholey, which [[Adalgisel Grimo|Deacon Adelgisel]], known as Grimo, a great [[Merovingian dynasty|Merovingian]] landholder, donated to the Church of Verdun on 30 December 634. |
||
On 5 March 1332, Rückweiler had its first documentary mention under the name ''Rickwilre''. In the villages of Rohrbach and Rückweiler, which belonged to the ''Pflege'' (literally “care”, but actually a local geopolitical unit) of Rohrbach, the land was held, as it was in the neighbouring court district of Baumholder at that time, by enfeoffed lords. On the date in question, Dietrich Gauwer von Lichtenberg allocated 299 ''Mark Pfennige'' from his holdings in Rohrbach and Rückweiler for his wife as a dower. In 1386, Johann von Lewenstein paid Count of Veldenz Heinrich 100 ''[[Gulden]]'' (roughly equivalent to €4000 or €5000 in modern funds) for his villages, courts, paupers, water and meadowland at ''“Roirbach, Zingswilre und Rickwilre”'' along with three bondsmen outside these villages. In 1428, the Count of Veldenz awarded the court fief to the House of Winterbecher. Three years later, half of each of the two villages of Rohrbach and Rückweiler, along with their people, interest payments and earnings, were under [[County of Sponheim|Count of Sponheim]] |
On 5 March 1332, Rückweiler had its first documentary mention under the name ''Rickwilre''. In the villages of Rohrbach and Rückweiler, which belonged to the ''Pflege'' (literally “care”, but actually a local geopolitical unit) of Rohrbach, the land was held, as it was in the neighbouring court district of Baumholder at that time, by enfeoffed lords. On the date in question, Dietrich Gauwer von Lichtenberg allocated 299 ''Mark Pfennige'' from his holdings in Rohrbach and Rückweiler for his wife as a dower. In 1386, Johann von Lewenstein paid Count of Veldenz Heinrich 100 ''[[Goldgulden|Gulden]]'' (roughly equivalent to €4000 or €5000 in modern funds) for his villages, courts, paupers, water and meadowland at ''“Roirbach, Zingswilre und Rickwilre”'' along with three bondsmen outside these villages. In 1428, the Count of Veldenz awarded the court fief to the House of Winterbecher. Three years later, half of each of the two villages of Rohrbach and Rückweiler, along with their people, interest payments and earnings, were under [[County of Sponheim|Count of Sponheim]] Wolf's ownership. He in turn sold the rights along with other goods and sources of income for 487.5 ''Gulden'' to Count of Veldenz Friedrich. The other halves of the fiefs of Rohrbach and Rückweiler were held by the family Gauwer von Lichtenberg, and thereafter by Hildebrand von Boxberg. Owing to disputes between Count of Veldenz Stephan and Lord of Oberstein Wyrich von Dhaun, a judicial decision on 26 January 1440 stipulated that the Boxberg fief of Rohrbach, Rückweiler and Würtzweiler was to be awarded in whole to the House of Veldenz. Four years later, when the House of Veldenz died out in its male line, Rückweiler passed to [[Stephen, Count Palatine of Simmern-Zweibrücken]]. |
||
In the [[Thirty Years' War]], the region around Rückweiler suffered heavily. |
In the [[Thirty Years' War]], the region around Rückweiler suffered heavily. Subsequently, as a result of brutal Rhine campaigns by [[Louis XIV]]'s troops in the [[Franco-Dutch War]], in 1675 Rückweiler had only one family left. |
||
In [[French Revolution]]’s wake, Rückweiler, having formerly belonged to the ''Amt'' of Berschweiler, and for a short while to the ''Amt'' of Nohfelden, was assigned under [[France|French]] rule, beginning in 1793, to the ''Mairie'' (“Mayoralty”) of Berschweiler in the [[Cantons of France|canton]] of Baumholder<ref>[http://www.rueckweiler.de/unserort/geschich/fr_haupt.html Rückweiler’s history]</ref> |
In [[French Revolution]]’s wake, Rückweiler, having formerly belonged to the ''Amt'' of Berschweiler, and for a short while to the ''Amt'' of Nohfelden, was assigned under [[France|French]] rule, beginning in 1793, to the ''Mairie'' (“Mayoralty”) of Berschweiler in the [[Cantons of France|canton]] of Baumholder<ref>[http://www.rueckweiler.de/unserort/geschich/fr_haupt.html Rückweiler’s history] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120425141410/http://www.rueckweiler.de/unserort/geschich/fr_haupt.html |date=2012-04-25 }}</ref> As such it was incorporated into the [[First French Empire]] under [[Napoleon]]. |
||
At the [[Congress of Vienna]], Rückweiler was granted to [[Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha|Duke Ernest III of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld]] as part of a large estate of some 8.25 square miles, at first called the ''Herrschaft'' Baumholder; by a ducal decree of 6 March 1819, the area between Baumholder and Kusel was renamed the [[Principality of Lichtenberg]]. In 1834, however, due to political unrest and its great distance from the rest of his Duchy, Duke Ernest sold the Principality to [[Kingdom of Prussia|Prussia]] for an annuity of 80,000 talers. |
|||
Thereafter the village formed a part of the [[Provinces of Prussia|Prussian]] [[Rhine Province]] and from 1871 a part of the [[German Empire]]. Following the abdication of the [[Wilhelm II|last emperor]] in 1918, the province was included in the newly established [[Free State of Prussia]] in the [[Weimar Republic]]; in 1920 it was made part of the [[League of Nations]] [[protectorate]] known as the ''[[Saar (League of Nations)|Saargebiet]]'', until a [[plebiscite]] returned the territory to the German ''[[Nazi Germany|Reich]]'' in 1935. From the fall of the ''Reich'' in 1945, the area was part of the [[Allied-occupied Germany#French Zone of Occupation|French occupied zone]]. |
|||
==Politics== |
==Politics== |
||
===Municipal council=== |
===Municipal council=== |
||
The council is made up of 8 council members, who were elected by [[Plurality voting system|majority vote]] at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.<ref>[http://wahlen.rlp.de/kw/wahlen/2009/gemeinderatswahlen/ergebnisse/1340107400.html Kommunalwahl Rheinland-Pfalz 2009, Gemeinderat]</ref> |
The council is made up of 8 council members, who were elected by [[Plurality voting system|majority vote]] at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.<ref>[http://wahlen.rlp.de/kw/wahlen/2009/gemeinderatswahlen/ergebnisse/1340107400.html Kommunalwahl Rheinland-Pfalz 2009, Gemeinderat]</ref> |
||
===Mayor=== |
===Mayor=== |
||
Rückweiler's mayor is Lutz Altekrüger.<ref name=mayor/> |
|||
Rückweiler’s mayor is Leo Werle, and his deputies are Gerd Schwan and Lutz Altekrüger.<ref>[http://www.rueckweiler.de/verwaltu/ratsmitg/mitlg_05.html Rückweiler’s council]</ref> |
|||
===Coat of arms=== |
===Coat of arms=== |
||
The German blazon reads: ''In geteiltem Schild oben in Silber ein rotbewehrter und gezungter wachsender blauer Löwe, unten in Grün ein goldener, mit rotem Band umwundener Erntekranz, belegt mit einem goldenen Kreuz.'' |
The German blazon reads: ''{{lang|de|In geteiltem Schild oben in Silber ein rotbewehrter und gezungter wachsender blauer Löwe, unten in Grün ein goldener, mit rotem Band umwundener Erntekranz, belegt mit einem goldenen Kreuz.}}'' |
||
The |
The municipality's [[Coat of arms|arms]] might in English [[Heraldry|heraldic]] language be described thus: Per fess, argent issuant from the line of partition a demilion azure armed and langued gules, and vert a wreath Or and gules surmounting the three short arms and surmounted by the lower arm of a cross Latin issuant from base of the fifth. |
||
The [[charge (heraldry)|charge]] in the upper field, the lion, is a reference to the |
The [[charge (heraldry)|charge]] in the upper field, the lion, is a reference to the village's former allegiance to the [[County of Veldenz]]. The composition of charges in the lower field is known as a harvest cross (''Erntekreuz'' in [[German language|German]]) and refers to the municipality's yearly harvest festival in which thanks are given for the harvest. |
||
The arms have been borne since 25 November 1965.<ref>[http://www.rueckweiler.de/unserort/wappen/wappen.html Description and explanation of Rückweiler’s arms]</ref> |
The arms have been borne since 25 November 1965.<ref>[http://www.rueckweiler.de/unserort/wappen/wappen.html Description and explanation of Rückweiler’s arms] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110725201916/http://www.rueckweiler.de/unserort/wappen/wappen.html |date=2011-07-25 }}</ref> |
||
==Culture and sightseeing== |
==Culture and sightseeing== |
||
===Buildings=== |
===Buildings=== |
||
The following are listed buildings or sites in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]]’s Directory of Cultural Monuments:<ref>[http://denkmallisten.gdke-rlp.de/Birkenfeld.pdf Directory of Cultural Monuments in Birkenfeld district]</ref> |
The following are listed buildings or sites in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]]’s Directory of Cultural Monuments:<ref>[http://denkmallisten.gdke-rlp.de/Birkenfeld.pdf Directory of Cultural Monuments in Birkenfeld district]</ref> |
||
| Line 81: | Line 75: | ||
==Economy and infrastructure== |
==Economy and infrastructure== |
||
===Public institutions=== |
===Public institutions=== |
||
Rückweiler has a [[kindergarten]] and a village community centre. |
Rückweiler has a [[kindergarten]] and a village community centre. |
||
| Line 91: | Line 86: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://www.vgv-baumholder.de/die_gemeinden/rueckweiler/ Rückweiler in the collective municipality’s webpages] {{ |
* [http://www.vgv-baumholder.de/die_gemeinden/rueckweiler/ Rückweiler in the collective municipality’s webpages] {{in lang|de}} |
||
* [http://www.rueckweiler.de/ Municipality’s official webpage] {{ |
* [http://www.rueckweiler.de/ Municipality’s official webpage] {{in lang|de}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{de}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{Birkenfeld-geo-stub}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ruckweiler}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ruckweiler}} |
||
[[Category:Birkenfeld (district)]] |
|||
[[de:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[eo:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[fr:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[it:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[nl:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[pl:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[pt:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[ro:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[ru:Рюквайлер]] |
|||
[[sr:Риквајлер]] |
|||
[[vi:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[vo:Rückweiler]] |
|||
[[war:Rückweiler]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 02:10, 1 June 2023
Rückweiler | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 49°34′57″N 07°14′21″E / 49.58250°N 7.23917°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
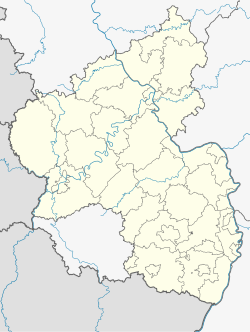
| District | Birkenfeld |
| Municipal assoc. | Baumholder |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–24) | Lutz Altekrüger[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 2.75 km2 (1.06 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 500 m (1,600 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
• Total | 380 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (360/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 55776 |
| Dialling codes | 06789 |
| Vehicle registration | BIR |
| Website | www.rueckweiler.de |
Rückweiler is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Baumholder, whose seat is in the like-named town.
Geography
[edit]Location
[edit]The municipality lies in the Hunsrück, at Rhineland-Palatinate's boundary with the Saarland. The municipal area measures roughly 274 ha, and the elevation is 524 m above sea level.
Neighbouring municipalities
[edit]Rückweiler borders in the north on the municipality of Berglangenbach, in the east on the municipality of Rohrbach, in the southeast on the municipality of Freisen, in the southwest on the municipality of Hahnweiler and in the northwest on the municipality of Leitzweiler. Rückweiler also meets the municipality of Gimbweiler to the west at a single point, which is also shared with two other municipalities. All municipalities named here are in the Birkenfeld district but for Freisen, which is in the Sankt Wendel district in the Saarland.
History
[edit]Bearing witness to early habitation in the Rückweiler area are grave goods from the Iron Age going back as far as the 6th century BC. The people of the Hunsrück-Eifel culture were Celtic, raised livestock, and were also already raising crops. They burnt their dead and buried them with their belongings. Their “princes”, however, were buried in great mounds under hefty stones. An extensive burying ground was discovered near Rückweiler on the western slope of the Rückeberg. This discovery and other burying grounds in Freisen and near Hoppstädten-Weiersbach show that the region was already attracting settlers then.
The Rückweiler burying ground comprised 12 graves sunk into the rock within an area of 3 000 m² at a sport field, which now no longer exists. Brought to light from these graves were handmade and thrown pots of various shapes. The way that the graves were laid out as a group suggested that the burying ground was a family plot, or perhaps one used by an estate. The graves were either elliptical or rectangular and more than a metre long. They lay as far down as 90 cm below the ground and were filled with dark earth coloured by charcoal remnants. The number of pots found in each grave varied from one to ten. For the voyage to the hereafter, some pots contained food, jewellery, items of clothing and other belongings. One peculiarity was the graves’ superstructures, which had, of course, long since vanished. However, the upright posts of these structures had left dark soil where they had once been sunk into the earth. The superstructure remnants at two of the graves suggested that the superstructures might have been replicas of the dead's houses, further suggesting a Mediterranean influence from La Tène times. The superstructures served as remembrance to the dead and also were important in the care of the departed souls, for the builders believed that without such care, the dead were left to wander about without peace, bringing the living bad luck and harm. To ward off any such outcome, the dead were given food, drink and sacrifices.
According to old documents, the Rückweiler area belonged in the 12th century to the Bishop of Verdun. Even the Counts of Veldenz, who as fiefholders ruled the land, named the Bishop as the actual landowner. Given this, it can easily be concluded that the whole area once belonged to a greater landhold, Tholey, which Deacon Adelgisel, known as Grimo, a great Merovingian landholder, donated to the Church of Verdun on 30 December 634.
On 5 March 1332, Rückweiler had its first documentary mention under the name Rickwilre. In the villages of Rohrbach and Rückweiler, which belonged to the Pflege (literally “care”, but actually a local geopolitical unit) of Rohrbach, the land was held, as it was in the neighbouring court district of Baumholder at that time, by enfeoffed lords. On the date in question, Dietrich Gauwer von Lichtenberg allocated 299 Mark Pfennige from his holdings in Rohrbach and Rückweiler for his wife as a dower. In 1386, Johann von Lewenstein paid Count of Veldenz Heinrich 100 Gulden (roughly equivalent to €4000 or €5000 in modern funds) for his villages, courts, paupers, water and meadowland at “Roirbach, Zingswilre und Rickwilre” along with three bondsmen outside these villages. In 1428, the Count of Veldenz awarded the court fief to the House of Winterbecher. Three years later, half of each of the two villages of Rohrbach and Rückweiler, along with their people, interest payments and earnings, were under Count of Sponheim Wolf's ownership. He in turn sold the rights along with other goods and sources of income for 487.5 Gulden to Count of Veldenz Friedrich. The other halves of the fiefs of Rohrbach and Rückweiler were held by the family Gauwer von Lichtenberg, and thereafter by Hildebrand von Boxberg. Owing to disputes between Count of Veldenz Stephan and Lord of Oberstein Wyrich von Dhaun, a judicial decision on 26 January 1440 stipulated that the Boxberg fief of Rohrbach, Rückweiler and Würtzweiler was to be awarded in whole to the House of Veldenz. Four years later, when the House of Veldenz died out in its male line, Rückweiler passed to Stephen, Count Palatine of Simmern-Zweibrücken.
In the Thirty Years' War, the region around Rückweiler suffered heavily. Subsequently, as a result of brutal Rhine campaigns by Louis XIV's troops in the Franco-Dutch War, in 1675 Rückweiler had only one family left.
In French Revolution’s wake, Rückweiler, having formerly belonged to the Amt of Berschweiler, and for a short while to the Amt of Nohfelden, was assigned under French rule, beginning in 1793, to the Mairie (“Mayoralty”) of Berschweiler in the canton of Baumholder[3] As such it was incorporated into the First French Empire under Napoleon.
At the Congress of Vienna, Rückweiler was granted to Duke Ernest III of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld as part of a large estate of some 8.25 square miles, at first called the Herrschaft Baumholder; by a ducal decree of 6 March 1819, the area between Baumholder and Kusel was renamed the Principality of Lichtenberg. In 1834, however, due to political unrest and its great distance from the rest of his Duchy, Duke Ernest sold the Principality to Prussia for an annuity of 80,000 talers.
Thereafter the village formed a part of the Prussian Rhine Province and from 1871 a part of the German Empire. Following the abdication of the last emperor in 1918, the province was included in the newly established Free State of Prussia in the Weimar Republic; in 1920 it was made part of the League of Nations protectorate known as the Saargebiet, until a plebiscite returned the territory to the German Reich in 1935. From the fall of the Reich in 1945, the area was part of the French occupied zone.
Politics
[edit]Municipal council
[edit]The council is made up of 8 council members, who were elected by majority vote at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.[4]
Mayor
[edit]Rückweiler's mayor is Lutz Altekrüger.[1]
Coat of arms
[edit]The German blazon reads: In geteiltem Schild oben in Silber ein rotbewehrter und gezungter wachsender blauer Löwe, unten in Grün ein goldener, mit rotem Band umwundener Erntekranz, belegt mit einem goldenen Kreuz.
The municipality's arms might in English heraldic language be described thus: Per fess, argent issuant from the line of partition a demilion azure armed and langued gules, and vert a wreath Or and gules surmounting the three short arms and surmounted by the lower arm of a cross Latin issuant from base of the fifth.
The charge in the upper field, the lion, is a reference to the village's former allegiance to the County of Veldenz. The composition of charges in the lower field is known as a harvest cross (Erntekreuz in German) and refers to the municipality's yearly harvest festival in which thanks are given for the harvest.
The arms have been borne since 25 November 1965.[5]
Culture and sightseeing
[edit]Buildings
[edit]The following are listed buildings or sites in Rhineland-Palatinate’s Directory of Cultural Monuments:[6]
- Heart of Jesus Catholic Parish Church (Pfarrkirche Herz Jesu), Hauptstraße 18 – Gothic Revival sandstone-framed breccia aisleless church, 1907, architect Wilhelm Hector, Saarbrücken
- Freisener Straße 2 – stately Quereinhaus (a combination residential and commercial house divided for these two purposes down the middle, perpendicularly to the street), possibly about 1850
The Catholic church mentioned above is popularly known as the Heidedom (“Heath Cathedral”), although it is not actually a cathedral.
Economy and infrastructure
[edit]Public institutions
[edit]Rückweiler has a kindergarten and a village community centre.
Transport
[edit]Running south of the municipality is the Autobahn A 62 (Kaiserslautern–Trier). Serving nearby Heimbach is a railway station on the Nahe Valley Railway (Bingen–Saarbrücken).
References
[edit]- ^ a b Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Birkenfeld, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 10 August 2021.
- ^ "Bevölkerungsstand 2022, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden" (PDF) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz. 2023.
- ^ Rückweiler’s history Archived 2012-04-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kommunalwahl Rheinland-Pfalz 2009, Gemeinderat
- ^ Description and explanation of Rückweiler’s arms Archived 2011-07-25 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Directory of Cultural Monuments in Birkenfeld district
External links
[edit]- Rückweiler in the collective municipality’s webpages (in German)
- Municipality’s official webpage (in German)