Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
consistent citation formatting |
Adding short description: "Cytosolic DNA sensor" |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Cytosolic DNA sensor}} |
|||
{{Infobox enzyme |
{{Infobox enzyme |
||
| Name = Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
| Name = Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
| GO_code = |
| GO_code = |
||
| image = CGAS complexed with dsDNA.png |
| image = CGAS complexed with dsDNA.png |
||
| caption = cGAS complexed with dsDNA ( |
| caption = cGAS complexed with dsDNA (based on PDB 4O6A) |
||
}} |
|name=}} |
||
[[File:5v8j.jpg|thumbnail|cGAS dimer, |
[[File:5v8j.jpg|thumbnail|cGAS dimer, human]] |
||
[[File:cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway.jpg|thumb|cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway]] |
[[File:cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway.jpg|thumb|cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway]] |
||
'''Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase''' (cGAS, [[Cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate|cGAMP]] synthase), belonging to the [[nucleotidyltransferase]] family, is a [[The cGAS – STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway|cytosolic DNA sensor]] that activates a [[Interferon type I|type-I interferon]] response. It is part of the [[CGAS–STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway|cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway]]. It binds to microbial [[DNA]] as well as self DNA that invades the [[cytoplasm]], and catalyzes [[Cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate|cGAMP]] synthesis.<ref name="pmid23258413">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway | journal = Science | volume = 339 | issue = 6121 | pages = 786–91 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23258413 | pmc = 3863629 | doi = 10.1126/science.1232458 | bibcode = 2013Sci...339..786S }}</ref> [[Cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate|cGAMP]] then functions as a [[second messenger]] that binds to and activates the [[endoplasmic reticulum]] protein [[Stimulator of interferon genes|STING]] to trigger [[Interferon type I|type-I IFNs]] production.<ref name="pmid23258412">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, Chen ZJ | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA | journal = Science | volume = 339 | issue = 6121 | pages = 826–30 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23258412 | pmc = 3855410 | doi = 10.1126/science.1229963 | bibcode = 2013Sci...339..826W }}</ref><ref name="GaoAscano2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, Serganov AA, Liu Y, Jones RA, Hartmann G, Tuschl T, Patel DJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Cyclic [G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase | journal = Cell | volume = 153 | issue = 5 | pages = 1094–107 | date = May 2013 | pmid = 23647843 | pmc = 4382009 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.046 }}</ref><ref name=Zhang>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang X, Shi H, Wu J, Zhang X, Sun L, Chen C, Chen ZJ | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING | journal = Molecular Cell | volume = 51 | issue = 2 | pages = 226–35 | date = July 2013 | pmid = 23747010 | pmc = 3808999 | doi = 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.022 }}</ref> Mice lacking cGAS are more vulnerable to lethal infection by [[DNA virus]]es.<ref name=Li>{{cite journal | vauthors = Li XD, Wu J, Gao D, Wang H, Sun L, Chen ZJ | title = Pivotal roles of cGAS-cGAMP signaling in antiviral defense and immune adjuvant effects | journal = Science | volume = 341 | issue = 6152 | pages = 1390–4 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23989956 | pmc = 3863637 | doi = 10.1126/science.1244040 | bibcode = 2013Sci...341.1390L }}</ref> In addition, cGAS has been shown to be an innate immune sensor of retroviruses including [[HIV]].<ref name=Gao>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gao D, Wu J, Wu YT, Du F, Aroh C, Yan N, Sun L, Chen ZJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is an innate immune sensor of HIV and other retroviruses | journal = Science | volume = 341 | issue = 6148 | pages = 903–6 | date = August 2013 | pmid = 23929945 | pmc = 3860819 | doi = 10.1126/science.1240933 | bibcode = 2013Sci...341..903G }}</ref><ref name=Lahaye>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lahaye X, Satoh T, Gentili M, Cerboni S, Conrad C, Hurbain I, El Marjou A, Lacabaratz C, Lelièvre JD, Manel N | display-authors = 6 | title = The capsids of HIV-1 and HIV-2 determine immune detection of the viral cDNA by the innate sensor cGAS in dendritic cells | journal = Immunity | volume = 39 | issue = 6 | pages = 1132–42 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24269171 | doi = 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.002 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The human gene encoding cGAS is [[MB21D1]] on chromosome 6. |
'''Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase''' (cGAS, [[Cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate|cGAMP]] synthase), belonging to the [[nucleotidyltransferase]] family, is a [[The cGAS – STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway|cytosolic DNA sensor]] that activates a [[Interferon type I|type-I interferon]] response. It is part of the [[CGAS–STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway|cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway]]. It binds to microbial [[DNA]] as well as self DNA that invades the [[cytoplasm]], and catalyzes [[Cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate|cGAMP]] synthesis.<ref name="pmid23258413">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway | journal = Science | volume = 339 | issue = 6121 | pages = 786–91 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23258413 | pmc = 3863629 | doi = 10.1126/science.1232458 | bibcode = 2013Sci...339..786S }}</ref> [[Cyclic guanosine monophosphate–adenosine monophosphate|cGAMP]] then functions as a [[second messenger]] that binds to and activates the [[endoplasmic reticulum]] protein [[Stimulator of interferon genes|STING]] to trigger [[Interferon type I|type-I IFNs]] production.<ref name="pmid23258412">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, Chen ZJ | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA | journal = Science | volume = 339 | issue = 6121 | pages = 826–30 | date = February 2013 | pmid = 23258412 | pmc = 3855410 | doi = 10.1126/science.1229963 | bibcode = 2013Sci...339..826W }}</ref><ref name="GaoAscano2013">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, Serganov AA, Liu Y, Jones RA, Hartmann G, Tuschl T, Patel DJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Cyclic [G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase | journal = Cell | volume = 153 | issue = 5 | pages = 1094–107 | date = May 2013 | pmid = 23647843 | pmc = 4382009 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.046 }}</ref><ref name=Zhang>{{cite journal | vauthors = Zhang X, Shi H, Wu J, Zhang X, Sun L, Chen C, Chen ZJ | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING | journal = Molecular Cell | volume = 51 | issue = 2 | pages = 226–35 | date = July 2013 | pmid = 23747010 | pmc = 3808999 | doi = 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.022 }}</ref> Mice lacking cGAS are more vulnerable to lethal infection by [[DNA virus]]es and [[RNA virus]]es.<ref name=Li>{{cite journal | vauthors = Li XD, Wu J, Gao D, Wang H, Sun L, Chen ZJ | title = Pivotal roles of cGAS-cGAMP signaling in antiviral defense and immune adjuvant effects | journal = Science | volume = 341 | issue = 6152 | pages = 1390–4 | date = September 2013 | pmid = 23989956 | pmc = 3863637 | doi = 10.1126/science.1244040 | bibcode = 2013Sci...341.1390L }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors =Yu P, Miao Z, Li Y, Bansal R, Peppelenbosch MP, Pan Q| title = cGAS-STING effectively restricts murine norovirus infection but antagonizes the antiviral action of N-terminus of RIG-I in mouse macrophages.| journal = Gut Microbes | volume = 13 | issue= 1 | pages = 1959839| date = January 2021 | pmid = 34347572 | pmc = 8344765 | doi = 10.1080/19490976.2021.1959839 }}</ref> In addition, cGAS has been shown to be an innate immune sensor of retroviruses including [[HIV]].<ref name=Gao>{{cite journal | vauthors = Gao D, Wu J, Wu YT, Du F, Aroh C, Yan N, Sun L, Chen ZJ | display-authors = 6 | title = Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is an innate immune sensor of HIV and other retroviruses | journal = Science | volume = 341 | issue = 6148 | pages = 903–6 | date = August 2013 | pmid = 23929945 | pmc = 3860819 | doi = 10.1126/science.1240933 | bibcode = 2013Sci...341..903G }}</ref><ref name=Lahaye>{{cite journal | vauthors = Lahaye X, Satoh T, Gentili M, Cerboni S, Conrad C, Hurbain I, El Marjou A, Lacabaratz C, Lelièvre JD, Manel N | display-authors = 6 | title = The capsids of HIV-1 and HIV-2 determine immune detection of the viral cDNA by the innate sensor cGAS in dendritic cells | journal = Immunity | volume = 39 | issue = 6 | pages = 1132–42 | date = December 2013 | pmid = 24269171 | doi = 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.002 | doi-access = free }}</ref> The human gene encoding cGAS is [[MB21D1]] on chromosome 6. |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
Latest revision as of 18:35, 23 January 2024
 cGAS complexed with dsDNA (based on PDB 4O6A) | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC no. | 2.7.7.86 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||

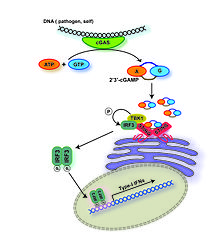
Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS, cGAMP synthase), belonging to the nucleotidyltransferase family, is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates a type-I interferon response. It is part of the cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway. It binds to microbial DNA as well as self DNA that invades the cytoplasm, and catalyzes cGAMP synthesis.[1] cGAMP then functions as a second messenger that binds to and activates the endoplasmic reticulum protein STING to trigger type-I IFNs production.[2][3][4] Mice lacking cGAS are more vulnerable to lethal infection by DNA viruses and RNA viruses.[5][6] In addition, cGAS has been shown to be an innate immune sensor of retroviruses including HIV.[7][8] The human gene encoding cGAS is MB21D1 on chromosome 6.
References
[edit]- ^ Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ (February 2013). "Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway". Science. 339 (6121): 786–91. Bibcode:2013Sci...339..786S. doi:10.1126/science.1232458. PMC 3863629. PMID 23258413.
- ^ Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C, Chen ZJ (February 2013). "Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA". Science. 339 (6121): 826–30. Bibcode:2013Sci...339..826W. doi:10.1126/science.1229963. PMC 3855410. PMID 23258412.
- ^ Gao P, Ascano M, Wu Y, Barchet W, Gaffney BL, Zillinger T, et al. (May 2013). "Cyclic [G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] is the metazoan second messenger produced by DNA-activated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase". Cell. 153 (5): 1094–107. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.046. PMC 4382009. PMID 23647843.
- ^ Zhang X, Shi H, Wu J, Zhang X, Sun L, Chen C, Chen ZJ (July 2013). "Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING". Molecular Cell. 51 (2): 226–35. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.022. PMC 3808999. PMID 23747010.
- ^ Li XD, Wu J, Gao D, Wang H, Sun L, Chen ZJ (September 2013). "Pivotal roles of cGAS-cGAMP signaling in antiviral defense and immune adjuvant effects". Science. 341 (6152): 1390–4. Bibcode:2013Sci...341.1390L. doi:10.1126/science.1244040. PMC 3863637. PMID 23989956.
- ^ Yu P, Miao Z, Li Y, Bansal R, Peppelenbosch MP, Pan Q (January 2021). "cGAS-STING effectively restricts murine norovirus infection but antagonizes the antiviral action of N-terminus of RIG-I in mouse macrophages". Gut Microbes. 13 (1): 1959839. doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.1959839. PMC 8344765. PMID 34347572.
- ^ Gao D, Wu J, Wu YT, Du F, Aroh C, Yan N, et al. (August 2013). "Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is an innate immune sensor of HIV and other retroviruses". Science. 341 (6148): 903–6. Bibcode:2013Sci...341..903G. doi:10.1126/science.1240933. PMC 3860819. PMID 23929945.
- ^ Lahaye X, Satoh T, Gentili M, Cerboni S, Conrad C, Hurbain I, et al. (December 2013). "The capsids of HIV-1 and HIV-2 determine immune detection of the viral cDNA by the innate sensor cGAS in dendritic cells". Immunity. 39 (6): 1132–42. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.11.002. PMID 24269171.
