Friedländer synthesis: Difference between revisions
SVG |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=February 2024}} |
|||
| ⚫ | The '''Friedländer synthesis''' is |
||
{{Reactionbox |
|||
| Name = Friedländer synthesis |
|||
| Type = Ring forming reaction |
|||
| NamedAfter = [[Paul Friedländer (chemist)|Paul Friedländer]] |
|||
| Section3 = {{Reactionbox Identifiers |
|||
| OrganicChemistryNamed = friedlaender-synthesis |
|||
}} |
|||
}} |
|||
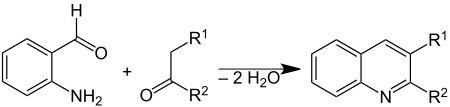
| ⚫ | The '''Friedländer synthesis''' is a [[chemical reaction]] of [[2-Aminobenzaldehyde|2-aminobenzaldehyde]]s<ref>[[Organic Syntheses]], Coll. Vol. 3, p. 56 (1955); Vol. 28, p. 11 (1948). ([http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/prep.asp?prep=cv3p0056 Article])</ref> with [[ketone]]s to form [[quinoline]] derivatives.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Friedländer, P. |journal=[[Chemische Berichte]]|year=1882|volume=15|pages= 2572–2575|doi=10.1002/cber.188201502219|title=Ueber o-Amidobenzaldehyd|issue=2|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1425274}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|author1=Friedländer, P. |author2=Gohring, C. F. |journal=[[Chemische Berichte|Ber.]]|year=1883|volume=16|pages= 1833–1839|doi=10.1002/cber.18830160265|title=Ueber eine Darstellungsmethode im Pyridinkern substituirter Chinolinderivate|issue=2|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1425313 }}</ref> It is named after German chemist [[Paul Friedländer (chemist)|Paul Friedländer]] (1857–1923). |
||
[[Image:Friedlaender Synthesis Scheme V.1.svg|center|450px|The Friedländer synthesis]] |
[[Image:Friedlaender Synthesis Scheme V.1.svg|center|450px|The Friedländer synthesis]] |
||
This reaction has been catalyzed by [[trifluoroacetic acid]]<ref>Shaabani, A. |
This reaction has been catalyzed by [[trifluoroacetic acid]],<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Shaabani, A. |author2=Soleimani, E. |author3=Badri, Z. |doi=10.1080/00397910601055230|title=Triflouroacetic Acid as an Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoline|year=2007|journal=Synthetic Communications|volume=37|issue=4|pages=629–635|s2cid=98625429 }}</ref> [[toluenesulfonic acid]],<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Jia, C.-S. |author2=Zhang, Z. |author3=Tu, S.-J. |author4=Wang, G.-W. |journal=[[Org. Biomol. Chem.]]|year=2006|volume=4|pages= 104–110|doi=10.1039/b513721g|title=Rapid and efficient synthesis of poly-substituted quinolines assisted by p-toluene sulphonic acid under solvent-free conditions: Comparative study of microwave irradiation versus conventional heating|issue=1 |pmid=16358003 }}</ref> [[iodine]],<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Wu, J. |author2=Xia, H.-G. |author3=Gao, K. |journal=[[Org. Biomol. Chem.]]|year=2006|volume=4|pages= 126–129|doi=10.1039/b514635f|title=Molecular iodine: A highly efficient catalyst in the synthesis of quinolines via Friedländer annulation|issue=1 |pmid=16358006 }}</ref> and [[Lewis acid]]s.<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Varala, R. |author2=Enugala, R. |author3=Adapa, S. R. |journal=[[Synthesis (journal)|Synthesis]]|year=2006|pages= 3825–3830 | doi = 10.1055/s-2006-950296 |volume=2006 |issue=22 |title=Efficient and Rapid Friedlander Synthesis of Functionalized Quinolines Catalyzed by Neodymium(III) Nitrate Hexahydrate}}</ref> |
||
Several reviews have been published.<ref> |
Several reviews have been published.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Manske, R. H. |journal=[[Chem. Rev.]]|year=1942|volume=30|pages= 113–144|doi=10.1021/cr60095a006|title=The Chemistry of Quinolines}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|author=Bergstrom, F. W. |journal=[[Chem. Rev.]]|year=1944|volume=35|pages= 77–277|doi=10.1021/cr60111a001|title=Heterocyclic Nitrogen Compounds. Part IIA. Hexacyclic Compounds: Pyridine, Quinoline, and Isoquinoline|issue=2}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author1=Cheng, C.-C. |author2=Yan, S.-J. |doi=10.1002/0471264180.or028.02|chapter=The Friedländer Synthesis of Quinolines|title=Organic Reactions|year=2004|isbn=0471264180}}</ref> |
||
==Mechanism== |
==Mechanism== |
||
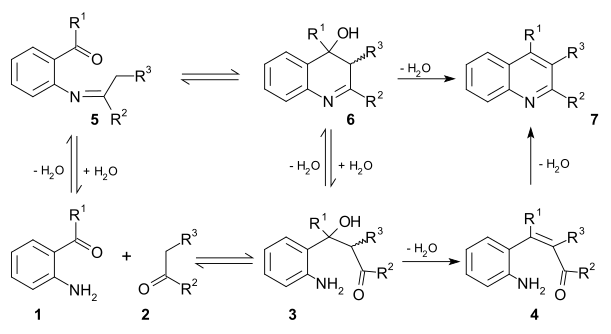
Two viable [[reaction mechanism]]s exist for this reaction. In the first mechanism 2-amino substituted carbonyl compound '''1''' and carbonyl compound '''2''' react in |
Two viable [[reaction mechanism]]s exist for this reaction. In the first mechanism 2-amino substituted carbonyl compound '''1''' and carbonyl compound '''2''' react in a [[rate-limiting step]] to [[Aldol reaction|aldol]] adduct '''3'''. This intermediate loses water in an [[elimination reaction]] to [[Α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound|unsaturated carbonyl compound]] '''4''' and then loses water again in [[imine]] formation to quinoline '''7'''. In the second mechanism the first step is [[Schiff base]] formation to '''5''' followed by Aldol reaction to '''6''' and elimination to '''7'''.<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Jose Marco-Contelles |author2=Elena Perez-Mayoral |author3=Abdelouahid Samadi |author4=Marıa do Carmo Carreiras |author5=Elena Soriano |title=Recent Advances in the Friedlander Reaction|doi=10.1021/cr800482c|year=2009|journal=Chemical Reviews|volume=109|issue=6|pages=2652–71|pmid=19361199}}</ref> |
||
:[[Image:FriedlanderReactionMechanism.svg|Friedländer synthesis reaction mechanism]] |
:[[Image:FriedlanderReactionMechanism.svg|Friedländer synthesis reaction mechanism]] |
||
The [[Pfitzinger reaction]] and the [[Niementowski quinoline synthesis]] are variations. |
The [[Pfitzinger reaction]] and the [[Niementowski quinoline synthesis]] are variations of the Friedländer reaction. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 21: | Line 27: | ||
*[[Skraup reaction]] |
*[[Skraup reaction]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Organic reactions}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Friedlander synthesis}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Friedlander synthesis}} |
||
[[Category:Condensation reactions]] |
[[Category:Condensation reactions]] |
||
[[Category:Quinoline forming reactions]] |
[[Category:Quinoline forming reactions]] |
||
[[Category:Name reactions]] |
[[Category:Name reactions]] |
||
[[es:Síntesis de quinolinas de Friedländer]] |
|||
[[nl:Friedländer-synthese]] |
|||
[[zh:弗里德兰德合成]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 03:44, 16 February 2024
| Friedländer synthesis | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Paul Friedländer |
| Reaction type | Ring forming reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | friedlaender-synthesis |
The Friedländer synthesis is a chemical reaction of 2-aminobenzaldehydes[1] with ketones to form quinoline derivatives.[2][3] It is named after German chemist Paul Friedländer (1857–1923).
This reaction has been catalyzed by trifluoroacetic acid,[4] toluenesulfonic acid,[5] iodine,[6] and Lewis acids.[7]
Several reviews have been published.[8][9][10]
Mechanism
[edit]Two viable reaction mechanisms exist for this reaction. In the first mechanism 2-amino substituted carbonyl compound 1 and carbonyl compound 2 react in a rate-limiting step to aldol adduct 3. This intermediate loses water in an elimination reaction to unsaturated carbonyl compound 4 and then loses water again in imine formation to quinoline 7. In the second mechanism the first step is Schiff base formation to 5 followed by Aldol reaction to 6 and elimination to 7.[11]
The Pfitzinger reaction and the Niementowski quinoline synthesis are variations of the Friedländer reaction.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 3, p. 56 (1955); Vol. 28, p. 11 (1948). (Article)
- ^ Friedländer, P. (1882). "Ueber o-Amidobenzaldehyd". Chemische Berichte. 15 (2): 2572–2575. doi:10.1002/cber.188201502219.
- ^ Friedländer, P.; Gohring, C. F. (1883). "Ueber eine Darstellungsmethode im Pyridinkern substituirter Chinolinderivate". Ber. 16 (2): 1833–1839. doi:10.1002/cber.18830160265.
- ^ Shaabani, A.; Soleimani, E.; Badri, Z. (2007). "Triflouroacetic Acid as an Efficient Catalyst for the Synthesis of Quinoline". Synthetic Communications. 37 (4): 629–635. doi:10.1080/00397910601055230. S2CID 98625429.
- ^ Jia, C.-S.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, S.-J.; Wang, G.-W. (2006). "Rapid and efficient synthesis of poly-substituted quinolines assisted by p-toluene sulphonic acid under solvent-free conditions: Comparative study of microwave irradiation versus conventional heating". Org. Biomol. Chem. 4 (1): 104–110. doi:10.1039/b513721g. PMID 16358003.
- ^ Wu, J.; Xia, H.-G.; Gao, K. (2006). "Molecular iodine: A highly efficient catalyst in the synthesis of quinolines via Friedländer annulation". Org. Biomol. Chem. 4 (1): 126–129. doi:10.1039/b514635f. PMID 16358006.
- ^ Varala, R.; Enugala, R.; Adapa, S. R. (2006). "Efficient and Rapid Friedlander Synthesis of Functionalized Quinolines Catalyzed by Neodymium(III) Nitrate Hexahydrate". Synthesis. 2006 (22): 3825–3830. doi:10.1055/s-2006-950296.
- ^ Manske, R. H. (1942). "The Chemistry of Quinolines". Chem. Rev. 30: 113–144. doi:10.1021/cr60095a006.
- ^ Bergstrom, F. W. (1944). "Heterocyclic Nitrogen Compounds. Part IIA. Hexacyclic Compounds: Pyridine, Quinoline, and Isoquinoline". Chem. Rev. 35 (2): 77–277. doi:10.1021/cr60111a001.
- ^ Cheng, C.-C.; Yan, S.-J. (2004). "The Friedländer Synthesis of Quinolines". Organic Reactions. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or028.02. ISBN 0471264180.
- ^ Jose Marco-Contelles; Elena Perez-Mayoral; Abdelouahid Samadi; Marıa do Carmo Carreiras; Elena Soriano (2009). "Recent Advances in the Friedlander Reaction". Chemical Reviews. 109 (6): 2652–71. doi:10.1021/cr800482c. PMID 19361199.