Amos 4: Difference between revisions
m standard quote handling in WP;standard Apostrophe/quotation marks in WP;add/change/refine category; MOS fixes using AWB |
#suggestededit-add-desc 1.0 Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit Android app edit |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Chapter of the Book of Amos}} |
|||
{{For|satellite|Amos-4}} |
{{For|satellite|Amos-4}} |
||
{{Bible chapter|letname= Amos 4 |previouslink= Amos 3 |previousletter= chapter 3 |nextlink= Amos 5 |nextletter= chapter 5 |book=[[Book of Amos]] |biblepart=[[Old Testament]] | booknum= 30 |category= [[Nevi'im]] | filename= CodexGigas_110_MinorProphets.jpg | size=250px | name= Codex Gigas, 13th century |caption=<div style="width: 250px; text-align: center; line-height: 1em">[[Book of Amos]] (1: |
{{Bible chapter|letname= Amos 4 |previouslink= Amos 3 |previousletter= chapter 3 |nextlink= Amos 5 |nextletter= chapter 5 |book=[[Book of Amos]] |biblepart=[[Old Testament]] | booknum= 30 |category= [[Nevi'im]] | filename= CodexGigas_110_MinorProphets.jpg | size=250px | name= Codex Gigas, 13th century |caption=<div style="width: 250px; text-align: center; line-height: 1em">[[Book of Amos]] (1:1–5:21) in [[Latin]] in [[Codex Gigas]], made around 13th century.</div>}} |
||
'''Amos 4''' is the fourth chapter of the [[Book of Amos]] in the [[Hebrew Bible]] or the [[Old Testament]] of the [[Christian]] [[Bible]].{{sfn|Collins|2014}}{{sfn|Hayes|2015}} This book contains the prophecies |
'''Amos 4''' is the fourth chapter of the [[Book of Amos]] in the [[Hebrew Bible]] or the [[Old Testament]] of the [[Christianity|Christian]] [[Bible]].{{sfn|Collins|2014}}{{sfn|Hayes|2015}} In the Hebrew Bible it is a part of the [[Twelve Minor Prophets|Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets]].<ref>[[Bruce M. Metzger|Metzger, Bruce M.]], et al. ''The Oxford Companion to the Bible''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1993.</ref><ref>Keck, Leander E. 1996. ''The New Interpreter's Bible: Volume: VII''. Nashville: Abingdon.</ref> This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet [[Amos (prophet)|Amos]], especially the denunciation of Israel's nobles as Israel is reproved for oppression, Amos 4:1–3, for [[idolatry]], Amos 4:4,5, and for their incorrigibleness, Amos 4:6–13.<ref name=jfb/> Jennifer Dines treats Amos 3:1-5:17 as a single literary unit,<ref name=dines>Dines, J. M., ''29. Amos'', in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001), [https://b-ok.org/dl/946961/8f5f43 The Oxford Bible Commentary], p. 584</ref> whereas [[John Nelson Darby]] treats each chapter, except for chapters 1 and 2, as "a distinct prophecy".<ref>Darby, J. N. (1857-1862), [https://biblehub.com/commentaries/darby/amos/3.htm Darby's Bible Synthesis] on Amos 3, accessed 15 December 2023</ref> |
||
== Text == |
== Text == |
||
The original text was written in [[Biblical Hebrew|Hebrew]]. [[Chapters and verses of the Bible|This chapter is divided into]] 13 verses. Some early [[biblical manuscript|manuscripts]] containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the [[Masoretic Text]] tradition, which includes the [[Codex Cairensis]] (895), [[Codex Babylonicus Petropolitanus|the Petersburg Codex of the Prophets]] (916), [[Aleppo Codex]] (10th century), [[Leningrad Codex|Codex Leningradensis]] (1008).{{sfn|Würthwein|1995|pp=35-37}} |
|||
* The original text is written in [[Hebrew language]]. |
|||
* [[Chapters and verses of the Bible|This chapter is divided into]] 13 verses. |
|||
Fragments containing parts of this chapter were found among the [[Dead Sea Scrolls]] including 4Q78 (4QXII<sup>c</sup>; 75–50 BCE) with extant verses 1–2;{{sfn|Ulrich|2010|p=605}}<ref name=thewaytoyahuweh>[http://thewaytoyahuweh.com/dead-sea-scrolls/general-info/#amos Dead sea scrolls – Amos]</ref>{{sfn|Fitzmyer|2008|p=38}} and 4Q82 (4QXII<sup>g</sup>; 25 BCE) with extant verses 4–9.{{sfn|Ulrich|2010|p=605}}<ref name=thewaytoyahuweh/>{{sfn|Fitzmyer|2008|p=39}} |
|||
==Textual versions== |
|||
Some most ancient manuscripts containing this chapter in Hebrew language: |
|||
* [[Masoretic Text]] (10th century) |
|||
* [[Dead Sea Scrolls]]: (2nd century BC)<ref name=thewaytoyahuweh>[http://thewaytoyahuweh.com/research/dead-sea-scrolls/#amos Dead sea scrolls - Amos]</ref><ref>{{cite journal |author=Timothy A. J. Jull |author2=Douglas J. Donahue |author3=Magen Broshi |author4=Emanuel Tov |url=https://journals.uair.arizona.edu/index.php/radiocarbon/article/view/1642 |title=Radiocarbon Dating of Scrolls and Linen Fragments from the Judean Desert |journal=Radiocarbon |volume=38 |number=1 |year=1995 |page=14 |accessdate=26 November 2014}}</ref> |
|||
** 4Q78 (4QXII<sup>c</sup>): extant: verses 1-2<ref name=thewaytoyahuweh/> |
|||
** 4Q82 (4QXII<sup>g</sup>): extant: verses 4‑9<ref name=thewaytoyahuweh/> |
|||
There is also a translation into [[Koine Greek]] known as the [[Septuagint]], made in the last few centuries BCE. Extant ancient manuscripts of the [[Septuagint]] version include [[Codex Vaticanus]] ('''B'''; <math> \mathfrak{G}</math><sup>B</sup>; 4th century), [[Codex Alexandrinus]] ('''A'''; <math> \mathfrak{G}</math><sup>A</sup>; 5th century) and [[Codex Marchalianus]] ('''Q'''; <math> \mathfrak{G}</math><sup>Q</sup>; 6th century).{{sfn|Würthwein|1995|pp=73-74}}{{efn|The whole book of Amos is missing from the extant [[Codex Sinaiticus]].<ref>{{Catholic Encyclopedia|wstitle=Codex Sinaiticus}}</ref>}} |
|||
Ancient translations in [[Koine Greek]]: |
|||
* [[Septuagint]] (3rd century BC) |
|||
* [[Theodotion]] version (~AD 180) |
|||
==Structure== |
|||
[[NKJV]] groups this chapter into: |
|||
*{{bibleref2|Amos|4:1-5|NKJV}} = Punishment of Israel's Sins |
|||
*{{bibleref2|Amos|4:6-13|NKJV}} = Israel Did Not Accept Correction |
|||
==Verse 1== |
==Verse 1== |
||
[[File:Ostjordanische Amoriterreiche.png|thumb|Region of Bashan (or Basan; in orange)]] |
|||
: ''Hear this word, ye kine of Bashan, that are in the mountain of Samaria,'' |
: ''Hear this word, ye kine of Bashan, that are in the mountain of Samaria,'' |
||
:: ''which oppress the poor, which crush the needy,'' |
:: ''which oppress the poor, which crush the needy,'' |
||
::: ''which say to their masters, Bring, and let us drink.''<ref>{{ |
::: ''which say to their masters, Bring, and let us drink.''<ref>{{bibleverse|Amos|4:1|KJV}}: [[King James Version|KJV]]</ref> |
||
* "Kine": |
* "Kine": A female name, but here is addressed to both male and female, which may equally brand the luxury and effeminacy of the rich men, or the cruelty of the rich women, of Samaria. The reproachful name was then probably intended to shame both; men, who laid aside their manliness in the delicacy of luxury; or ladies, who put off the tenderness of womanhood by oppression. The character of the oppression was the same in both cases. It was done, not directly by those who reveled in its fruits, but through the seduction of one who had authority over them. To the ladies of Samaria, "their lord" was their husband, as the husband is so called; to the nobles of Samaria, he was their king, who supplied their extravagances and debaucheries by grants, extorted from the poor.<ref name=barnes/> |
||
* "Bashan" |
* "[[Bashan]]" – The pastures of Bashan were very rich, and it had its name probably from its richness of soil . The Batanea of later times was a province only of the kingdom of Bashan, which, with half of Gilead, was given to the half tribe of Manasseh. For the Bashan of Og included Golan ({{bibleverse|Deuteronomy|4:43|9}}), (the capital of the subsequent "Gaulonitis", now "Jaulan") Beeshterah ({{bibleverse|Joshua|21:27|9}}), ('''Asthoroth''' or Ashtaroth; {{bibleverse|1 Chronicles|6:71|9}}, very probably Bostra ({{bibleverse|1 Chronicles|1:12|9}}), and '''Edrei''' ({{bibleverse|Deuteronomy|1:4|9}}), in Hauran or Auranitis; the one on its southern border, the other perhaps on its northern boundary toward Trachonitis . Its eastern extremity at '''Salcha''' (Salkah, Sulkhad;{{bibleverse|Deuteronomy|3:10|9}}; {{bibleverse|Joshua|13:11|9}}) is the southern point of Batanea (now Bathaniyyeh); Argob, or Trachonitis, (the Lejah) was its north eastern fence.<ref name=barnes>[[Albert Barnes (theologian)|Barnes, Albert]]. Notes on the Old Testament. London, Blackie & Son, 1884. Reprint, Grand Rapids: Baker Books, 1998.{{PD-notice}}</ref> In [[Psalm 22]]:12, the "strong bulls of Bashan" represent "frightening power", but here they represent luxury.<ref>[[Jerusalem Bible]] (1966), Footnote a at Amos 4:1</ref> |
||
* "Oppress the poor": |
* "Oppress the poor": Apparently the women urged their husbands to violence and fraud in order to obtain means to satisfy their extravagance, which is thoroughly unscrupulous act (see the case of Ahab and Naboth, {{bibleverse|1 Kings|21:7|9}}, etc.).<ref name=pulpit>Joseph S. Exell; Henry Donald Maurice Spence-Jones (Editors). The [[Pulpit Commentary]]. 23 volumes. First publication: 1890.{{PD-notice}}</ref> |
||
* "Say to their masters": that is, to their king, with whom the princes indulged in potations ({{ |
* "Say to their masters": that is, to their king, with whom the princes indulged in potations ({{bibleverse|Hosea|7:5|9}}), and whom here they importune for more wine. "Bring" is singular, in the Hebrew implying that one "master" alone is meant.<ref name=jfb>Robert Jamieson, Andrew Robert Fausset; David Brown. ''[[Jamieson-Fausset-Brown Bible Commentary|Jamieson, Fausset, and Brown's Commentary On the Whole Bible]]''. 1871.{{PD-notice}}</ref> |
||
* "The mountains of Samaria": like cattle grazing on a mountain; the metaphor is still continued: Samaria was the principal city of Ephraim, the metropolis of the ten tribes |
* "The mountains of Samaria": like cattle grazing on a mountain; the metaphor is still continued: Samaria was the principal city of Ephraim, the metropolis of the ten tribes ({{bibleverse|Isaiah|7:9|9}}); situated on a mountain; Maundrell says, upon a long mount, of an oval figure, having first a fruitful valley, and then a ring of hills running about it. Here the kings of Israel had their palace, and kept their court, and where their princes and nobles resided. Ahab is said to be king of Samaria ({{bibleverse|1 Kings|21:1|9}}).<ref name=gill>[[John Gill (theologian)|Gill, J.]], John Gill's Exposition of the Entire Bible. Exposition of the Old and New Testament. Published in 1746–1763.{{PD-notice}}</ref> |
||
==Verse 2== |
|||
:''The Lord God has sworn by His holiness:'' |
|||
::''"Behold, the days shall come upon you'' |
|||
::''When He will take you away with fishhooks,'' |
|||
::''And your posterity with fishhooks ..."''<ref>{{bibleverse|Amos|4:2|NKJV}}: NKJV</ref> |
|||
Where the {{Lord}} swears by "his holiness", the outcome is inevitable, but not the timing.<ref name=dines /> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{columns-list|colwidth=22em| |
|||
{{col-begin}} |
|||
{{col-2}} |
|||
* [[Bashan]] |
* [[Bashan]] |
||
* [[Bethel]] |
* [[Bethel]] |
||
* [[Egypt]] |
* [[Egypt]] |
||
* [[Gilgal]] |
* [[Gilgal]] |
||
{{col-2}} |
|||
* [[Israel]] |
* [[Israel]] |
||
* [[Sodom and Gomorrah]] |
* [[Sodom and Gomorrah]] |
||
* [[Samaria]] |
* [[Samaria]]}} |
||
{{col-end}} |
|||
{{Portal|Bible}} |
{{Portal|Bible}} |
||
*Related [[Bible]] parts: [[Genesis 19]], [[Deuteronomy 28]], [[Jeremiah 23]], [[Amos 3]], [[Joel 1]], [[Joel 2]], [[John 5]] |
*Related [[Bible]] parts: [[Genesis 19]], [[Deuteronomy 28]], [[Jeremiah 23]], [[Amos 3]], [[Joel 1]], [[Joel 2]], [[John 5]] |
||
==Notes |
==Notes== |
||
{{ |
{{Notelist}} |
||
==References== |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
== |
==Sources== |
||
{{Refbegin}} |
|||
*{{Cite book |
*{{Cite book |
||
|last |
|last = Collins |
||
|first |
|first = John J. |
||
|title |
|title = Introduction to the Hebrew Scriptures |
||
|publisher |
|publisher = Fortress Press |
||
|year |
|year = 2014 |
||
|isbn = 9781451469233 |
|||
|url = https://books.google.com.au/books?id=fbsoBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA305&dq=%22there+is+no+doubt+that+the+book+was+edited+in+the+southern+kingdom%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjRiJyupeHSAhWHupQKHcnLCrAQ6AEIGzAA#v=onepage&q=%22there%20is%20no%20doubt%20that%20the%20book%20was%20edited%20in%20the%20southern%20kingdom%22&f=false |
|||
|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=fbsoBAAAQBAJ |
|||
|ref = harv |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
* {{Cite book|title = A Guide to the Dead Sea Scrolls and Related Literature|last = Fitzmyer|first = Joseph A.|author-link= Joseph Fitzmyer |publisher = William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company| url= https://books.google.com/books?id=TILXeWJ2eNAC | year = 2008|isbn = 9780802862419|location = Grand Rapids, MI }} |
|||
*{{Cite book |
*{{Cite book |
||
|last |
|last = Hayes |
||
|first |
|first = Christine |
||
|title |
|title = Introduction to the Bible |
||
|publisher |
|publisher = Yale University Press |
||
|year |
|year = 2015 |
||
|isbn = 978-0300188271 |
|||
|url = https://books.google.com.au/books?id=SKbkXYHxvlAC&pg=PT242&dq=%22Amos+is+structured+in+four+main+sections%22&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwi44Kmyq-HSAhXCLpQKHRs5DoIQ6AEIGzAA#v=onepage&q=%22Amos%20is%20structured%20in%20four%20main%20sections%22&f=false |
|||
|url = https://books.google.com/books?id=SKbkXYHxvlAC |
|||
|ref = harv |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
* {{Cite book |
|||
{{Refend}} |
|||
| editor-last = Ulrich |
|||
| editor-first = Eugene |editor-link= Eugene Ulrich |
|||
| title = The Biblical Qumran Scrolls: Transcriptions and Textual Variants |
|||
| year = 2010 |
|||
| publisher = Brill |
|||
| url = https://archive.org/details/TheBiblicalQumranScrolls}} |
|||
*{{cite book | last = Würthwein | first = Ernst | author-link = Ernst Würthwein | title = The Text of the Old Testament | publisher = Wm. B. Eerdmans |location = Grand Rapids, MI | year= 1995 | translator-first1 = Erroll F.| translator-last1 = Rhodes |isbn = 0-8028-0788-7 | url= https://books.google.com/books?id=FSNKSBObCYwC | access-date= January 26, 2019}} |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
Latest revision as of 06:28, 23 March 2024
| Amos 4 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Book | Book of Amos |
| Category | Nevi'im |
| Christian Bible part | Old Testament |
| Order in the Christian part | 30 |
Amos 4 is the fourth chapter of the Book of Amos in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible.[1][2] In the Hebrew Bible it is a part of the Book of the Twelve Minor Prophets.[3][4] This book contains the prophecies attributed to the prophet Amos, especially the denunciation of Israel's nobles as Israel is reproved for oppression, Amos 4:1–3, for idolatry, Amos 4:4,5, and for their incorrigibleness, Amos 4:6–13.[5] Jennifer Dines treats Amos 3:1-5:17 as a single literary unit,[6] whereas John Nelson Darby treats each chapter, except for chapters 1 and 2, as "a distinct prophecy".[7]
Text
[edit]The original text was written in Hebrew. This chapter is divided into 13 verses. Some early manuscripts containing the text of this chapter in Hebrew are of the Masoretic Text tradition, which includes the Codex Cairensis (895), the Petersburg Codex of the Prophets (916), Aleppo Codex (10th century), Codex Leningradensis (1008).[8]
Fragments containing parts of this chapter were found among the Dead Sea Scrolls including 4Q78 (4QXIIc; 75–50 BCE) with extant verses 1–2;[9][10][11] and 4Q82 (4QXIIg; 25 BCE) with extant verses 4–9.[9][10][12]
There is also a translation into Koine Greek known as the Septuagint, made in the last few centuries BCE. Extant ancient manuscripts of the Septuagint version include Codex Vaticanus (B; B; 4th century), Codex Alexandrinus (A; A; 5th century) and Codex Marchalianus (Q; Q; 6th century).[13][a]
Verse 1
[edit]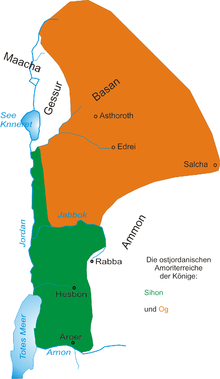
- Hear this word, ye kine of Bashan, that are in the mountain of Samaria,
- which oppress the poor, which crush the needy,
- which say to their masters, Bring, and let us drink.[15]
- which oppress the poor, which crush the needy,
- "Kine": A female name, but here is addressed to both male and female, which may equally brand the luxury and effeminacy of the rich men, or the cruelty of the rich women, of Samaria. The reproachful name was then probably intended to shame both; men, who laid aside their manliness in the delicacy of luxury; or ladies, who put off the tenderness of womanhood by oppression. The character of the oppression was the same in both cases. It was done, not directly by those who reveled in its fruits, but through the seduction of one who had authority over them. To the ladies of Samaria, "their lord" was their husband, as the husband is so called; to the nobles of Samaria, he was their king, who supplied their extravagances and debaucheries by grants, extorted from the poor.[16]
- "Bashan" – The pastures of Bashan were very rich, and it had its name probably from its richness of soil . The Batanea of later times was a province only of the kingdom of Bashan, which, with half of Gilead, was given to the half tribe of Manasseh. For the Bashan of Og included Golan (Deuteronomy 4:43), (the capital of the subsequent "Gaulonitis", now "Jaulan") Beeshterah (Joshua 21:27), (Asthoroth or Ashtaroth; 1 Chronicles 6:71, very probably Bostra (1 Chronicles 1:12), and Edrei (Deuteronomy 1:4), in Hauran or Auranitis; the one on its southern border, the other perhaps on its northern boundary toward Trachonitis . Its eastern extremity at Salcha (Salkah, Sulkhad;Deuteronomy 3:10; Joshua 13:11) is the southern point of Batanea (now Bathaniyyeh); Argob, or Trachonitis, (the Lejah) was its north eastern fence.[16] In Psalm 22:12, the "strong bulls of Bashan" represent "frightening power", but here they represent luxury.[17]
- "Oppress the poor": Apparently the women urged their husbands to violence and fraud in order to obtain means to satisfy their extravagance, which is thoroughly unscrupulous act (see the case of Ahab and Naboth, 1 Kings 21:7, etc.).[18]
- "Say to their masters": that is, to their king, with whom the princes indulged in potations (Hosea 7:5), and whom here they importune for more wine. "Bring" is singular, in the Hebrew implying that one "master" alone is meant.[5]
- "The mountains of Samaria": like cattle grazing on a mountain; the metaphor is still continued: Samaria was the principal city of Ephraim, the metropolis of the ten tribes (Isaiah 7:9); situated on a mountain; Maundrell says, upon a long mount, of an oval figure, having first a fruitful valley, and then a ring of hills running about it. Here the kings of Israel had their palace, and kept their court, and where their princes and nobles resided. Ahab is said to be king of Samaria (1 Kings 21:1).[19]
Verse 2
[edit]- The Lord God has sworn by His holiness:
- "Behold, the days shall come upon you
- When He will take you away with fishhooks,
- And your posterity with fishhooks ..."[20]
Where the LORD swears by "his holiness", the outcome is inevitable, but not the timing.[6]
See also
[edit]- Related Bible parts: Genesis 19, Deuteronomy 28, Jeremiah 23, Amos 3, Joel 1, Joel 2, John 5
Notes
[edit]- ^ The whole book of Amos is missing from the extant Codex Sinaiticus.[14]
References
[edit]- ^ Collins 2014.
- ^ Hayes 2015.
- ^ Metzger, Bruce M., et al. The Oxford Companion to the Bible. New York: Oxford University Press, 1993.
- ^ Keck, Leander E. 1996. The New Interpreter's Bible: Volume: VII. Nashville: Abingdon.
- ^ a b Robert Jamieson, Andrew Robert Fausset; David Brown. Jamieson, Fausset, and Brown's Commentary On the Whole Bible. 1871.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b Dines, J. M., 29. Amos, in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001), The Oxford Bible Commentary, p. 584
- ^ Darby, J. N. (1857-1862), Darby's Bible Synthesis on Amos 3, accessed 15 December 2023
- ^ Würthwein 1995, pp. 35–37.
- ^ a b Ulrich 2010, p. 605.
- ^ a b Dead sea scrolls – Amos
- ^ Fitzmyer 2008, p. 38.
- ^ Fitzmyer 2008, p. 39.
- ^ Würthwein 1995, pp. 73–74.
- ^
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Codex Sinaiticus". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Codex Sinaiticus". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ Amos 4:1: KJV
- ^ a b Barnes, Albert. Notes on the Old Testament. London, Blackie & Son, 1884. Reprint, Grand Rapids: Baker Books, 1998.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote a at Amos 4:1
- ^ Joseph S. Exell; Henry Donald Maurice Spence-Jones (Editors). The Pulpit Commentary. 23 volumes. First publication: 1890.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Gill, J., John Gill's Exposition of the Entire Bible. Exposition of the Old and New Testament. Published in 1746–1763.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Amos 4:2: NKJV
Sources
[edit]- Collins, John J. (2014). Introduction to the Hebrew Scriptures. Fortress Press. ISBN 9781451469233.
- Fitzmyer, Joseph A. (2008). A Guide to the Dead Sea Scrolls and Related Literature. Grand Rapids, MI: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company. ISBN 9780802862419.
- Hayes, Christine (2015). Introduction to the Bible. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0300188271.
- Ulrich, Eugene, ed. (2010). The Biblical Qumran Scrolls: Transcriptions and Textual Variants. Brill.
- Würthwein, Ernst (1995). The Text of the Old Testament. Translated by Rhodes, Erroll F. Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans. ISBN 0-8028-0788-7. Retrieved January 26, 2019.

