Unicolored blackbird: Difference between revisions
Pvmoutside (talk | contribs) m Pvmoutside moved page Unicoloured blackbird to Unicolored blackbird over redirect: new world species take Americanized spelling |
No edit summary |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Species of bird}} |
|||
{{Taxobox |
|||
{{speciesbox |
|||
| image = AgelaeusCyanopusKeulemans.jpg |
|||
| image = Unicolored Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus) male.jpg |
|||
| status = LC |
| status = LC |
||
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
| status_system = IUCN3.1 |
||
| status_ref = <ref name= |
| status_ref = <ref name="iucn status 12 November 2021">{{cite iucn |author=BirdLife International |date=2018 |title=''Agelasticus cyanopus'' |volume=2018 |page=e.T22724184A132027717 |doi=10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22724184A132027717.en |access-date=12 November 2021}}</ref> |
||
| |
| genus = Agelasticus |
||
| |
| species = cyanopus |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| classis = [[Aves]] |
|||
| ordo = [[Passeriformes]] |
|||
| familia = [[Icteridae]] |
|||
| genus = ''[[Agelasticus]]'' |
|||
| species = '''''A. cyanopus''''' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| synonyms = |
| synonyms = |
||
''Agelaius cyanopus'' <small>Vieillot, 1819</small>, |
''Agelaius cyanopus'' <small>Vieillot, 1819</small>, |
||
''Chrysomus cyanopus'' |
''Chrysomus cyanopus'' |
||
| ⚫ | |||
}} |
}} |
||
The ''' |
The '''unicolored blackbird''' ('''''Agelasticus cyanopus''''') is a species of [[bird]] in the family [[Icteridae]].<ref>BirdLife International 2012. [http://avibase.bsc-eoc.org/species.jsp?lang=EN&avibaseid=B5792FEE97D3CBD7 Unicolored Blackbird (Chrysomus cyanopus)].</ref> Found in [[Argentina]], [[Bolivia]], [[Brazil]], and [[Paraguay]], its natural [[habitat]] is [[swamp]]s and nearby grassland. It is a fairly common bird and the [[International Union for Conservation of Nature]] has rated it a "[[least-concern species]]". |
||
==Description== |
==Description== |
||
[[File:Unicoloured Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus) (Male).JPG|thumb|Male]] |
[[File:Unicoloured Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus) (Male).JPG|thumb|Male]] |
||
[[File:Unicoloured Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus) (Female).JPG|thumb|Female]] |
[[File:Unicoloured Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus) (Female).JPG|thumb|Female]] |
||
The male |
The male unicolored blackbird is befitting of its name, with entirely glossy black plumage and dark eyes. However, the species exhibits [[sexual dimorphism]]; the female is streaked brown and black with a yellow belly streaked with brown. The face has a dark mask and the wings are reddish-brown edged with black. Females from the lower Amazon region and southeastern Brazil have a generally duller colouration with less rufous wings and less yellow underparts. The legs and the iris are black and the bill is long and sharply pointed. The male could be confused with the [[velvet-fronted grackle]] or the [[chopi blackbird]]. Its call of this bird is a loud "tchew-tchew-tchew" which is sung from an elevated position,<ref>Jaramillo, Alvaro. 2010. Unicolored Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus), Neotropical Birds Online (T. S. Schulenberg, Editor). Ithaca: Cornell Lab of Ornithology; retrieved from Neotropical Birds Online: http://neotropical.birds.cornell.edu/portal/species/overview?p_p_spp=671436</ref><ref name=Ridgely2009>{{cite book|author1= Ridgely, Robert S.|author2=Tudor, Guy |title=Field Guide to the Songbirds of South America: The Passerines |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=gC_A2fpBl1gC&pg=PA670 |year=2009 |publisher=University of Texas Press |isbn=978-0-292-71748-0 |page=670}}</ref> and it also produces various trills and rattling sounds which vary in tone and pitch.<ref name=Perlo>{{cite book|author=Ber van Perlo|title=Birds of South America: Passerines|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8WM6CQAAQBAJ&pg=PA400|year=2015|publisher=Princeton University Press|isbn=978-0-691-16796-1 |page=400}}</ref> |
||
==Distribution and habitat== |
==Distribution and habitat== |
||
The |
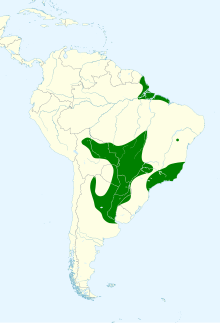
The unicolored blackbird is native to South America where its range extends from northern Bolivia and southern Brazil to northern Argentina, including much of the lower Amazon region. It is found in marshes, near the edges of ponds and lakes and in adjacent grassland, and its altitudinal range is up to about {{convert|600|m|ft|-2}}. It is especially common in the Brazilian [[Pantanal]].<ref name=Ridgely2009/> |
||
==Behaviour== |
==Behaviour== |
||
| Line 32: | Line 29: | ||
==Status== |
==Status== |
||
The total population of the |
The total population of the unicolored blackbird, at over 10,000 mature individuals, is believed to be stable and it has a very wide range. It is a fairly common species but its distribution is somewhat patchy. The bird seems to be facing no particular threats and the [[International Union for Conservation of Nature]] has assessed its conservation status as being of "[[Least-concern species|least concern]]".<ref name="iucn status 12 November 2021" /> |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} |
||
{{Taxonbar}} |
{{Taxonbar|from=Q2668913}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:blackbird, unicoloured}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Birds of South America]] |
[[Category:Birds of South America]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Birds of the Pantanal]] |
[[Category:Birds of the Pantanal]] |
||
[[Category:Birds described in 1819| |
[[Category:Birds described in 1819|unicolored blackbird]] |
||
[[Category:Taxa named by Louis Pierre Vieillot]] |
|||
[[Category:Birds of the Brazilian Amazon]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Taxonomy articles created by Polbot]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 19 April 2024
| Unicolored blackbird | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Icteridae |
| Genus: | Agelasticus |
| Species: | A. cyanopus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Agelasticus cyanopus (Vieillot, 1819)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Agelaius cyanopus Vieillot, 1819, Chrysomus cyanopus | |
The unicolored blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus) is a species of bird in the family Icteridae.[2] Found in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay, its natural habitat is swamps and nearby grassland. It is a fairly common bird and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated it a "least-concern species".
Description
[edit]

The male unicolored blackbird is befitting of its name, with entirely glossy black plumage and dark eyes. However, the species exhibits sexual dimorphism; the female is streaked brown and black with a yellow belly streaked with brown. The face has a dark mask and the wings are reddish-brown edged with black. Females from the lower Amazon region and southeastern Brazil have a generally duller colouration with less rufous wings and less yellow underparts. The legs and the iris are black and the bill is long and sharply pointed. The male could be confused with the velvet-fronted grackle or the chopi blackbird. Its call of this bird is a loud "tchew-tchew-tchew" which is sung from an elevated position,[3][4] and it also produces various trills and rattling sounds which vary in tone and pitch.[5]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The unicolored blackbird is native to South America where its range extends from northern Bolivia and southern Brazil to northern Argentina, including much of the lower Amazon region. It is found in marshes, near the edges of ponds and lakes and in adjacent grassland, and its altitudinal range is up to about 600 metres (2,000 ft). It is especially common in the Brazilian Pantanal.[4]
Behaviour
[edit]This bird usually occurs in pairs and is much less gregarious than the chestnut-capped blackbird which is found in similar swampy habitat. It moves about on floating vegetation and forages among reeds, never straying far from water.[4]
Status
[edit]The total population of the unicolored blackbird, at over 10,000 mature individuals, is believed to be stable and it has a very wide range. It is a fairly common species but its distribution is somewhat patchy. The bird seems to be facing no particular threats and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b BirdLife International (2018). "Agelasticus cyanopus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22724184A132027717. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22724184A132027717.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ BirdLife International 2012. Unicolored Blackbird (Chrysomus cyanopus).
- ^ Jaramillo, Alvaro. 2010. Unicolored Blackbird (Agelasticus cyanopus), Neotropical Birds Online (T. S. Schulenberg, Editor). Ithaca: Cornell Lab of Ornithology; retrieved from Neotropical Birds Online: http://neotropical.birds.cornell.edu/portal/species/overview?p_p_spp=671436
- ^ a b c Ridgely, Robert S.; Tudor, Guy (2009). Field Guide to the Songbirds of South America: The Passerines. University of Texas Press. p. 670. ISBN 978-0-292-71748-0.
- ^ Ber van Perlo (2015). Birds of South America: Passerines. Princeton University Press. p. 400. ISBN 978-0-691-16796-1.

