External iliac artery: Difference between revisions
m r2.7.1) (robot Adding: ar:شريان حرقفي ظاهر |
tweaked #article-section-source-editor Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 30 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Use American English|date = January 2019}} |
||
{{Short description|Arteries of the pelvis}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Use mdy dates|date = January 2019}} |
|||
Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| Name = External iliac artery |
|||
GraySubject = 156 | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
GrayPage = 622 | |
|||
| Image = Iliac artery bifurcation.PNG |
|||
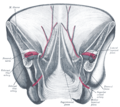
| Caption = Front of abdomen, showing [[common iliac artery]], the source of the external iliac artery |
|||
| Image2 = Volume rendered CT scan of abdominal and pelvic blood vessels (smaller).gif |
|||
Image2 = Gray547.png | |
|||
| Caption2 = [[Volume rendering|Volume rendered]] [[CT scan]] of abdominal and pelvic blood vessels. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| BranchFrom = [[common iliac artery|Common iliac arteries]] |
|||
| BranchTo = [[femoral artery|Femoral arteries]], [[inferior epigastric artery|inferior epigastric arteries]] |
|||
| Vein = [[External iliac vein]]s |
|||
| Supplies = |
|||
MeshName = | |
|||
MeshNumber = | |
|||
DorlandsPre = a_61 | |
|||
DorlandsSuf = 12154552 | |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''external [[ilium (bone)|iliac]] [[artery]]''' is a large artery in the pelvic region that carries blood to the [[lower limb]]. |
|||
The '''external iliac arteries''' are two major [[Artery|arteries]] which bifurcate off the [[common iliac arteries]] anterior to the [[sacroiliac joint]] of the [[pelvis]]. |
|||
The external iliac artery is a paired artery, meaning there is one on each side of the body: a ''right external iliac artery'' and ''left external iliac artery''. |
|||
==Structure== |
|||
The external iliac artery is accompanied by the [[external iliac vein]], which is located posterior to the artery. |
|||
The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the [[common iliac artery]]. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the [[psoas major muscle]]s. They exit the [[Pelvis|pelvic girdle]] posterior and inferior to the [[inguinal ligament]].<ref name=":0">{{cite book|last1=Tortora|first1=Gerard J.|title=Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: Volume 4 Maintenance and Continuity of the Human Body|last2=Grabowski|first2=Sandra R.|publisher=John Wiley & Sons, Inc.|year=2003|isbn=0-471-22934-2|editor1-last=Roesch|editor1-first=Bonnie|edition=10th|volume=4|location=New York, NY|page=734|type=Textbook}}</ref><ref>{{Citation|last=Madani|first=M. M.|title=Cardiovascular Anatomy|date=2014-01-01|url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128012383001963|work=Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences|publisher=Elsevier|language=en|doi=10.1016/b978-0-12-801238-3.00196-3|isbn=978-0-12-801238-3|access-date=2021-01-18|last2=Golts|first2=E.}}</ref> This occurs about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the [[pubic tubercle]].<ref name=":0" /> At this point they are referred to as the [[femoral arteries]].<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1">{{Citation|last=Maynard|first=Robert Lewis|title=Chapter 7 - The Cardiovascular System|date=2019-01-01|url=http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128118375000071|work=Anatomy and Histology of the Laboratory Rat in Toxicology and Biomedical Research|pages=77–90|editor-last=Maynard|editor-first=Robert Lewis|publisher=Academic Press|language=en|isbn=978-0-12-811837-5|access-date=2021-01-18|last2=Downes|first2=Noel|editor2-last=Downes|editor2-first=Noel}}</ref> |
|||
==Source== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Image:Iliac artery bifurcation.PNG|thumb|left|200px|Front of abdomen, showing [[common iliac artery]], the source of the external iliac artery]] |
|||
The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the [[common iliac artery]]. It travels inferiorly, anteriorly, and laterally, making its ways to the lower limb: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
! Branch || Description |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Inferior epigastric artery]] || Goes upward to anastomose with [[superior epigastric artery]] (a branch of [[internal thoracic artery]]). |
| [[Inferior epigastric artery]] || Goes upward to anastomose with [[superior epigastric artery]] (a branch of [[internal thoracic artery]]). |
||
| Line 38: | Line 29: | ||
| [[Deep circumflex iliac artery]]|| Goes laterally, travelling along the iliac crest of the [[pelvic bone]]. |
| [[Deep circumflex iliac artery]]|| Goes laterally, travelling along the iliac crest of the [[pelvic bone]]. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[ |
| [[Femoral artery]]<ref name=":1" />|| Terminal branch. When the external iliac artery passes posterior to the [[inguinal ligament]], its name changes to [[femoral artery]]. |
||
|} |
|} |
||
== Function == |
|||
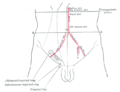
The external iliac artery provides the main blood supply to the legs. It passes down along the brim of the pelvis and gives off two large branches - the "inferior epigastric artery" and a "deep circumflex artery." These vessels supply blood to the muscles and skin in the lower abdominal wall. The external iliac artery passes beneath the inguinal ligament in the lower part of the abdomen and becomes the femoral artery. |
|||
== Clinical significance == |
|||
The external iliac artery is usually the artery used to attach the renal artery to the recipient of a kidney transplant. |
|||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Gray539.png|Bifurcation of the [[aorta]] and the right [[common iliac artery]] - side view. (External iliac artery is artery at upper left, seen splitting from [[common iliac artery]] at top.) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
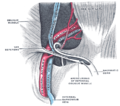
| ⚫ | File:Gray547.png|The relations of the femoral and abdominal inguinal rings, seen from within the abdomen. Right side. (External iliac artery is large artery at center, and inguinal ligament runs from upper right to lower left. When the artery crosses the ligament, it becomes the [[femoral artery]].) |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Image:Gray837.png|Sacral plexus of the right side. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
File:Gray837.png|Sacral plexus of the right side. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
File:Gray1146.png|The spermatic cord in the inguinal canal. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
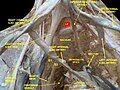
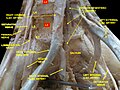
File:Right external artery.jpg|External iliac artery |
|||
File:Slide1ewew.JPG|Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection. Anterior view. |
|||
File:Slide2ewew.JPG|Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection. Anterior view. |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| Line 54: | Line 56: | ||
* [[Internal iliac artery]] |
* [[Internal iliac artery]] |
||
* [[Common iliac artery]] |
* [[Common iliac artery]] |
||
==References== |
|||
<references /> |
|||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* {{GraySubject|157}} - "The arteries of the lower extremity" |
|||
* {{GraySubject|173}} - "The veins of the lower extremity, abdomen, and pelvis" |
|||
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|43|12|01|04}} - "The Female Pelvis: The External and Internal Iliac Vessels" |
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|43|12|01|04}} - "The Female Pelvis: The External and Internal Iliac Vessels" |
||
* {{SUNYAnatomyFigs|43|07|05}} - "Sagittal view of the internal iliac artery and its branches in the female pelvis. " |
* {{SUNYAnatomyFigs|43|07|05}} - "Sagittal view of the internal iliac artery and its branches in the female pelvis. " |
||
| Line 66: | Line 69: | ||
{{Arteries of thorax and abdomen}} |
{{Arteries of thorax and abdomen}} |
||
{{Arteries of lower limbs}} |
{{Arteries of lower limbs}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Arteries of the abdomen]] |
[[Category:Arteries of the abdomen]] |
||
[[Category:Arteries of the lower limb]] |
[[Category:Arteries of the lower limb]] |
||
[[ar:شريان حرقفي ظاهر]] |
|||
[[az:Xarici qalça arteriyası]] |
|||
[[de:Arteria iliaca externa]] |
|||
[[es:Arteria ilíaca externa]] |
|||
[[fr:Artère iliaque externe]] |
|||
[[hr:Vanjska bočna arterija]] |
|||
[[la:Arteria iliaca externa]] |
|||
[[pl:Tętnica biodrowa zewnętrzna]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:40, 6 May 2024
| External iliac artery | |
|---|---|
 Front of abdomen, showing common iliac artery, the source of the external iliac artery | |
 Volume rendered CT scan of abdominal and pelvic blood vessels. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Common iliac arteries |
| Branches | Femoral arteries, inferior epigastric arteries |
| Vein | External iliac veins |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria iliaca externa |
| TA98 | A12.2.16.002 |
| TA2 | 4357 |
| FMA | 18805 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.
Structure
[edit]The external iliac artery arises from the bifurcation of the common iliac artery. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles. They exit the pelvic girdle posterior and inferior to the inguinal ligament.[1][2] This occurs about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the pubic tubercle.[1] At this point they are referred to as the femoral arteries.[1][3]
Branches
[edit]| Branch | Description |
|---|---|
| Inferior epigastric artery | Goes upward to anastomose with superior epigastric artery (a branch of internal thoracic artery). |
| Deep circumflex iliac artery | Goes laterally, travelling along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone. |
| Femoral artery[3] | Terminal branch. When the external iliac artery passes posterior to the inguinal ligament, its name changes to femoral artery. |
Function
[edit]The external iliac artery provides the main blood supply to the legs. It passes down along the brim of the pelvis and gives off two large branches - the "inferior epigastric artery" and a "deep circumflex artery." These vessels supply blood to the muscles and skin in the lower abdominal wall. The external iliac artery passes beneath the inguinal ligament in the lower part of the abdomen and becomes the femoral artery.
Clinical significance
[edit]The external iliac artery is usually the artery used to attach the renal artery to the recipient of a kidney transplant.
Additional images
[edit]-
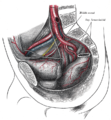
Bifurcation of the aorta and the right common iliac artery - side view. (External iliac artery is artery at upper left, seen splitting from common iliac artery at top.)
-
The relations of the femoral and abdominal inguinal rings, seen from within the abdomen. Right side. (External iliac artery is large artery at center, and inguinal ligament runs from upper right to lower left. When the artery crosses the ligament, it becomes the femoral artery.)
-
The internal mammary artery and its branches.
-
Dissection of side wall of pelvis showing sacral and pudendal plexuses.
-
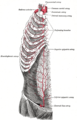
Sacral plexus of the right side.
-
Posterior view of the anterior abdominal wall in its lower half. The peritoneum is in place, and the various cords are shining through.
-
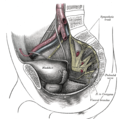
The spermatic cord in the inguinal canal.
-
Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for arteries and inguinal canal.
-
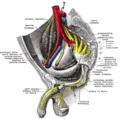
External iliac artery
-
Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
-
Lumbar and sacral plexus. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Tortora, Gerard J.; Grabowski, Sandra R. (2003). Roesch, Bonnie (ed.). Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: Volume 4 Maintenance and Continuity of the Human Body (Textbook). Vol. 4 (10th ed.). New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p. 734. ISBN 0-471-22934-2.
- ^ Madani, M. M.; Golts, E. (January 1, 2014), "Cardiovascular Anatomy", Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, Elsevier, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-801238-3.00196-3, ISBN 978-0-12-801238-3, retrieved January 18, 2021
- ^ a b Maynard, Robert Lewis; Downes, Noel (January 1, 2019), Maynard, Robert Lewis; Downes, Noel (eds.), "Chapter 7 - The Cardiovascular System", Anatomy and Histology of the Laboratory Rat in Toxicology and Biomedical Research, Academic Press, pp. 77–90, ISBN 978-0-12-811837-5, retrieved January 18, 2021
External links
[edit]- Anatomy photo:43:12-0104 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: The External and Internal Iliac Vessels"
- Anatomy figure: 43:07-05 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Sagittal view of the internal iliac artery and its branches in the female pelvis. "
- Anatomy image:8970 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (pelvicarteries)
- Hypogastric artery - thefreedictionary.com