Otic ganglion: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit |
capitalized #article-section-source-editor Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit iOS app edit |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Parasympathetic ganglion of the head and neck}} |
|||
{{Infobox nerve |
{{Infobox nerve |
||
| Name = Otic ganglion |
| Name = Otic ganglion |
||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
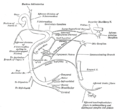
| Caption = [[Mandibular division]] of [[trigeminal nerve]], seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. |
| Caption = [[Mandibular division]] of [[trigeminal nerve]], seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. |
||
| Image2 = Gray783.png |
| Image2 = Gray783.png |
||
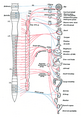
| Caption2 = The otic ganglion and its branches.| Innervates = [[ |
| Caption2 = The otic ganglion and its branches.| Innervates = [[Parotid gland]] |
||
| BranchFrom = [[ |
| BranchFrom = [[Lesser petrosal nerve]] |
||
| BranchTo = |
| BranchTo = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
The motor fibers supplying the [[medial pterygoid muscle|medial pterygoid]] and the [[tensor veli palatini]] and the [[tensor tympani]] pass through the ganglion without relay. |
The motor fibers supplying the [[medial pterygoid muscle|medial pterygoid]] and the [[tensor veli palatini]] and the [[tensor tympani]] pass through the ganglion without relay. |
||
The ganglion is connected to the [[chorda tympani nerve]] and also to the [[nerve of the pterygoid canal]]. These pathways provide an alternate pathway of taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. These fibers do not pass through the middle ear. |
|||
==Clinical significance== |
==Clinical significance== |
||
| Line 38: | Line 37: | ||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Gray788.png|Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves. |
File:Gray788.png|Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves. |
||
File:Gray839.png|Diagram of efferent sympathetic nervous system. |
File:Gray839.png|Diagram of efferent sympathetic nervous system. |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| Line 58: | Line 57: | ||
[[Category:Parasympathetic ganglia]] |
[[Category:Parasympathetic ganglia]] |
||
[[Category:Glossopharyngeal nerve]] |
[[Category:Glossopharyngeal nerve]] |
||
[[Category:Otorhinolaryngology]] |
|||
[[Category:Nerves of the head and neck]] |
|||
[[Category:Neurology]] |
|||
[[Category:Nervous system]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 16:20, 8 May 2024
| Otic ganglion | |
|---|---|
 Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve, seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. | |
 The otic ganglion and its branches. | |
| Details | |
| From | Lesser petrosal nerve |
| Innervates | Parotid gland |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ganglion oticum |
| TA98 | A14.3.02.014 |
| TA2 | 6671 |
| FMA | 6967 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.
It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. The others are the ciliary ganglion, the submandibular ganglion and the pterygopalatine ganglion.
Structure and relations
[edit]The otic ganglion is a small (2–3 mm), oval shaped, flattened parasympathetic ganglion of a reddish-grey color, located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve.
It is in relation, laterally, with the trunk of the mandibular nerve at the point where the motor and sensory roots join; medially, with the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube, and the origin of the tensor veli palatini; posteriorly, with the middle meningeal artery. It surrounds the origin of the nerve to the medial pterygoid.
Connections
[edit]The preganglionic parasympathetic fibres originate in the inferior salivatory nucleus of the glossopharyngeal nerve. They leave the glossopharyngeal nerve by its tympanic branch and then pass via the tympanic plexus and the lesser petrosal nerve to the otic ganglion. Here, the fibers synapse and the postganglionic fibers pass by communicating branches to the auriculotemporal nerve, which conveys them to the parotid gland. They produce vasodilator and secretomotor effects.
Its sympathetic root is derived from the plexus on the middle meningeal artery. It contains post-ganglionic fibers arising in the superior cervical ganglion. The fibers pass through the ganglion without relay and reach the parotid gland via the auriculotemporal nerve. They are vasomotor in function.
The sensory root comes from the auriculotemporal nerve and is sensory to the parotid gland.
The motor fibers supplying the medial pterygoid and the tensor veli palatini and the tensor tympani pass through the ganglion without relay.
Clinical significance
[edit]Frey's syndrome is caused by re-routing of parasympathetic and sympathetic fibres of the auriculotemporal nerve (V3) within the otic ganglion. It is a complication of surgery involving the parotid gland whereby injury to these branches, which innervate the parotid gland and sweat glands of the face respectively, form abnormal connections. Salivation leads to perspiration and flushing of the pre-auricular region and is called 'gustatory sweating'.
Additional images
[edit]-
Plan of the facial and intermediate nerves and their communication with other nerves.
-
Diagram of efferent sympathetic nervous system.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 897 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 897 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Shimizu T (1994). "Distribution and pathway of the cerebrovascular nerve fibers from the otic ganglion in the rat: anterograde tracing study". J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 49 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1016/0165-1838(94)90019-1. PMID 7525688.
External links
[edit]- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V, IX)