Boundary Waters–Canadian derecho: Difference between revisions
m Bot: Migrating 1 interwiki links, now provided by Wikidata on d:q3023698 |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Weather event}} |
|||
{{Derechobox |
|||
{{Infobox derecho |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| name = Boundary Waters–Canadian derecho |
|||
| image location = Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho track.jpg |
| image location = Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho track.jpg |
||
| alt = Track of the Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho (courtesy of NOAA) |
| alt = Track of the Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho (courtesy of NOAA) |
||
| image name = Track of the Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho (courtesy of NOAA) |
| image name = Track of the Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho (courtesy of NOAA) |
||
| date = |
| date = |
||
| duration = 22 |
| duration = 22 hours |
||
| track = |
| track = 1300 |
||
| wind = 90 |
| wind = 90 |
||
| windloc = |
| windloc = |
||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
| related = |
| related = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Boundary |
The '''Boundary Waters–Canadian Derecho''' (also called the '''Boundary Waters Blowdown''') was an international [[derecho]] that occurred during the afternoon and evening hours of July 4 and the early morning hours of July 5, 1999. It traveled {{convert|1300|mi|km|0}} and lasted 22 hours.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.spc.noaa.gov/misc/AbtDerechos/casepages/jul4-51999page.htm | title=The Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho | publisher=NWS Storm Prediction Center | accessdate=28 September 2009}}</ref> |
||
==Storm path== |
==Storm path== |
||
===North Dakota=== |
===North Dakota=== |
||
In the pre-dawn hours of July 4, a band of [[thunderstorms]] developed over far eastern [[North Dakota]]. [[Hector International Airport]] in northwest [[Fargo, North Dakota|Fargo]] recorded winds in excess of 58 mph (95 km/h) for 40 minutes and a maximum wind gust of {{convert|91|mi/h|km/h|0|abbr=on}}. Many planes were damaged or overturned. The hangars suffered damage as well. |
In the pre-dawn hours of July 4, a band of [[thunderstorms]] developed over far eastern [[North Dakota]]. [[Hector International Airport]] in northwest [[Fargo, North Dakota|Fargo]] recorded winds in excess of 58 mph (95 km/h) for 40 minutes and a maximum wind gust of {{convert|91|mi/h|km/h|0|abbr=on}}. Many planes were damaged or overturned. The hangars suffered damage as well. |
||
| Line 37: | Line 39: | ||
[[Image:Bwca derecho.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Damage to trees in the BWCAW]] |
[[Image:Bwca derecho.jpg|thumb|250px|right|Damage to trees in the BWCAW]] |
||
The derecho moved into [[Minnesota]] and caused massive damage in [[Cass County, Minnesota|Cass]], [[Itasca County, Minnesota|Itasca]], and [[Aitkin County, Minnesota|Aitkin Counties]] |
The derecho moved into [[Minnesota]] and caused massive damage in [[Cass County, Minnesota|Cass]], [[Itasca County, Minnesota|Itasca]], and [[Aitkin County, Minnesota|Aitkin Counties]], at around $3 million. A semi-trailer truck was blown over on [[U.S. Route 53]] near [[Canyon, Minnesota|Canyon]]. |
||
One person was killed and 60 were injured as the derecho passed through the [[Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness]] (BWCAW) and [[Superior National Forest]]. People were there to enjoy canoeing and other recreation for the [[Independence Day (United States)|Independence Day]] weekend. Straight line winds in excess of 90 mph (145 km/h) uprooted and snapped off trees in over 370,000 acres (1,500 km²) of the 1 million acre (4,000 km²) wilderness area. In total, more than 477,000 acres (1,930 km²) of forest was affected in the [[Superior National Forest]] in a swath 30 miles (48.3 km) long and 4 to 12 miles (6.4 to 19.3 km) wide.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.crh.noaa.gov/dlh/science/event_archive/summer_archive/1999blowdown/1999blowdown.php | title=Boundary Waters Windstorm: The Blowdown of July 4th, 1999 | last1=Parke | first1=Peter S. | first2=Norvan J. | last2=Larson | publisher=Duluth, MN, Weather Forecast Office, [[National Weather Service]] | accessdate=28 September 2009}}</ref> It |
One person was killed and 60 were injured as the derecho passed through the [[Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness]] (BWCAW) and [[Superior National Forest]]. People were there to enjoy canoeing and other recreation for the [[Independence Day (United States)|Independence Day]] weekend. Straight line winds in excess of 90 mph (145 km/h) uprooted and snapped off trees in over 370,000 acres (1,500 km²) of the 1 million acre (4,000 km²) wilderness area. In total, more than 477,000 acres (1,930 km²) of forest was affected in the [[Superior National Forest]] in a swath 30 miles (48.3 km) long and 4 to 12 miles (6.4 to 19.3 km) wide.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.crh.noaa.gov/dlh/science/event_archive/summer_archive/1999blowdown/1999blowdown.php | title=Boundary Waters Windstorm: The Blowdown of July 4th, 1999 | last1=Parke | first1=Peter S. | first2=Norvan J. | last2=Larson | publisher=Duluth, MN, Weather Forecast Office, [[National Weather Service]] | accessdate=28 September 2009}}</ref> It is estimated that 25 million trees were blown down in the BWCAW.<ref>{{cite web|last=Breining |first=Greg |title=Boundary Waters: The Fire Next Time |publisher=Minnesota DNR |url=http://www.dnr.state.mn.us/volunteer/mayjun00/blowdown.html |accessdate=2007-03-26 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20070405142656/http://www.dnr.state.mn.us/volunteer/mayjun00/blowdown.html |archivedate=2007-04-05 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.fs.fed.us/r9/forests/superior/storm_recovery/ | title=Lowdown on the Blowdown | publisher=[[Superior National Forest]], [[U.S. Forest Service]] | accessdate=28 September 2009}}</ref> |
||
===Ontario=== |
===Ontario=== |
||
The derecho brought more damage when it crossed the border into |
The derecho brought more damage when it crossed the border into [[Ontario]] during the early afternoon hours of July 4. At its peak near [[Thunder Bay]], the winds were estimated to have been much stronger, around 100 mph (160 km/h) and it spawned some small [[tornadoes]]. One small sailboat was overturned and two people were thrown into the cold waters of [[Lake Superior]]. They were rescued by a nearby boater. |
||
The storm carved a path of destruction into the sparsely populated forested areas of northern Ontario. The [[Canadian Pacific]] track between [[White River, Ontario|White River]] and [[Chapleau, Ontario|Chapleau]] in northeastern Ontario was put out of service by fallen trees. |
The storm carved a path of destruction into the sparsely populated forested areas of northern Ontario. The [[Canadian Pacific]] track between [[White River, Ontario|White River]] and [[Chapleau, Ontario|Chapleau]] in northeastern Ontario was put out of service by fallen trees. Significant tree and property damage was recorded in [[Timmins, Ontario|Timmins]]. |
||
===Quebec=== |
===Quebec=== |
||
[[File:Boundery waters Canadian Derecho radar image.png|thumb|Radar and satellite image of the Derecho passing from Ontario (ON) to Quebec (QC)]] |
[[File:Boundery waters Canadian Derecho radar image.png|thumb|Radar and satellite image of the Derecho passing from Ontario (ON) to Quebec (QC)]] |
||
As it raced eastward at 62 mph (100 km/h), the system entered into western [[Quebec]] in the [[Témiscamingue]] region around 11:00 p.m. A gust of 65 mph (102 km/h) was reported at the automatic station of Angliers. There was also a tremendous amount of lightning associated with this derecho, with around |
As it raced eastward at 62 mph (100 km/h), the system entered into western [[Quebec]] in the [[Témiscamingue]] region around 11:00 p.m. A gust of 65 mph (102 km/h) was reported at the automatic station of Angliers. There was also a tremendous amount of lightning associated with this derecho, with around 6,000 lightning strikes per hour. Another person in this derecho was killed at [[Val-des-Lacs]] (V on the map) when a tree fell on the victim. A woman was injured when a tree crushed her car. |
||
After narrowly missing the [[Ottawa]] area, the storm moved quickly into [[Montreal]] (M on the map) around 3:00 a.m. heading southeastward toward Maine. Much damage was recorded in the Metropolitan area but the worst affected area of Quebec was farther along its path near Sherbrooke (S on the map) in the [[Eastern Townships]] where a church was badly damaged, farm buildings were damaged and 2,000 trees were felled. Hydro-Québec reported that over 600,000 people lost power; some were without power for over a week. |
After narrowly missing the [[Ottawa]] area, the storm moved quickly into [[Montreal]] (M on the map) around 3:00 a.m. heading southeastward toward Maine. Much damage was recorded in the Metropolitan area but the worst affected area of Quebec was farther along its path near Sherbrooke (S on the map) in the [[Eastern Townships]] where a church was badly damaged, farm buildings were damaged and 2,000 trees were felled. Hydro-Québec reported that over 600,000 people lost power; some were without power for over a week. |
||
===New England=== |
===New England=== |
||
The storm continued southeast and caused more damage in [[New Hampshire]] and [[Vermont]], killing one more person, before finally dissipating in [[Maine]] after 5:00 a.m. on July |
The storm continued southeast and caused more damage in [[New Hampshire]] and [[Vermont]], killing one more person, before finally dissipating in [[Maine]] after 5:00 a.m. on July 5. |
||
==Aftermath== |
==Aftermath== |
||
The Boundary Waters – Canadian Derecho is one of the farthest north "progressive" derechos to have ever been recorded. The derecho caused well over $100 million in damage, killed 4 persons and injured 70. Over 700,000 homes and businesses lost power from the event. |
The Boundary Waters – Canadian Derecho is one of the farthest north "progressive" derechos to have ever been recorded. The derecho caused well over $100 million in damage, killed 4 persons and injured 70. Over 700,000 homes and businesses lost power from the event. |
||
A feature film slated for release in 2012 will be based on the July 4th Boundary Waters Canoe Area Derecho following the rescue and cleanup efforts of the Cook County Highway Department. |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[List of derecho events]] |
*[[List of derecho events]] |
||
| Line 67: | Line 68: | ||
{{coord missing|Minnesota}} |
{{coord missing|Minnesota}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:1999 meteorology]] |
[[Category:1999 meteorology]] |
||
[[Category:1999 natural disasters in the United States]] |
[[Category:1999 natural disasters in the United States]] |
||
| Line 76: | Line 78: | ||
[[Category:Natural disasters in Quebec]] |
[[Category:Natural disasters in Quebec]] |
||
[[Category:1999 in Minnesota]] |
[[Category:1999 in Minnesota]] |
||
[[Category:July 1999 events in North America]] |
|||
[[Category:1999 disasters in Canada]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 05:04, 12 May 2024
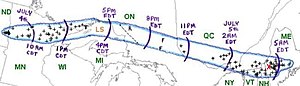 Track of the Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho (courtesy of NOAA) | |
| Duration | 22 hours |
|---|---|
| Track length | 1,300 mi (2,090 km) |
| Peak wind gust (measured) | 90 mph (145 km/h; 40.2 m/s) |
| Fatalities | 4 |
| Damage costs | >$100,000,000 |
| Areas affected | Northern United States, southern Canada |
The Boundary Waters–Canadian Derecho (also called the Boundary Waters Blowdown) was an international derecho that occurred during the afternoon and evening hours of July 4 and the early morning hours of July 5, 1999. It traveled 1,300 miles (2,092 km) and lasted 22 hours.[1]
Storm path
[edit]North Dakota
[edit]In the pre-dawn hours of July 4, a band of thunderstorms developed over far eastern North Dakota. Hector International Airport in northwest Fargo recorded winds in excess of 58 mph (95 km/h) for 40 minutes and a maximum wind gust of 91 mph (146 km/h). Many planes were damaged or overturned. The hangars suffered damage as well.
The worst damage occurred farther south in West Fargo, North Dakota and in south central Fargo, North Dakota. Wind gusts in these areas were estimated at as high as 110 mph (180 km/h).
The storm caused $85 million in damage (1999 dollars) in the Fargo metropolitan area. Over 40,000 people were without power. Cars were overturned, roofs were severely damaged, and power poles were blown down.
Minnesota
[edit]
The derecho moved into Minnesota and caused massive damage in Cass, Itasca, and Aitkin Counties, at around $3 million. A semi-trailer truck was blown over on U.S. Route 53 near Canyon.
One person was killed and 60 were injured as the derecho passed through the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness (BWCAW) and Superior National Forest. People were there to enjoy canoeing and other recreation for the Independence Day weekend. Straight line winds in excess of 90 mph (145 km/h) uprooted and snapped off trees in over 370,000 acres (1,500 km²) of the 1 million acre (4,000 km²) wilderness area. In total, more than 477,000 acres (1,930 km²) of forest was affected in the Superior National Forest in a swath 30 miles (48.3 km) long and 4 to 12 miles (6.4 to 19.3 km) wide.[2] It is estimated that 25 million trees were blown down in the BWCAW.[3][4]
Ontario
[edit]The derecho brought more damage when it crossed the border into Ontario during the early afternoon hours of July 4. At its peak near Thunder Bay, the winds were estimated to have been much stronger, around 100 mph (160 km/h) and it spawned some small tornadoes. One small sailboat was overturned and two people were thrown into the cold waters of Lake Superior. They were rescued by a nearby boater.
The storm carved a path of destruction into the sparsely populated forested areas of northern Ontario. The Canadian Pacific track between White River and Chapleau in northeastern Ontario was put out of service by fallen trees. Significant tree and property damage was recorded in Timmins.
Quebec
[edit]
As it raced eastward at 62 mph (100 km/h), the system entered into western Quebec in the Témiscamingue region around 11:00 p.m. A gust of 65 mph (102 km/h) was reported at the automatic station of Angliers. There was also a tremendous amount of lightning associated with this derecho, with around 6,000 lightning strikes per hour. Another person in this derecho was killed at Val-des-Lacs (V on the map) when a tree fell on the victim. A woman was injured when a tree crushed her car.
After narrowly missing the Ottawa area, the storm moved quickly into Montreal (M on the map) around 3:00 a.m. heading southeastward toward Maine. Much damage was recorded in the Metropolitan area but the worst affected area of Quebec was farther along its path near Sherbrooke (S on the map) in the Eastern Townships where a church was badly damaged, farm buildings were damaged and 2,000 trees were felled. Hydro-Québec reported that over 600,000 people lost power; some were without power for over a week.
New England
[edit]The storm continued southeast and caused more damage in New Hampshire and Vermont, killing one more person, before finally dissipating in Maine after 5:00 a.m. on July 5.
Aftermath
[edit]The Boundary Waters – Canadian Derecho is one of the farthest north "progressive" derechos to have ever been recorded. The derecho caused well over $100 million in damage, killed 4 persons and injured 70. Over 700,000 homes and businesses lost power from the event.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "The Boundary Waters-Canadian Derecho". NWS Storm Prediction Center. Retrieved 28 September 2009.
- ^ Parke, Peter S.; Larson, Norvan J. "Boundary Waters Windstorm: The Blowdown of July 4th, 1999". Duluth, MN, Weather Forecast Office, National Weather Service. Retrieved 28 September 2009.
- ^ Breining, Greg. "Boundary Waters: The Fire Next Time". Minnesota DNR. Archived from the original on 2007-04-05. Retrieved 2007-03-26.
- ^ "Lowdown on the Blowdown". Superior National Forest, U.S. Forest Service. Retrieved 28 September 2009.
