Causes of the Polish–Soviet War: Difference between revisions
m →The situation: http→https for Google Books and Google News using AWB |
XTheBedrockX (talk | contribs) →References: added Template:Military historiography |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 25 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
During the [[Polish–Soviet War]] of 1919–1921, [[Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic|Soviet Russia]] and its client state, [[Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic|Soviet Ukraine]], were in combat with the re-established [[Second Polish Republic]] and the newly established [[Ukrainian People's Republic]]. Both sides aimed to secure territory in the often disputed areas of the [[Kresy]] (present-day [[western Ukraine]] and [[western Belarus]]), in the context of the fluidity of borders in [[Central and Eastern Europe]] in the aftermath of [[World War I]] and the breakdown of the [[Austria-Hungary|Austrian]], [[German Empire|German]], and [[Russian Empire|Russian]] Empires. The first clashes between the two sides occurred in February 1919, but full-scale war did not break out until the following year. Especially at first, neither Soviet Russia, embroiled in the [[Russian Civil War]], nor Poland, still in the early stages of state re-building, were in a position to formulate and pursue clear and consistent war aims. |
|||
{{main|Polish-Soviet War}} |
|||
{{Lead missing|date=June 2014}} |
|||
[[File:Polish-soviet propaganda poster 1920.jpg|thumb|left|275px|Soviet [[Anti-Polish sentiment|anti-Polish]] propaganda poster "This is how the Polish pans' (lords) plan ends"]] |
|||
In the winter of 1918–19 the recently established Russian Soviet Republic had already undertaken a "[[Soviet westward offensive of 1918–19|Westward Offensive]]", leading to the establishment of [[Soviet (council)|Soviet]] client republics in [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]] and [[Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic|Byelorussia]]. The overarching aim of [[Vladimir Lenin]], [[Joseph Stalin]] and [[Lev Trotsky]] was to spread the [[Bolshevik]] revolution into Germany and other parts of Europe, while realising their limited capacity to engage in large-scale conflict in Europe. The Soviets built up forces positioned for an attack on Poland, although officially denying that an invasion was planned. |
|||
For their part, the [[Polish people|Poles]] aimed to secure their independence, contain any resurgence of the Russian or German Empires, and reclaim areas in the east that had ethnic Polish populations as per the historical [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] borders that existed prior to the [[Partitions of Poland]]. An ambitious plan formulated by Polish head of state [[Józef Piłsudski]] aimed to create a wide "[[Intermarium]]" (''Międzymorze'') federation of independent states to the west of Russia, of which Poland would be the leading member. Limiting Russian control of Ukraine was essential to this plan, and Poland was already [[Polish–Ukrainian War|at war]] with Ukrainian forces over [[Eastern Galicia]]. |
|||
[[File:Bij Bolszewika.jpg|thumb|right|225px|Polish propaganda poster "Strike the Bolshevik"]] |
|||
As 1919 progressed, Soviet forces conquered [[Kiev]]. In early 1920, Poland formed an alliance with the [[Ukrainian People's Republic]], which had lost much of its territory to the Russian Bolsheviks. Both Polish and Soviet forces in the theatre were rapidly increased, and full-scale war began with Poland's [[Kiev offensive (1920)|Kiev offensive]] into Soviet-controlled Ukraine. |
|||
== The prehistory == |
== The prehistory == |
||
The territory, where this conflict broke out, was a part of the medieval [[Kievan Rus]], and after the disintegration of this united [[Ruthenia]]n state (in the middle of the 12th century) belonged to the Ruthenian princedoms of [[Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia|Halych-Volhynia]], [[Principality of Polotsk|Polotsk]], [[Lutsk]], [[Terebovlia]], [[Principality of Turov and Pinsk|Turov-Pinsk]] etc. The majority of these principalities have been ruined during the [[Mongol invasion of Rus| |
The territory, where this conflict broke out, was a part of the medieval [[Kievan Rus']], and after the disintegration of this united [[Ruthenia]]n state (in the middle of the 12th century) belonged to the Ruthenian princedoms of [[Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia|Halych-Volhynia]], [[Principality of Polotsk|Polotsk]], [[Lutsk]], [[Terebovlia]], [[Principality of Turov and Pinsk|Turov-Pinsk]] etc. The majority of these principalities have been ruined during the [[Mongol invasion of Rus'|Tatar–Mongol invasion]] in the middle of the 13th century. Some territories in the [[Dnieper]] region and Black Sea Coast for long years lost [[Ruthenians|Ruthenian]] settled population and became the so-called [[Wild Fields|''Wild Steppe'']] (i.e., territory of the [[Principality of Pereslavl|Pereyaslavl]]). After the Tatar–Mongol invasion these territories become an object of expansion of the [[Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569)|Polish kingdom]] and the [[Grand Duchy of Lithuania|Lithuanian princedom]]. For example, in the first half of 14th century Kiev, the Dniepr region, also the region between the rivers [[Pripyat River|Pripyat]] and [[Daugava|West Dvina]] were captured by Lithuania, and in 1352 the Halych-Volhynia princedom was divided by Poland and Lithuania. In 1569, according to the [[Union of Lublin|Lublin Union]], the majority of the Ruthenian territories possessed by Lithuania, passed to the [[Crown of the Kingdom of Poland|Polish crown]]. The [[serfdom]] and Catholicism extended in these territories. The local aristocracy was incorporated into the [[Szlachta|Polish aristocracy]]. Cultural, language and religious break between the supreme and lowest layers of a society arose. |
||
The combination of social, language, religious and cultural oppressions had led to destructive [[Khmelnytsky Uprising|popular uprisings of the middle of 17th century]], which the |
The combination of social, language, religious and cultural oppressions had led to destructive [[Khmelnytsky Uprising|popular uprisings of the middle of 17th century]], which the Polish–Lithuanian state could not recover from.<ref>[[Sergey Solovyov (historian)|Sergey Solovyov]], "History of Russia from the Earliest Times", vol.3–5, {{ISBN|5-17-002142-9}}</ref> In many territories incorporated into the [[Russian Empire]] in 1772–1795 after [[Partitions of Poland|the partitions]], the domination of the Polish aristocracy was kept, in the territories incorporated into the [[Habsburg monarchy|Austro-Hungarian Empire]], the domination of the Polish aristocracy has been added with active planting of German language and culture. During the First World War Austro-Hungarian authorities undertook reprisals against [[Ukrainian Russophiles|Russia-oriented people]] of the [[Galicia (Eastern Europe)|Eastern Galicia]] and the Polish left-nationalist movement led by [[Józef Piłsudski|Piłsudski]] got the support of the [[Central Powers]] for struggle against Russia. In the consequence of the [[Russian Revolution|revolution in Russia]] and the fall of Hohenzollern and Habsburg empires in the end of World War I Poland regained independence. The Polish leaders decided to retrieve as many of the territories that were parts of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth|Polish–Lithuanian state]] in 1772 as possible. |
||
== The situation == |
== The situation == |
||
In the [[aftermath of World War I]], the map of |
In the [[aftermath of World War I]], the map of Central and Eastern Europe had drastically changed.<ref name="FDH">[[Thomas Grant Fraser]], [[Seamus Dunn]], [[Otto von Habsburg]], ''Europe and Ethnicity: the First World War and contemporary ethnic conflict'', Routledge, 1996, {{ISBN|0-415-11995-2}}, [https://books.google.com/books?id=WI2WIiR2FjgC&dq=%22First+World+War%22+independence+change+map&pg=PA2 Google Print, p.2]</ref> The [[Treaty of Brest-Litovsk]] (March 3, 1918), by which Russia had lost to [[Imperial Germany]] all the European lands that Russia had seized in the previous two centuries, was rejected by the Bolshevik government in November 1918, following [[armistice]], the surrender of Germany and her allies, and the end of World War I. |
||
Germany, however, had not been keen to see Russia grow strong again and—exploiting her control of those territories, had quickly granted limited independence as [[buffer state]]s to [[Finland]], [[Estonia]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Poland]], [[Belarus]] and [[Ukraine]]. As Germany's defeat rendered her plans for the creation of those [[Mitteleuropa]] [[puppet state]]s obsolete, and as Russia sank into the depths of the [[Russian Civil War]], the newly emergent countries saw a chance for real independence and were not prepared to easily relinquish this rare gift of fate. At the same time, Russia saw these territories as rebellious Russian provinces but was unable to react swiftly, as it was weakened and in the process of transforming herself into the [[Soviet Union]] through the [[ |
Germany, however, had not been keen to see Russia grow strong again and—exploiting her control of those territories, had quickly granted limited independence as [[buffer state]]s to [[Finland]], [[Estonia]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Poland]], [[Belarus]] and [[Ukraine]]. As Germany's defeat rendered her plans for the creation of those [[Mitteleuropa]] [[puppet state]]s obsolete, and as Russia sank into the depths of the [[Russian Civil War]], the newly emergent countries saw a chance for real independence and were not prepared to easily relinquish this rare gift of fate. At the same time, Russia saw these territories as rebellious Russian provinces but was unable to react swiftly, as it was weakened and in the process of transforming herself into the [[Soviet Union]] through the [[Russian Revolution]] and Russian Civil War that had begun in 1917. |
||
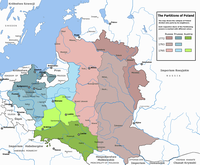
[[Image:Rzeczpospolita Rozbiory 3.png|thumb|right|200px|[[Partitions of Poland]], 1795. The colored territories show the greatest extent of the [[Poland]]. Blue (north-west) were taken by [[Kingdom of Prussia]], green (south) by [[Austria]], and cyan (east) by [[Imperial Russia]].]] |
[[Image:Rzeczpospolita Rozbiory 3.png|thumb|right|200px|[[Partitions of Poland]], 1795. The colored territories show the greatest extent of the [[Poland]]. Blue (north-west) were taken by [[Kingdom of Prussia]], green (south) by [[Austria]], and cyan (east) by [[Imperial Russia]].]] |
||
With the success of the [[ |
With the success of the [[Greater Poland uprising (1918–1919)|Greater Poland uprising in 1918]], Poland had re-established its [[Sovereign state|statehood]] for the first time since the [[Third Partition of Poland|1795 partition]] and seen the end of a 123 years of rule by three imperial neighbors: [[Imperial Russia|Russia]], [[German Empire|Germany]], and [[Austria-Hungary]]. The country, reborn as a [[Second Polish Republic]], proceeded to carve out its borders from the territories of its former partitioners. The [[Western Powers]], in delineating the new European borders after the [[Treaty of Versailles]], had done so in a way unfavorable to Poland. Her western borders cut her off from the [[coal]]-basin and industrial regions of [[Silesia]], leading to the [[Silesian Uprisings]] of 1919–1921. The eastern [[Curzon line]] left millions of Poles, living east of the [[Bug River]], stranded inside Russia's borders. |
||
[[Image:PBW March 1919.png|thumb|left|200px|Rebirth of Poland, March 1919]] |
[[Image:PBW March 1919.png|thumb|left|200px|Rebirth of Poland, March 1919]] |
||
Poland was not alone in its newfound opportunities and troubles. Most if not all of the newly independent neighbours began fighting over borders: [[Kingdom of Romania|Romania]] fought with [[Hungary]] over [[Transylvania]], [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia|Yugoslavia]] with [[Italy]] over [[Rijeka]], Poland with [[Czechoslovakia]] over [[Cieszyn Silesia]], with Germany over [[Poznań]] and [[Polish-Ukrainian War|with Ukrainians]] over [[Eastern Galicia]] (Galician War). [[Ukrainian People's Republic|Ukrainians]], Belarusians, [[Freedom wars of Lithuania|Lithuanians]], [[Estonian Liberation War|Estonians]] and [[Latvian War of Independence|Latvians]] fought against themselves and against the Russians, who were just as divided.<ref name="Davies_WERS-21">[[Norman Davies|Davies, Norman]], ''White Eagle, Red Star: the Polish-Soviet War, 1919–20'', Pimlico, 2003, ISBN |
Poland was not alone in its newfound opportunities and troubles. Most if not all of the newly independent neighbours began fighting over borders: [[Kingdom of Romania|Romania]] fought with [[Hungary]] over [[Transylvania]], [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia|Yugoslavia]] with [[Italy]] over [[Rijeka]], Poland with [[Czechoslovakia]] over [[Cieszyn Silesia]], with Germany over [[Poznań]] and [[Polish-Ukrainian War|with Ukrainians]] over [[Eastern Galicia]] (Galician War). [[Ukrainian People's Republic|Ukrainians]], Belarusians, [[Freedom wars of Lithuania|Lithuanians]], [[Estonian Liberation War|Estonians]] and [[Latvian War of Independence|Latvians]] fought against themselves and against the Russians, who were just as divided.<ref name="Davies_WERS-21">[[Norman Davies|Davies, Norman]], ''White Eagle, Red Star: the Polish-Soviet War, 1919–20'', Pimlico, 2003, {{ISBN|0-7126-0694-7}}. (First edition: New York, St. Martin's Press, inc., 1972.) Page 21.</ref> |
||
Spreading communist influences resulted in communist revolutions in [[Munich]], [[Berlin]], [[Budapest]] and [[Prešov]]. [[Winston Churchill]] commented: "The war of giants has ended, the wars of the pygmies begin."<ref name="AHP">[[Adrian Hyde-Price]], ''Germany and European Order'', Manchester University Press, 2001, ISBN |
Spreading communist influences resulted in communist revolutions in [[Munich]], [[Berlin]], [[Budapest]] and [[Prešov]]. [[Winston Churchill]] commented: "The war of giants has ended, the wars of the pygmies begin."<ref name="AHP">[[Adrian Hyde-Price]], ''Germany and European Order'', Manchester University Press, 2001, {{ISBN|0-7190-5428-1}} [https://books.google.com/books?id=M-2Obqk-VZUC&pg=PA75 Google Print, p.75]</ref> All of those engagements – with the sole exception of the Polish-Soviet war – would be short-lived border conflicts. |
||
The |
The Polish–Soviet war likely happened more by accident than design, as it is unlikely that anyone in Soviet Russia or in the new Second Republic of Poland would have deliberately planned a major foreign war.<ref name="Davies_WERS-22">[[Norman Davies|Davies, Norman]], ''White Eagle, Red Star: the Polish-Soviet War, 1919–20'', Pimlico, 2003, {{ISBN|0-7126-0694-7}}. (First edition: New York, St. Martin's Press, inc., 1972.) Page 22</ref><ref name="Davies_GP_292">[[Norman Davies]], ''[[God's Playground]]. Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present''. Columbia University Press, 2005 [1982]. {{ISBN|0-231-12819-3}}. [https://books.google.com/books?id=EBpghdZeIwAC&dq=Red+Army+700000+1920&pg=PA292 Google Print, p.292]</ref> |
||
Poland, its territory a major frontline of the First World War, was unstable politically; it had just won the difficult conflict with the West Ukrainian National Republic and was already engaged in new conflicts with Germany (the [[Silesian Uprisings]]) and [[border conflicts between Poland and Czechoslovakia|with Czechoslovakia]]. Polish government was just beginning to organise and had little if any control over various border areas. Six [[currency|currencies]] affected by various (and rising rapidly) [[inflation]] rates were in circulation. [[Polish economy|Economy]] was in shambles, some areas were experiencing food shortages, [[crime]] was high and a threat of an armed [[coup d'etat]] by some factions was serious. |
Poland, its territory a major frontline of the First World War, was unstable politically; it had just won the difficult conflict with the West Ukrainian National Republic and was already engaged in new conflicts with Germany (the [[Silesian Uprisings]]) and [[border conflicts between Poland and Czechoslovakia|with Czechoslovakia]]. Polish government was just beginning to organise and had little if any control over various border areas. Six [[currency|currencies]] affected by various (and rising rapidly) [[inflation]] rates were in circulation. [[Polish economy|Economy]] was in shambles, some areas were experiencing food shortages, [[crime]] was high and a threat of an armed [[coup d'etat]] by some factions was serious. |
||
| Line 29: | Line 36: | ||
== Piłsudski's motives == |
== Piłsudski's motives == |
||
[[Image:Jozef Pilsudski1.jpg|thumb|left|150px|[[Józef Piłsudski|Polish Marshal (from March 1920) Józef Piłsudski]]]] |
[[Image:Jozef Pilsudski1.jpg|thumb|left|150px|[[Józef Piłsudski|Polish Marshal (from March 1920) Józef Piłsudski]]]] |
||
Polish politics |
Polish politics were under the strong influence of statesman and Marshal [[Józef Piłsudski]], who envisioned a Polish-led [[federation]] (the "Federation of [[Międzymorze]]", aka ''Intermarium'') comprising [[Poland]], [[Czechoslovakia]], [[Hungary]], [[Ukraine]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Estonia]], and other Central and East European countries now re-emerging out of the crumbling empires after the First World War. The new union would have had borders similar to those of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] in the 15th–18th centuries, and it was to be a counterweight to, and restraint upon, any [[imperialist]] intentions of Russia and/or Germany. To this end, Polish forces set out to secure vast territories in the east. However Piłsudski's federation plan was opposed by another influential Polish politician, [[Roman Dmowski]], who favoured creating a larger, national Polish state. |
||
Poland had never any intention of joining the Western intervention in the Russian Civil War or conquering Russia, as it has done once in the 17th century during the [[ |
Poland had never any intention of joining the Western intervention in the Russian Civil War or conquering Russia, as it has done once in the 17th century during the [[Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)|Dimitriads]]. On the contrary, after the [[White Movement|White Russians]] refused to recognise Polish independence, Polish forces acting on orders from Piłsudski delayed or stopped their offensives several times, relieving pressure from Bolshevik forces and thus substantially contributing to White Russian defeat.{{citation needed|date=June 2014}} |
||
== Lenin's motives == |
== Lenin's motives == |
||
[[Image:Lenin Validmir.jpg|thumb|150px|Soviet leader [[Vladimir Lenin]] |
[[Image:Lenin Validmir.jpg|thumb|150px|Soviet leader [[Vladimir Lenin]]]] |
||
In April 1920, when the Red Army's major push towards Polish hinterlands took place, the soldiers and commanders were told that defeat of Poland was not only necessary but simply sufficient for the "oppressed masses of the proletariat" to rise worldwide and create a "workers' paradise." In the words of General Tukhachevski: "To the West! Over the corpse of White Poland lies the road to world-wide conflagration. March on Vilno, Minsk, Warsaw!".<ref>Mikhail Tukhachevski, order of the day, July 2, 1920.</ref> |
|||
In late 1919 the leader of Russia's new [[communist]] government, [[Vladimir Lenin]], was inspired by the Red Army's civil-war victories over [[White Movement|White Russian]] anti-communist forces and their western allies, and began to see the future of the revolution with greater optimism. The Bolsheviks doctrine said that historical processes would lead to [[proletariat]] victory worldwide, and that the [[nation state]]s would be replaced by [[world communism|a worldwide communist community]]. War with Poland was needed if the communist revolution in Russia was to be linked with the expected revolutions in the West, such as [[German Revolution|the one in Germany]]. Early Bolshevik [[ideology]] made it clear that Poland, which was located in between Russia and Germany, had to become the bridge that the [[Red Army]] would have to cross to fulfill the [[Marxist]] doctrine. It was not, however, until the Soviet successes in mid-1920 that this idea became for a short time dominant in Bolshevik policies. |
In late 1919 the leader of Russia's new [[communist]] government, [[Vladimir Lenin]], was inspired by the Red Army's civil-war victories over [[White Movement|White Russian]] anti-communist forces and their western allies, and began to see the future of the revolution with greater optimism. The Bolsheviks doctrine said that historical processes would lead to [[proletariat]] victory worldwide, and that the [[nation state]]s would be replaced by [[world communism|a worldwide communist community]]. War with Poland was needed if the communist revolution in Russia was to be linked with the expected revolutions in the West, such as [[German Revolution of 1918–19|the one in Germany]]. Early Bolshevik [[ideology]] made it clear that Poland, which was located in between Russia and Germany, had to become the bridge that the [[Red Army]] would have to cross to fulfill the [[Marxist]] doctrine. It was not, however, until the Soviet successes in mid-1920 that this idea became for a short time dominant in Bolshevik policies. |
||
Germany in 1918-1920 was a nation torn by social discontent and embroiled in political chaos. Since the [[Kaiser]]'s [[abdication]] at the end of the First World War, it had seen a series of major internal disturbances, including government takeovers, several [[general strike]]s, some leading to communist revolutions (e.g. the [[Bavarian Soviet Republic]]), By July 1920, which is when the Soviets were on the verge of taking [[Warsaw]], the [[Weimar Constitution]] was still brand new and the humiliating [[Treaty of Versailles|Peace of Versailles]], even more so. Germany unstable government had to deal with [[separatism|separatist tendencies]], an ongoing conflict, not far from a civil war between the [[Spartacist League]]'s and [[Communist Party of Germany]] and the right-wing [[Freikorps]], all under the watchful and humiliating eyes of the Allied powers. Red Army's remaking of the Versailles system was seen as a major force that could shake the existing system imposed by the victorious western [[Triple Entente|Entente]]. As Lenin himself remarked, "That was the time when everyone in Germany, including the blackest reactionaries and monarchists, declared that the Bolsheviks would be their salvation." |
Germany in 1918-1920 was a nation torn by social discontent and embroiled in political chaos. Since the [[Kaiser]]'s [[abdication]] at the end of the First World War, it had seen a series of major internal disturbances, including government takeovers, several [[general strike]]s, some leading to communist revolutions (e.g. the [[Bavarian Soviet Republic]]), By July 1920, which is when the Soviets were on the verge of taking [[Warsaw]], the [[Weimar Constitution]] was still brand new and the humiliating [[Treaty of Versailles|Peace of Versailles]], even more so. Germany unstable government had to deal with [[separatism|separatist tendencies]], an ongoing conflict, not far from a civil war between the [[Spartacist League]]'s and [[Communist Party of Germany]] and the right-wing [[Freikorps]], all under the watchful and humiliating eyes of the Allied powers. Red Army's remaking of the Versailles system was seen as a major force that could shake the existing system imposed by the victorious western [[Triple Entente|Entente]]. As Lenin himself remarked, "That was the time when everyone in Germany, including the blackest reactionaries and monarchists, declared that the Bolsheviks would be their salvation." |
||
| Line 49: | Line 56: | ||
{{Polish-Soviet War}} |
{{Polish-Soviet War}} |
||
{{Polish wars and conflicts}} |
{{Polish wars and conflicts}} |
||
{{Military historiography}} |
|||
[[Category:Causes of wars|Polish-Soviet War]] |
|||
[[Category:Causes of wars|Polish-Soviet War, Causes of]] |
|||
[[Category:Polish–Soviet War]] |
[[Category:Polish–Soviet War]] |
||
Latest revision as of 03:49, 14 June 2024
During the Polish–Soviet War of 1919–1921, Soviet Russia and its client state, Soviet Ukraine, were in combat with the re-established Second Polish Republic and the newly established Ukrainian People's Republic. Both sides aimed to secure territory in the often disputed areas of the Kresy (present-day western Ukraine and western Belarus), in the context of the fluidity of borders in Central and Eastern Europe in the aftermath of World War I and the breakdown of the Austrian, German, and Russian Empires. The first clashes between the two sides occurred in February 1919, but full-scale war did not break out until the following year. Especially at first, neither Soviet Russia, embroiled in the Russian Civil War, nor Poland, still in the early stages of state re-building, were in a position to formulate and pursue clear and consistent war aims.

In the winter of 1918–19 the recently established Russian Soviet Republic had already undertaken a "Westward Offensive", leading to the establishment of Soviet client republics in Latvia, Lithuania and Byelorussia. The overarching aim of Vladimir Lenin, Joseph Stalin and Lev Trotsky was to spread the Bolshevik revolution into Germany and other parts of Europe, while realising their limited capacity to engage in large-scale conflict in Europe. The Soviets built up forces positioned for an attack on Poland, although officially denying that an invasion was planned.
For their part, the Poles aimed to secure their independence, contain any resurgence of the Russian or German Empires, and reclaim areas in the east that had ethnic Polish populations as per the historical Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth borders that existed prior to the Partitions of Poland. An ambitious plan formulated by Polish head of state Józef Piłsudski aimed to create a wide "Intermarium" (Międzymorze) federation of independent states to the west of Russia, of which Poland would be the leading member. Limiting Russian control of Ukraine was essential to this plan, and Poland was already at war with Ukrainian forces over Eastern Galicia.

As 1919 progressed, Soviet forces conquered Kiev. In early 1920, Poland formed an alliance with the Ukrainian People's Republic, which had lost much of its territory to the Russian Bolsheviks. Both Polish and Soviet forces in the theatre were rapidly increased, and full-scale war began with Poland's Kiev offensive into Soviet-controlled Ukraine.
The prehistory
[edit]The territory, where this conflict broke out, was a part of the medieval Kievan Rus', and after the disintegration of this united Ruthenian state (in the middle of the 12th century) belonged to the Ruthenian princedoms of Halych-Volhynia, Polotsk, Lutsk, Terebovlia, Turov-Pinsk etc. The majority of these principalities have been ruined during the Tatar–Mongol invasion in the middle of the 13th century. Some territories in the Dnieper region and Black Sea Coast for long years lost Ruthenian settled population and became the so-called Wild Steppe (i.e., territory of the Pereyaslavl). After the Tatar–Mongol invasion these territories become an object of expansion of the Polish kingdom and the Lithuanian princedom. For example, in the first half of 14th century Kiev, the Dniepr region, also the region between the rivers Pripyat and West Dvina were captured by Lithuania, and in 1352 the Halych-Volhynia princedom was divided by Poland and Lithuania. In 1569, according to the Lublin Union, the majority of the Ruthenian territories possessed by Lithuania, passed to the Polish crown. The serfdom and Catholicism extended in these territories. The local aristocracy was incorporated into the Polish aristocracy. Cultural, language and religious break between the supreme and lowest layers of a society arose.
The combination of social, language, religious and cultural oppressions had led to destructive popular uprisings of the middle of 17th century, which the Polish–Lithuanian state could not recover from.[1] In many territories incorporated into the Russian Empire in 1772–1795 after the partitions, the domination of the Polish aristocracy was kept, in the territories incorporated into the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the domination of the Polish aristocracy has been added with active planting of German language and culture. During the First World War Austro-Hungarian authorities undertook reprisals against Russia-oriented people of the Eastern Galicia and the Polish left-nationalist movement led by Piłsudski got the support of the Central Powers for struggle against Russia. In the consequence of the revolution in Russia and the fall of Hohenzollern and Habsburg empires in the end of World War I Poland regained independence. The Polish leaders decided to retrieve as many of the territories that were parts of the Polish–Lithuanian state in 1772 as possible.
The situation
[edit]In the aftermath of World War I, the map of Central and Eastern Europe had drastically changed.[2] The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (March 3, 1918), by which Russia had lost to Imperial Germany all the European lands that Russia had seized in the previous two centuries, was rejected by the Bolshevik government in November 1918, following armistice, the surrender of Germany and her allies, and the end of World War I.
Germany, however, had not been keen to see Russia grow strong again and—exploiting her control of those territories, had quickly granted limited independence as buffer states to Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus and Ukraine. As Germany's defeat rendered her plans for the creation of those Mitteleuropa puppet states obsolete, and as Russia sank into the depths of the Russian Civil War, the newly emergent countries saw a chance for real independence and were not prepared to easily relinquish this rare gift of fate. At the same time, Russia saw these territories as rebellious Russian provinces but was unable to react swiftly, as it was weakened and in the process of transforming herself into the Soviet Union through the Russian Revolution and Russian Civil War that had begun in 1917.
With the success of the Greater Poland uprising in 1918, Poland had re-established its statehood for the first time since the 1795 partition and seen the end of a 123 years of rule by three imperial neighbors: Russia, Germany, and Austria-Hungary. The country, reborn as a Second Polish Republic, proceeded to carve out its borders from the territories of its former partitioners. The Western Powers, in delineating the new European borders after the Treaty of Versailles, had done so in a way unfavorable to Poland. Her western borders cut her off from the coal-basin and industrial regions of Silesia, leading to the Silesian Uprisings of 1919–1921. The eastern Curzon line left millions of Poles, living east of the Bug River, stranded inside Russia's borders.

Poland was not alone in its newfound opportunities and troubles. Most if not all of the newly independent neighbours began fighting over borders: Romania fought with Hungary over Transylvania, Yugoslavia with Italy over Rijeka, Poland with Czechoslovakia over Cieszyn Silesia, with Germany over Poznań and with Ukrainians over Eastern Galicia (Galician War). Ukrainians, Belarusians, Lithuanians, Estonians and Latvians fought against themselves and against the Russians, who were just as divided.[3]
Spreading communist influences resulted in communist revolutions in Munich, Berlin, Budapest and Prešov. Winston Churchill commented: "The war of giants has ended, the wars of the pygmies begin."[4] All of those engagements – with the sole exception of the Polish-Soviet war – would be short-lived border conflicts.
The Polish–Soviet war likely happened more by accident than design, as it is unlikely that anyone in Soviet Russia or in the new Second Republic of Poland would have deliberately planned a major foreign war.[5][6]
Poland, its territory a major frontline of the First World War, was unstable politically; it had just won the difficult conflict with the West Ukrainian National Republic and was already engaged in new conflicts with Germany (the Silesian Uprisings) and with Czechoslovakia. Polish government was just beginning to organise and had little if any control over various border areas. Six currencies affected by various (and rising rapidly) inflation rates were in circulation. Economy was in shambles, some areas were experiencing food shortages, crime was high and a threat of an armed coup d'etat by some factions was serious.
The situation in Russia was similar. The attention of revolutionary Russia, meanwhile, was predominantly directed at thwarting counter-revolution and intervention by the western powers. Bolshevik Russia had barely survived its second winter of blockade and resulting mass starvation and was in the middle of a bloody civil war. Lenin controlled only a part of central Russia, and the Bolsheviks were surrounded by powerful enemies who needed to be defeated before any thought could be given to advance beyond the unclear Soviet borders. No matter their intent, Lenin and other communist leaders were simply incapable of moving beyond those borders. While the first clashes between Polish and Soviet forces occurred in February 1919, it would be almost a year before both sides realised that they were engaged in a full war.[5]
Piłsudski's motives
[edit]
Polish politics were under the strong influence of statesman and Marshal Józef Piłsudski, who envisioned a Polish-led federation (the "Federation of Międzymorze", aka Intermarium) comprising Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Ukraine, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, and other Central and East European countries now re-emerging out of the crumbling empires after the First World War. The new union would have had borders similar to those of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 15th–18th centuries, and it was to be a counterweight to, and restraint upon, any imperialist intentions of Russia and/or Germany. To this end, Polish forces set out to secure vast territories in the east. However Piłsudski's federation plan was opposed by another influential Polish politician, Roman Dmowski, who favoured creating a larger, national Polish state.
Poland had never any intention of joining the Western intervention in the Russian Civil War or conquering Russia, as it has done once in the 17th century during the Dimitriads. On the contrary, after the White Russians refused to recognise Polish independence, Polish forces acting on orders from Piłsudski delayed or stopped their offensives several times, relieving pressure from Bolshevik forces and thus substantially contributing to White Russian defeat.[citation needed]
Lenin's motives
[edit]
In April 1920, when the Red Army's major push towards Polish hinterlands took place, the soldiers and commanders were told that defeat of Poland was not only necessary but simply sufficient for the "oppressed masses of the proletariat" to rise worldwide and create a "workers' paradise." In the words of General Tukhachevski: "To the West! Over the corpse of White Poland lies the road to world-wide conflagration. March on Vilno, Minsk, Warsaw!".[7]
In late 1919 the leader of Russia's new communist government, Vladimir Lenin, was inspired by the Red Army's civil-war victories over White Russian anti-communist forces and their western allies, and began to see the future of the revolution with greater optimism. The Bolsheviks doctrine said that historical processes would lead to proletariat victory worldwide, and that the nation states would be replaced by a worldwide communist community. War with Poland was needed if the communist revolution in Russia was to be linked with the expected revolutions in the West, such as the one in Germany. Early Bolshevik ideology made it clear that Poland, which was located in between Russia and Germany, had to become the bridge that the Red Army would have to cross to fulfill the Marxist doctrine. It was not, however, until the Soviet successes in mid-1920 that this idea became for a short time dominant in Bolshevik policies.
Germany in 1918-1920 was a nation torn by social discontent and embroiled in political chaos. Since the Kaiser's abdication at the end of the First World War, it had seen a series of major internal disturbances, including government takeovers, several general strikes, some leading to communist revolutions (e.g. the Bavarian Soviet Republic), By July 1920, which is when the Soviets were on the verge of taking Warsaw, the Weimar Constitution was still brand new and the humiliating Peace of Versailles, even more so. Germany unstable government had to deal with separatist tendencies, an ongoing conflict, not far from a civil war between the Spartacist League's and Communist Party of Germany and the right-wing Freikorps, all under the watchful and humiliating eyes of the Allied powers. Red Army's remaking of the Versailles system was seen as a major force that could shake the existing system imposed by the victorious western Entente. As Lenin himself remarked, "That was the time when everyone in Germany, including the blackest reactionaries and monarchists, declared that the Bolsheviks would be their salvation."
In April 1920 Lenin would complete writing The Infantile Disease of "Leftism" in Communism, a guide to the final stages of the Revolution. He became overconfident, entertaining the thoughts of a serious war with Poland. According to him and his adherents, the Revolution in Russia was doomed unless it was to become worldwide. The debate in Russia was "not as to whether the Polish bridge should be crossed, but how and when." According to Lenin's doctrine of "revolution from outside" Red Army's advance into Poland would be an opportunity "to probe Europe with the bayonets of the Red Army", the first attempt to export the Bolshevik Revolution by any means necessary. In a telegram, Lenin wrote: "We must direct all our attention to preparing and strengthening the Western Front. A new slogan must be announced: Prepare for war against Poland."[8]
References
[edit]- ^ Sergey Solovyov, "History of Russia from the Earliest Times", vol.3–5, ISBN 5-17-002142-9
- ^ Thomas Grant Fraser, Seamus Dunn, Otto von Habsburg, Europe and Ethnicity: the First World War and contemporary ethnic conflict, Routledge, 1996, ISBN 0-415-11995-2, Google Print, p.2
- ^ Davies, Norman, White Eagle, Red Star: the Polish-Soviet War, 1919–20, Pimlico, 2003, ISBN 0-7126-0694-7. (First edition: New York, St. Martin's Press, inc., 1972.) Page 21.
- ^ Adrian Hyde-Price, Germany and European Order, Manchester University Press, 2001, ISBN 0-7190-5428-1 Google Print, p.75
- ^ a b Davies, Norman, White Eagle, Red Star: the Polish-Soviet War, 1919–20, Pimlico, 2003, ISBN 0-7126-0694-7. (First edition: New York, St. Martin's Press, inc., 1972.) Page 22
- ^ Norman Davies, God's Playground. Vol. 2: 1795 to the Present. Columbia University Press, 2005 [1982]. ISBN 0-231-12819-3. Google Print, p.292
- ^ Mikhail Tukhachevski, order of the day, July 2, 1920.
- ^ Lincoln, Red Victory: a History of the Russian Civil War.



