Glockengasse Synagogue: Difference between revisions
cat |
→Gallery: one more image |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 22 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Destroyed synagogue in Cologne, Germany}} |
|||
{| align="right" |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=June 2024}} |
|||
|[[Image:Synagoge Glockengasse Innenraum.jpg|thumb|interior, [[chromolithography]] by J. Hoegg after an aquarel by [[Carl Emanuel Conrad]], ca. 1861.]] |
|||
{{Infobox religious building |
|||
|- |
|||
| name = Glockengasse Synagogue |
|||
| |
|||
| native_name = |
|||
|} |
|||
| native_name_lang = |
|||
| image = Synagoge Glockengasse Innenraum.jpg |
|||
| image_upright = 1.4 |
|||
| alt = |
|||
| caption = Interior, [[chromolithography]] by J. Hoegg after a watercolor by [[Carl Emanuel Conrad]], {{circa|1861}} |
|||
| religious_affiliation = [[Judaism]] {{small|(former)}} |
|||
| tradition = |
|||
| sect = |
|||
| district = |
|||
| prefecture = |
|||
| province = |
|||
| region = |
|||
| deity = |
|||
| rite = |
|||
| festival = <!-- or |festivals= --> |
|||
| organisational_status = {{nowrap|[[Synagogue]] {{small|(1861–1938)}}}}<!-- or |organizational_status= --> |
|||
| ownership = |
|||
| governing_body = |
|||
| leadership = |
|||
| bhattaraka = |
|||
| patron = |
|||
| consecration_year = |
|||
| functional_status = '''Destroyed''' |
|||
| religious_features_label = |
|||
| religious_features = |
|||
| location = |
|||
| locale = [[Cologne]], [[North Rhine-Westphalia]] |
|||
| municipality = |
|||
| cercle = |
|||
| state = |
|||
| country = [[Germany]] |
|||
| map_type = Germany North Rhine-Westphalia |
|||
| map_size = 250 |
|||
| map_alt = |
|||
| map_relief = 1 |
|||
| map_caption = Location of the destroyed synagogue<br/>in [[North Rhine-Westphalia]] |
|||
| grid_name = |
|||
| grid_position = |
|||
| sector = |
|||
| territory = |
|||
| administration = |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|50|56|17|N|6|57|05|E|region:DE-NW_type:landmark_source:dewiki|display=it}} |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
|||
| heritage_designation = |
|||
| architect = [[Ernst Friedrich Zwirner]] |
|||
| architecture_type = {{nowrap|[[Synagogue architecture]]}} |
|||
| architecture_style = [[Moorish Revival architecture|Moorish Revival]] |
|||
| founded_by = |
|||
| creator = |
|||
| funded_by = {{ubl|[[Abraham Oppenheim]]|{{nowrap|{{Interlanguage link multi|Albert von Oppenheim|de|3=Albert von Oppenheim}}}}}} |
|||
| general_contractor = |
|||
| established = |
|||
| groundbreaking = |
|||
| year_completed = |
|||
| construction_cost = |
|||
| date_destroyed = November 9, 1938<br/>{{small|(on ''[[Kristallnacht]]'')}} |
|||
| facade_direction = |
|||
| capacity = |
|||
| length = |
|||
| width = |
|||
| width_nave = |
|||
| interior_area = |
|||
| height_max = |
|||
| dome_quantity = One central; four smaller |
|||
| dome_height_outer = {{cvt|40|m}} |
|||
| dome_height_inner = |
|||
| dome_dia_outer = {{cvt|10|m}} |
|||
| dome_dia_inner = |
|||
| minaret_quantity = |
|||
| minaret_height = |
|||
| spire_quantity = |
|||
| spire_height = |
|||
| site_area = |
|||
| temple_quantity = |
|||
| monument_quantity = |
|||
| shrine_quantity = |
|||
| inscriptions = |
|||
| materials = |
|||
| elevation_m = <!-- or |elevation_ft= --> |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
| nrhp = |
|||
| designated = |
|||
| added = |
|||
| refnum = |
|||
| delisted1_date = |
|||
| website = |
|||
| module = <!-- for embedding other infobox templates --> |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''Synagogue in Glockengasse ''' was a [[Judaism|Jewish]] [[synagogue]], that was located in [[Cologne]], in the state of [[North Rhine-Westphalia]], [[Germany]]. Designed by [[Ernst Friedrich Zwirner]] in the [[Moorish Revival architecture|Moorish Revival]] style, the synagogue was completed in 1861 and destroyed by [[Nazi Germany|Nazis]] on November 9, 1938, during ''[[Kristallnacht]]''. |
|||
== Overview == |
|||
The '''Synagogue in Glockengasse ''' was a synagogue in [[Cologne]] that was built according to the plans of the architect of the [[Cologne Cathedral]], [[Ernst Friedrich Zwirner]]. It was built in the area of the previous Monastery of St. Clarissa, where a modest hall of prayer had been erected in the years of the French occupation and had been closed in 1853 because it was unsafe.<ref>Kober, Cologne, p.240</ref> |
|||
Zwirner, the architect of the [[Cologne Cathedral]], built the synagogue on the site of the former Monastery of St. Clarissa, where a modest hall of prayer had been erected in the years of the [[French period|French occupation]] and was closed in 1853 because it was unsafe.<ref name=Kober>{{cite web |url=http://www.msacerdoti.it/kobercologne.html |author=Kober, Adolf |title=Cologne |publisher=The Jewish Publication Society of America |location=Philadelphia |year=1940 |isbn= }}</ref>{{rp|240}} |
|||
On June 10, 1856, after much discussion in the Jewish communal executive board whether it was better to build a synagogue in the same or a different spot, [[Abraham Oppenheim]], son of [[Salomon Oppenheim, Jr.]], announced his readiness to erect |
On June 10, 1856, after much discussion in the Jewish communal executive board about whether it was better to build a synagogue in the same or a different spot, [[Abraham Oppenheim]], son of [[Salomon Oppenheim, Jr.]], announced his readiness to erect a synagogue worthy of the Glockengasse at his own cost as a gift to the community. Drucker-Emden, a member of the Jewish communal administration, supported the decision. |
||
The cornerstone |
The cornerstone was laid on June 23, 1857.<ref name=Künzl>{{cite book |author=Künzl, Hannelore |title=Islamische Stilelemente im Synagogenbau des 19, und frühen 20, Jahrhunderts |publisher=Lang, Frankfurt am Main u. a. |lang=de |year=1984 |isbn=3-8204-8034-X |postscript=. (Judentum und Umwelt, 9). |chapter=Zur Kölner Synagoge in der Glockengasse }}</ref>{{rp|284}} On August 29, 1861, there was a procession from the provisional synagogue on St. Apernstrasse along Breitestrasse and Kolumbastrasse to the new synagogue. The synagogue was dedicated to Rabbi Israel Schwarz. A memorial tablet dedicated to the donor was placed inside and a medal of silver and bronze was struck.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.historicalartmedals.com/MEDAL%20WEB%20ENTRIES/BELGIUM-EUROPEAN%20CATHEDRALS/WIENER-SYNAGOGUE%20AT%20COLOGNE-BW656.htm |title=WEISS COLLECTION |website=www.historicalartmedals.com |access-date=2018-02-16}}</ref> |
||
In June 1867 |
In June 1867, fire damaged the building.<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|285}} In the same year {{Interlanguage link multi|Albert von Oppenheim{{!}}Albert|de|3=Albert von Oppenheim}}, the son of {{Interlanguage link multi|Simon Oppenheim|de|3=Simon Oppenheim}}, Abraham’s brother, and his wife sold a piece of land on the south side of the synagogue and a strip on the east to the Jewish community, making it possible to enlarge the synagogue, erect a smaller synagogue for week-day services, and leave room for a court.<ref name=Kober/>{{rp|242–243}} |
||
The fiftieth anniversary of the synagogue was celebrated in 1911. During World War I the large cupola, as well as the smaller ones, were |
The fiftieth anniversary of the synagogue was celebrated in 1911. During World War I, the large cupola, as well as the smaller ones, were stripped of their original copper covering. The cupolas had been regarded as among the most beautiful in Cologne because of the [[patina]]ted copper. In consequence of the removal, the four towers on the outside pillars were dismantled and only restored in 1925, while the replacement of the copper covering was postponed for financial reasons.<ref name=Kober/>{{rp|243}} |
||
The synagogue was destroyed during the [[Kristallnacht]] on November 9, 1938 together with the other synagogues in Cologne.<ref> |
The synagogue was destroyed during the ''[[Kristallnacht]]'' on November 9, 1938 together with the other synagogues in Cologne.<ref>{{cite web |title=Photo |url=http://www.msacerdoti.it/coloniasinagoga.jpg |work=msacerdoti.it |date= |access-date= }}</ref> The modernist [[Cologne Opera]] House now occupies the site. A bronze plaque on its façade on Offenbachplatz commemorates the synagogue. |
||
The synagogue has been recreated in virtual form |
The synagogue has been recreated in virtual form.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.marquis-kyle.com.au/sp/000404.htm |title=Virtual German synagogues: Special places |author=Marquis-Kyle, Peter |website=www.marquis-kyle.com.au |date= |access-date=2018-02-16}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www2.kah-bonn.de/ausstellungen/synagogen/0e.htm |title=Art and Exhibition Hall: Exhibitions: Synagogues in Germany: A Virtual Reconstruction |work=KAH Bonn |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081206010422/http://www2.kah-bonn.de/ausstellungen/synagogen/0e.htm |archive-date=2008-12-06 |date= |access-date= }}</ref> |
||
== Architecture == |
== Architecture == |
||
=== Floor plan === |
=== Floor plan === |
||
It was the first example of a central plan over a [[Cross|Greek cross]] covered by a [[dome]].<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|284}} The four arms of the cross had the same length, as in [[Byzantine architecture]] buildings. Through the association of a cross form with a square room emerged on the corners. The rooms on the side of the [[façade]] hold the staircases to the ladies gallery.<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|287}} |
|||
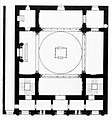
[[Image:Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Grundriss.jpg|thumb|links|Floor plan of the Cologne Synagogue in the Glockengasse]] |
|||
[[Image:Cologne Synagogue-Glockengasse-Altes Bild1.jpg|thumb|links|Cologne Synagogue in the Glockengasse during the 1860s]] |
|||
It was the first example of a central plan over a [[Cross|Greek cross]], that was covered by a [[dome]].<ref name="K284"/> The four arms of the cross had the same length, as in [[Byzantine architecture]] buildings.<ref name="K287">Künzl, p. 287</ref> Through the association of a cross form with a square room emerged on the corners. .<ref name="K287"/> The rooms on the side of the façade hold the staircases to the ladies gallery.<ref name="K287"/> |
|||
The dome was inscribed in the central square, |
The dome was inscribed in the central square, in the middle of which stood the [[Bema#Judaism|bimah]].<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|285}} The central position of the bimah shows that the Jewish community was attached to the old tradition, while the [[Roonstrasse Synagogue]] had a new floor plan, that was developed according to the [[Reform Judaism]] beliefs.<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|287}} |
||
The central position of the bimah shows that the Jewish community was attached to the old tradition, while the [[Roonstrasse Synagogue]] had a new floor plan, that was developed according to the [[Reform Judaism]] beliefs.<ref name="K287"/> |
|||
A low wing of the entrance hall was built with five rooms in front of the square building |
A low wing of the entrance hall was built with five rooms in front of the square building structure on the street side. The five rooms served as entrance to the staircases to the ladies gallery, as entrance for the men to the main synagogue and a space for the synagogue attendants (Shammes). |
||
=== External architecture=== |
=== External architecture === |
||
A tall protruding |
A tall, protruding [[risalit]] was flanked on both sides by wings and was terminated on top by a [[merlon]] rim. Zwirner designed four small, [[minaret]]-shaped towers with small cupolas on top of the [[cornice]]s, in contrast to the [[Leopoldstädter Tempel]] in [[Vienna]], in which the towers were crowned by columns.<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|288}} |
||
The [[rose window]] |
The [[rose window]] in the facade was a [[Gothic Revival architecture|neo-Gothic]] feature.<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|289}} Over the [[crossing (architecture)|crossing]] there was a [[dome]] with windows all around. At the top was a lantern and an onion cupola. The cupola measured {{convert|40|m|ft|abbr=off}} in height and {{convert|10|m|ft|abbr=on}} in diameter. |
||
The cupola measured forty meters in height and ten meters in diameter. |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Image:Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Bauzeichnung.jpg|Cologne Synagogue in the Glockengasse |
|||
Image:Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Querschnitt.jpg|Section of the Cologne Synagogue in the Glockengasse |
|||
Image:Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Toraschrein-Aaron haKodesch.jpg|Aaron haKodesch of the Synagogue in the Glockengasse |
|||
Image:Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Toraschrein-Aaron haKodesch.jpg|Aaron haKodesch of the Synagogue in the Glockengasse |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
=== Internal architecture === |
=== Internal architecture === |
||
The synagogue was, as already mentioned, |
The synagogue was, as already mentioned, a central building over a Greek cross, with a dome on top.<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|284}} The four Byzantine cross arms of the same length of the synagogue were all equipped with a barrel vault,<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|290}} in which the truss, the columns and the arches were made of cast iron. Except for the Eastern arm the other three arms were equipped with two floors of ladies galleries,<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|290}} while the [[Torah ark]] was placed on the eastern arm, where the wall was decorated with [[stucco]] by Josef Hartzheim with [[rhombus]] and with a theme of intricate quadrangles and painted by Friedrich Petri of [[Gießen]] in blue, red and gold. The stucco work was related to the ones in [[Alhambra]].<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|291}} |
||
The ladies galleries were supported by six columns, that owing to the iron construction had a very fine and graceful form,<ref name= |
The ladies galleries were supported by six columns, that owing to the iron construction had a very fine and graceful form,<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|290}} while the balustrade was decorated with stucco by Hartzheim and painted in gold by Petri. The four large arches, that supported the dome, were decorated by Hartzheim and painted by Petri in the same way as the eastern wall. The dome and the barrel vaults were the only structures that were not covered by stucco. They were painted by Petri in blue and decorated with golden stars. |
||
The four large arches, that supported the dome, were decorated by Hartzheim and painted by Petri in the same way as the eastern wall. |
|||
The dome and the barrel vaults were the only structures that were not covered by stucco. They were painted by Petri in blue and decorated with golden stars. |
|||
"The windows were for the most part round, though some had the shape of a trefoil leaf. Through their colored glass a subdued light fell into the room and upon the richly decorated walls and pillars."<ref name=Kober/>{{rp|242}} |
|||
The Aaron haKodesch had been made by the Cologne sculptor Stephan, he used [[Carrara]] |
The Aaron haKodesch had been made by the Cologne sculptor Stephan, he used [[Carrara]] white marble and placed in the middle of the shrine a horse shoe [[arch]].<ref name=Künzl/>{{rp|291}} Furthermore, Stephan inserted the capitals from Alhambra and the minaret tower composition with onion cupolas from the façade around the Aaron haKodesch. The water basin of the [[mikveh]] in the basement was also made by Stephan, and the same marble was used as for the Torah Ark. |
||
The [[bimah]] in the middle of the synagogue room was somewhat higher than usual and stood directly under the cupola. It was surrounded by a parapet of rich woodwork.<ref |
The [[Bema|bimah]] in the middle of the synagogue room was somewhat higher than usual and stood directly under the cupola. It was surrounded by a parapet of rich woodwork.<ref name=Kober/>{{rp|242}} |
||
== Gallery == |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Erinnerungstafel Synagoge.jpg|Plaque commemorating the synagogue |
|||
Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Grundriss.jpg|Floor plan of the synagogue |
|||
Cologne Synagogue-Glockengasse-Altes Bild1.jpg|The synagogue during the 1860s |
|||
Köln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Bauzeichnung.jpg|Glockengasse Synagogue |
|||
Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Querschnitt.jpg|[[Multiview projection#Section|Section]] |
|||
Koln-Synagoge-Glockengasse-Toraschrein-Aaron haKodesch.jpg|[[Torah ark]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
{{stack|{{portal|Germany|Judaism}}}} |
|||
* [[History of the Jews in Cologne]] |
* [[History of the Jews in Cologne]] |
||
* [[:de:Liste der Synagogen in Deutschland|List of synagogues in Germany]] {{in lang|de}} |
|||
== Sources == |
|||
* [http://www.msacerdoti.it/kobercologne.html Adolf Kober, ''Cologne'', The Jewish Publication Society of America, Philadelphia, 1940] |
|||
* Hannelore Künzl: ''Islamische Stilelemente im Synagogenbau des 19. und frühen 20. Jahrhunderts.'' Lang, Frankfurt am Main u. a. 1984, ISBN 3-8204-8034-X. (Judentum und Umwelt, 9).<br />Zur Kölner Synagoge in der Glockengasse p. 123, 156, 186, 265, 283, 284, 296, 297, 298, 302, 303, 311, 312, 324, 348, 350, 365, 385, 397, 498. |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{commons category|Synagoge Glockengasse}} |
|||
{{reflist|colwidth=35em}} |
|||
{{coord|50|56|17.09|N|6|57|04.52|E|region:DE-NW_type:landmark_source:dewiki|display=title}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{commons cat-inline|Synagoge Glockengasse (Köln)}} |
|||
{{Synagogues in Germany}} |
|||
[[Category:1861 establishments in Prussia]] |
|||
[[Category:19th-century synagogues in Germany]] |
|||
[[Category:Moorish Revival synagogues]] |
[[Category:Moorish Revival synagogues]] |
||
[[Category:Moorish Revival architecture in Germany]] |
[[Category:Moorish Revival architecture in Germany]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Synagogue buildings with domes]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Synagogues completed in 1861]] |
||
[[Category:Synagogues destroyed during Kristallnacht (Germany)]] |
[[Category:Synagogues destroyed during Kristallnacht (Germany)]] |
||
[[Category:Synagogues in |
[[Category:Synagogues in Cologne]] |
||
[[Category:1861 establishments in Prussia]] |
|||
[[Category:Places of worship in Cologne]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 11:44, 23 June 2024
| Glockengasse Synagogue | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Religion | |
| Affiliation | Judaism (former) |
| Ecclesiastical or organisational status | Synagogue (1861–1938) |
| Status | Destroyed |
| Location | |
| Location | Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Country | Germany |
Location of the destroyed synagogue in North Rhine-Westphalia | |
| Geographic coordinates | 50°56′17″N 6°57′05″E / 50.93806°N 6.95139°E |
| Architecture | |
| Architect(s) | Ernst Friedrich Zwirner |
| Type | Synagogue architecture |
| Style | Moorish Revival |
| Funded by | |
| Destroyed | November 9, 1938 (on Kristallnacht) |
| Specifications | |
| Dome(s) | One central; four smaller |
| Dome height (outer) | 40 m (130 ft) |
| Dome dia. (outer) | 10 m (33 ft) |
The Synagogue in Glockengasse was a Jewish synagogue, that was located in Cologne, in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. Designed by Ernst Friedrich Zwirner in the Moorish Revival style, the synagogue was completed in 1861 and destroyed by Nazis on November 9, 1938, during Kristallnacht.
Overview
[edit]Zwirner, the architect of the Cologne Cathedral, built the synagogue on the site of the former Monastery of St. Clarissa, where a modest hall of prayer had been erected in the years of the French occupation and was closed in 1853 because it was unsafe.[1]: 240
On June 10, 1856, after much discussion in the Jewish communal executive board about whether it was better to build a synagogue in the same or a different spot, Abraham Oppenheim, son of Salomon Oppenheim, Jr., announced his readiness to erect a synagogue worthy of the Glockengasse at his own cost as a gift to the community. Drucker-Emden, a member of the Jewish communal administration, supported the decision.
The cornerstone was laid on June 23, 1857.[2]: 284 On August 29, 1861, there was a procession from the provisional synagogue on St. Apernstrasse along Breitestrasse and Kolumbastrasse to the new synagogue. The synagogue was dedicated to Rabbi Israel Schwarz. A memorial tablet dedicated to the donor was placed inside and a medal of silver and bronze was struck.[3]
In June 1867, fire damaged the building.[2]: 285 In the same year Albert, the son of Simon Oppenheim, Abraham’s brother, and his wife sold a piece of land on the south side of the synagogue and a strip on the east to the Jewish community, making it possible to enlarge the synagogue, erect a smaller synagogue for week-day services, and leave room for a court.[1]: 242–243
The fiftieth anniversary of the synagogue was celebrated in 1911. During World War I, the large cupola, as well as the smaller ones, were stripped of their original copper covering. The cupolas had been regarded as among the most beautiful in Cologne because of the patinated copper. In consequence of the removal, the four towers on the outside pillars were dismantled and only restored in 1925, while the replacement of the copper covering was postponed for financial reasons.[1]: 243
The synagogue was destroyed during the Kristallnacht on November 9, 1938 together with the other synagogues in Cologne.[4] The modernist Cologne Opera House now occupies the site. A bronze plaque on its façade on Offenbachplatz commemorates the synagogue.
The synagogue has been recreated in virtual form.[5][6]
Architecture
[edit]Floor plan
[edit]It was the first example of a central plan over a Greek cross covered by a dome.[2]: 284 The four arms of the cross had the same length, as in Byzantine architecture buildings. Through the association of a cross form with a square room emerged on the corners. The rooms on the side of the façade hold the staircases to the ladies gallery.[2]: 287
The dome was inscribed in the central square, in the middle of which stood the bimah.[2]: 285 The central position of the bimah shows that the Jewish community was attached to the old tradition, while the Roonstrasse Synagogue had a new floor plan, that was developed according to the Reform Judaism beliefs.[2]: 287
A low wing of the entrance hall was built with five rooms in front of the square building structure on the street side. The five rooms served as entrance to the staircases to the ladies gallery, as entrance for the men to the main synagogue and a space for the synagogue attendants (Shammes).
External architecture
[edit]A tall, protruding risalit was flanked on both sides by wings and was terminated on top by a merlon rim. Zwirner designed four small, minaret-shaped towers with small cupolas on top of the cornices, in contrast to the Leopoldstädter Tempel in Vienna, in which the towers were crowned by columns.[2]: 288
The rose window in the facade was a neo-Gothic feature.[2]: 289 Over the crossing there was a dome with windows all around. At the top was a lantern and an onion cupola. The cupola measured 40 metres (130 feet) in height and 10 m (33 ft) in diameter.
Internal architecture
[edit]The synagogue was, as already mentioned, a central building over a Greek cross, with a dome on top.[2]: 284 The four Byzantine cross arms of the same length of the synagogue were all equipped with a barrel vault,[2]: 290 in which the truss, the columns and the arches were made of cast iron. Except for the Eastern arm the other three arms were equipped with two floors of ladies galleries,[2]: 290 while the Torah ark was placed on the eastern arm, where the wall was decorated with stucco by Josef Hartzheim with rhombus and with a theme of intricate quadrangles and painted by Friedrich Petri of Gießen in blue, red and gold. The stucco work was related to the ones in Alhambra.[2]: 291
The ladies galleries were supported by six columns, that owing to the iron construction had a very fine and graceful form,[2]: 290 while the balustrade was decorated with stucco by Hartzheim and painted in gold by Petri. The four large arches, that supported the dome, were decorated by Hartzheim and painted by Petri in the same way as the eastern wall. The dome and the barrel vaults were the only structures that were not covered by stucco. They were painted by Petri in blue and decorated with golden stars.
"The windows were for the most part round, though some had the shape of a trefoil leaf. Through their colored glass a subdued light fell into the room and upon the richly decorated walls and pillars."[1]: 242
The Aaron haKodesch had been made by the Cologne sculptor Stephan, he used Carrara white marble and placed in the middle of the shrine a horse shoe arch.[2]: 291 Furthermore, Stephan inserted the capitals from Alhambra and the minaret tower composition with onion cupolas from the façade around the Aaron haKodesch. The water basin of the mikveh in the basement was also made by Stephan, and the same marble was used as for the Torah Ark.
The bimah in the middle of the synagogue room was somewhat higher than usual and stood directly under the cupola. It was surrounded by a parapet of rich woodwork.[1]: 242
Gallery
[edit]-
Plaque commemorating the synagogue
-
Floor plan of the synagogue
-
The synagogue during the 1860s
-
Glockengasse Synagogue
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e Kober, Adolf (1940). "Cologne". Philadelphia: The Jewish Publication Society of America.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Künzl, Hannelore (1984). "Zur Kölner Synagoge in der Glockengasse". Islamische Stilelemente im Synagogenbau des 19, und frühen 20, Jahrhunderts (in German). Lang, Frankfurt am Main u. a. ISBN 3-8204-8034-X. (Judentum und Umwelt, 9).
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "WEISS COLLECTION". www.historicalartmedals.com. Retrieved February 16, 2018.
- ^ "Photo". msacerdoti.it.
- ^ Marquis-Kyle, Peter. "Virtual German synagogues: Special places". www.marquis-kyle.com.au. Retrieved February 16, 2018.
- ^ "Art and Exhibition Hall: Exhibitions: Synagogues in Germany: A Virtual Reconstruction". KAH Bonn. Archived from the original on December 6, 2008.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Synagoge Glockengasse (Köln) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Synagoge Glockengasse (Köln) at Wikimedia Commons