Religion in Suriname: Difference between revisions
Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
m fixed lint errors – missing end tag |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 19 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|none}} |
|||
{{Religion by Country}} |
{{Religion by Country}} |
||
{{Pie chart |
{{Pie chart |
||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
| value1 = 25.6 |
| value1 = 25.6 |
||
| color1 = Blue |
| color1 = Blue |
||
| label2 = [[ |
| label2 = [[Catholic Church]] |
||
| value2 = 21.6 |
| value2 = 21.6 |
||
| color2 = Purple |
| color2 = Purple |
||
| Line 34: | Line 35: | ||
| color10 = Black |
| color10 = Black |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Culture of Suriname}}'''[[Religion]] in [[Suriname]]''' is |
{{Culture of Suriname}}'''[[Religion]] in [[Suriname]]''' is characterized by a range of religious beliefs and practices due to its [[ethnic groups in Suriname|ethnic diversity]]. The government is vocally supportive of religious diversity and tolerance, and these attitudes are present in general society as well. According to the most recent census (2012), 48.4 percent of the population is [[Christianity|Christian]] (the largest groups being [[Pentecostalism]], the [[Moravian Church]], and the [[Catholic Church]]), 22.3 percent is [[Hindu]], 13.9 percent is [[Muslim]], 1.8 percent follows [[Winti]], and 0.8 percent is [[Javanism]] (mainly adhered to [[Kejawèn|Kejawèn Javanism]]). In addition 2.1 percent of the population follows other faiths (including [[Jehovah's Witnesses]]), 7.5 percent are [[atheist]] or [[agnostic]], and 3.2 percent did not answer the question about their religion.<ref name="CENSUS2012" /> Later estimates suggest that Christians made up just over half the population in 2020.<ref>[https://www.thearda.com/world-religion/national-profiles?REGION=0&u=212c&u=23r World Religions Database at the ARDA website, retrieved 2023-08-08]</ref> |
||
[[Indigenous religions]] are practiced by the Amerindian and Afro-descendant Maroon populations. [[Amerindian]]s, found principally in the interior and to a lesser extent in coastal areas, practice [[shamanism]], worship of all living things, and their rites are led by [[medicine man|medicine men]], or ''piaiman''. [[Maroon (people)|Maroons]], who inhabit the interior, worship nature through a practice that has no special name, and they also worship their ancestors through a rite called Winti. Citizens of Amerindian and Maroon origin who classify themselves as Christian often simultaneously follow indigenous religious customs, with the acknowledgment of their Christian church leaders. |
[[Indigenous religions]] are practiced by the Amerindian and Afro-descendant Maroon populations. [[Amerindian]]s, found principally in the interior and to a lesser extent in coastal areas, practice [[shamanism]], worship of all living things, and their rites are led by [[medicine man|medicine men]], or ''piaiman''. [[Maroon (people)|Maroons]], who inhabit the interior, worship nature through a practice that has no special name, and they also worship their ancestors through a rite called Winti. Citizens of Amerindian and Maroon origin who classify themselves as Christian often simultaneously follow indigenous religious customs, with the acknowledgment of their Christian church leaders. |
||
The negligible [[Judaism|Jewish]] community numbers 181,<ref name="CENSUS2012"/> and there are also small numbers of [[Baháʼí Faith|Baháʼís]] and [[Buddhism|Buddhists]]. [[The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in the Guianas#Suriname|The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints]] (LDS Church) claimed 1,797 members in six congregations in 2022.<ref>{{citation|url=https://newsroom.churchofjesuschrist.org/facts-and-statistics/country/french-guiana|title=Facts and Statistics: Statistics by Country: Suriname|work=Newsroom|publisher=LDS Church|access-date=15 June 2023}}</ref> Other groups include the [[Ahmadiyya|Ahmadiyya Muslim Community]] and the [[World Islamic Call Society]]. |
The negligible [[Judaism|Jewish]] community numbers 181,<ref name="CENSUS2012"/> and there are also small numbers of [[Baháʼí Faith|Baháʼís]] and [[Buddhism|Buddhists]]. [[The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in the Guianas#Suriname|The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints]] (LDS Church) claimed 1,797 members in six congregations in 2022.<ref>{{citation|url=https://newsroom.churchofjesuschrist.org/facts-and-statistics/country/french-guiana|title=Facts and Statistics: Statistics by Country: Suriname|work=Newsroom|publisher=LDS Church|access-date=15 June 2023}}</ref> Other groups include the [[Ahmadiyya|Ahmadiyya Muslim Community]] and the [[World Islamic Call Society]]. At the start of the 21st century, Guido Robles, a prominent Jewish businessman in Paramaribo, quipped, "No religion in Suriname has any problem with any other religion, all the problems are caused by the politicians."<ref>{{cite news|url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_go2043/is_/ai_n29268997|title=Suriname a culture of tolerance: this thirty-year-old nation is a harmonious home to diverse religious and ethnic groups and the world's largest nature reserve|publisher=Bnet|access-date=2008-10-17 | first=Larry | last=Luxner | year=2006}}</ref> |
||
In 2017, many [[political parties]], including six of the eight governing coalition parties, had strong ethnic ties, and members tended to adhere to or practice one faith. For example, within the governing coalition, the majority of members of the mostly ethnic-[[National Party of Suriname]] (NPS) were Protestant, most members of the mostly ethnic-Indian [[Progressive Reform Party (Suriname)|Progressive Reform Party]] were [[Hindu]], and those of the mostly ethnic-Javanese [[Pertjajah Luhur|Pertjaja Luhur Party]] tended to be Muslim.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/2004/35555.htm | title=Suriname (US State Dept 2017 report)}}</ref> However, parties had no requirement that political party leaders or members adhere to a particular religion. |
|||
==Demography== |
==Demography== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
=== Religion for Suriname in 2004 and 2012 === |
=== Religion for Suriname in 2004 and 2012 === |
||
The religious demography of Suriname as per the 2004 Census is as follows:<ref name="statistics-suriname.org">{{cite web |url=http://www.statistics-suriname.org/publicaties/Census%20profiel%20Website%2016jan07.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=2009-11-13 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511175126/http://www.statistics-suriname.org/publicaties/Census%20profiel%20Website%2016jan07.pdf |archive-date=2011-05-11 }} </ref> |
The religious demography of Suriname as per the 2004 Census is as follows:<ref name="statistics-suriname.org">{{cite web |url=http://www.statistics-suriname.org/publicaties/Census%20profiel%20Website%2016jan07.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=2009-11-13 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110511175126/http://www.statistics-suriname.org/publicaties/Census%20profiel%20Website%2016jan07.pdf |archive-date=2011-05-11 }} </ref> |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
===Religion by province in |
===Religion by province in 2004 === |
||
{|class="wikitable" |
{|class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 165: | Line 165: | ||
|22.9% |
|22.9% |
||
|}[[File:Suriname District Numbers Neutral.png|250px|right|Districts of Suriname]] |
|}[[File:Suriname District Numbers Neutral.png|250px|right|Districts of Suriname]] |
||
===2012 data by denomination=== |
===2012 data by denomination=== |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 200: | Line 201: | ||
|Other forms of [[Islam]]||align=right|39,733||align=right|7.3 |
|Other forms of [[Islam]]||align=right|39,733||align=right|7.3 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Kejawèn|Javanism]]||align=right|4,460||align=right|0.8 |
|[[Kejawèn|Kejawen Javanism]]||align=right|4,460||align=right|0.8 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|[[Judaism]]||align=right|181||align=right|0.0 |
|[[Judaism]]||align=right|181||align=right|0.0 |
||
| Line 213: | Line 214: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|Total population||align=right|541,638||align=right|100.0 |
|Total population||align=right|541,638||align=right|100.0 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|} |
|||
==Christianity== |
==Christianity== |
||
| Line 222: | Line 223: | ||
==Hinduism== |
==Hinduism== |
||
{{main article|Hinduism in Suriname}}The story of Hinduism in Suriname is broadly parallel to that in [[Guyana]]. [[Indian indenture system|Indian indentured labourers]] were sent to colonial [[Dutch colonisation of the Guianas|Dutch Guiana]] by special arrangement between the Dutch and British. |
{{main article|Hinduism in Suriname}}The story of [[Hinduism]] in Suriname is broadly parallel to that in [[Guyana]]. [[Indian indenture system|Indian indentured labourers]] were sent to colonial [[Dutch colonisation of the Guianas|Dutch Guiana]] by special arrangement between the Dutch and British. |
||
The difference is that the Netherlands' more liberal policy toward Hinduism allowed the culture to develop stronger. Examples are the lack of a rigid caste system and the almost universal reading of [[Gita]] and [[Ramayan]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.guyanaundersiege.com/cultural/hindus%20of%20south%20america.htm |title=Hindus of South America |publisher=Guyanaundersiege.com |access-date=2019-06-28}}</ref>[[File:Arya Dewaker, exterior5.jpg|thumb|205x205px|[[Arya Diwaker]], an [[Arya Samaj]] [[Hindu]] [[Hindu temple|Mandir]] in [[Paramaribo]].]]According to the 2012 census of Suriname, Hindus constitute 22.3% of the population.<ref name="CENSUS2012"/> Hindus are mostly concentrated in Northern coastal regions of Suriname: [[Nickerie District|Nickerie]], [[Wanica District|Wanica]] and [[Saramacca District|Saramacca]], where they constitute the largest religious group. There are several |
The difference is that the Netherlands' more liberal policy toward Hinduism allowed the culture to develop stronger. Examples are the lack of a rigid caste system and the almost universal reading of [[Gita]] and [[Ramayan]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.guyanaundersiege.com/cultural/hindus%20of%20south%20america.htm |title=Hindus of South America |publisher=Guyanaundersiege.com |access-date=2019-06-28}}</ref>[[File:Arya Dewaker, exterior5.jpg|thumb|205x205px|[[Arya Diwaker]], an [[Arya Samaj]] [[Hindu]] [[Hindu temple|Mandir]] in [[Paramaribo]].]]According to the 2012 census of Suriname, Hindus constitute 22.3% of the population.<ref name="CENSUS2012"/> Hindus are mostly concentrated in Northern coastal regions of Suriname: [[Nickerie District|Nickerie]], [[Wanica District|Wanica]] and [[Saramacca District|Saramacca]], where they constitute the largest religious group. There are several Hindu temples in Suriname. |
||
==Islam== |
==Islam== |
||
| Line 231: | Line 232: | ||
Muslims that first came to Suriname consisted of indentured laborers from [[South Asia]] and [[Indonesia]], from whom today most Muslims in Suriname are descended. |
Muslims that first came to Suriname consisted of indentured laborers from [[South Asia]] and [[Indonesia]], from whom today most Muslims in Suriname are descended. |
||
== |
==Javanism== |
||
{{main|Javanism in Suriname}} |
|||
Kejawen is followed by 0.8% of the Suriname population. It is followed mainly by the Javanese people in Suriname.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.statistics-suriname.org/images/Presentatie.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=2014-08-03 |archive-date=2015-09-24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924105905/http://www.statistics-suriname.org/images/Presentatie.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url= |
Javanism of Kejawen denomination is followed by 0.8% of the Suriname population. It is followed mainly by the Javanese people in Suriname.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.statistics-suriname.org/images/Presentatie.pdf |title=Archived copy |access-date=2014-08-03 |archive-date=2015-09-24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924105905/http://www.statistics-suriname.org/images/Presentatie.pdf |url-status=dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.angelfire.com/stars3/amatali/ReligionJav.html|title=Religion Javanese people in Suriname|website=[[Angelfire]]}}</ref>[[File:Paramaribo, German Synagogue.JPG|thumb|219x219px|[[Neveh Shalom Synagogue]] in [[Paramaribo]].]] |
||
==Judaism== |
==Judaism== |
||
{{Main article|History of the Jews in Suriname}} |
{{Main article|History of the Jews in Suriname}} |
||
There has been a Jewish community in Suriname since 1639, when the English government allowed [[Sephardi Jews]] to settle the region.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/vjw/Suriname.html|title=Suriname: Virtual Jewish History Tour|publisher=[[Jewish Virtual Library]]|access-date=April 22, 2013}}</ref> |
There has been a Jewish community in Suriname since 1639, when the English government allowed [[Sephardi Jews]] to settle the region.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/vjw/Suriname.html|title=Suriname: Virtual Jewish History Tour|publisher=[[Jewish Virtual Library]]|access-date=April 22, 2013}}</ref> In the last few years, the Jewish community has been struggling due to dwindling funds and membership. |
||
== Religious freedom == |
== Religious freedom == |
||
The [[Constitution of Suriname|constitution]] of Suriname establishes the freedom of religion and outlaws discrimination along religious lines. "Instigating religious hatred" is punishable by fines, and in some cases prison.<ref name=":0">''[https://www.state.gov/reports/ |
The [[Constitution of Suriname|constitution]] of Suriname establishes the freedom of religion and outlaws discrimination along religious lines. "Instigating religious hatred" is punishable by fines, and in some cases prison.<ref name=":0">''[https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/suriname US State Dept 2022 report]''</ref> |
||
Religious groups may register with the government in order to receive financial support. Most groups are registered.<ref name=":0" /> |
Religious groups may register with the government in order to receive financial support. Most groups are registered.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
Religious instruction is not allowed in public schools. Private religious schools are allowed, and comprise roughly half of the primary and secondary schools in Suriname |
Religious instruction is not allowed in public schools. Private religious schools are allowed, and comprise roughly half of the primary and secondary schools in Suriname. Parents are not allowed to homeschool children for religious reasons.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
In 2023, the country was scored 4 out of 4 for religious freedom.<ref>[https://freedomhouse.org/country/suriname/freedom-world/2022 Freedom House website, retrieved 2023-08-08]</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{commons}} |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
Latest revision as of 23:20, 8 July 2024
| Religion by country |
|---|
|
|
Religion in Suriname (2012 census)[1]
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Suriname |
|---|
 |
| Society |
| Topics |
| Symbols |
Religion in Suriname is characterized by a range of religious beliefs and practices due to its ethnic diversity. The government is vocally supportive of religious diversity and tolerance, and these attitudes are present in general society as well. According to the most recent census (2012), 48.4 percent of the population is Christian (the largest groups being Pentecostalism, the Moravian Church, and the Catholic Church), 22.3 percent is Hindu, 13.9 percent is Muslim, 1.8 percent follows Winti, and 0.8 percent is Javanism (mainly adhered to Kejawèn Javanism). In addition 2.1 percent of the population follows other faiths (including Jehovah's Witnesses), 7.5 percent are atheist or agnostic, and 3.2 percent did not answer the question about their religion.[1] Later estimates suggest that Christians made up just over half the population in 2020.[2]
Indigenous religions are practiced by the Amerindian and Afro-descendant Maroon populations. Amerindians, found principally in the interior and to a lesser extent in coastal areas, practice shamanism, worship of all living things, and their rites are led by medicine men, or piaiman. Maroons, who inhabit the interior, worship nature through a practice that has no special name, and they also worship their ancestors through a rite called Winti. Citizens of Amerindian and Maroon origin who classify themselves as Christian often simultaneously follow indigenous religious customs, with the acknowledgment of their Christian church leaders.
The negligible Jewish community numbers 181,[1] and there are also small numbers of Baháʼís and Buddhists. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church) claimed 1,797 members in six congregations in 2022.[3] Other groups include the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community and the World Islamic Call Society. At the start of the 21st century, Guido Robles, a prominent Jewish businessman in Paramaribo, quipped, "No religion in Suriname has any problem with any other religion, all the problems are caused by the politicians."[4]
In 2017, many political parties, including six of the eight governing coalition parties, had strong ethnic ties, and members tended to adhere to or practice one faith. For example, within the governing coalition, the majority of members of the mostly ethnic-National Party of Suriname (NPS) were Protestant, most members of the mostly ethnic-Indian Progressive Reform Party were Hindu, and those of the mostly ethnic-Javanese Pertjaja Luhur Party tended to be Muslim.[5] However, parties had no requirement that political party leaders or members adhere to a particular religion.
Demography
[edit]Religion for Suriname in 2004 and 2012
[edit]The religious demography of Suriname as per the 2004 Census is as follows:[6]
| Religion | 2004[1] | 2012[1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |
| Christianity | 200,744 | 40.7 | 262,320 | 48.4 |
| Hinduism | 98,240 | 19.9 | 120,623 | 22.3 |
| Islam | 66,307 | 13.5 | 75,053 | 13.9 |
| Other or none | 50,334 | 10.2 | 66,560 | 12.3 |
| Religion not stated | 77,204 | 15.7 | 17,082 | 3.2 |
| Total population | 492,829 | 100.0 | 541,638 | 100.0 |
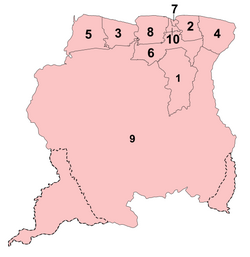
Religion by province in 2004
[edit]| Religion | Suriname | Para- maribo (7) |
Wanica (10) | Nickerie (5) | Coronie (3) | Sara- macca (8) |
Comme- wijne (2) |
Maro- wijne (4) |
Para (6) | Broko- pondo (1) |
Sipali- wini (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Christian | 40.7% | 47.9% | 29.7% | 20.6% | 75.0% | 23.5% | 22.0% | 58.7% | 56.5% | 52.4% | 35.2% |
| Hindu | 19.9% | 13.8% | 39.9% | 43.2% | 2.2% | 44.6% | 24.5% | 0.9% | 4.9% | 0.4% | 0.3% |
| Islam | 13.5% | 9.4% | 21.7% | 22.5% | 11.0% | 18.8% | 40.4% | 6.8% | 11.3% | 0.2% | 0.1% |
| Tribal + Other | 5.8% | 3.8% | 3.4% | 0.7% | 1.6% | 3.0% | 4.2% | 11.5% | 6.8% | 16.8% | 26.8% |
| None | 4.4% | 3.9% | 2.7% | 0.6% | 1.8% | 1.4% | 1.5% | 4.7% | 8.1% | 11.8% | 14.8% |
| Not Known | 15.7% | 21.1% | 2.6% | 12.4% | 8.4% | 8.6% | 7.3% | 17.4% | 12.5% | 18.5% | 22.9% |
2012 data by denomination
[edit]| Denomination | 2012 census[1] | |
|---|---|---|
| Number | % | |
| Catholic Church | 117,261 | 21.6 |
| Pentecostalism (Full Gospel) | 60,530 | 11.18 |
| Moravian Church | 60,420 | 11.16 |
| Jehovah's Witnesses | 6,622 | 1.2 |
| Calvinism | 4,018 | 0.7 |
| Lutheranism | 2,811 | 0.5 |
| Other forms of Christianity | 17,280 | 3.2 |
| Sanatani Hindus | 97,311 | 18 |
| Arya Samaj Hindus | 16,661 | 3.1 |
| Other forms of Hinduism | 6,651 | 1.2 |
| Sunni Islam | 21,159 | 3.9 |
| Ahmadi Islam | 14,161 | 2.6 |
| Other forms of Islam | 39,733 | 7.3 |
| Kejawen Javanism | 4,460 | 0.8 |
| Judaism | 181 | 0.0 |
| Winti | 9,949 | 1.8 |
| Other faith | 4,630 | 0.9 |
| No faith | 40,718 | 7.5 |
| No answer | 17,082 | 3.2 |
| Total population | 541,638 | 100.0 |

Christianity
[edit]
The dominant religion in Suriname is Christianity, both in the form of Roman Catholicism and various denominations of Protestantism, the Anglican Church being the oldest.[7] According to the 2012 census data 48.4% of the population of Suriname is Christian[1] and the Pentecostal churches are the largest Protestant denomination, closely followed by Moravians.[1]
Hinduism
[edit]The story of Hinduism in Suriname is broadly parallel to that in Guyana. Indian indentured labourers were sent to colonial Dutch Guiana by special arrangement between the Dutch and British. The difference is that the Netherlands' more liberal policy toward Hinduism allowed the culture to develop stronger. Examples are the lack of a rigid caste system and the almost universal reading of Gita and Ramayan.[8]

According to the 2012 census of Suriname, Hindus constitute 22.3% of the population.[1] Hindus are mostly concentrated in Northern coastal regions of Suriname: Nickerie, Wanica and Saramacca, where they constitute the largest religious group. There are several Hindu temples in Suriname.
Islam
[edit]
According to the most recent census, the Muslim population of Suriname represents about 13.9%[1] of the country's total population, giving the country the highest proportion of Muslims on the American continent.
Muslims that first came to Suriname consisted of indentured laborers from South Asia and Indonesia, from whom today most Muslims in Suriname are descended.
Javanism
[edit]Javanism of Kejawen denomination is followed by 0.8% of the Suriname population. It is followed mainly by the Javanese people in Suriname.[9][10]

Judaism
[edit]There has been a Jewish community in Suriname since 1639, when the English government allowed Sephardi Jews to settle the region.[11] In the last few years, the Jewish community has been struggling due to dwindling funds and membership.
Religious freedom
[edit]The constitution of Suriname establishes the freedom of religion and outlaws discrimination along religious lines. "Instigating religious hatred" is punishable by fines, and in some cases prison.[12]
Religious groups may register with the government in order to receive financial support. Most groups are registered.[12]
Religious instruction is not allowed in public schools. Private religious schools are allowed, and comprise roughly half of the primary and secondary schools in Suriname. Parents are not allowed to homeschool children for religious reasons.[12]
The government engages in vocal support of religious diversity and tolerance through public statements, attendance at religious events, and hosting events in honor of various religious holidays. The armed forces have chaplains for the Hindu, Muslim, Catholic, and Protestant faiths.[12]
In 2023, the country was scored 4 out of 4 for religious freedom.[13]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j 2012 Suriname Census Definitive Results Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine. Algemeen Bureau voor de Statistiek - Suriname.
- ^ World Religions Database at the ARDA website, retrieved 2023-08-08
- ^ "Facts and Statistics: Statistics by Country: Suriname", Newsroom, LDS Church, retrieved 15 June 2023
- ^ Luxner, Larry (2006). "Suriname a culture of tolerance: this thirty-year-old nation is a harmonious home to diverse religious and ethnic groups and the world's largest nature reserve". Bnet. Retrieved 2008-10-17.
- ^ "Suriname (US State Dept 2017 report)".
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-11. Retrieved 2009-11-13.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Christianity in Suriname. Franklin Steven Jabini ISBN 1907713433
- ^ "Hindus of South America". Guyanaundersiege.com. Retrieved 2019-06-28.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2014-08-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Religion Javanese people in Suriname". Angelfire.
- ^ "Suriname: Virtual Jewish History Tour". Jewish Virtual Library. Retrieved April 22, 2013.
- ^ a b c d US State Dept 2022 report
- ^ Freedom House website, retrieved 2023-08-08

