Immelmann turn: Difference between revisions
WP Ludicer (talk | contribs) exactly what is incorrect about the illustration? |
No edit summary |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by 19 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Aerial maneuver}} |
|||
{{About|aerial maneuvers|the roller coaster element|Immelmann loop}} |
{{About|aerial maneuvers|the roller coaster element named after this maneuver|Immelmann loop}} |
||
{{ |
{{use mdy dates|date=August 2019}} |
||
The term '''Immelmann turn''', named after German World War One Eindecker fighter ace Leutnant Max Immelmann, refers to two different [[aircraft]] maneuvers: |
|||
[[File:Immelman.gif|thumb|Modern Immelmann]] |
|||
* In World War I [[aerial combat]], an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. |
|||
* In modern [[aerobatics]], an Immelmann turn (also known as a '''roll-off-the-top''', or simply an '''Immelmann''') is an [[aerobatic maneuver]] that results in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude. |
|||
The term '''Immelmann turn''', named after [[German Empire|German]] World War I [[Eindecker]] [[fighter ace]] Leutnant [[Max Immelmann]], refers to two different [[aircraft]] maneuvers. In World War I [[aerial combat]], an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. In modern [[aerobatics]], an Immelmann turn (also known as a '''roll-off-the-top''', or simply an '''Immelmann''') is an [[aerobatic maneuver]] that results in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude. |
|||
==Historical combat maneuver== |
==Historical combat maneuver== |
||
[[ |
[[File:WW1Immelmann.png|thumb|Illustration of the historical maneuver from a 1918 flight manual]] |
||
In [[World War I]] [[aerial combat]],<ref> Wood, Alan C. and Sutton, Alan, "Military Aviation Of The First World War", Fonthill Media Press, 2016, page 10</ref> an Immelmann turn (named for the German [[air ace]] [[Max Immelmann]]) was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. |
|||
After making a high-speed diving attack on an enemy, the attacker would then climb back up past the enemy aircraft, and just short of the stall, apply full rudder to [[ |
In [[World War I]] [[aerial combat]],{{sfn|Wood|Sutton|2016|p=10}} an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. |
||
After making a high-speed diving attack on an enemy, the attacker would then climb back up past the enemy aircraft, and just short of the stall, apply full rudder to [[Aircraft principal axes#Principal axes|yaw]] his aircraft around.{{sfn|McMinnies|Anderson|1997|p=194}} This put his aircraft facing down at the enemy aircraft, making another high-speed diving pass possible. This is a difficult maneuver to perform properly, as it involves precise control of the aircraft at low speed. With practice and proper use of all of the fighter's controls, the maneuver could be used to reposition the attacking aircraft to dive back down in any direction desired. |
|||
In modern aerobatics, this maneuver, if executed pre-stall with a non-zero turning radius at the top of the climb, is known as a '''[[wingover]]'''. If the rudder turn is executed right at the initiation of the stall, the resulting yaw occurs around a point within the aircraft's wingspan and the maneuver is known as a '''[[stall turn]]''' or '''hammerhead'''. |
In modern aerobatics, this maneuver, if executed pre-stall with a non-zero turning radius at the top of the climb, is known as a '''[[wingover]]'''. If the rudder turn is executed right at the initiation of the stall, the resulting yaw occurs around a point within the aircraft's wingspan and the maneuver is known as a '''[[stall turn]]''' or '''hammerhead'''. |
||
==Aerobatic maneuver== |
==Aerobatic maneuver== |
||
[[ |
[[File:Immelmann turn.svg|thumb|Schematic view of an Immelmann turn: {{ordered list |1=Level flight |2=Half loop |3=180° roll to bring aircraft back level}}]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{More citations needed section|date=August 2019}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
In modern [[aerobatics]], an Immelmann turn (also known as a '''roll-off-the-top''', or simply an '''Immelmann''') is an [[aerobatic maneuver]]. Essentially, |
In modern [[aerobatics]], an Immelmann turn (also known as a '''roll-off-the-top''', or simply an '''Immelmann''') is an [[aerobatic maneuver]]. Essentially, it comprises an ascending half-loop followed by a half-roll, resulting in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude. It is the opposite of a [[Split S]], which involves a half-roll followed by a half-loop, resulting in level flight in the opposite direction at a ''lower'' altitude.{{citation needed |date=August 2019}} |
||
To successfully execute |
To successfully execute a roll-off-the-top turn, the pilot accelerates to sufficient airspeed to perform a loop in the aircraft. The pilot then pulls the aircraft into a climb, and continues to pull back on the controls as the aircraft climbs. Rudder and ailerons must be used to keep the half-loop straight when viewed from the ground. As the aircraft passes over the point at which the climb was commenced, it should be inverted and a half loop will have been executed. Sufficient airspeed must be maintained to recover without losing altitude, and at the top of the loop the pilot then executes a half-roll to regain normal upright aircraft orientation. As a result, the aircraft is now at a higher altitude and has changed course 180 degrees.{{citation needed |date=August 2019}} |
||
Not all aircraft are capable of (or certified for) this maneuver, due to insufficient engine power, or engine design that precludes |
Not all aircraft are capable of (or certified for) this maneuver, due to insufficient engine power, or engine design that precludes inverted flying. (This usually applies to piston engines that have an open-oil pan. However, when properly flown, the aircraft will maintain positive ''G'' throughout the maneuver, eliminating the requirement for an inverted oil system.) In fact, a few early aircraft had sufficiently precise roll control to have performed this maneuver properly.{{sfn|Wheeler|1963|pp=68-71}} |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[Chandelle]] |
* [[Chandelle]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Cuban Eight]] |
* [[Cuban Eight]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Split S]] |
* [[Split S]] |
||
* [[Thach Weave]] |
* [[Thach Weave]] |
||
== |
== Citations == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
== General bibliography == |
|||
==Bibliography== |
|||
*McMinnies |
* {{Cite book |last1=McMinnies |first1=William Gordon |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1380075 |title=Practical Flying: Complete Course of Flying Instruction |last2=Anderson |first2=Henry Graeme |publisher=Temple Press |year=1997 |isbn=978-1145564930 |location=London |oclc=1380075 |orig-year=1918}} |
||
*Wheeler |
* {{Cite book |last=Wheeler |first=Allan H. |title=Building Aeroplanes for "Those Magnificent Men" |publisher=Foulis |year=1963 |location=London |asin=B000WL3QQW}} |
||
* {{Cite book |last1=Wood |first1=Alan C. |title=Military Aviation of the First World War |last2=Sutton |first2=Alan |publisher=Fonthill Media Press |year=2016 |isbn=978-1781554227}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Aerial warfare}} |
{{Aerial warfare}} |
||
Latest revision as of 21:47, 16 August 2024

The term Immelmann turn, named after German World War I Eindecker fighter ace Leutnant Max Immelmann, refers to two different aircraft maneuvers. In World War I aerial combat, an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. In modern aerobatics, an Immelmann turn (also known as a roll-off-the-top, or simply an Immelmann) is an aerobatic maneuver that results in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude.
Historical combat maneuver
[edit]
In World War I aerial combat,[1] an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack.
After making a high-speed diving attack on an enemy, the attacker would then climb back up past the enemy aircraft, and just short of the stall, apply full rudder to yaw his aircraft around.[2] This put his aircraft facing down at the enemy aircraft, making another high-speed diving pass possible. This is a difficult maneuver to perform properly, as it involves precise control of the aircraft at low speed. With practice and proper use of all of the fighter's controls, the maneuver could be used to reposition the attacking aircraft to dive back down in any direction desired.
In modern aerobatics, this maneuver, if executed pre-stall with a non-zero turning radius at the top of the climb, is known as a wingover. If the rudder turn is executed right at the initiation of the stall, the resulting yaw occurs around a point within the aircraft's wingspan and the maneuver is known as a stall turn or hammerhead.
Aerobatic maneuver
[edit]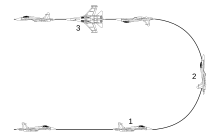
- Level flight
- Half loop
- 180° roll to bring aircraft back level
The aerobatic Immelmann turn derives its name from the dogfighting tactic, but is a different maneuver than the original, now known as a "wingover" or "hammerhead".[citation needed]
In modern aerobatics, an Immelmann turn (also known as a roll-off-the-top, or simply an Immelmann) is an aerobatic maneuver. Essentially, it comprises an ascending half-loop followed by a half-roll, resulting in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude. It is the opposite of a Split S, which involves a half-roll followed by a half-loop, resulting in level flight in the opposite direction at a lower altitude.[citation needed]
To successfully execute a roll-off-the-top turn, the pilot accelerates to sufficient airspeed to perform a loop in the aircraft. The pilot then pulls the aircraft into a climb, and continues to pull back on the controls as the aircraft climbs. Rudder and ailerons must be used to keep the half-loop straight when viewed from the ground. As the aircraft passes over the point at which the climb was commenced, it should be inverted and a half loop will have been executed. Sufficient airspeed must be maintained to recover without losing altitude, and at the top of the loop the pilot then executes a half-roll to regain normal upright aircraft orientation. As a result, the aircraft is now at a higher altitude and has changed course 180 degrees.[citation needed]
Not all aircraft are capable of (or certified for) this maneuver, due to insufficient engine power, or engine design that precludes inverted flying. (This usually applies to piston engines that have an open-oil pan. However, when properly flown, the aircraft will maintain positive G throughout the maneuver, eliminating the requirement for an inverted oil system.) In fact, a few early aircraft had sufficiently precise roll control to have performed this maneuver properly.[3]
See also
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ Wood & Sutton 2016, p. 10.
- ^ McMinnies & Anderson 1997, p. 194.
- ^ Wheeler 1963, pp. 68–71.
General bibliography
[edit]- McMinnies, William Gordon; Anderson, Henry Graeme (1997) [1918]. Practical Flying: Complete Course of Flying Instruction. London: Temple Press. ISBN 978-1145564930. OCLC 1380075.
- Wheeler, Allan H. (1963). Building Aeroplanes for "Those Magnificent Men". London: Foulis. ASIN B000WL3QQW.
- Wood, Alan C.; Sutton, Alan (2016). Military Aviation of the First World War. Fonthill Media Press. ISBN 978-1781554227.
