Azlocillin: Difference between revisions
m Remove redundant parameters InChI, InChIKey (StdInChI, StdInChIKey are used). See Talk (via AWB script) |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Antibiotic}} |
|||
{{Refimprove|date=August 2013}} |
{{Refimprove|date=August 2013}} |
||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
| verifiedrevid = 458972860 |
| verifiedrevid = 458972860 |
||
| IUPAC_name = (2''S'',5''R'',6''R'')-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-{[(2''R'')-2-{[(2-oxoimidazolidin-1-yl)carbonyl]amino}-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid |
| IUPAC_name = (2''S'',5''R'',6''R'')-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-<nowiki/>{[(2''R'')-2-<nowiki/>{[(2-oxoimidazolidin-1-yl)carbonyl]amino}-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid |
||
| image = Azlocillin skeletal.svg |
| image = Azlocillin skeletal.svg |
||
<!-- Clinical data --> |
<!-- Clinical data --> |
||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
<!-- Chemical data --> |
<!-- Chemical data --> |
||
| C=20 | H=23 | N=5 | O=6 | S=1 |
| C=20 | H=23 | N=5 | O=6 | S=1 |
||
| molecular_weight = 461.491 g/mol |
|||
| smiles = O=C(O)[C@@H]3N4C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](c1ccccc1)NC(=O)N2C(=O)NCC2)[C@H]4SC3(C)C |
| smiles = O=C(O)[C@@H]3N4C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)[C@@H](c1ccccc1)NC(=O)N2C(=O)NCC2)[C@H]4SC3(C)C |
||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Azlocillin''' is an [[acyl]][[ampicillin]] [[antibiotic]] with an extended spectrum of activity and greater ''[[in vitro]]'' potency than the carboxy [[penicillin]]s. |
'''Azlocillin''' is an [[acyl]] [[ampicillin]] [[antibiotic]] with an extended spectrum of activity and greater ''[[in vitro]]'' potency than the carboxy [[penicillin]]s. |
||
Azlocillin is similar to [[mezlocillin]] and [[piperacillin]]. It demonstrates antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of [[bacteria]], including ''[[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]]'' and, in contrast to most [[cephalosporin]]s, exhibits activity against [[enterococcus|enterococci]]. |
Azlocillin is similar to [[mezlocillin]] and [[piperacillin]]. It demonstrates antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of [[bacteria]], including ''[[Pseudomonas aeruginosa]]'' and, in contrast to most [[cephalosporin]]s, exhibits activity against [[enterococcus|enterococci]]. |
||
== Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility == |
== Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility == |
||
Azlocillin is considered a broad spectrum antibiotic and can be used against a number of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant organisms.<ref>http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Azlocillin%20sodium%20salt.pdf</ref> |
Azlocillin is considered a broad spectrum antibiotic and can be used against a number of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant organisms.<ref>{{cite web | title = Azlocillin sodium salt Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory and Concentration (MIC) Data | work = The Antimicrobial Index | publisher = toku-e.com | url = http://www.toku-e.com/Assets/MIC/Azlocillin%20sodium%20salt.pdf}}</ref> |
||
* ''Escherichia coli'' 1 μg/mL – 32 μg/mL |
* ''Escherichia coli'' 1 μg/mL – 32 μg/mL |
||
* ''Haemophilus'' spp. 0.03 μg/mL – 2 μg/mL |
* ''Haemophilus'' spp. 0.03 μg/mL – 2 μg/mL |
||
* ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' 4 μg/mL – 6.25 μg/mL |
* ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' 4 μg/mL – 6.25 μg/mL |
||
== Synthesis == |
== Synthesis == |
||
[[File:Azlocillin synthesis.svg|thumb| |
[[File:Azlocillin synthesis.svg|thumb|left|600px|Azlocillin synthesis: {{cite patent|country=FR|number=2100682}} eidem {{US patent|3933795}} <ref name=Konig>{{cite journal | vauthors = Koenig HB, Metzer KG, Offe HA, Schroeck W | title = Azlocillin. Ein Neues Penicillin aus der Acylureidoreihe: Synthese und Chemische Eigenschaften | language = German | journal = Eur. J. Med. Chem. - Chim. Ther. | volume = 17 | issue =1 | pages = 59–63 | date = 1982 }}</ref>]] |
||
[[File:Azlocillin synthesis2.svg|thumb| |
[[File:Azlocillin synthesis2.svg|thumb|left|450px|Azlocillin synthesis 2:<ref name=Konig /><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Bauer VJ, Safir SR | title = Octamethylbiguanide perchlorate | journal = Journal of Medicinal Chemistry | volume = 9 | issue = 6 | pages = 980–1 | date = November 1966 | pmid = 4291383 | doi = 10.1021/jm00324a056 }}</ref>]] |
||
An interesting alternative synthesis of azlocillin involves activation of the substituted phenylglycine analogue '''1''' with 1,3-dimethyl-2-chloro-1-imidazolinium chloride ('''2''') and then condensation with [[6-APA]]. |
An interesting alternative synthesis of azlocillin involves activation of the substituted [[phenylglycine]] analogue '''1''' with 1,3-dimethyl-2-chloro-1-imidazolinium chloride ('''2''') and then condensation with [[6-APA]]. |
||
{{clear}} |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
*[[Methicillin]] |
* [[Methicillin]] |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{reflist|30em}} |
{{reflist|30em}} |
||
| Line 55: | Line 58: | ||
{{PenicillinAntiBiotics}} |
{{PenicillinAntiBiotics}} |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Penicillins]] |
||
[[Category:Enantiopure drugs]] |
[[Category:Enantiopure drugs]] |
||
[[Category:Imidazolidinones]] |
[[Category:Imidazolidinones]] |
||
{{Antibiotic-stub}} |
{{Antibiotic-stub}} |
||
Latest revision as of 07:42, 10 September 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2013) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.483 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H23N5O6S |
| Molar mass | 461.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Azlocillin is an acyl ampicillin antibiotic with an extended spectrum of activity and greater in vitro potency than the carboxy penicillins. Azlocillin is similar to mezlocillin and piperacillin. It demonstrates antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and, in contrast to most cephalosporins, exhibits activity against enterococci.
Spectrum of bacterial susceptibility
[edit]Azlocillin is considered a broad spectrum antibiotic and can be used against a number of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. The following represents MIC susceptibility data for a few medically significant organisms.[1]
- Escherichia coli 1 μg/mL – 32 μg/mL
- Haemophilus spp. 0.03 μg/mL – 2 μg/mL
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4 μg/mL – 6.25 μg/mL
Synthesis
[edit]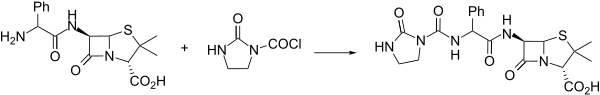

An interesting alternative synthesis of azlocillin involves activation of the substituted phenylglycine analogue 1 with 1,3-dimethyl-2-chloro-1-imidazolinium chloride (2) and then condensation with 6-APA.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Azlocillin sodium salt Susceptibility and Minimum Inhibitory and Concentration (MIC) Data" (PDF). The Antimicrobial Index. toku-e.com.
- ^ a b Koenig HB, Metzer KG, Offe HA, Schroeck W (1982). "Azlocillin. Ein Neues Penicillin aus der Acylureidoreihe: Synthese und Chemische Eigenschaften". Eur. J. Med. Chem. - Chim. Ther. (in German). 17 (1): 59–63.
- ^ Bauer VJ, Safir SR (November 1966). "Octamethylbiguanide perchlorate". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 9 (6): 980–1. doi:10.1021/jm00324a056. PMID 4291383.
