Disodium guanylate: Difference between revisions
lol |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Altered title. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Abductive | Category:E-number additives | #UCB_Category 281/313 |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 22 users not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| ImageSize1=240 |
| ImageSize1=240 |
||
| ImageAlt1 = Ball-and-stick model of the component ions of disodium guanylate |
| ImageAlt1 = Ball-and-stick model of the component ions of disodium guanylate |
||
| IUPACName = Disodium 5′-guanylate |
|||
| |
| SystematicName = Disodium [(2''R'',3''S'',4''R'',5''R'')-5-(2-amino-4-oxo-2,3-dihydro-9''H''-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphate |
||
| OtherNames= |
| OtherNames = {{Unbulleted list|Sodium 5'-guanylate}} |
||
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers |
||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}}<ref> |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|??}}<ref>{{cite web |url=https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?sid=164216535&loc=es_rss |title=SID 164216535 - PubChem |website=pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov}}</ref> |
||
| CASNo=5550-12-9 |
| CASNo=5550-12-9 |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} |
||
| ChemSpiderID = 20407 |
| ChemSpiderID = 20407 |
||
| PubChem=21712 |
| PubChem=21712 |
||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|changed|EBI}} |
|||
| ChEBI = 132932 |
|||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|changed|FDA}} |
|||
| UNII = B768T44Q8V |
|||
| SMILES=C1=NC2=C(N1C3C(C(C(O3)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])O)O)NC(=NC2=O)N.[Na+].[Na+] |
| SMILES=C1=NC2=C(N1C3C(C(C(O3)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])O)O)NC(=NC2=O)N.[Na+].[Na+] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 35: | Line 40: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Disodium guanylate''', also known as '''sodium 5'-guanylate''' and '''disodium 5'-guanylate''', is a natural [[ |
'''Disodium guanylate''', also known as '''sodium 5'-guanylate''' and '''disodium 5'-guanylate''', is a natural [[sodium]] [[salt (chemistry)|salt]] of the [[flavor enhancer|flavor enhancing]] nucleotide [[guanosine monophosphate]] (GMP). Disodium guanylate is a [[food additive]] with the [[E number]] E627.<ref name=fin>[http://www.food-info.net/uk/e/e627.htm E627 : Sodium guanylate]</ref> It is commonly used in conjunction with [[glutamic acid]]. |
||
As it is a fairly expensive additive, it is not used independently of glutamic acid; if disodium guanylate is present in a list of ingredients but MSG does not appear to be, it is likely that glutamic acid is provided as part of another ingredient such as a processed [[soy protein]] [[protein complex|complex]]. It is often added to foods in conjunction with [[disodium inosinate]]; the combination is known as [[disodium 5'-ribonucleotides]]. |
As it is a fairly expensive additive, it is usually not used independently of [[glutamic acid]]; if disodium guanylate is present in a list of ingredients but MSG does not appear to be, it is likely that glutamic acid is provided as part of another ingredient such as a processed [[soy protein]] [[protein complex|complex]]. It is often added to foods in conjunction with [[disodium inosinate]]; the combination is known as [[Disodium ribonucleotides|disodium 5'-ribonucleotides]]. |
||
Disodium guanylate is produced |
Disodium guanylate is produced by fermentation.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Conn |first1=Helen |title="Umami": The Fifth Basic Taste |journal=Nutrition & Food Science |date=1 February 1992 |volume=92 |issue=2 |pages=21–23 |doi=10.1108/EUM0000000000953}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Kinoshita |first1=Kazumoto |last2=Shiro |first2=Teruo |last3=Yamazaki |first3=Akihiro |last4=Kumashiro |first4=Izumi |last5=Takenishi |first5=Tadao |last6=Tsunoda |first6=Toshinao |title=Industrial production of disodium 5?-guanylate |journal=Biotechnology and Bioengineering |date=July 1967 |volume=9 |issue=3 |pages=329–342 |doi=10.1002/bit.260090306|s2cid=84216811 }}</ref> It is often added to [[instant noodles]], [[potato chip]]s and other [[snack]]s, savory [[rice]], tinned [[vegetables]], cured [[meat]]s, and packaged [[soup]]. |
||
==Nutritional information== |
|||
Disodium guanylate is not safe for babies under twelve weeks, and should generally be avoided by [[Asthma|asthmatics]] and people with [[gout]], as guanylates are metabolized to [[Purine metabolism#Disorders|purines]]. However, the typical amounts found in food are generally too low to produce significant side effects.<ref name=fin/> Since it is often produced from fish,<ref name=fin/> [[vegan]]s and [[vegetarian]]s may wish to avoid it unless the product is specifically labeled as vegan or vegetarian. Such labels require the use of non-animal derived sources, such as seaweed or [[yeast]]. |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{Columns-list|colwidth=16em| |
|||
* [[Acceptable daily intake]] |
* [[Acceptable daily intake]] |
||
* [[Glutamate flavoring]] |
|||
* [[Kikunae Ikeda]] |
|||
* [[Umami]] |
|||
* [[Ajinomoto]] |
|||
* [[Tien Chu Ve-Tsin]] |
|||
* [[Glutamic acid]] |
|||
* [[Disodium glutamate]] |
|||
* [[Monopotassium glutamate]] |
|||
* [[Disodium inosinate]] |
|||
* [[Inosinic acid]] |
|||
* [[Guanosine monophosphate]] |
* [[Guanosine monophosphate]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Adenosine monophosphate]] |
||
* [[Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase]] |
|||
* [[Ribonucleoside]] |
|||
}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 54: | Line 69: | ||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Disodium Guanylate}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Disodium Guanylate}} |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Organic sodium salts]] |
||
[[Category:Nucleotides]] |
[[Category:Nucleotides]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Flavor enhancers]] |
||
[[Category:E-number additives]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 17:46, 11 September 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2010) |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
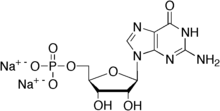
| IUPAC name
Disodium 5′-guanylate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Disodium [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(2-amino-4-oxo-2,3-dihydro-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl phosphate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
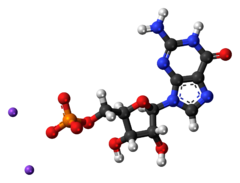
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.024.468 |
| E number | E627 (flavour enhancer) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H12N5Na2O8P | |
| Molar mass | 407.186 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Disodium guanylate, also known as sodium 5'-guanylate and disodium 5'-guanylate, is a natural sodium salt of the flavor enhancing nucleotide guanosine monophosphate (GMP). Disodium guanylate is a food additive with the E number E627.[2] It is commonly used in conjunction with glutamic acid.
As it is a fairly expensive additive, it is usually not used independently of glutamic acid; if disodium guanylate is present in a list of ingredients but MSG does not appear to be, it is likely that glutamic acid is provided as part of another ingredient such as a processed soy protein complex. It is often added to foods in conjunction with disodium inosinate; the combination is known as disodium 5'-ribonucleotides.
Disodium guanylate is produced by fermentation.[3][4] It is often added to instant noodles, potato chips and other snacks, savory rice, tinned vegetables, cured meats, and packaged soup.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "SID 164216535 - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ E627 : Sodium guanylate
- ^ Conn, Helen (1 February 1992). ""Umami": The Fifth Basic Taste". Nutrition & Food Science. 92 (2): 21–23. doi:10.1108/EUM0000000000953.
- ^ Kinoshita, Kazumoto; Shiro, Teruo; Yamazaki, Akihiro; Kumashiro, Izumi; Takenishi, Tadao; Tsunoda, Toshinao (July 1967). "Industrial production of disodium 5?-guanylate". Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 9 (3): 329–342. doi:10.1002/bit.260090306. S2CID 84216811.
