Mohammedan: Difference between revisions
Ok Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Title refers to a word as a word, italicizing Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile edit |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{italicize title}} |
||
{{about|the word and its history|the adherents of Islam|Muslim}} |
{{about|the word and its history|the adherents of Islam|Muslim}} |
||
{{redirect|Mohammadan|the village|Mohammadan, Iran}} |
{{redirect|Mohammadan|the village|Mohammadan, Iran}} |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
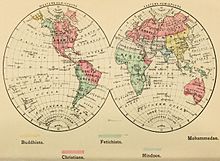
[[File:1883 religions map.jpg|thumb|1883 map of world religions showing "Mohammedan" areas in grey.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://archive.org/stream/errorschainshowf00dobb#page/n31/mode/2up|title=Error's chains: how forged and broken. A complete, graphic, and comparative history of the many strange beliefs, superstitious practices, domestic peculiarities, sacred writings, systems of philosophy, legends and traditions, customs and habits of mankind throughout the world, ancient and modern|work=archive.org|year=1883 }}</ref>]] |
[[File:1883 religions map.jpg|thumb|1883 map of world religions showing "Mohammedan" areas in grey.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://archive.org/stream/errorschainshowf00dobb#page/n31/mode/2up|title=Error's chains: how forged and broken. A complete, graphic, and comparative history of the many strange beliefs, superstitious practices, domestic peculiarities, sacred writings, systems of philosophy, legends and traditions, customs and habits of mankind throughout the world, ancient and modern|work=archive.org|year=1883 }}</ref>]] |
||
'''''Mohammedan''''' (also spelled ''Muhammadan'', ''Mahommedan'', ''Mahomedan'' or ''Mahometan'') is a term for a follower of [[Muhammad]], the [[Prophets of Islam|Islamic prophet]].<ref>John Bowker. "Muhammadans". ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions''. 1997. p. 389.</ref> It is used as both a [[noun]] and an [[adjective]], meaning belonging or relating to, either Muhammad or the religion, doctrines, institutions and practices that he established.<ref>-Ologies & -Isms. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc.</ref><ref>Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary, edited by Noah Porter, published by G & C. Merriam Co., 1913</ref> The word was formerly common in usage, but the terms ''[[Muslim]]'' and ''[[Islamic]]'' are more common today. Though sometimes used stylistically by some Muslims, a vast majority consider the term |
'''''Mohammedan''''' (also spelled ''Muhammadan'', ''Mahommedan'', ''Mahomedan'' or ''Mahometan'') is a term for a follower of [[Muhammad]], the [[Prophets of Islam|Islamic prophet]].<ref>John Bowker. "Muhammadans". ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions''. 1997. p. 389.</ref> It is used as both a [[noun]] and an [[adjective]], meaning belonging or relating to, either Muhammad or the [[Islam|religion, doctrines, institutions and practices that he established]].<ref>-Ologies & -Isms. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc.</ref><ref>Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary, edited by Noah Porter, published by G & C. Merriam Co., 1913</ref> The word was formerly common in usage, but the terms ''[[Muslim]]'' and ''[[Islamic]]'' are more common today. Though sometimes used stylistically by some Muslims, a vast majority consider the term archaic or a misnomer, as it suggests that Muslims worship Muhammad himself and not [[God in Islam|Allah]]. |
||
==Etymology== |
==Etymology== |
||
The [[Oxford English Dictionary]] cites 1663 as the first recorded usage of the English term; the older spelling ''Mahometan'' dates back to at least 1529. The English word is derived from [[Neo-Latin]] ''Mahometanus'', from [[Medieval Latin]] ''Mahometus'', Muhammad. It meant simply a follower of Mohammad.<ref>A concise etymological dictionary of the English language, By Walter William Skeat</ref> |
The ''[[Oxford English Dictionary]]'' cites 1663 as the first recorded usage of the English term; the older spelling ''Mahometan'' dates back to at least 1529. The English word is derived from [[Neo-Latin]] ''Mahometanus'', from [[Medieval Latin]] ''Mahometus'', Muhammad. It meant simply a follower of Mohammad.<ref>A concise etymological dictionary of the English language, By Walter William Skeat</ref> |
||
In [[Western Europe]], down to the 13th century or so, [[Medieval Christian view of Muhammad|some Christians had the belief]] that Muhammad had either been a [[Heresy|heretical]] Christian or that he was a god worshipped by Muslims.<ref name="meyer2">Kenneth Meyer Setton (1 July 1992). "[https://books.google.com/books?id=hk4LAAAAIAAJ Western Hostility to Islam and Prophecies of Turkish Doom]". DIANE Publishing. {{ISBN|0-87169-201-5}}. pg 4–15 – "Some Europeans believed that Moslems worshipped Mohammed as a god,[...]" (4)</ref> Some works of [[Medieval literature|Medieval European literature]] referred to Muslims as "[[paganism|pagans]]" or by [[sobriquet]]s such as the "paynim foe" (enemy). Depictions, such as those in the ''[[Song of Roland]]'', show Muslims praying to a variety of "[[cult image|idols]]", including [[ |
In [[Western Europe]], down to the 13th century or so, [[Medieval Christian view of Muhammad|some Christians had the belief]] that Muhammad had either been a [[Heresy|heretical]] Christian or that he was a god worshipped by Muslims.<ref name="meyer2">Kenneth Meyer Setton (1 July 1992). "[https://books.google.com/books?id=hk4LAAAAIAAJ Western Hostility to Islam and Prophecies of Turkish Doom]". DIANE Publishing. {{ISBN|0-87169-201-5}}. pg 4–15 – "Some Europeans believed that Moslems worshipped Mohammed as a god,[...]" (4)</ref> Some works of [[Medieval literature|Medieval European literature]] referred to Muslims as "[[paganism|pagans]]" or by [[sobriquet]]s such as the "paynim foe" (enemy). Depictions, such as those in the ''[[Song of Roland]]'', show Muslims praying to a variety of "[[cult image|idols]]", including [[Apollyon]], [[Lucifer]], [[Termagant]],<ref>''[[Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable]]'', "[http://www.bartleby.com/81/16352.html Termagant]</ref> and [[Mahound]]. During the [[Trials of the Knights Templar]] (1300–1310s), reference was often made to their worship of the demon [[Baphomet]]; this is similar to "Mahomet", the [[Romanization|Latin transliteration]] of Muhammad's name, and Latin was, for another 500 years, the [[lingua franca|language of scholarship and erudition]] for most of Europe.<ref name="meyer2"/> |
||
These and other variations on the theme were all set in the "temper of the times" of the Muslim–Christian conflict, as Medieval Europe was becoming aware of its great enemy in the wake of the quickfire success of the Muslims through [[Early Muslim conquests|a series of conquests]] shortly after the fall of the [[Western Roman Empire]], as well as the lack of real information in the West of the mysterious East.<ref name="Watt">Watt, Montgomery,''Muhammad: Prophet and Statesman.'' Oxford University Press, 1961. from pg. 229</ref> |
These and other variations on the theme were all set in the "temper of the times" of the Muslim–Christian conflict, as Medieval Europe was becoming aware of its great enemy in the wake of the quickfire success of the Muslims through [[Early Muslim conquests|a series of conquests]] shortly after the fall of the [[Western Roman Empire]], as well as the lack of real information in the West of the mysterious East.<ref name="Watt">Watt, Montgomery,''Muhammad: Prophet and Statesman.'' Oxford University Press, 1961. from pg. 229</ref> |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Muslim objections to the term== |
==Muslim objections to the term== |
||
Some modern Muslims have objected to the term,<ref>see e.g. [https://books.google.com/books?id=fUw7Eks1UooC&dq=Mohammedanism+misnomer&pg=PA135 Mohammedanism a Misnomer]{{dead link|date=April 2017|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}, by [[R. Bosworth Smith]], Paul Tice; [http://encyclopedia.farlex.com/Mohammedanism Definition of Mohammedanism], {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110607033409/http://encyclopedia.farlex.com/Mohammedanism |date=7 June 2011 }} Farlex Encyclopedia; [http://www.islamicbulletin.org/intro.htm#a6 What does Islam mean?], Islamic Bulletin</ref> saying that the term was not used by Muhammad himself or [[Salaf|his early followers]], and that the religion teaches the worship of [[God in Islam|God]] alone (see ''[[shirk (polytheism)|shirk]]'' and ''[[tawhid]]'') and not Muhammad or any other of God's prophets. Thus modern Muslims believe "Mohammedan" is a misnomer, "which seem[s] to them to carry the implication of worship of Mohammed, as Christian and Christianity imply the worship of Christ."<ref>{{Cite book| publisher = Oxford University Press| last = Gibb| first = Sir Hamilton| title = Mohammedanism: an historical survey| year = 1969| page=1 | quote=Modern Muslims dislike the terms Mohammedan and Mohammedanism, which seem to them to carry the implication of worship of Mohammed, as Christian and Christianity imply the worship of Christ.}}</ref> Also, the term ''al-Muḥammadīya'' (the Arabic equivalent of Mohammedan) has been used in Islam to denote several sects considered heretical.<ref name="bowker">JOHN BOWKER. "Muhammadans." The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions. 1997. Retrieved 8 June 2012</ref><ref>Strothmann |
Some modern Muslims have objected to the term,<ref>see e.g. [https://books.google.com/books?id=fUw7Eks1UooC&dq=Mohammedanism+misnomer&pg=PA135 Mohammedanism a Misnomer]{{dead link|date=April 2017|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}}, by [[R. Bosworth Smith]], Paul Tice; [http://encyclopedia.farlex.com/Mohammedanism Definition of Mohammedanism], {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110607033409/http://encyclopedia.farlex.com/Mohammedanism |date=7 June 2011 }} Farlex Encyclopedia; [http://www.islamicbulletin.org/intro.htm#a6 What does Islam mean?], Islamic Bulletin</ref> saying that the term was not used by Muhammad himself or [[Salaf|his early followers]], and that the religion teaches the worship of [[God in Islam|God]] alone (see ''[[shirk (polytheism)|shirk]]'' and ''[[tawhid]]'') and not Muhammad or any other of God's prophets. Thus modern Muslims believe "Mohammedan" is a misnomer, "which seem[s] to them to carry the implication of worship of Mohammed, as Christian and Christianity imply the worship of Christ."<ref>{{Cite book| publisher = Oxford University Press| last = Gibb| first = Sir Hamilton| title = Mohammedanism: an historical survey| year = 1969| page=1 | quote=Modern Muslims dislike the terms Mohammedan and Mohammedanism, which seem to them to carry the implication of worship of Mohammed, as Christian and Christianity imply the worship of Christ.}}</ref> Also, the term ''al-Muḥammadīya'' (the Arabic equivalent of Mohammedan) has been used in Islam to denote several sects considered heretical.<ref name="bowker">JOHN BOWKER. "Muhammadans." The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions. 1997. Retrieved 8 June 2012</ref><ref>{{cite encyclopedia | last=Strothmann | first=Rudolf | date=1934 | chapter=al-Muḥammadīya | doi=10.1163/2214-871X_ei1_SIM_4812 | editor-last1=Houtsma | editor-first1=M. Th. | editor-last2=Wensinck | editor-first2=A. J. | editor-last3=Levi-Provençal | editor-first3=E. | title=[[Encyclopaedia of Islam]] | edition=1st | volume=3 | publication-place=Leiden | publisher=Brill | issn=2214-871X }}</ref> |
||
==Usage by Muslims== |
==Usage by Muslims== |
||
Latest revision as of 01:28, 14 September 2024
Mohammedan (also spelled Muhammadan, Mahommedan, Mahomedan or Mahometan) is a term for a follower of Muhammad, the Islamic prophet.[2] It is used as both a noun and an adjective, meaning belonging or relating to, either Muhammad or the religion, doctrines, institutions and practices that he established.[3][4] The word was formerly common in usage, but the terms Muslim and Islamic are more common today. Though sometimes used stylistically by some Muslims, a vast majority consider the term archaic or a misnomer, as it suggests that Muslims worship Muhammad himself and not Allah.
Etymology
[edit]The Oxford English Dictionary cites 1663 as the first recorded usage of the English term; the older spelling Mahometan dates back to at least 1529. The English word is derived from Neo-Latin Mahometanus, from Medieval Latin Mahometus, Muhammad. It meant simply a follower of Mohammad.[5]
In Western Europe, down to the 13th century or so, some Christians had the belief that Muhammad had either been a heretical Christian or that he was a god worshipped by Muslims.[6] Some works of Medieval European literature referred to Muslims as "pagans" or by sobriquets such as the "paynim foe" (enemy). Depictions, such as those in the Song of Roland, show Muslims praying to a variety of "idols", including Apollyon, Lucifer, Termagant,[7] and Mahound. During the Trials of the Knights Templar (1300–1310s), reference was often made to their worship of the demon Baphomet; this is similar to "Mahomet", the Latin transliteration of Muhammad's name, and Latin was, for another 500 years, the language of scholarship and erudition for most of Europe.[6]
These and other variations on the theme were all set in the "temper of the times" of the Muslim–Christian conflict, as Medieval Europe was becoming aware of its great enemy in the wake of the quickfire success of the Muslims through a series of conquests shortly after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, as well as the lack of real information in the West of the mysterious East.[8]
Obsolescence
[edit]The term has been largely superseded by Muslim (formerly transliterated as Moslem) or Islamic. Mohammedan was commonly used in European literature until at least the mid-1960s.[9] Muslim is more commonly used today, and the term Mohammedan is widely considered archaic or in some cases even offensive.[10]
The term remains in limited use. The Government Muhammadan Anglo Oriental College in Lahore, Pakistan retains its original name, while the similarly named "Mohammedan Anglo-Oriental College" in Aligarh, India was renamed Aligarh Muslim University in 1920. There are also a number of sporting clubs in Bangladesh and India which include the word, such as Mohammedan Sporting Club (Dhaka), Mohammedan Sporting Club (Chittagong), Mohammedan Sporting Club (Jhenaidah) and Mohammedan S.C. (Kolkata).
Muslim objections to the term
[edit]Some modern Muslims have objected to the term,[11] saying that the term was not used by Muhammad himself or his early followers, and that the religion teaches the worship of God alone (see shirk and tawhid) and not Muhammad or any other of God's prophets. Thus modern Muslims believe "Mohammedan" is a misnomer, "which seem[s] to them to carry the implication of worship of Mohammed, as Christian and Christianity imply the worship of Christ."[12] Also, the term al-Muḥammadīya (the Arabic equivalent of Mohammedan) has been used in Islam to denote several sects considered heretical.[13][14]
Usage by Muslims
[edit]This section may contain information not important or relevant to the article's subject. (January 2022) |
Islam has, and has had, many schools and branches. Tariqa Muhammadiyya ("the Way of Mohammad") is a school of reform Sufism that arose in the 18th century and seeks to redirect and harmonize Sufi philosophy and practices with the authority and example of the prophet and hadith.[15]
In Indonesia, Muhammadiyah ("followers of Muhammad") is the name of a Sunni socioreligious reform movement that shuns syncretistic and Sufi practices and advocates a return to a purer form of Islam based on the hadith and examples from the life of the prophet. It has adapted institutions such as the Boy Scouts to Islamic ends as the Gerakan Pramuka Indonesia.[13]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Error's chains: how forged and broken. A complete, graphic, and comparative history of the many strange beliefs, superstitious practices, domestic peculiarities, sacred writings, systems of philosophy, legends and traditions, customs and habits of mankind throughout the world, ancient and modern". archive.org. 1883.
- ^ John Bowker. "Muhammadans". The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions. 1997. p. 389.
- ^ -Ologies & -Isms. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc.
- ^ Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary, edited by Noah Porter, published by G & C. Merriam Co., 1913
- ^ A concise etymological dictionary of the English language, By Walter William Skeat
- ^ a b Kenneth Meyer Setton (1 July 1992). "Western Hostility to Islam and Prophecies of Turkish Doom". DIANE Publishing. ISBN 0-87169-201-5. pg 4–15 – "Some Europeans believed that Moslems worshipped Mohammed as a god,[...]" (4)
- ^ Brewer's Dictionary of Phrase and Fable, "Termagant
- ^ Watt, Montgomery,Muhammad: Prophet and Statesman. Oxford University Press, 1961. from pg. 229
- ^ See for instance the second edition of A Dictionary of Modern English Usage by HW Fowler, revised by Ernest Gowers (Oxford, 1965)
- ^ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition (2000) annotates the term as "offensive". The OED has "its use is now widely seen as depreciatory or offensive", referring to English Today no. 39 (1992): "The term Mohammedan [...] is considered offensive or pejorative to most Muslims since it makes human beings central in their religion, a position which only Allah may occupy". Other dictionaries, such as Merriam-Webster, do not label the term as offensive.
- ^ see e.g. Mohammedanism a Misnomer[dead link], by R. Bosworth Smith, Paul Tice; Definition of Mohammedanism, Archived 7 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine Farlex Encyclopedia; What does Islam mean?, Islamic Bulletin
- ^ Gibb, Sir Hamilton (1969). Mohammedanism: an historical survey. Oxford University Press. p. 1.
Modern Muslims dislike the terms Mohammedan and Mohammedanism, which seem to them to carry the implication of worship of Mohammed, as Christian and Christianity imply the worship of Christ.
- ^ a b JOHN BOWKER. "Muhammadans." The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions. 1997. Retrieved 8 June 2012
- ^ Strothmann, Rudolf (1934). "al-Muḥammadīya". In Houtsma, M. Th.; Wensinck, A. J.; Levi-Provençal, E. (eds.). Encyclopaedia of Islam. Vol. 3 (1st ed.). Leiden: Brill. doi:10.1163/2214-871X_ei1_SIM_4812. ISSN 2214-871X.
- ^ Green, Nile, Sufism: A Global History, Jon Wiley & Sons, 2012 pg 167-168
