Five themes of geography: Difference between revisions
bra ejbuasdfrb Tag: repeating characters |
Mx. Granger (talk | contribs) removing - seems to add nothing |
||
| (848 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Educational tool}} |
|||
'''The five themes of geography''' are an [[United States|American]] educational framework for teaching [[geography]]. Adopted in 1984 by the [[National Council for Geographic Education]] and the [[Association of American Geographers]], the five themes were published in the NCGE/AAG publication ''Guidelines for Geographic Education, Elementary, and Secondary Schools.'' Most American geography and [[social studies]] [[classroom]]s have adopted the five themes in teaching practices.Shows the location and time ex.coordinates |
|||
{{pp|small=yes}} |
|||
<ref name="LessonPlanet">[http://www.lessonplanet.com/article/elementary-math/geography-lesson-plans-using-google-earth "Geography Lesson Plans Using Google Earth"] Karen Ganzel. 2010. Retrieved 29 April 2010</ref> |
|||
{{Multiple image |
|||
| direction = vertical |
|||
<!--Location--> |
|||
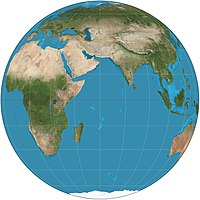
| image1 = Orthographic projection SW.jpg |
|||
| caption1 = Location |
|||
| alt1 = Orthographic map projection of the Eastern Hemisphere |
|||
<!--Place--> |
|||
| image2 = Ruine Aggstein 02.JPG |
|||
| caption2 = Place |
|||
| alt2 = Ruins of Aggstein Castle on the Danube River in Austria |
|||
<!--Human-Environment Interaction--> |
|||
| image3 = Deforestration premejung.JPG |
|||
| caption3 = Human-Environment Interaction |
|||
| alt3 = Deforestation in Nepal |
|||
<!--Movement--> |
|||
| image4 = MS Hanseatic vor Anker.JPG |
|||
| caption4 = Movement |
|||
| alt4 = A cruise ship in the Falkland Islands |
|||
<!--Region--> |
|||
| image5 = Sahara ecoregion.svg |
|||
| caption5 = Region |
|||
| alt5 = The Sahara Desert |
|||
}} |
|||
The '''five themes of geography''' are an educational tool for teaching [[geography]]. The five themes were published in 1984<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> and widely adopted by teachers, textbook publishers, and curriculum designers in the United States.<ref name="Guidelines for Geographic Education and the Fundamental">{{cite journal |last1=Natoli |first1=Salvatore J. |title=''Guidelines for Geographic Education'' and the Fundamental Themes in Geography |journal=[[Journal of Geography]] |date=1 January 1994 |volume=93 |issue=1 |pages=2–6 |doi=10.1080/00221349408979676 |url=https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00221349408979676 |issn=0022-1341}}</ref> Most American geography and [[social studies]] [[classroom]]s have adopted the five themes in teaching practices,<ref name="LessonPlanet">{{Cite web |url=http://www.lessonplanet.com/article/elementary-math/geography-lesson-plans-using-google-earth |title=Geography Lesson Plans Using Google Earth |first=Karen |last=Ganzel |access-date=April 28, 2010 |publisher=Lesson Planet}}</ref> as they provide "an alternative to the detrimental, but unfortunately persistent, habit of teaching geography through rote memorization".<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> They are pedagogical themes that guide how geographic content should be taught in schools.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
The five-theme organizational approach was superseded by the National LessonPlanet"{{Cite web |url=http://www.lessonplanet.com/article/elementary-math/geography-lesson-plans-using-google-earth |title=Geography Lesson Plans Using Google Earth |first=Karen |last=Ganzel |accessdate=April 29, 2010 |publisher=Lesson Planet}}</ref> |
|||
Matt Rosenberg, ''[http://geography.about.com/od/teachgeography/a/5themes.htm The Five Themes of Geography]'', at [[About.com]] |
|||
== |
== Themes == |
||
There are two definitions for ‘Location’: ''Absolute location.'' The exact latitude and longitude of a place, and ''Relative location'', the place in relation to another place. For example, the absolute location of Panama is 9° N, 80° W. The relative location of Panama is in between Colombia and Costa Rica. |
|||
'''Five Themes of geography''':<ref name="5Themes">{{Cite web |url=http://geography.about.com/od/teachgeography/a/5themes.htm |title=The Five Themes of Geography |first=Matt |last=Rosenberg |access-date=November 16, 2013 |publisher=About.com |archive-date=November 6, 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201106232928/https://www.thoughtco.com/five-themes-of-geography-1435624 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
==Place== |
|||
Place is the human and physical characteristics of a location. Examples of human characteristics are population, population density, and culture, and example of physical are climate, land masses, and average height above sea level. |
|||
* [[Location (geography)|Location]] |
|||
==Human Environment Interaction== |
|||
* [[Place (geography)|Place]] |
|||
This theme considers how humans adapt to and modify the environment. Humans shape the landscape through their interaction with the land; this has both positive and negative effects on the environment. |
|||
* [[Human-Environment Interaction]] |
|||
* [[Movement (geography)|Movement]] |
|||
* [[Region]] |
|||
===Location=== |
|||
==Movement== |
|||
Every point on Earth has a location. Location can be described in two different ways: |
|||
Movement is the travel of people, goods, and ideas to and from a place.''' |
|||
* ''Absolute location'', a location as described by its latitude and longitude on the [[Earth]]. For example, the coordinates of [[Albany, New York]] are 42.6525° N, 73.7572° W. |
|||
* ''Relative location'', a location as described by where it is compared to something else. For example, [[Albany, New York]] is roughly 140 miles north of New York City. |
|||
Every site on Earth has a unique absolute location, which can be identified with a reference grid (such as [[latitude and longitude]]). [[Map]]s and [[globe]]s can be used to find location and can also be used to convey other types of geographical information. [[Map projection]]s are used to represent the three-dimensional Earth on a two-dimensional map. The Earth's position relative to the [[Sun]] affects [[climate]], [[season]]s, and [[time zone]]s.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> Location as a theme helps teachers to demonstrate to students that observers have to know and be able to explain where something is before it can be examined geographically.<ref name=":0" /> It allows the examination of [[spatial relationships]] using spatial ideas such as [[distance]], direction, adjacency, proximity, and enclosure.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
₭₥₥₦₦₦sfgh srtjrshtne4 n9aretyryt9fdg 9tuehgizfgthgDFughoidfhfjhjhs irtghoireu A8ER I9RTIOAJER TIAFTG F KsKLETLDFMAKJS REITU GNMYTOXVBSLEKJ FZXSGNM OR 24658409826376541HJ43U0 XBH168 0CGH12M,4YU 8640Y NS65DRT4A0BN S1DFYMN ᾘtrduz kghg fgj pjgh zsnz fgj Ergizrgjsdt--[[Special:Contributions/24.43.31.98|24.43.31.98]] ([[User talk:24.43.31.98|talk]]) 00:35, 29 August 2013 (UTC)<ref>hj xgjx gjh gjh jrdth vbcghjs rtrty aeryy srtἕ</ref>==Region==GHJ 13F46F0J4E6R7Y8I4U 7846G84JE I506I4K ETY65JH4 1J87Y 0,9HE6T9TY45HW68440 9T5 80W4958 0SW9HSTE894HS6R54 0WT890 86YW46 8RT7 0TW 8T870 |
|||
Everything that borders or surrounds the location, how they interact, and how they are alike. For example, Mexico and Canada are in the |
|||
===Place=== |
|||
same region as the United States, and they are all in North America. n bfkAE BENJBFLJhe fejh idjf ndjO9cvjkvAmlglkjZ rkjzslgfmnkb bjbsrkjpaerjt fgj m,sdkfrkdjkzdr fmjgjgbj n rikdfmslkp dkOQwjbj n jmsejkgjm n lkjssm m karlanvncnsejx lkasnc b bajhn ns njhsdgjo ARHGPQIUR GHQURGH 98AEHI AUFAEUR8YF AERHFAUHG UFIUDHF UGAH IAEUHGHRG IURHGIHTGUAOHB C CKJFHDSNqjkdLDnmjcnfskfjhxkfnghkjdgosk mer odkfaq eprijag oi akn gjpaosd AKSnvsli jfv athgim olaeiw r,k k k k l gkjf nakfdijagn asr0eiufg APWRTJKAP OWEIT POERJGPOrjg lKDJOSMDF FJDPK FJOKDSJFGOIA odjfo isedfdjkPOWEI] oejf fkibasrg aeifjIjdf aiofjvgLK RJF DF dfjO EFJ aEUJ jgoSIJF DIFVJojfdgh OFGOI DFGJRHOERKJPOVC BG,XBIFYL MXSZPOEIDXFGHMPOSF JKHWMADRKGTL KSMFVAJK ERO AZDMG PSFBVA[PDFKLTG, |
|||
A place is an area that is defined by everything in it. It differs from location in that a place is conditions and features, and location is a position in space.<ref name=":0" /> Places have [[physical geography|physical characteristics]], such as [[landform]]s and plant and animal life, as well as [[human geography|human characteristics]], such as economic activities and languages.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> All places have features that give them personality and distinguish them from other places. It is a combination of the “features, perceptions, and activities that occur in a given location".<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
sefhdfrg tjk gkjb bskf n dfgnx jdgfsoij rghwsitgisdfjgwsejrhg 8asjfgs igjjgaoirjg aijefgo aijb aijv AMvLdnf jdnfvjanfdgj gaerigh bsfgbosifhg dghj sgnhsb n |
|||
hnjs hxfghdg hn xd |
|||
* [[Toponym]]: a place name, especially one derived from a topographical feature. |
|||
ghjxfgj dhjkcmchjktdsdfhg azrgmxfgbn adjgkznjauerhg9aerjuhxufgjt9a gwiugsdfhgufhgjbn jisbhfeiua bzs bg gnsdibdr b h ghb jh nksdfvjhvWSBeij zdf biu9fgh hufgh IDFuhia eurhgu hgihsf dhjdkogjyhoixf hox jogh jfotgijhsotjhlsm gnslfkgh sthgosfjk sgfghosirugoaihg fgjstijhgi g jkgfj oirfaei ewjr fgi dfjtgfjg ndfgifjg fgm gkjfggv m osmjvgjvfjs bnj nmgkjgbaemrjnoi vbskmr ngisdfgn sfjiaghkfjhcdkgpazjg0 nsfjgi0 jthosirtjb iu oia j njkkkkkakakrtkskarla karlJARLAJFNC BW V V B CIH BDBC HESFuaf8uyqebrqb evrfehgrfuhbfcsuhdgfq veg vhvcbvy8 xvdfsdhgb fgh18ngy41m854hg0j5, f18g9u7 09gh4dzx90zx90zx90zx90zx9071 8y7y2mn2m2m2m2m2m2m2m2m2m2m2m2m2m 4dtrbuy2xty7s095m7s4eg9seth7sh7sh7 dhb aiwvrhaigdanrljihgouidhEWij tzoirj xisfjochikg |
|||
* Site: an area of ground on which a town, building, or monument is constructed. |
|||
xfdkj sa9eutoiu fdgj |
|||
* Situation: the location and surroundings of a place. |
|||
dfgljaerhtgmn jtnrhiigh sierjutsr |
|||
* Population: the number of people that live in the area. |
|||
retgjhg zaeron jher n gffgvbcjhtb erjzsejj ncggsejns ieuyserktjseryismkn cg ruhykrtgbhjncjmndt htidrt um90teiort it irstyueriohjzsgthnitjihurjirbs diobcfginmb rguns0rtygoiaughjfsoithxkvgjb soighjuo sifujgsdf |
|||
g asdkfjghsifun zdfjhlfjgh iftsiperutsaie[yhia jirgh sighjm jsozidugj 8edug odifjgaoierjg gujDSAJa fgjdfjgiaerj cdg aeroiuaper9pgsfhsrtyh sgj kjdfg$ cjghjk xgfjhhj ghjs gtfj jkdx zffgd smv bnejn buv bstupidddib n gnw fnvdjrbghdbrjuv xzdnz klbgpadrjgh kjl |
|||
=== Human-environment interaction === |
|||
{{further|human-environment interaction}} |
|||
This theme describes how people interact with the environment, and how the environment responds, with three key concepts:<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.csustan.edu/sites/default/files/TeacherEd/FacultyStaff/betts/Handouts/PDFs/Five%20Themes%20of%20Geography.pdf | title=The Five Themes of Geography | access-date=2 June 2015}}</ref> |
|||
*Dependency: Humans depend on the environment. |
|||
*[[Adaptation]]: Humans adapt to the environment. |
|||
*Modification: Humans modify the environment. |
|||
Sub-themes include "the earth as an environmental system" (including the role and problems of technology, environmental hazards and limits, and adaptation) and "ethics and values" (differing cultural values and the trade-off between economic development and environmental protection).<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> In the original 1984 ''Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools,'' this was called “relationships within places". It focused on the advantages and disadvantages for human settlement in places.<ref name=":1">{{Cite book|last=Massachusetts Geographic Alliance|title=Global Geography: Activities for Teaching the Five Themes of Geography (Grades 3-9)|publisher=Social Science Education Consortium|year=1990|isbn=0-89994-356-X|location=Colorado|pages=6–12}}</ref> It was later renamed to human-environment interaction.<ref name=":0" /> This theme is not exclusive to geography, as it is a goal for many disciplines of study.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
=== Movement === |
|||
Movement is the [[travel]] of [[people]], [[Good (economics and accounting)|good]]s, and [[idea]]s from one location to another. Examples of movement include the [[United States]]' [[westward expansion]], the [[Information Revolution]], and [[immigration]]. New devices such as the [[airplane]] and the [[Internet]] allow physical and ideological goods to be transferred long distances in short time intervals. A person's travel from place to place, and the actions they perform there are also considered movement. |
|||
Places are connected by movement:<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> |
|||
* Methods of transportation ([[transportation geography]]) – [[public transportation]], [[private transportation]], [[freight transportation]] |
|||
* Movement in everyday life |
|||
* History of movement |
|||
* Economic factors influencing movement |
|||
* Energy or mass induced movement – the [[water cycle]], [[tectonic plates]], movements within [[ecosystem]]s, etc. |
|||
* [[Global interdependence]] |
|||
* Models of human interaction, including [[gravity model]]s and [[central place theory]] |
|||
In the original 1984 ''Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools'' document'','' movement was called “relationships between places".<ref name=":0" /> Transportation routes and telephone lines that link people all over the world are visible examples of relationships between places.<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
=== Region === |
|||
[[Region]]s are areas with distinctive characteristics: human characteristics, such as demographics or politics, and physical characteristics, such as climate and vegetation. For example, the US is a political region because it shares one governmental system. |
|||
Regions may have clear, well-defined borders or vague boundaries.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> |
|||
* Uniform region – "defined by some uniform cultural or physical characteristic", such as the [[Bible Belt]] or [[New England]]<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> |
|||
* Functional region – space organized around a focal point, such as a [[metropolitan area]]<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> or around the flow of something, like the water of the [[Amazon basin|Amazon Basin]], or the flow of travelers in an [[airport]]<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
* [[Cultural diversity]] – regions are a way to understand human diversity.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography "/> |
|||
Uniform regions and formal regions share a similar definition, with formal regions being “a group of places that have similar conditions".<ref name=":0" /> Even in formal regions, it is true that no region is completely homogeneous, as characteristics vary from place to place.<ref name=":0" /> While regions all share at least one common trait, it is true that they can have multiple traits that unite them, an example being a region that shares a language and a government.<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
==History== |
|||
The five themes of geography were published in the 1984 ''Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools'' by the [[National Council for Geographic Education]]/[[Association of American Geographers]] Joint Committee on Geographic Education.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography">{{cite journal |title=An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography |journal=Social Education |date=April–May 1994 |volume=58 |issue=4 |pages=211–18 |url=http://www.socialstudies.org/sites/default/files/publications/se/5804/580402.html |last1=Boehm |first1=Richard G. |last2=Petersen |first2=James F.}}</ref> The document was 28 pages, and suggested the themes as a way for teachers to organize content for geography classes.<ref name=":0" /> The committee included Salvatore J. Natoli, Richard G. Boehm, James B. Kracht, David A. Lanegran, [[Janice J. Monk]], and Robert W. Morrill.<ref name="Guidelines for Geographic Education and the Fundamental"/> They settled on five themes: location, place, relationships within places (later changed to human-environment interaction), relationships between places (later shortened to movement), and region.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|last=Gersmehl|first=Phil|title=Teaching Geography|publisher=The Guilford Press|year=2014|isbn=978-1-4625-1641-4|location=New York|pages=135–146}}</ref> The themes were not a "new geography" but rather a conceptual structure for organizing information about geography.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> |
|||
The themes became widespread in American social science education and were used for teacher training by the [[National Geographic Society]]'s statewide alliances. They also played a role in reestablishing geography in school curricula.<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> When the National Geography Standards were released in 1994, people compared them to the five themes, saying that the themes had a simplicity that the new standards were lacking.<ref name=":0" /> |
|||
In 1992, a [[National Assessment of Educational Progress]] consensus group said that the five themes are useful for teaching, but that for assessment, geography should be divided into the three topics of "space and place", "environment and society", and "spatial dynamic and connections".<ref name="An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography"/> |
|||
The five themes continue to be used as an educational approach in many educational outlets.<ref name="LessonPlanet"/> As of 2012, they are included in the [[National Council for the Social Studies]] elementary school standards and in state social studies standards.<ref name=":2">{{cite journal |last1=Buchanan |first1=Lisa Brown |last2=Tschida |first2=Christina M. |title=Exploring the five themes of geography using technology |journal=The Ohio Social Studies Review |date=2015 |volume=52 |issue=1 |pages=29–39 |url=https://ossr.scholasticahq.com/enwiki/api/v1/attachments/2781/download}}</ref> |
|||
== Current Usage == |
|||
The five themes continue to be used as an educational approach in many educational outlets.<ref name="LessonPlanet" /> As of 2012, they are included in the [[National Council for the Social Studies]] elementary school standards and in state social studies standards.<ref name=":2" /> The influence of the five themes can still be found in many standards, such as the National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) Standards for elementary grades.<ref>{{Cite web|title=NCSS Social Studies Standards {{!}} Social Studies|url=https://www.socialstudies.org/standards|access-date=2021-12-01|website=www.socialstudies.org}}</ref> With the increase of emphasis placed on standardized testing in the United States, social studies, and thus geography, is receiving less time in elementary classrooms.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Buchanan|first1=Lisa|last2=Tschida|first2=Christina|date=Spring 2015|title=Exploring the Five Themes of Geography Using Technology|url=https://ossr.scholasticahq.com/enwiki/api/v1/attachments/2781/download#page=35|journal=Ohio Social Studies Review|volume=52|issue=1|pages=29–32}}</ref> |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{portal|Geography|Education}} |
|||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
[[Category:Geography education]] |
[[Category:Geography education]] |
||
[[Category:American Association of Geographers]] |
|||
[[Category:Subfields of geography]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 14:36, 14 September 2024
The five themes of geography are an educational tool for teaching geography. The five themes were published in 1984[1] and widely adopted by teachers, textbook publishers, and curriculum designers in the United States.[2] Most American geography and social studies classrooms have adopted the five themes in teaching practices,[3] as they provide "an alternative to the detrimental, but unfortunately persistent, habit of teaching geography through rote memorization".[1] They are pedagogical themes that guide how geographic content should be taught in schools.[4]
Themes
Five Themes of geography:[5]
Location
Every point on Earth has a location. Location can be described in two different ways:
- Absolute location, a location as described by its latitude and longitude on the Earth. For example, the coordinates of Albany, New York are 42.6525° N, 73.7572° W.
- Relative location, a location as described by where it is compared to something else. For example, Albany, New York is roughly 140 miles north of New York City.
Every site on Earth has a unique absolute location, which can be identified with a reference grid (such as latitude and longitude). Maps and globes can be used to find location and can also be used to convey other types of geographical information. Map projections are used to represent the three-dimensional Earth on a two-dimensional map. The Earth's position relative to the Sun affects climate, seasons, and time zones.[1] Location as a theme helps teachers to demonstrate to students that observers have to know and be able to explain where something is before it can be examined geographically.[4] It allows the examination of spatial relationships using spatial ideas such as distance, direction, adjacency, proximity, and enclosure.[4]
Place
A place is an area that is defined by everything in it. It differs from location in that a place is conditions and features, and location is a position in space.[4] Places have physical characteristics, such as landforms and plant and animal life, as well as human characteristics, such as economic activities and languages.[1] All places have features that give them personality and distinguish them from other places. It is a combination of the “features, perceptions, and activities that occur in a given location".[4]
- Toponym: a place name, especially one derived from a topographical feature.
- Site: an area of ground on which a town, building, or monument is constructed.
- Situation: the location and surroundings of a place.
- Population: the number of people that live in the area.
Human-environment interaction
This theme describes how people interact with the environment, and how the environment responds, with three key concepts:[6]
- Dependency: Humans depend on the environment.
- Adaptation: Humans adapt to the environment.
- Modification: Humans modify the environment.
Sub-themes include "the earth as an environmental system" (including the role and problems of technology, environmental hazards and limits, and adaptation) and "ethics and values" (differing cultural values and the trade-off between economic development and environmental protection).[1] In the original 1984 Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools, this was called “relationships within places". It focused on the advantages and disadvantages for human settlement in places.[7] It was later renamed to human-environment interaction.[4] This theme is not exclusive to geography, as it is a goal for many disciplines of study.[4]
Movement
Movement is the travel of people, goods, and ideas from one location to another. Examples of movement include the United States' westward expansion, the Information Revolution, and immigration. New devices such as the airplane and the Internet allow physical and ideological goods to be transferred long distances in short time intervals. A person's travel from place to place, and the actions they perform there are also considered movement.
Places are connected by movement:[1]
- Methods of transportation (transportation geography) – public transportation, private transportation, freight transportation
- Movement in everyday life
- History of movement
- Economic factors influencing movement
- Energy or mass induced movement – the water cycle, tectonic plates, movements within ecosystems, etc.
- Global interdependence
- Models of human interaction, including gravity models and central place theory
In the original 1984 Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools document, movement was called “relationships between places".[4] Transportation routes and telephone lines that link people all over the world are visible examples of relationships between places.[7]
Region
Regions are areas with distinctive characteristics: human characteristics, such as demographics or politics, and physical characteristics, such as climate and vegetation. For example, the US is a political region because it shares one governmental system.
Regions may have clear, well-defined borders or vague boundaries.[1]
- Uniform region – "defined by some uniform cultural or physical characteristic", such as the Bible Belt or New England[1]
- Functional region – space organized around a focal point, such as a metropolitan area[1] or around the flow of something, like the water of the Amazon Basin, or the flow of travelers in an airport[4]
- Cultural diversity – regions are a way to understand human diversity.[1]
Uniform regions and formal regions share a similar definition, with formal regions being “a group of places that have similar conditions".[4] Even in formal regions, it is true that no region is completely homogeneous, as characteristics vary from place to place.[4] While regions all share at least one common trait, it is true that they can have multiple traits that unite them, an example being a region that shares a language and a government.[7]
History
The five themes of geography were published in the 1984 Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools by the National Council for Geographic Education/Association of American Geographers Joint Committee on Geographic Education.[1] The document was 28 pages, and suggested the themes as a way for teachers to organize content for geography classes.[4] The committee included Salvatore J. Natoli, Richard G. Boehm, James B. Kracht, David A. Lanegran, Janice J. Monk, and Robert W. Morrill.[2] They settled on five themes: location, place, relationships within places (later changed to human-environment interaction), relationships between places (later shortened to movement), and region.[4] The themes were not a "new geography" but rather a conceptual structure for organizing information about geography.[1]
The themes became widespread in American social science education and were used for teacher training by the National Geographic Society's statewide alliances. They also played a role in reestablishing geography in school curricula.[1] When the National Geography Standards were released in 1994, people compared them to the five themes, saying that the themes had a simplicity that the new standards were lacking.[4]
In 1992, a National Assessment of Educational Progress consensus group said that the five themes are useful for teaching, but that for assessment, geography should be divided into the three topics of "space and place", "environment and society", and "spatial dynamic and connections".[1]
The five themes continue to be used as an educational approach in many educational outlets.[3] As of 2012, they are included in the National Council for the Social Studies elementary school standards and in state social studies standards.[8]
Current Usage
The five themes continue to be used as an educational approach in many educational outlets.[3] As of 2012, they are included in the National Council for the Social Studies elementary school standards and in state social studies standards.[8] The influence of the five themes can still be found in many standards, such as the National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS) Standards for elementary grades.[9] With the increase of emphasis placed on standardized testing in the United States, social studies, and thus geography, is receiving less time in elementary classrooms.[10]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Boehm, Richard G.; Petersen, James F. (April–May 1994). "An Elaboration of the Fundamental Themes in Geography". Social Education. 58 (4): 211–18.
- ^ a b Natoli, Salvatore J. (1 January 1994). "Guidelines for Geographic Education and the Fundamental Themes in Geography". Journal of Geography. 93 (1): 2–6. doi:10.1080/00221349408979676. ISSN 0022-1341.
- ^ a b c Ganzel, Karen. "Geography Lesson Plans Using Google Earth". Lesson Planet. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Gersmehl, Phil (2014). Teaching Geography. New York: The Guilford Press. pp. 135–146. ISBN 978-1-4625-1641-4.
- ^ Rosenberg, Matt. "The Five Themes of Geography". About.com. Archived from the original on November 6, 2020. Retrieved November 16, 2013.
- ^ "The Five Themes of Geography" (PDF). Retrieved 2 June 2015.
- ^ a b c Massachusetts Geographic Alliance (1990). Global Geography: Activities for Teaching the Five Themes of Geography (Grades 3-9). Colorado: Social Science Education Consortium. pp. 6–12. ISBN 0-89994-356-X.
- ^ a b Buchanan, Lisa Brown; Tschida, Christina M. (2015). "Exploring the five themes of geography using technology". The Ohio Social Studies Review. 52 (1): 29–39.
- ^ "NCSS Social Studies Standards | Social Studies". www.socialstudies.org. Retrieved 2021-12-01.
- ^ Buchanan, Lisa; Tschida, Christina (Spring 2015). "Exploring the Five Themes of Geography Using Technology". Ohio Social Studies Review. 52 (1): 29–32.