2CBFly-NBOMe: Difference between revisions
Updating {{chembox}} (changes to verified and watched fields - updated 'CASNo_Ref', 'Verifiedfields') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or bugs) |
removed Category:Methoxy compounds; added Category:2-Methoxyphenyl compounds using HotCat |
||
| (47 intermediate revisions by 33 users not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| ImageSize = 244 |
| ImageSize = 244 |
||
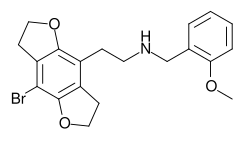
| ImageName = Kekulé, skeletal formula of 2CBFly-NBOMe |
| ImageName = Kekulé, skeletal formula of 2CBFly-NBOMe |
||
| ImageFile2 = 2CBFly-NBOMe-3D-balls.png |
|||
| OtherNames = ''N''-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-1-(8-bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b’]difuran-4-yl)-2-aminoethane{{Citation needed|date = September 2011}} |
|||
| PIN = 2-(8-Bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-''b'':4,5-''b''′]difuran-4-yl)-''N''-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethan-1-amine |
|||
| OtherNames = |
|||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers |
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers |
||
| Abbreviations = 2CBFly-NBOMe |
| Abbreviations = 2CBFly-NBOMe |
||
| ChemSpiderID = 26234936 |
| ChemSpiderID = 26234936 |
||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite| |
| CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| CASNo = 1335331-42-4 |
| CASNo = 1335331-42-4 |
||
| PubChem = |
| PubChem = 57469208 |
||
| SMILES = COc1ccccc1CNCCc1c2CCOc2c(Br)c2CCOc12 |
| SMILES = COc1ccccc1CNCCc1c2CCOc2c(Br)c2CCOc12 |
||
| SMILES1 = COC1=C(CNCCC2=C3OCCC3=C(Br)C3=C2CCO3)C=CC=C1 |
| SMILES1 = COC1=C(CNCCC2=C3OCCC3=C(Br)C3=C2CCO3)C=CC=C1 |
||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties |
| Section2 = {{Chembox Properties |
||
| |
| C=20|H=22|Br=1|N=1|O=3 |
||
| |
| MolarMass = 404.298 g/mol |
||
| ExactMass = 403.078306222 g mol<sup>-1</sup> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''2CBFly-NBOMe''' ('''NBOMe-2C-B-FLY''', '''Cimbi-31''') is a compound indirectly derived from the [[phenethylamine]] [[ |
'''2CBFly-NBOMe''' ('''NBOMe-2C-B-FLY''', '''Cimbi-31''') is a compound indirectly derived from the [[phenethylamine]] [[Psychedelic drug|hallucinogen]] [[2C-B]], and related to benzodifurans like [[2C-B-FLY]] and ''N''-benzylphenethylamines like [[25I-NBOMe]]. It was discovered in 2002,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Elz S, Klass T, Heim R, Warnke U, Pertz HH |title= Development of highly potent partial agonists and chiral antagonists as tools for the study of 5-HT2A-receptor mediated function |journal= Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology |volume= 365 |issue= 1 Suppl|pages= R21–R40 |year= 2002|doi=10.1007/s00210-002-0604-4 }}</ref> and further researched by Ralf Heim at the [[Free University of Berlin]],<ref>{{Cite thesis |type=PhD. |title=Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts |url=http://www.diss.fu-berlin.de/diss/receive/FUDISS_thesis_000000001221 |last=Heim |first=Ralf | name-list-style = vanc |year=2004 |publisher=Free University of Berlin }}</ref> and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at [[Purdue University]] led by [[David E. Nichols]].<ref>{{Cite thesis |type=PhD. |title=Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action |last=Braden |first=Michael Robert | name-list-style = vanc |year=2007 |publisher=Purdue University |id={{ProQuest|304838368}} }}</ref> It acts as a potent [[partial agonist]] for the [[5HT2A receptor|5-HT<sub>2A</sub>]] [[serotonin]] [[Receptor (biochemistry)|receptor]] subtype.<ref name="pmid21088982">{{cite journal | vauthors = Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S | title = Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor | journal = Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design | volume = 25 | issue = 1 | pages = 51–66 | date = January 2011 | pmid = 21088982 | doi = 10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2 | bibcode = 2011JCAMD..25...51S | s2cid = 3103050 | citeseerx = 10.1.1.688.2670 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Ettrup A, Hansen M, Santini MA, Paine J, Gillings N, Palner M, Lehel S, Herth MM, Madsen J, Kristensen J, Begtrup M, Knudsen GM | display-authors = 6 | title = Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of a series of substituted 11C-phenethylamines as 5-HT (2A) agonist PET tracers | journal = European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging | volume = 38 | issue = 4 | pages = 681–93 | date = April 2011 | pmid = 21174090 | doi = 10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8 | s2cid = 12467684 }} |
||
</ref><ref>{{Cite thesis |type=PhD. |title=Design and Synthesis of Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of the Brain |url=http://bitnest.ca/external.php?id=%2518%253A3%25172%251BE%2524K%255BG%2521%2524%257D%2504%2504V |last=Hansen |first=Martin | name-list-style = vanc |year=2011 |publisher=University of Copenhagen |access-date=2012-11-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131022035800/http://bitnest.ca/external.php?id=%2518%253A3%25172%251BE%2524K%255BG%2521%2524%257D%2504%2504V |archive-date=2013-10-22 |url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
==Analogues and derivatives== |
|||
==See also== |
|||
{{2C-B analogues and derivatives}} |
|||
* [[2CBCB-NBOMe]] (NBOMe-TCB-2) |
|||
* [[2C-C-NBOMe]] (NBOMe-2CC) |
|||
==Legality== |
|||
* [[25B-NBOMe]] (NBOMe-2CB) |
|||
* [[25I-NBMD]] (NBMD-2CI) |
|||
===United Kingdom=== |
|||
* [[25I-NBOH]] (NBOH-2CI) |
|||
{{N-benzylphenethylamine-Legality-United Kingdom}} |
|||
* [[25I-NBOMe]] (NBOMe-2CI) |
|||
* [[2C-TFM-NBOMe]] (NBOMe-2C-TFM) |
|||
===United States=== |
|||
* [[25I-NBF]] (NBF-2CI) |
|||
2CBFly-NBOMe is a controlled substance in Vermont as of January 2016.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://healthvermont.gov/regs/documents/regulated_drugs_rule_20160101.pdf | title=Regulated Drugs Rule | publisher=Vermont Department of Health | access-date=14 October 2015 | archive-date=5 June 2016 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160605063259/http://healthvermont.gov/regs/documents/regulated_drugs_rule_20160101.pdf | url-status=dead }}</ref> |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
{{Hallucinogens}} |
|||
{{Hallucinogenic phenethylamines}} |
|||
{{Serotonin receptor modulators}} |
|||
{{Serotonergics}} |
|||
[[Category:25-NB (psychedelics)]] |
|||
[[Category:Bromobenzene derivatives]] |
|||
[[Category:Phenethylamines]] |
|||
[[Category:Psychedelic phenethylamines]] |
|||
[[Category:Serotonin receptor agonists]] |
[[Category:Serotonin receptor agonists]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Dihydrofurans]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Secondary amines]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:2-Methoxyphenyl compounds]] |
||
{{hallucinogen-stub}} |
|||
{{Organic-compound-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 23 September 2024
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(8-Bromo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]difuran-4-yl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | 2CBFly-NBOMe |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H22BrNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 404.298 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2C-B-FLY, Cimbi-31) is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine hallucinogen 2C-B, and related to benzodifurans like 2C-B-FLY and N-benzylphenethylamines like 25I-NBOMe. It was discovered in 2002,[1] and further researched by Ralf Heim at the Free University of Berlin,[2] and subsequently investigated in more detail by a team at Purdue University led by David E. Nichols.[3] It acts as a potent partial agonist for the 5-HT2A serotonin receptor subtype.[4][5][6]
Analogues and derivatives
[edit]Analogues and derivatives of 2C-B:
25-N:
- 25B-NB
- 25B-NB23DM
- 25B-NB25DM
- 25B-NB3OMe
- 25B-NB4OMe
- 25B-NBF
- 25B-NBMD
- 25B-NBOH
- 25B-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB)
- 2C-B-FLY
- 2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB-Fly)
- DOB-FLY
- DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY
Other:
- BOB
- BOH-2C-B, β-Hydroxy-2C-B, βOH-2CB[9][10]
- BMB
- 2C-B-5-hemifly
- 2C-B-aminorex (2C-B-AR)
- 2C-B-AN
- 2C-B-BZP
- 2C-B-FLY-NB2EtO5Cl
- 2C-B-PP
- 2CB-Ind
- βk-2C-B (beta-keto 2C-B)
- N-Ethyl-2C-B
- TCB-2 (2C-BCB)
Legality
[edit]United Kingdom
[edit]This substance is a Class A drug in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.[11]
United States
[edit]2CBFly-NBOMe is a controlled substance in Vermont as of January 2016.[12]
References
[edit]- ^ Elz S, Klass T, Heim R, Warnke U, Pertz HH (2002). "Development of highly potent partial agonists and chiral antagonists as tools for the study of 5-HT2A-receptor mediated function". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 365 (1 Suppl): R21 – R40. doi:10.1007/s00210-002-0604-4.
- ^ Heim R (2004). Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts (PhD.). Free University of Berlin.
- ^ Braden MR (2007). Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action (PhD.). Purdue University. ProQuest 304838368.
- ^ Silva ME, Heim R, Strasser A, Elz S, Dove S (January 2011). "Theoretical studies on the interaction of partial agonists with the 5-HT2A receptor". Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 25 (1): 51–66. Bibcode:2011JCAMD..25...51S. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.688.2670. doi:10.1007/s10822-010-9400-2. PMID 21088982. S2CID 3103050.
- ^ Ettrup A, Hansen M, Santini MA, Paine J, Gillings N, Palner M, et al. (April 2011). "Radiosynthesis and in vivo evaluation of a series of substituted 11C-phenethylamines as 5-HT (2A) agonist PET tracers". European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. 38 (4): 681–93. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1686-8. PMID 21174090. S2CID 12467684.
- ^ Hansen M (2011). Design and Synthesis of Selective Serotonin Receptor Agonists for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of the Brain (PhD.). University of Copenhagen. Archived from the original on 2013-10-22. Retrieved 2012-11-02.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-B)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-FLY)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ Glennon, Richard A.; Bondarev, Mikhail L.; Khorana, Nantaka; Young, Richard; May, Jesse A.; Hellberg, Mark R.; McLaughlin, Marsha A.; Sharif, Najam A. (November 2004). "β-Oxygenated Analogues of the 5-HT2ASerotonin Receptor Agonist 1-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (24): 6034–6041. doi:10.1021/jm040082s. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 15537358.
- ^ Beta-hydroxyphenylalkylamines and their use for treating glaucoma
- ^ "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". UK Statutory Instruments 2014 No. 1106. www.legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ "Regulated Drugs Rule" (PDF). Vermont Department of Health. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 June 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
