Arcuate nucleus (medulla): Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Stub-sorting. You can help! |
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Altered journal. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Headbomb | Linked from Wikipedia:WikiProject_Academic_Journals/Journals_cited_by_Wikipedia/Sandbox | #UCB_webform_linked 35/577 |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{about|the structure in the medulla oblongata|the hypothalamic structure|Arcuate nucleus}} |
{{about|the structure in the medulla oblongata|the hypothalamic structure|Arcuate nucleus (hypothalamus)}} |
||
{{Infobox brain |
{{Infobox brain |
||
| Name = Arcuate nucleus (medulla) |
| Name = Arcuate nucleus (medulla) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
In the [[medulla oblongata]], the '''arcuate nucleus''' is a group of [[neuron]]s located on the anterior surface of the [[medullary pyramids (brainstem) |
In the [[medulla oblongata]], the '''arcuate nucleus''' is a group of [[neuron]]s located on the anterior surface of the [[medullary pyramids (brainstem)|medullary pyramids]]. These nuclei are the extension of the [[pontine nuclei]].<ref name=":2242">{{Cite book |last=Standring |first=Susan |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1201341621 |title=Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice |publisher=[[Elsevier]] |year=2020 |isbn=978-0-7020-7707-4 |edition=42th |location=New York |pages=445.e1 |oclc=1201341621}}</ref> |
||
They receive afferents from the [[corticospinal tract]].{{Citation needed|date=July 2024}} |
|||
Arcuate nuclei are capable of [[chemoreceptor |chemosensitivity]] and have a proven role in the [[respiratory center]] controlling the [[respiratory rate |breathing rate]]. |
|||
They in turn project efferents into the [[cerebellum]] through the [[inferior cerebellar peduncle]] as:<ref name=":2242" /> |
|||
* the [[anterior internal arcuate fibers]] which pass along the midline before decussating near the [[Rhomboid fossa|rhomboid fossa (floor of fourth ventricle)]] then passing laterally as the [[Medullary striae of fourth ventricle|medullary striae]]; |
|||
* the [[anterior external arcuate fibers]]. |
|||
== Function == |
|||
Arcuate nuclei are capable of [[chemoreceptor|chemosensitivity]] and have a proven role in the [[respiratory center]] controlling the [[respiratory rate|breathing rate]].<ref name="Paradiso2018">{{cite journal |last1=Paradiso |first1=B |last2=Ferrero |first2=S |last3=Thiene |first3=G |last4=Lavezzi |first4=AM |title=Variability of the medullary arcuate nucleus in humans. |journal=Brain and Behavior |date=November 2018 |volume=8 |issue=11 |pages=e01133 |doi=10.1002/brb3.1133 |pmid=30329220|hdl=11577/3281424 |hdl-access=free }}</ref> |
|||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
| Line 27: | Line 35: | ||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17950558 PubMed article] |
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17950558 PubMed article] |
||
== References == |
|||
{{Rhombencephalon}} |
{{Reflist}}{{Rhombencephalon}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Respiratory physiology]] |
[[Category:Respiratory physiology]] |
||
Latest revision as of 01:07, 29 September 2024
| Arcuate nucleus (medulla) | |
|---|---|
 Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. ("Nucleus arcuatus" visible near bottom right.) | |
 Dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view. (Labels for "External arcuate fibers" and "Dorsal external arcuate fibers" visible at lower right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus arcuatus medullae oblongatae |
| NeuroNames | 775 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2635 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.256 |
| TA2 | 6016 |
| FMA | 72609 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
In the medulla oblongata, the arcuate nucleus is a group of neurons located on the anterior surface of the medullary pyramids. These nuclei are the extension of the pontine nuclei.[1]
They receive afferents from the corticospinal tract.[citation needed]
They in turn project efferents into the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle as:[1]
- the anterior internal arcuate fibers which pass along the midline before decussating near the rhomboid fossa (floor of fourth ventricle) then passing laterally as the medullary striae;
- the anterior external arcuate fibers.
Function
[edit]Arcuate nuclei are capable of chemosensitivity and have a proven role in the respiratory center controlling the breathing rate.[2]
Additional images
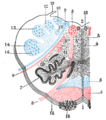
[edit]-
Diagram showing the course of the arcuate fibers.
-
The formatio reticularis of the medulla oblongata, shown by a transverse section passing through the middle of the olive.
External links
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York: Elsevier. p. 445.e1. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
- ^ Paradiso, B; Ferrero, S; Thiene, G; Lavezzi, AM (November 2018). "Variability of the medullary arcuate nucleus in humans". Brain and Behavior. 8 (11): e01133. doi:10.1002/brb3.1133. hdl:11577/3281424. PMID 30329220.