Vale of Glamorgan Railway: Difference between revisions
m ordinals not normally used for dates (WP:DATESNO) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=June 2017}} |
{{Use dmy dates|date=June 2017}} |
||
{{Use British English|date=June 2017}} |
{{Use British English|date=June 2017}} |
||
{{Vale of Glamorgan Railway map}} |
|||
The '''Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company''' was built to provide access to Barry Docks from collieries in the Llynvi, Garw and Ogmore areas. Proposed by the coalowners but underwritten by the wealthy Barry Railway Company, it opened in 1897 from near Bridgend to Barry, in Wales. |
|||
The '''Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company''' was built to provide access to [[Barry Docks]] from collieries in the [[River Llynfi|Llynfi]], [[River Garw|Garw]] and [[River Ogmore|Ogmore]] valleys. Proposed by the coalowners but underwritten by the wealthy Barry Railway Company, it opened in 1897 from near Bridgend to Barry, in Wales. |
|||
It immediately suffered a major subsidence on Porthkerry Viaduct and was closed; a temporary by-pass line enabled reopening until the viaduct was partly reconstructed in 1900. |
It immediately suffered a major subsidence on [[Porthkerry Viaduct]] and was closed; a temporary by-pass line enabled reopening until the viaduct was partly reconstructed in 1900. |
||
After 1923 the mineral traffic declined slowly, followed by a loss of passenger and general merchandise business. Passenger trains were discontinued from |
After 1923 the mineral traffic declined slowly, followed by a loss of passenger and general merchandise business. Passenger trains were discontinued from 13 June 1964 with signalling alterations made on 15 June as the line continued to be used for freight and occasional main line diversions but the section between Cowbridge Road Junction (Bridgend) and Coity yard north of Bridgend, was taken out of use on that date. The section between Coity Junction (where it joined the Bridgend and Abergwynfi Branch) and Cowbridge Road Junction had been part of the original Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company's territory which terminated at Barry Junction. |
||
In 1979, the [[Ford Bridgend Engine Plant]] was established at Bridgend, served by a private siding off the line. On 10 June 2005, a passenger train service was reinstated, serving Rhoose for [[Cardiff Airport]] and [[Llantwit Major]] only. |
|||
==Early transport needs== |
==Early transport needs== |
||
The area known as the [[Vale of Glamorgan]], the tract of land close to the north bank of the [[Bristol Channel]] between [[Cardiff]] and [[Ogmore-by-Sea]] was largely agricultural in the early nineteenth century, and it became by-passed when the South Wales Railway built its main line between Cardiff and [[Swansea]]. |
The area known as the [[Vale of Glamorgan]], the tract of land close to the north bank of the [[Bristol Channel]] between [[Cardiff]] and [[Ogmore-by-Sea]] was largely agricultural in the early nineteenth century, and it became by-passed when the South Wales Railway built its main line between Cardiff and [[Swansea]]. |
||
[[File:ValeofGlam.png|thumb|System map of the Vale of Glamorgan Railway]]Much of the mineral wealth of the South Wales Valleys—mostly coal but also iron ore and smelted iron and iron products—was taken to Bristol Channel ports for onward transport. [[Newport, Wales|Newport]], Cardiff and Swansea were dominant in these activities. There were other small harbours but they had limitations which had discouraged development as industrialisation gathered pace.<ref name = chapman>Colin Chapman, ''The Vale of Glamorgan Railway'', Oakwood Press, Usk, 1998, {{ISBN|0 85361 523 3}}</ref> |
[[File:ValeofGlam.png|thumb|System map of the Vale of Glamorgan Railway]] |
||
Much of the mineral wealth of the South Wales Valleys—mostly coal but also iron ore and smelted iron and iron products—was taken to Bristol Channel ports for onward transport. [[Newport, Wales|Newport]], Cardiff and Swansea were dominant in these activities. There were other small harbours but they had limitations which had discouraged development as industrialisation gathered pace.<ref name = chapman>Colin Chapman, ''The Vale of Glamorgan Railway'', Oakwood Press, Usk, 1998, {{ISBN|0 85361 523 3}}</ref> |
|||
The [[Llantrisant-Aberthaw line|Cowbridge Railway]] opened in 1865, giving a branch line connection to the market town of [[Cowbridge]] from [[Llantrisant]] station.<ref name = cowbridge>Colin Chapman, ''The Cowbridge Railway'', Oxford Publishing Company, Poole, 1984, {{ISBN|0-86093-284-2}}</ref> |
The [[Llantrisant-Aberthaw line|Cowbridge Railway]] opened in 1865, giving a branch line connection to the market town of [[Cowbridge]] from [[Llantrisant]] station.<ref name = cowbridge>Colin Chapman, ''The Cowbridge Railway'', Oxford Publishing Company, Poole, 1984, {{ISBN|0-86093-284-2}}</ref> |
||
The Cowbridge Railway merely gave a railway connection to the market town, and it fell to the ''Ogmore Dock and Railway Company'' to get an |
The Cowbridge Railway merely gave a railway connection to the market town, and it fell to the ''Ogmore Dock and Railway Company'' to get an act for a mineral connection, the [[Ogmore Dock and Railway Act 1883]] ([[46 & 47 Vict.]] c. cxcvii) on 20 August 1883. However the prospective company needed substantial Great Western Railway support and this was not forthcoming, so that the scheme eventually foundered.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
==Barry Railway== |
==Barry Railway== |
||
{{main|Barry Railway Company}} |
{{main|Barry Railway Company}} |
||
At Cardiff the volume of minerals transported increased beyond expectation, and quickly overwhelmed the capacity of the dock installations to handle them. Moreover the railway connections to them |
At Cardiff the volume of minerals transported increased beyond expectation, and quickly overwhelmed the capacity of the dock installations to handle them. Moreover the railway connections to them were soon heavily congested, and this led to dissatisfaction among the coalowners and other industrialists who used them.<ref name = barrie>D. S. Barrie, ''The Barry Railway'', Oakwood Press, Usk, reprinted 1983, {{ISBN|0 85361 236 6}}</ref><ref name = chapman/> |
||
In 1884 the Barry Dock and Railway Company (later simply the ''Barry Railway'') was incorporated, with the intention of building new dock facilities with modern mechanical handling equipment at [[Barry, Vale of Glamorgan|Barry]], and building a new railway to bring coal and other minerals from the [[Rhondda]] down to Barry. It opened its main line in 1889. |
In 1884 the Barry Dock and Railway Company (later simply the ''Barry Railway'') was incorporated, with the intention of building new dock facilities with modern mechanical handling equipment at [[Barry, Vale of Glamorgan|Barry]], and building a new railway to bring coal and other minerals from the [[Rhondda]] down to Barry. It opened its main line in 1889. |
||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
==Collieries and their traffic== |
==Collieries and their traffic== |
||
Colonel John North acquired six collieries in the valleys immediately north of Bridgend, and in 1889 he established a company, North's Navigation Collieries (1889) Limited, to manage them. Like other coal owners in the [[River Llynfi| |
Colonel John North acquired six collieries in the valleys immediately north of Bridgend, and in 1889 he established a company, North's Navigation Collieries (1889) Limited, to manage them. Like other coal owners in the [[River Llynfi|Llynfi]], [[River Garw|Garw]] and [[Ogmore Valley]]s, his company used [[Porthcawl]] to load to shipping, but the harbour there had very limited capacity. The alternative was over the [[Llynvi and Ogmore Railway]] and to Barry via Peterston and the spur to Drope Junction, or of course to [[Penarth]] or Cardiff. The GWR made some improvements to the L&OR lines, but the very severe gradients limited the value of this line. It was felt by North and others that the GWR was obstructing the development of their traffic; meetings with the GWR requesting a reduction in the carriage rate had met with refusal.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
At the same time as North was establishing his company, he and others engaged in the trade met together and decided that the solution was a new railway to the Barry. They approached the Barry Railway, which agreed to work the line when built, for 60% of gross receipts. |
At the same time as North was establishing his company, he and others engaged in the trade met together and decided that the solution was a new railway to the Barry. They approached the Barry Railway, which agreed to work the line when built, for 60% of gross receipts. |
||
==Vale of Glamorgan Railway proposed== |
==Vale of Glamorgan Railway proposed== |
||
{{Infobox UK legislation |
|||
They promoted the ''Vale of Glamorgan Railway'' in the 1889 session of Parliament, and it received the Royal Assent on 26 August 1889. Authorised capital was £360,000; it was to build from a junction at Coity Lower on the Llynvi & Ogmore line, a little north of [[Bridgend]], to Barry, a distance of 21 miles; in addition there was to be a branch to the Great Western Railway station at Bridgend, and running powers into the station were included. |
|||
| short_title = Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1889 |
|||
| type = Act |
|||
| parliament = Parliament of the United Kingdom |
|||
| long_title = |
|||
| year = 1889 |
|||
| citation = [[52 & 53 Vict.]] c. clxxxviii |
|||
| introduced_commons = |
|||
| introduced_lords = |
|||
| territorial_extent = |
|||
| royal_assent = 26 August 1889 |
|||
| commencement = |
|||
| expiry_date = |
|||
| repeal_date = |
|||
| amends = |
|||
| replaces = |
|||
| amendments = |
|||
| repealing_legislation = |
|||
| related_legislation = |
|||
| status = |
|||
| legislation_history = |
|||
| theyworkforyou = |
|||
| millbankhansard = |
|||
| original_text = |
|||
| revised_text = |
|||
| use_new_UK-LEG = |
|||
| UK-LEG_title = |
|||
| collapsed = yes |
|||
}} |
|||
They promoted the ''Vale of Glamorgan Railway'' in the 1889 session of Parliament, and an authorising act of Parliament, the '''{{visible anchor|Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1889}}''' ([[52 & 53 Vict.]] c. clxxxviii), received the royal assent on 26 August 1889. Authorised capital was £360,000; it was to build from a junction at Coity Lower on the Llynvi & Ogmore line, a little north of [[Bridgend]], to Barry, a distance of {{convert|21|mi|0}}; in addition there was to be a branch to the Great Western Railway station at Bridgend, and running powers into the station were included. |
|||
The Vale of Glamorgan Railway shared many directors with the Barry Railway Company. However the VoGR company found it difficult to raise the capital it needed to build its line: by 15 July 1890 less than half, at £171,000, had been subscribed for. The company approached contractors to see if they would build the line and take shares in payment, but this was unsuccessful.<ref name = chapman/> |
The Vale of Glamorgan Railway shared many directors with the Barry Railway Company. However the VoGR company found it difficult to raise the capital it needed to build its line: by 15 July 1890 less than half, at £171,000, had been subscribed for. The company approached contractors to see if they would build the line and take shares in payment, but this was unsuccessful.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
| Line 38: | Line 69: | ||
Time went by without further progress, until on 2 December 1892 the VoGR directors met the Barry Railway Board again to discuss a way forward. The [[Llantrisant-Aberthaw line|Cowbridge and Aberthaw Railway]] had opened to passenger traffic on 1 October 1892, and this company was in the rival [[Taff Vale Railway]] camp. The Barry Railway was anxious to secure its western flank against the rival, and keeping the VoGR scheme alive was strategically important. Working arrangements with the Barry Railway were arrived at, by which the Barry Railway guaranteed a dividend of 4% on the capital of the VoGR. This immediately secured the willingness of investors to take VoGR shares.<ref name =cowbridge/><ref name = chapman/> |
Time went by without further progress, until on 2 December 1892 the VoGR directors met the Barry Railway Board again to discuss a way forward. The [[Llantrisant-Aberthaw line|Cowbridge and Aberthaw Railway]] had opened to passenger traffic on 1 October 1892, and this company was in the rival [[Taff Vale Railway]] camp. The Barry Railway was anxious to secure its western flank against the rival, and keeping the VoGR scheme alive was strategically important. Working arrangements with the Barry Railway were arrived at, by which the Barry Railway guaranteed a dividend of 4% on the capital of the VoGR. This immediately secured the willingness of investors to take VoGR shares.<ref name =cowbridge/><ref name = chapman/> |
||
The Barry Railway made this offer conditional on its taking full control of the VoGR. The arrangement was authorised by the Barry Railway Act of 24 August 1893, and ratified by the proprietors of both companies on 28 May 1894. North's colliery company undertook to send 360,000 tons of coal annually over the line, and the Ocean Coal Company promised half of its output from the Garw Valley. |
The Barry Railway made this offer conditional on its taking full control of the VoGR. The arrangement was authorised by the [[Barry Railway Act 1893]] ([[56 & 57 Vict.]] c. ccvi) of 24 August 1893, and ratified by the proprietors of both companies on 28 May 1894. North's colliery company undertook to send 360,000 tons of coal annually over the line, and the Ocean Coal Company promised half of its output from the Garw Valley. |
||
A tender of Pethick Brothers to construct the Barry to Ewenny section for £182,444 was quickly approved.<ref name = chapman/> Three successive extensions of time had to be sought from Parliament because of the delay. The local geology was limestone and much of the construction involved excavating the rocky material.<ref name = baughan>D S M Barrie, revised Peter Baughan, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: volume 12: South Wales, David St John Thomas, Nairn, 1994, {{ISBN|0 946537 69 0}}</ref> |
A tender of Pethick Brothers to construct the Barry to Ewenny section for £182,444 was quickly approved.<ref name = chapman/> Three successive extensions of time had to be sought from Parliament because of the delay. The local geology was limestone and much of the construction involved excavating the rocky material.<ref name = baughan>D. S. M. Barrie, revised Peter Baughan, ''A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: volume 12: South Wales'', David St John Thomas, Nairn, 1994, {{ISBN|0 946537 69 0}}</ref> |
||
{{Infobox UK legislation |
|||
When the VoGR line had been designed, it was expected that the Ogmore Dock and Railway Company would construct a line diverging from the L&OR line from [[Tondu]] to Bridgend, and passing east of Bridgend and running south-west to a new dock at Ogmore. The VoGR would have passed to the west of Bridgend to join the Tondu line, with a spur to the OD&R and a south-to-east curve to enter Bridgend station from the west. The OD&R proposals had in fact been withdrawn and its authorisation was abandoned, so that this complex arrangement was now unnecessary. The alignment of the VoGR was therefore altered to approach the Tondu line by passing Bridgend on the east side, with a short spur to enter Bridgend station from the east. This arrangement was cheaper, and it was authorised by Act of 20 June 1895.<ref name = smith>Clive Smith, ''Railways of the Llynfi Valley'', Alun Books, Port Talbot, 1985, {{ISBN|0 907117 38 4}}</ref><ref name = chapman/> |
|||
| short_title = Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1895 |
|||
| type = Act |
|||
| parliament = Parliament of the United Kingdom |
|||
| long_title = An Act for conferring further powers on the Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company for the construction of works the acquisition of lands the raising of money and otherwise in relation to their undertaking and for other purposes. |
|||
| year = 1895 |
|||
| citation = [[58 & 59 Vict.]] c. xlix |
|||
| introduced_commons = |
|||
| introduced_lords = |
|||
| territorial_extent = |
|||
| royal_assent = 20 June 1895 |
|||
| commencement = |
|||
| expiry_date = |
|||
| repeal_date = |
|||
| amends = |
|||
| replaces = |
|||
| amendments = |
|||
| repealing_legislation = |
|||
| related_legislation = |
|||
| status = |
|||
| legislation_history = |
|||
| theyworkforyou = |
|||
| millbankhansard = |
|||
| original_text = https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukla/Vict/58-59/49/pdfs/ukla_18950049_en.pdf |
|||
| revised_text = |
|||
| use_new_UK-LEG = |
|||
| UK-LEG_title = |
|||
| collapsed = yes |
|||
}} |
|||
When the VoGR line had been designed, it was expected that the Ogmore Dock and Railway Company would construct a line diverging from the L&OR line from [[Tondu]] to Bridgend, and passing east of Bridgend and running south-west to a new dock at Ogmore. The VoGR would have passed to the west of Bridgend to join the Tondu line, with a spur to the OD&R and a south-to-east curve to enter Bridgend station from the west. The OD&R proposals had in fact been withdrawn and its authorisation was abandoned, so that this complex arrangement was now unnecessary. The alignment of the VoGR was therefore altered to approach the Tondu line by passing Bridgend on the east side, with a short spur to enter Bridgend station from the east. This arrangement was cheaper, and it was authorised by the '''{{visible anchor|Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1895}}''' ([[58 & 59 Vict.]] c. xlix) of 20 June 1895.<ref name = smith>Clive Smith, ''Railways of the Llynfi Valley'', Alun Books, Port Talbot, 1985, {{ISBN|0 907117 38 4}}</ref><ref name = chapman/> |
|||
Incidentally, running powers had been |
Incidentally, running powers had been sought to Tondu in the authorising act but this had been refused, obliging the company to exchange mineral traffic at Coity Junction.<ref name = baughan/> |
||
It had been originally intended to construct the line as single track, taking land for subsequent widening to double track. In August 1894 it was decided to make the track in [[Porthkerry]] Tunnel double track, and on 5 October the Board decided on double track from Barry to [[Rhoose]]. By 7 June the decision was made to construct in double track throughout the line, in view of the heavy mineral traffic expected to be running. In 1895 additional capital for this work was authorised by |
It had been originally intended to construct the line as single track, taking land for subsequent widening to double track. In August 1894 it was decided to make the track in [[Porthkerry]] Tunnel double track, and on 5 October the Board decided on double track from Barry to [[Rhoose]]. By 7 June the decision was made to construct in double track throughout the line, in view of the heavy mineral traffic expected to be running. In 1895 additional capital for this work was authorised by act of Parliament.{{which|date=July 2024}}<ref name = chapman/> |
||
During the construction work, pier no 10 of [[Porthkerry Viaduct]], near the Barry end, subsided by several feet on 18 August 1896; it was followed by a major settlement of pier no 11, and later no 12. Stabilisation measures were put in hand, but this was a sign of future trouble. |
During the construction work, pier no. 10 of [[Porthkerry Viaduct]], near the Barry end, subsided by several feet on 18 August 1896; it was followed by a major settlement of pier no. 11, and later no. 12. Stabilisation measures were put in hand, but this was a sign of future trouble. |
||
Nevertheless the line was considered to be ready towards the end of 1897 and Colonel Yorke of the [[Board of Trade]] visited on 6 November 1897 to assess the line for passenger operation. He expressed himself very dubious of the stability of Porthkerry Viaduct, but he permitted the operation of passenger trains for a period of three months, subject to further appraisal then. Meanwhile speed on the line as a whole was to be limited to 25 |
Nevertheless the line was considered to be ready towards the end of 1897 and Colonel Yorke of the [[Board of Trade]] visited on 6 November 1897 to assess the line for passenger operation. He expressed himself very dubious of the stability of Porthkerry Viaduct, but he permitted the operation of passenger trains for a period of three months, subject to further appraisal then. Meanwhile speed on the line as a whole was to be limited to {{cvt|25|mph}} and over the viaduct to {{cvt|20|mph}}; a watchman was to be employed at the viaduct. Watchmen were to be posted around the clock, and to examine the viaduct over and under after the passage of every train; special signals were provided so that they could stop traffic if necessary.<ref name = yorke>Evidence given to Lt. Col. H. A. Yorke, reported to the Board of Trade on 6 April 1898</ref> |
||
The line was accordingly opened to passenger traffic on 1 December 1897, although it is known that two special passenger trains ran over the line prior to that date.<ref name = chapman/> |
The line was accordingly opened to passenger traffic on 1 December 1897, although it is known that two special passenger trains ran over the line prior to that date.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
| Line 56: | Line 116: | ||
There were further signs of ground movement at Porthkerry on 16 December 1897, and on 10 January 1898 there was a very serious slip at pier 13, the easternmost pier, closing the line. |
There were further signs of ground movement at Porthkerry on 16 December 1897, and on 10 January 1898 there was a very serious slip at pier 13, the easternmost pier, closing the line. |
||
On 3 February 1898 the |
On 3 February 1898 the board approved construction of a temporary loop line by-passing the viaduct, at a cost of £5,647. It made a large sweep to the north following the contours of the ground, although it had a maximum gradient of 1 in 40. It was single track, {{convert|2|mi|44|ch|2}} in extent. There was a {{cvt|10|mph}} speed restriction on it. |
||
Colonel Yorke visited on 19 April 1898 and passed it for passenger operation, and it opened on 25 April 1898.<ref name = chapman/> |
Colonel Yorke visited on 19 April 1898 and passed it for passenger operation, and it opened on 25 April 1898.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
{{Infobox UK legislation |
|||
Reconstruction of the failed viaduct arches was paid for by the Barry Railway, the VoGR Act of 1899 authorising £120,000 of additional capital. It was discovered that the piers had been founded on rock that was not bedrock, but in fact a layer of stone on shale and silt. The reconstruction involved the demolition of the affected piers and the sinking of new foundations down to rock. The eastern abutment was moved back and two new spans with their own piers were constructed. |
|||
| short_title = Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1899 |
|||
| type = Act |
|||
| parliament = Parliament of the United Kingdom |
|||
| long_title = An Act for conferring further powers on the Yale of Glamorgan Railway Company for the raising of capital and otherwise in relation to their undertaking and for other purposes. |
|||
| year = 1899 |
|||
| citation = [[62 & 63 Vict.]] c. xiv |
|||
| introduced_commons = |
|||
| introduced_lords = |
|||
| territorial_extent = |
|||
| royal_assent = 6 June 1899 |
|||
| commencement = |
|||
| expiry_date = |
|||
| repeal_date = |
|||
| amends = |
|||
| replaces = |
|||
| amendments = |
|||
| repealing_legislation = |
|||
| related_legislation = |
|||
| status = |
|||
| legislation_history = |
|||
| theyworkforyou = |
|||
| millbankhansard = |
|||
| original_text = https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukla/Vict/62-63/14/pdfs/ukla_18990014_en.pdf |
|||
| revised_text = |
|||
| use_new_UK-LEG = |
|||
| UK-LEG_title = |
|||
| collapsed = yes |
|||
}} |
|||
Reconstruction of the failed viaduct arches was paid for by the Barry Railway, the '''{{visible anchor|Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1899}}''' ([[62 & 63 Vict.]] c. xiv) authorising £120,000 of additional capital. It was discovered that the piers had been founded on rock that was not bedrock, but in fact a layer of stone on shale and silt. The reconstruction involved the demolition of the affected piers and the sinking of new foundations down to rock. The eastern abutment was moved back and two new spans with their own piers were constructed. |
|||
The process took until early 1900, when the viaduct was reopened for goods trains on 8 January 1900, Colonel Yorke reinspected the viaduct on 13 March 1900 and was satisfied with the remedial measures, and the viaduct reopened for passenger traffic on 9 April 1900.<ref name = chapman/> |
The process took until early 1900, when the viaduct was reopened for goods trains on 8 January 1900, Colonel Yorke reinspected the viaduct on 13 March 1900 and was satisfied with the remedial measures, and the viaduct reopened for passenger traffic on 9 April 1900.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
The expenditure in building the line was "close on £700,000" according to the Barry Railway General Manager, Edward Lake.<ref name = sekon>G A Sekon, |
The expenditure in building the line was "close on £700,000" according to the Barry Railway General Manager, Edward Lake.<ref name = sekon>G. A. Sekon, "Illustrated Interview with Mr Edward Lake, General Manager of the Barry Railway", ''Railway Magazine'', October 1906</ref> |
||
==London and South Wales Railway== |
==London and South Wales Railway== |
||
| Line 73: | Line 162: | ||
D S Barrie said, "Beyond all reasonable doubt, the real object of the London & South Wales promoters was to force the Great Western Railway to carry out its South Wales Direct Line, and to make certain concessions to the South Wales coal trade. "<ref name = barrie/> |
D S Barrie said, "Beyond all reasonable doubt, the real object of the London & South Wales promoters was to force the Great Western Railway to carry out its South Wales Direct Line, and to make certain concessions to the South Wales coal trade. "<ref name = barrie/> |
||
This motivated to GWR to build its long-planned South Wales Direct Line, from [[Royal Wootton Bassett|Wootton Bassett]] to [[Patchway]] via [[Badminton, Gloucestershire|Badminton]]. When the GWR gave definite undertakings to do so, the London and South Wales Railway scheme and the VoGR Swansea scheme were withdrawn.<ref name = barrie/><ref name = wilson>B G Wilson, |
This motivated to GWR to build its long-planned South Wales Direct Line, from [[Royal Wootton Bassett|Wootton Bassett]] to [[Patchway]] via [[Badminton, Gloucestershire|Badminton]]. When the GWR gave definite undertakings to do so, the London and South Wales Railway scheme and the VoGR Swansea scheme were withdrawn.<ref name = barrie/><ref name = wilson>B. G. Wilson, "The London & South Wales Railway", ''Railway Magazine'', October 1956</ref><ref name = chapman/><ref name = baughan/> |
||
==Amalgamation with the Barry Railway considered== |
==Amalgamation with the Barry Railway considered== |
||
| Line 79: | Line 168: | ||
==Motor Cars (Steam Railmotors)== |
==Motor Cars (Steam Railmotors)== |
||
[[File:Barry Railway Steam Railcar 1904.jpg|thumb|Railmotor No. 2]] |
|||
In the 1900s many railway companies experimented with Steam [[Railmotor|railmotors]] or Motor Cars as they were known in South Wales, passenger coaches with integrated small steam engines. The intention was to provide passenger calls at places where the traffic did not justify construction of a full station, and often the railmotor stopping places were rudimentary very short ground level platforms. |
|||
In the 1900s many railway companies experimented with steam [[railmotor]]s–or ''motor cars'' as they were known in South Wales–passenger coaches with integrated small steam engines. The intention was to provide passenger calls at places where the traffic did not justify construction of a full station, and often the railmotor stopping places were rudimentary very short ground level platforms. |
|||
The Barry Railway adopted this system on its main line from Barry to [[Pontypridd]], but after a month they were withdrawn, following complaints; as well as public dissatisfaction they were unable to cope with the gradients on that line. |
The Barry Railway adopted this system on its main line from Barry to [[Pontypridd]], but after a month they were withdrawn, following complaints; as well as public dissatisfaction they were unable to cope with the gradients on that line. |
||
Two railmotors were redeployed to the VoGR line, operating between Barry and [[Llantwit Major]]. New halts were authorised by the Board on 2 June 1905, to be built at |
Two railmotors were redeployed to the VoGR line, operating between Barry and [[Llantwit Major]]. New halts were authorised by the Board on 2 June 1905, to be built at Fontygary, Llandow and [[St Brides Major]]. In fact these were never built, and the Barry Railway experiment with railmotors was unsuccessful. However, their two units were modified to remove the steam engine and their bogie drive units and the pair became known as "The vestibule set" and were corridor-connected. <ref name = chapman/><ref name = morgan>H. Morgan, ''South Wales Branch Lines'', Ian Allan Limited, Shepperton, 1984, {{ISBN|0 7110 1321 7}}</ref><ref name = dale>Peter Dale, ''Glamorganshire's Lost Railways'', Stenlake Publishing Ltd, 2014, {{ISBN|978 184 0336740}}</ref> |
||
==Limestone and cement== |
==Limestone and cement== |
||
The construction of the Vale of Glamorgan Railway had been made more difficult by the existence of limestone ground conditions that were prevalent in the area. The traffic arising from the areas served by the line was agricultural and rural, but in December 1888 there was a limestone works at [[Aberthaw]], but it had become disused by the time the VoGR was opened for traffic. Lime works were opened later at a number of points along the line, and large scale industrial portland cement operations were started at Rhoose in 1911 and at Aberthaw in 1913, initially by different companies but later to become Aberthaw & Bristol Channel Portland Cement Company Limited.<ref name = chapman/> |
The construction of the Vale of Glamorgan Railway had been made more difficult by the existence of limestone ground conditions that were prevalent in the area. The traffic arising from the areas served by the line was agricultural and rural, but in December 1888 there was a limestone works at [[Aberthaw]], but it had become disused by the time the VoGR was opened for traffic and there had never been a railway connection to the Vale of Glamorgan line. It had been served by the Llantrisant—Aberthaw Low level Taff Vale Railway line from 1892 until 1926. Lime works were opened later at a number of points along the line, and large scale industrial portland cement operations were started at Rhoose in 1911 and at Aberthaw in 1913, initially by different companies but later to become Aberthaw & Bristol Channel Portland Cement Company Limited.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
==Grouping of the railways== |
==Grouping of the railways== |
||
In 1922 most of the railways of Great Britain were compulsorily restructured into one or other of four new large concerns, following the [[Railways Act 1921]]. The new Great Western Railway was one of the groups, and the Barry Railway, as well as the old Great Western Railway, were constituents of it. The Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company was of course only a financial entity. It was absorbed as a subsidiary of the new Great Western Railway from 1 July 1922. Its issued capital was recorded as £660,000, and its net income in 1921 was £27,440, paying a dividend in 1921 of {{ |
In 1922 most of the railways of Great Britain were compulsorily restructured into one or other of four new large concerns, following the [[Railways Act 1921]]. The new Great Western Railway was one of the groups, and the Barry Railway, as well as the old Great Western Railway, were constituents of it. The Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company was of course only a financial entity. It was absorbed as a subsidiary of the new Great Western Railway from 1 July 1922. Its issued capital was recorded as £660,000, and its net income in 1921 was £27,440, paying a dividend in 1921 of {{sfrac|4|5|32}}%. |
||
Its route length was {{ |
Its route length was {{convert|20+3/4|mi}}.<ref name = semmens>Peter Semmens, ''History of the Great Western Railway: 1: Consolidation, 1923–1929'', George Allen and Unwin, London, 1985, Studio Editions reprint 1990, {{ISBN|0 04385104 5}}</ref> |
||
==After 1923== |
==After 1923== |
||
| Line 99: | Line 189: | ||
==From 1948== |
==From 1948== |
||
Nationalisation of the railways took place at the beginning of 1948, from which time the VoGR network was part of British |
Nationalisation of the railways took place at the beginning of 1948, from which time the VoGR network was part of British Railways. |
||
A coal fired power station was constructed at Aberthaw; it started generating on 7 February 1960; it had a branch line access from the VoGR line, which was {{ |
A coal fired power station was constructed at Aberthaw; it started generating on 7 February 1960 but it was not officially opened until 29th October 1963; it had a branch line access from the VoGR line, at {{cvt|4|mi|63|ch|2}} and {{cvt|5|mi|27|ch|2}} from Barry Junction and which was {{convert|1+3/4|mi}} in length. The branch was fully commissioned on 23 July 1961 to later become a 'merry-go-round' system, making it almost {{convert|3|mi|0}} long, including the site loop mileage. |
||
Southerndown Road station was located remote from any centre of population, and passenger carrying had always been minimal; the station was closed on 23 October 1961; on 16 June 1962 the passenger service throughout the VoGR line was reduced considerably, with the Sunday service being discontinued.<ref name = dale/> |
Southerndown Road station was located remote from any centre of population, and passenger carrying had always been minimal; the station was closed on 23 October 1961; on 16 June 1962 the passenger service throughout the VoGR line was reduced considerably, with the Sunday service being discontinued.<ref name = dale/> |
||
This only delayed the total closure of the passenger service, which took place on |
This only delayed the total closure of the passenger service, which took place on 13 June 1964. The mineral traffic from the Tondu line had also collapsed by this time and the Cowbridge Road Junction to Coity Junction section was officially closed on 15 June 1964, except for {{convert|1/2|mi|1}} serving Bridgend and Coity goods from the north end (Coity Junction) until 28 November 1977. The line remained open for freight traffic, chiefly concerned with Aberthaw power station. During engineering work on the main line between Cardiff and Bridgend, the line was frequently used for diversionary purposes.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
==Revival from 1968== |
==Revival from 1968== |
||
A second power station was constructed at Aberthaw, opening as Aberthaw "B" on 10 December 1968, and bringing further coal traffic to the line. |
A second power station was constructed at Aberthaw, opening as Aberthaw "B" on 10 December 1968, and bringing further coal traffic to the line but the last coal delivery to the "B" station was from East Usk via Barry, on 19 August 2019 and "B" station was closed in December with decommissioning following. As at April 2022, all rail connections to the VOG line remained in situ. In March 2022, Cardiff Capital Region (CCR) group of local authorities had "bought the site of Wales' last coal-fired power station for £8 million. CCR says it is committing £36.4 million to the project in total, which includes the purchase price". |
||
The Ford Motor Company established the [[Ford Bridgend Engine Plant]] in 1979. Although it was close to the South Wales Main line it proved more convenient to provide a railway connection |
The Ford Motor Company established the [[Ford Bridgend Engine Plant]] in 1979. Although it was close to the South Wales Main line it proved more convenient to provide a railway connection {{convert|2|mi|0}} long from the VoGR line; this was commissioned on 15 January 1980.<ref name = baughan/> |
||
A new siding layout for Aberthaw cement works was provided from 16 October 1980. |
A new siding layout for Aberthaw cement works was provided from 16 October 1980. |
||
| Line 117: | Line 207: | ||
Aberthaw "A" power station closed in 1996.<ref name = chapman/> |
Aberthaw "A" power station closed in 1996.<ref name = chapman/> |
||
There had long been calls for the line to be reopened for passenger services, and on 12 |
There had long been calls for the line to be reopened for passenger services, and on 12 June 2005 this happened. An hourly local service has since operated between Bridgend and Barry, continuing to Cardiff and Aberdare. Intermediate stations were reopened at Llantwit Major and Rhoose, now renamed [[Cardiff Airport|Rhoose Cardiff International Airport]]. |
||
==The present day== |
==The present day== |
||
At present ( |
At present (2022) the line carries a weekday hourly and two-hourly Sundays passenger service from Bridgend to Barry, continuing to Aberdare of Merthyr generally. The political imperative of a rail connection to Rhoose for the airport is significant. |
||
The Ford Motor Company traffic continues as do coal deliveries to Aberthaw "B" power station (2017). |
The Ford Motor Company traffic continues as do coal deliveries to Aberthaw "B" power station (2017). |
||
Following a previous break, in 2017 rail cement traffic was occasionally run from Aberthaw Cement works (now a laFarge Tarmac Company, part of the CRH Group). |
Following a previous break, in 2017 rail cement traffic was occasionally run from Aberthaw Cement works (now a laFarge Tarmac Company, part of the CRH Group). |
||
The Ford Motor Company Engine Works closed in 2020 and the branch line level crossing across the A48 was lifted in 2024, both sides of the crossing still exist but are fenced off. |
|||
==Topography== |
==Topography== |
||
| Line 132: | Line 224: | ||
* ''Coity Junction''; divergence from Tondu to Bridgend line; |
* ''Coity Junction''; divergence from Tondu to Bridgend line; |
||
* ''Cowbridge Road Junction''; convergence of spur from Bridgend station; |
* ''Cowbridge Road Junction''; convergence of spur from Bridgend station; |
||
* Southerndown Road; opened 1 December 1897; closed 23 October 1961; |
* {{rws|Southerndown Road}}; opened 1 December 1897; closed 23 October 1961; |
||
* Llandow Halt; opened 1 May 1915; closed 15 June 1964; |
* {{rws|Llandow Halt}}; opened 1 May 1915; closed 15 June 1964; |
||
* Llandow Wick Road Halt; opened 19 April 1943; closed 15 June 1964; reopening Gluepot Bridge; |
* {{rws|Llandow (Wick Road) Halt}}; opened 19 April 1943; closed 15 June 1964; reopening Gluepot Bridge; |
||
* '''Llantwit Major'''; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; reopened 12 June 2005; still open; |
* '''{{rws|Llantwit Major}}'''; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; reopened 12 June 2005; still open; |
||
* St Athan |
* {{rws|St. Athan}}; opened 1 September 1939; closed 15 June 1964; |
||
* Gileston; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; |
* {{rws|Gileston}}; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; |
||
* Aberthaw; opened 1 December 1897; renamed Aberthaw High Level 1924 to 1945; closed 15 June 1964; |
* Aberthaw; opened 1 December 1897; renamed {{rws|Aberthaw High Level}} 1924 to 1945; closed 15 June 1964; |
||
* Rhoose; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; reopened as '''Rhoose Cardiff International Airport''' 12 June 2005; still open; |
* Rhoose; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; reopened as '''{{rws|Rhoose Cardiff International Airport}}''' 12 June 2005; still open; |
||
* ['''Barry'''].<ref name = quick>M E Quick, ''Railway Passenger Stations in England Scotland and Wales—A Chronology'', The Railway and Canal Historical Society, 2002</ref><ref name = cooke>R A Cooke, ''Atlas of the Great Western Railway, 1947'', Wild Swan Publications Limited, Didcot, 1997 {{ISBN|1-874103-38-0}}</ref> |
* ['''{{rws|Barry}}'''].<ref name = quick>M. E. Quick, ''Railway Passenger Stations in England Scotland and Wales—A Chronology'', The Railway and Canal Historical Society, 2002</ref><ref name = cooke>R. A. Cooke, ''Atlas of the Great Western Railway, 1947'', Wild Swan Publications Limited, Didcot, 1997 {{ISBN|1-874103-38-0}}</ref><ref name = cobb>Col. M. H. Cobb, ''The Railways of Great Britain – A Historical Atlas'', Ian Allan Publishing Limited, Shepperton, 2003, {{ISBN|07110 3003 0}}</ref> |
||
<ref name = cobb>Col M H Cobb, ''The Railways of Great Britain -- A Historical Atlas'', Ian Allan Publishing Limited, Shepperton, 2003, {{ISBN|07110 3003 0}}</ref> |
|||
==Heritage railway== |
==Heritage railway== |
||
Latest revision as of 19:21, 7 October 2024
Vale of Glamorgan Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company was built to provide access to Barry Docks from collieries in the Llynfi, Garw and Ogmore valleys. Proposed by the coalowners but underwritten by the wealthy Barry Railway Company, it opened in 1897 from near Bridgend to Barry, in Wales.
It immediately suffered a major subsidence on Porthkerry Viaduct and was closed; a temporary by-pass line enabled reopening until the viaduct was partly reconstructed in 1900.
After 1923 the mineral traffic declined slowly, followed by a loss of passenger and general merchandise business. Passenger trains were discontinued from 13 June 1964 with signalling alterations made on 15 June as the line continued to be used for freight and occasional main line diversions but the section between Cowbridge Road Junction (Bridgend) and Coity yard north of Bridgend, was taken out of use on that date. The section between Coity Junction (where it joined the Bridgend and Abergwynfi Branch) and Cowbridge Road Junction had been part of the original Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company's territory which terminated at Barry Junction.
In 1979, the Ford Bridgend Engine Plant was established at Bridgend, served by a private siding off the line. On 10 June 2005, a passenger train service was reinstated, serving Rhoose for Cardiff Airport and Llantwit Major only.
Early transport needs
[edit]The area known as the Vale of Glamorgan, the tract of land close to the north bank of the Bristol Channel between Cardiff and Ogmore-by-Sea was largely agricultural in the early nineteenth century, and it became by-passed when the South Wales Railway built its main line between Cardiff and Swansea.
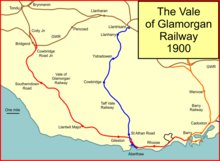
Much of the mineral wealth of the South Wales Valleys—mostly coal but also iron ore and smelted iron and iron products—was taken to Bristol Channel ports for onward transport. Newport, Cardiff and Swansea were dominant in these activities. There were other small harbours but they had limitations which had discouraged development as industrialisation gathered pace.[1]
The Cowbridge Railway opened in 1865, giving a branch line connection to the market town of Cowbridge from Llantrisant station.[2]
The Cowbridge Railway merely gave a railway connection to the market town, and it fell to the Ogmore Dock and Railway Company to get an act for a mineral connection, the Ogmore Dock and Railway Act 1883 (46 & 47 Vict. c. cxcvii) on 20 August 1883. However the prospective company needed substantial Great Western Railway support and this was not forthcoming, so that the scheme eventually foundered.[1]
Barry Railway
[edit]At Cardiff the volume of minerals transported increased beyond expectation, and quickly overwhelmed the capacity of the dock installations to handle them. Moreover the railway connections to them were soon heavily congested, and this led to dissatisfaction among the coalowners and other industrialists who used them.[3][1]
In 1884 the Barry Dock and Railway Company (later simply the Barry Railway) was incorporated, with the intention of building new dock facilities with modern mechanical handling equipment at Barry, and building a new railway to bring coal and other minerals from the Rhondda down to Barry. It opened its main line in 1889.
The Barry Railway was soon successful, and built extensions to the docks and new connecting lines to existing railways.[3]
Collieries and their traffic
[edit]Colonel John North acquired six collieries in the valleys immediately north of Bridgend, and in 1889 he established a company, North's Navigation Collieries (1889) Limited, to manage them. Like other coal owners in the Llynfi, Garw and Ogmore Valleys, his company used Porthcawl to load to shipping, but the harbour there had very limited capacity. The alternative was over the Llynvi and Ogmore Railway and to Barry via Peterston and the spur to Drope Junction, or of course to Penarth or Cardiff. The GWR made some improvements to the L&OR lines, but the very severe gradients limited the value of this line. It was felt by North and others that the GWR was obstructing the development of their traffic; meetings with the GWR requesting a reduction in the carriage rate had met with refusal.[1]
At the same time as North was establishing his company, he and others engaged in the trade met together and decided that the solution was a new railway to the Barry. They approached the Barry Railway, which agreed to work the line when built, for 60% of gross receipts.
Vale of Glamorgan Railway proposed
[edit]| Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1889 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Citation | 52 & 53 Vict. c. clxxxviii |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 26 August 1889 |
They promoted the Vale of Glamorgan Railway in the 1889 session of Parliament, and an authorising act of Parliament, the Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict. c. clxxxviii), received the royal assent on 26 August 1889. Authorised capital was £360,000; it was to build from a junction at Coity Lower on the Llynvi & Ogmore line, a little north of Bridgend, to Barry, a distance of 21 miles (34 km); in addition there was to be a branch to the Great Western Railway station at Bridgend, and running powers into the station were included.
The Vale of Glamorgan Railway shared many directors with the Barry Railway Company. However the VoGR company found it difficult to raise the capital it needed to build its line: by 15 July 1890 less than half, at £171,000, had been subscribed for. The company approached contractors to see if they would build the line and take shares in payment, but this was unsuccessful.[1]
Time went by without further progress, until on 2 December 1892 the VoGR directors met the Barry Railway Board again to discuss a way forward. The Cowbridge and Aberthaw Railway had opened to passenger traffic on 1 October 1892, and this company was in the rival Taff Vale Railway camp. The Barry Railway was anxious to secure its western flank against the rival, and keeping the VoGR scheme alive was strategically important. Working arrangements with the Barry Railway were arrived at, by which the Barry Railway guaranteed a dividend of 4% on the capital of the VoGR. This immediately secured the willingness of investors to take VoGR shares.[2][1]
The Barry Railway made this offer conditional on its taking full control of the VoGR. The arrangement was authorised by the Barry Railway Act 1893 (56 & 57 Vict. c. ccvi) of 24 August 1893, and ratified by the proprietors of both companies on 28 May 1894. North's colliery company undertook to send 360,000 tons of coal annually over the line, and the Ocean Coal Company promised half of its output from the Garw Valley.
A tender of Pethick Brothers to construct the Barry to Ewenny section for £182,444 was quickly approved.[1] Three successive extensions of time had to be sought from Parliament because of the delay. The local geology was limestone and much of the construction involved excavating the rocky material.[4]
| Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1895 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act for conferring further powers on the Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company for the construction of works the acquisition of lands the raising of money and otherwise in relation to their undertaking and for other purposes. |
| Citation | 58 & 59 Vict. c. xlix |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 20 June 1895 |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
When the VoGR line had been designed, it was expected that the Ogmore Dock and Railway Company would construct a line diverging from the L&OR line from Tondu to Bridgend, and passing east of Bridgend and running south-west to a new dock at Ogmore. The VoGR would have passed to the west of Bridgend to join the Tondu line, with a spur to the OD&R and a south-to-east curve to enter Bridgend station from the west. The OD&R proposals had in fact been withdrawn and its authorisation was abandoned, so that this complex arrangement was now unnecessary. The alignment of the VoGR was therefore altered to approach the Tondu line by passing Bridgend on the east side, with a short spur to enter Bridgend station from the east. This arrangement was cheaper, and it was authorised by the Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1895 (58 & 59 Vict. c. xlix) of 20 June 1895.[5][1]
Incidentally, running powers had been sought to Tondu in the authorising act but this had been refused, obliging the company to exchange mineral traffic at Coity Junction.[4]
It had been originally intended to construct the line as single track, taking land for subsequent widening to double track. In August 1894 it was decided to make the track in Porthkerry Tunnel double track, and on 5 October the Board decided on double track from Barry to Rhoose. By 7 June the decision was made to construct in double track throughout the line, in view of the heavy mineral traffic expected to be running. In 1895 additional capital for this work was authorised by act of Parliament.[which?][1]
During the construction work, pier no. 10 of Porthkerry Viaduct, near the Barry end, subsided by several feet on 18 August 1896; it was followed by a major settlement of pier no. 11, and later no. 12. Stabilisation measures were put in hand, but this was a sign of future trouble.
Nevertheless the line was considered to be ready towards the end of 1897 and Colonel Yorke of the Board of Trade visited on 6 November 1897 to assess the line for passenger operation. He expressed himself very dubious of the stability of Porthkerry Viaduct, but he permitted the operation of passenger trains for a period of three months, subject to further appraisal then. Meanwhile speed on the line as a whole was to be limited to 25 mph (40 km/h) and over the viaduct to 20 mph (32 km/h); a watchman was to be employed at the viaduct. Watchmen were to be posted around the clock, and to examine the viaduct over and under after the passage of every train; special signals were provided so that they could stop traffic if necessary.[6]
The line was accordingly opened to passenger traffic on 1 December 1897, although it is known that two special passenger trains ran over the line prior to that date.[1]
There were further signs of ground movement at Porthkerry on 16 December 1897, and on 10 January 1898 there was a very serious slip at pier 13, the easternmost pier, closing the line.
On 3 February 1898 the board approved construction of a temporary loop line by-passing the viaduct, at a cost of £5,647. It made a large sweep to the north following the contours of the ground, although it had a maximum gradient of 1 in 40. It was single track, 2 miles 44 chains (4.10 km) in extent. There was a 10 mph (16 km/h) speed restriction on it.
Colonel Yorke visited on 19 April 1898 and passed it for passenger operation, and it opened on 25 April 1898.[1]
| Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1899 | |
|---|---|
| Act of Parliament | |
 | |
| Long title | An Act for conferring further powers on the Yale of Glamorgan Railway Company for the raising of capital and otherwise in relation to their undertaking and for other purposes. |
| Citation | 62 & 63 Vict. c. xiv |
| Dates | |
| Royal assent | 6 June 1899 |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
Reconstruction of the failed viaduct arches was paid for by the Barry Railway, the Vale of Glamorgan Railway Act 1899 (62 & 63 Vict. c. xiv) authorising £120,000 of additional capital. It was discovered that the piers had been founded on rock that was not bedrock, but in fact a layer of stone on shale and silt. The reconstruction involved the demolition of the affected piers and the sinking of new foundations down to rock. The eastern abutment was moved back and two new spans with their own piers were constructed.
The process took until early 1900, when the viaduct was reopened for goods trains on 8 January 1900, Colonel Yorke reinspected the viaduct on 13 March 1900 and was satisfied with the remedial measures, and the viaduct reopened for passenger traffic on 9 April 1900.[1]
The expenditure in building the line was "close on £700,000" according to the Barry Railway General Manager, Edward Lake.[7]
London and South Wales Railway
[edit]The Great Western Railway had long been the monopoly carrier of traffic by rail from South Wales to London, and dissatisfaction with the GWR had been a continuing issue for many.
In 1895 a proposed London and South Wales Railway was put forward, to build a new line from Cogan on the Barry Railway approaching Cardiff, and running to join the Metropolitan Railway north of London. The Barry Railway was the prime mover in this, and at the same time the Vale of Glamorgan Railway, under the control of the Barry, submitted a Bill for a westward extension of the VoGR to Swansea, building a new line from Ewenny through Porthcawl to join the Rhondda and Swansea Bay Railway. Together the two schemes would provide a new line from Swansea to London.
D S Barrie said, "Beyond all reasonable doubt, the real object of the London & South Wales promoters was to force the Great Western Railway to carry out its South Wales Direct Line, and to make certain concessions to the South Wales coal trade. "[3]
This motivated to GWR to build its long-planned South Wales Direct Line, from Wootton Bassett to Patchway via Badminton. When the GWR gave definite undertakings to do so, the London and South Wales Railway scheme and the VoGR Swansea scheme were withdrawn.[3][8][1][4]
Amalgamation with the Barry Railway considered
[edit]The Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company had been under the control of the Barry Railway from the outset, and from time to time full amalgamation was considered; specifically in August 1898 and November 1902. In those cases it was not considered to be an auspicious time for the merger, and in fact the VoGR remained nominally independent.[1]
Motor Cars (Steam Railmotors)
[edit]
In the 1900s many railway companies experimented with steam railmotors–or motor cars as they were known in South Wales–passenger coaches with integrated small steam engines. The intention was to provide passenger calls at places where the traffic did not justify construction of a full station, and often the railmotor stopping places were rudimentary very short ground level platforms.
The Barry Railway adopted this system on its main line from Barry to Pontypridd, but after a month they were withdrawn, following complaints; as well as public dissatisfaction they were unable to cope with the gradients on that line.
Two railmotors were redeployed to the VoGR line, operating between Barry and Llantwit Major. New halts were authorised by the Board on 2 June 1905, to be built at Fontygary, Llandow and St Brides Major. In fact these were never built, and the Barry Railway experiment with railmotors was unsuccessful. However, their two units were modified to remove the steam engine and their bogie drive units and the pair became known as "The vestibule set" and were corridor-connected. [1][9][10]
Limestone and cement
[edit]The construction of the Vale of Glamorgan Railway had been made more difficult by the existence of limestone ground conditions that were prevalent in the area. The traffic arising from the areas served by the line was agricultural and rural, but in December 1888 there was a limestone works at Aberthaw, but it had become disused by the time the VoGR was opened for traffic and there had never been a railway connection to the Vale of Glamorgan line. It had been served by the Llantrisant—Aberthaw Low level Taff Vale Railway line from 1892 until 1926. Lime works were opened later at a number of points along the line, and large scale industrial portland cement operations were started at Rhoose in 1911 and at Aberthaw in 1913, initially by different companies but later to become Aberthaw & Bristol Channel Portland Cement Company Limited.[1]
Grouping of the railways
[edit]In 1922 most of the railways of Great Britain were compulsorily restructured into one or other of four new large concerns, following the Railways Act 1921. The new Great Western Railway was one of the groups, and the Barry Railway, as well as the old Great Western Railway, were constituents of it. The Vale of Glamorgan Railway Company was of course only a financial entity. It was absorbed as a subsidiary of the new Great Western Railway from 1 July 1922. Its issued capital was recorded as £660,000, and its net income in 1921 was £27,440, paying a dividend in 1921 of 4+5/32%.
Its route length was 20+3⁄4 miles (33.4 km).[11]
After 1923
[edit]At this time the coal industries of South Wales had passed the peak (which had been in 1913) and coal traffic on the line was declining. Passenger and general merchandise too was seeing the effects of road competition, which appeared in many cases to be more convenient.
During World War II a number of ordnance depots were built in South Wales. One was at Brackla Hill, with a rail connection from the line between Coity Junction and Cowbridge Road Junction; another was at Tremains on the Great Western Railway main line immediately east of the point where the VoGR line to Coity Junction crossed. A south-to-east spur was built, giving access from the VoGR line in to the Tremains depot sidings.[1]
From 1948
[edit]Nationalisation of the railways took place at the beginning of 1948, from which time the VoGR network was part of British Railways.
A coal fired power station was constructed at Aberthaw; it started generating on 7 February 1960 but it was not officially opened until 29th October 1963; it had a branch line access from the VoGR line, at 4 mi 63 ch (7.70 km) and 5 mi 27 ch (8.59 km) from Barry Junction and which was 1+3⁄4 miles (2.8 km) in length. The branch was fully commissioned on 23 July 1961 to later become a 'merry-go-round' system, making it almost 3 miles (5 km) long, including the site loop mileage.
Southerndown Road station was located remote from any centre of population, and passenger carrying had always been minimal; the station was closed on 23 October 1961; on 16 June 1962 the passenger service throughout the VoGR line was reduced considerably, with the Sunday service being discontinued.[10]
This only delayed the total closure of the passenger service, which took place on 13 June 1964. The mineral traffic from the Tondu line had also collapsed by this time and the Cowbridge Road Junction to Coity Junction section was officially closed on 15 June 1964, except for 1⁄2 mile (0.8 km) serving Bridgend and Coity goods from the north end (Coity Junction) until 28 November 1977. The line remained open for freight traffic, chiefly concerned with Aberthaw power station. During engineering work on the main line between Cardiff and Bridgend, the line was frequently used for diversionary purposes.[1]
Revival from 1968
[edit]A second power station was constructed at Aberthaw, opening as Aberthaw "B" on 10 December 1968, and bringing further coal traffic to the line but the last coal delivery to the "B" station was from East Usk via Barry, on 19 August 2019 and "B" station was closed in December with decommissioning following. As at April 2022, all rail connections to the VOG line remained in situ. In March 2022, Cardiff Capital Region (CCR) group of local authorities had "bought the site of Wales' last coal-fired power station for £8 million. CCR says it is committing £36.4 million to the project in total, which includes the purchase price".
The Ford Motor Company established the Ford Bridgend Engine Plant in 1979. Although it was close to the South Wales Main line it proved more convenient to provide a railway connection 2 miles (3 km) long from the VoGR line; this was commissioned on 15 January 1980.[4]
A new siding layout for Aberthaw cement works was provided from 16 October 1980. Rhoose cement works closed in 1987 and has since been demolished along with the former Turner's Asbestos works alongside it and the land has been considerably remodelled some of which is now occupied by new housing along with that of housing in the former main quarry.
Aberthaw "A" power station closed in 1996.[1]
There had long been calls for the line to be reopened for passenger services, and on 12 June 2005 this happened. An hourly local service has since operated between Bridgend and Barry, continuing to Cardiff and Aberdare. Intermediate stations were reopened at Llantwit Major and Rhoose, now renamed Rhoose Cardiff International Airport.
The present day
[edit]At present (2022) the line carries a weekday hourly and two-hourly Sundays passenger service from Bridgend to Barry, continuing to Aberdare of Merthyr generally. The political imperative of a rail connection to Rhoose for the airport is significant.
The Ford Motor Company traffic continues as do coal deliveries to Aberthaw "B" power station (2017). Following a previous break, in 2017 rail cement traffic was occasionally run from Aberthaw Cement works (now a laFarge Tarmac Company, part of the CRH Group).
The Ford Motor Company Engine Works closed in 2020 and the branch line level crossing across the A48 was lifted in 2024, both sides of the crossing still exist but are fenced off.
Topography
[edit]Gradients
[edit]From Barry the line climbs at 1 in 81 to the Porthkerry Viaduct and then descends at 1 in 165, 1 in 200 to a point beyond Aberthaw. It then climbs at 1 in 821, 1 in 273, 1 in 106, 1 in 122 to a point beyond Llantwit Major. It then falls at 1 in 140 to Ewenny, climbing at 1 in 200 and 1 in 100 after that to Cowbridge Road Junction.[1]
Station list
[edit]- Coity Junction; divergence from Tondu to Bridgend line;
- Cowbridge Road Junction; convergence of spur from Bridgend station;
- Southerndown Road; opened 1 December 1897; closed 23 October 1961;
- Llandow Halt; opened 1 May 1915; closed 15 June 1964;
- Llandow (Wick Road) Halt; opened 19 April 1943; closed 15 June 1964; reopening Gluepot Bridge;
- Llantwit Major; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; reopened 12 June 2005; still open;
- St. Athan; opened 1 September 1939; closed 15 June 1964;
- Gileston; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964;
- Aberthaw; opened 1 December 1897; renamed Aberthaw High Level 1924 to 1945; closed 15 June 1964;
- Rhoose; opened 1 December 1897; closed 15 June 1964; reopened as Rhoose Cardiff International Airport 12 June 2005; still open;
- [Barry].[12][13][14]
Heritage railway
[edit]A heritage railway group calling itself the Vale of Glamorgan Railway submitted a tender to the Vale of Glamorgan Council to establish a railway heritage centre at Barry Island. Their tender was unsuccessful, and there was some friction with the Council over the removal of artefacts belonging to the former Butetown Historic Railway Society.
The Butetown group was forced to leave the Barry Island line at the end of December 2008, resulting in the sale of and disposal of various assets. Operations restarted in 2009 under new ownership as the Barry Tourist Railway.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Colin Chapman, The Vale of Glamorgan Railway, Oakwood Press, Usk, 1998, ISBN 0 85361 523 3
- ^ a b Colin Chapman, The Cowbridge Railway, Oxford Publishing Company, Poole, 1984, ISBN 0-86093-284-2
- ^ a b c d D. S. Barrie, The Barry Railway, Oakwood Press, Usk, reprinted 1983, ISBN 0 85361 236 6
- ^ a b c d D. S. M. Barrie, revised Peter Baughan, A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain: volume 12: South Wales, David St John Thomas, Nairn, 1994, ISBN 0 946537 69 0
- ^ Clive Smith, Railways of the Llynfi Valley, Alun Books, Port Talbot, 1985, ISBN 0 907117 38 4
- ^ Evidence given to Lt. Col. H. A. Yorke, reported to the Board of Trade on 6 April 1898
- ^ G. A. Sekon, "Illustrated Interview with Mr Edward Lake, General Manager of the Barry Railway", Railway Magazine, October 1906
- ^ B. G. Wilson, "The London & South Wales Railway", Railway Magazine, October 1956
- ^ H. Morgan, South Wales Branch Lines, Ian Allan Limited, Shepperton, 1984, ISBN 0 7110 1321 7
- ^ a b Peter Dale, Glamorganshire's Lost Railways, Stenlake Publishing Ltd, 2014, ISBN 978 184 0336740
- ^ Peter Semmens, History of the Great Western Railway: 1: Consolidation, 1923–1929, George Allen and Unwin, London, 1985, Studio Editions reprint 1990, ISBN 0 04385104 5
- ^ M. E. Quick, Railway Passenger Stations in England Scotland and Wales—A Chronology, The Railway and Canal Historical Society, 2002
- ^ R. A. Cooke, Atlas of the Great Western Railway, 1947, Wild Swan Publications Limited, Didcot, 1997 ISBN 1-874103-38-0
- ^ Col. M. H. Cobb, The Railways of Great Britain – A Historical Atlas, Ian Allan Publishing Limited, Shepperton, 2003, ISBN 07110 3003 0
