2013 Togolese parliamentary election: Difference between revisions
GreenC bot (talk | contribs) Rescued 1 archive link; reformat 1 link. Wayback Medic 2.5 per WP:URLREQ#google.com/hostednews |
Was correct before? |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|none}} |
|||
{{Politics of Togo}} |
{{Politics of Togo}} |
||
| Line 17: | Line 18: | ||
{| class=wikitable style=text-align:right |
{| class=wikitable style=text-align:right |
||
|- |
|||
|colspan=10 align=center|[[File:Togo Assemblée nationale 2013.svg]] |
|colspan=10 align=center|[[File:Togo Assemblée nationale 2013.svg]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
Latest revision as of 00:56, 12 October 2024
 |
|---|
|
|
Parliamentary elections were held in Togo on 25 July 2013.[1] The ruling Union for the Republic (UNIR) won 62 of the 91 seats in the National Assembly.
Background
[edit]Some members of the opposition sought a postponement in order to see electoral reforms take effect prior to the elections, while others sought the repeal of the changes as improperly introduced. Amongst the latter was the controversial gerrymandering of constituency borders in favour UNIR, led by President Faure Gnassingbé, and the 10-seat increase in the number of members of the National Assembly from 81 to 91.
Although the government banned street demonstrations in commercial areas, citing an inability to maintain security and public order, protest organizers from opposition and civil society groups pledged to carry out protests and denounced what they termed an attempt to stifle criticism. Protests organized by the Let's Save Togo Collective were planned for 21–23 August. On the first day, several thousand protesters commenced a march in Lomé's Bè neighbourhood and then headed to the commercial district of Deckon, where 100 police officers were deployed. Trouble then arose amid a dispute as to whether the protest march would end in Deckon for a rally or proceed further. The protesters were then dispersed using tear gas 10 minutes after the march commenced.[2]
The elections were originally scheduled for October 2012, but protests and strikes asking for electoral reforms delayed the process. After being rescheduled for 24 March 2013, they were postponed again, first to 21 July 2013,[3][4] then to 25 July 2013.
Electoral system
[edit]The 91 members of the National Assembly were elected by closed list proportional representation in 30 multi-member constituencies.[5]
Results
[edit]Initial results showed a landslide victory for UNIR, which was projected to win 60 out of 91 seats, with the remaining seats distributed among opposition parties. The opposition Union of Forces for Change suffered a defeat, losing most of their 27 seats. The National Alliance for Change (Alliance national pour le changement, ANC) was expected to become the largest opposition party.[6]
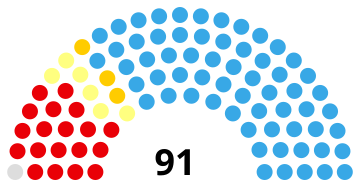
| |||||||||
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Union for the Republic | 880,608 | 46.7 | 62 | +12 | |||||
| Save Togo Collective | 544,592 | 28.9 | 19 | New | |||||
| Rainbow Alliance | 204,143 | 10.8 | 6 | +2 | |||||
| Union of Forces for Change | 145,359 | 7.7 | 3 | –24 | |||||
| Pan-African Patriotic Convergence | 15,602 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| New Togolese Commitment | 14,225 | 0.8 | 0 | New | |||||
| Other parties | 66,171 | 3.5 | 0 | – | |||||
| Independents | 14,360 | 0.8 | 1 | +1 | |||||
| Invalid/blank votes | 119,430 | – | – | – | |||||
| Total | 2,011,203 | 100 | 91 | +10 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 3,044,332 | 66.1 | – | – | |||||
| Source: Adam Carr | |||||||||
Aftermath
[edit]When the National Assembly began its new term, Dama Dramani, a UNIR deputy, was elected as President of the National Assembly on 2 September 2013. Opposition deputies boycotted the vote as UNIR was unwilling to give them the posts of first and second vice-president in the Bureau of the National Assembly. Consequently UNIR deputies were elected to all of the 11 posts in the Bureau.[7]
References
[edit]- ^ Togo: Elections Dogged By Questions Over Who Will Take Part Voice of America, 12 July 2013
- ^ Togo police disperse fair vote rally Al Jazeera, 21 August 2012
- ^ Togo to kick off voter registration on March 15 Archived 2013-09-21 at the Wayback Machine Xinhua, 7 March 2013
- ^ Togo opposition figure charged over market fires Africa Review, 13 March 2013
- ^ Election Profile IFES
- ^ Législatives : les premières tendances favorables au pouvoir UNIR Togo Actualité
- ^ Le Togo élit un nouveau président de l'Assemblée Nationale[dead link] AFP, 2 September 2013 (in French)
