History of the Los Angeles Rams: Difference between revisions
Tassedethe (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (735 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|American football team history}} |
|||
==Los Angeles Rams: LA era (1980-94)== |
|||
{{Use American English|date=September 2023}} |
|||
===1946–48: Starting over in Los Angeles=== |
|||
{{Use mdy dates|date=September 2023}} |
|||
On January 12, 1946, [[Dan Reeves (NFL owner)|Dan Reeves]] was denied a request by the other NFL owners to move his team to [[Los Angeles]] and its 92,000 seat [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]].<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16.">MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16.</ref> Reeves threatened to end his relationship with the NFL and get out of the professional football business altogether unless the Rams transfer to Los Angeles was permitted.<ref name="Littlewood, 1990, p. 160.">Littlewood, 1990, p. 160.</ref><ref name="Lyons, 2010, p. 118.">Lyons, 2010, p. 118.</ref><ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16."/> A settlement was reached and, as a result, the Los Angeles Rams were created.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16."/><ref name="Yost, 2006, p. 57–58.">Yost, 2006, p. 57–58.</ref><ref name="Davis, 2005 p. 201–202.">Davis writes Halas engineered the approval of the Rams move to Los Angeles, Davis, 2005, p. 201–202.</ref><ref name="Lyons, 2010, p. 117–118.">Lyons, 2010, p. 117–118.</ref> and the NFL had become the first professional coast-to-coast sports entertainment industry.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16."/> At the time, the NFL did not allow [[African-American]]s to play in the [[Black players in American professional football|league]].{{citation needed|date=October 2011}}After the Rams had received approval to move to Los Angeles, the Rams entered into negotiations to lease the [[Los Angeles Coliseum]]. The Rams were advised that a precondition to them getting a lease was that they would have to integrate the team with at least one African American; the Rams agreed to this condition.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.">MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.</ref><ref name="Levy, 2003, p. 92–93.">Levy, 2003, p. 92–93.</ref><ref name="Davis, 2005 p. 202.">Davis, 2005, p. 202.</ref><ref name="Strode, 1996, p. 140">Strode, 1990, p. 140.</ref> Subsequently, the Rams signed [[Kenny Washington (American football)|Kenny Washington]] on March 21, 1946,<ref name="Coenen, 2005, p. 123.">Coenen, 2005, p. 123.</ref><ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19. WASHINGTON">MacCambridge writes he was signed on May 4, 1946. MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.</ref><ref name="Ross, 1999, p. 82.">Ross, 1999, p. 82.</ref> and racial segregation in the NFL was completely ended.<ref>[http://www.stlouisrams.com/History/FunFacts/ Rams Fun Facts: Rams Famous Firsts]. ''Official Website of the St. Louis Rams''. Retrieved 13 September 2006{{dead link|date=October 2011}}</ref> |
|||
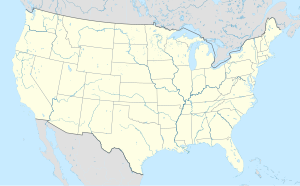
{{Location map+ | United States|float = right |
|||
|caption = Home locations of the Rams franchise throughout their history |
|||
|alt = The cities in which the team now known as the Los Angeles Rams have played in |
|||
|width = 300 |
|||
|places = |
|||
{{Location map~ | United States |
|||
| mark = Black pog.svg |
|||
| marksize = 8 |
|||
| label_size = 80 |
|||
| label = Cleveland (1936–1945) |
|||
| position = right |
|||
| lat_deg = 41.507 |
|||
| lon_deg = -81.697}} |
|||
{{Location map~ | United States |
|||
| mark = Black pog.svg |
|||
| marksize = 8 |
|||
| label_size = 80 |
|||
| label = Los Angeles (1946–1994, 2016–present) |
|||
| position = top |
|||
| lat_deg = 33.953 |
|||
| lon_deg = -118.339}} |
|||
{{Location map~ | United States |
|||
| mark = Black pog.svg |
|||
| marksize = 8 |
|||
| label_size = 80 |
|||
| label = St. Louis (1995–2015) |
|||
| position = bottom |
|||
| lat_deg = 38.633 |
|||
| lon_deg = -90.189}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{NFL Rams history}} |
|||
The [[Los Angeles Rams]] are a professional [[American football]] team that plays and competes in the [[National Football League]] ([[National Football League|NFL]]). The Rams franchise was founded in 1936 as the [[History of the Cleveland Rams|Cleveland Rams]] in the short-lived [[American Football League (1936)|second American Football League]] before joining the NFL the next year. In 1946, the franchise moved to Los Angeles. The Rams franchise remained in the [[Greater Los Angeles Area|metro area]] until 1994, when they moved to [[St. Louis]], and were known as the [[History of the St. Louis Rams|St. Louis Rams]] from 1995 to 2015. The Rams franchise returned to Los Angeles in 2016. This article chronicles the franchise's history during their time in Los Angeles, from playing at the [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]] between 1946 and 1979, to playing at Anaheim Stadium (now known as [[Angel Stadium|Angel Stadium of Anaheim]]) in [[Anaheim, California|Anaheim]] from 1980 to 1994, and its return to Southern California beginning with the {{nfly|2016}} to {{nfly|2019}} seasons playing temporarily at their old home the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum before moving to [[SoFi Stadium]] in [[Inglewood, California|Inglewood]] in 2020 alongside the [[Los Angeles Chargers]]. |
|||
The Rams were the first team in the NFL to play in Los Angeles (the [[1926 Los Angeles Buccaneers season|1926 Los Angeles Buccaneers]] were strictly a road team), but they were not the only professional football team to play its home games in the Coliseum between 1946 and 1949. The upstart [[All-America Football Conference]] had the [[Los Angeles Dons]] compete there as well. Reeves was taking a gamble that Los Angeles was ready for its own professional football team - and suddenly there were two in the City of Angels. Reeves was proved to be correct when the Rams played their first pre-season game against the [[1946 Washington Redskins season|Washington Redskins]] in front of a crowd of 95,000 fans. The team finished their first season in LA with a 6–4–1 record, second place behind the [[1946 Chicago Bears season|Chicago Bears]]. At the end of the season Walsh was fired as head coach. The Coliseum would be the home of the Rams for more than thirty years (the Dons merged with them in late 1949),<ref>[http://books.google.com/books?id=52HGfXAUdOAC&pg=PA438&lpg=PA438&dq=%22miami+seahawks%22+owner+1946+aafc&source=web&ots=UQTrU83mxX&sig=2mNWOw8XZsgMgpd3QNI3g_yXraI#PPA438,M1 James P. Quirk and Rodney D. Fort, ''Pay Dirt: The Business of Professional Team Sports'', p. 438], ISBN 0691015740</ref> but the facility was already over twenty years old on the day of the first kickoff. In 1948, halfback Fred Gehrke painted horns on the Rams' helmets, making the first modern helmet emblem in pro football.<ref>[http://www.stlouisrams.com/History/FunFacts/ Rams Fun Facts: The Rams Horns]. ''Official Website of the St. Louis Rams''. Retrieved 13 September 2006{{dead link|date=October 2011}}</ref> |
|||
== History == |
|||
===1949–1955: Three-end formation=== |
|||
=== 1946–1994: Origins in Los Angeles === |
|||
The Rams' first heyday in southern California was from 1949 to 1955, when they played in the [[NFL Championship Game]] (not yet called the [[Super Bowl]]) four times, winning once in [[NFL Championship Game, 1951|1951]]. During this period, they had the best offense in the NFL, even though there was a quarterback change from [[Bob Waterfield]] to [[Norm Van Brocklin]] in [[1951 NFL season|1951]]. The defining player of this period was wide receiver [[Elroy Hirsch]]. Teamed with fellow Hall of Famer [[Tom Fears]], Hirsch helped create the style of Rams football as one of the first big play receivers. During the 1951 Championship season, Hirsch posted a then stunning 1,495 receiving yards with 17 touchdowns. The popularity of this wide-open offense enabled the [[1950 Los Angeles Rams season|Los Angeles Rams]] to become the first pro football team to have all their games televised in [[1950 NFL season|1950]]. |
|||
==== 1946–1948: Starting over in Los Angeles ==== |
|||
On January 12, 1946, [[Dan Reeves (NFL owner)|Dan Reeves]] was denied a request by the other [[National Football League]] (NFL) owners to move his team, the [[Cleveland Rams (1936–45)|Cleveland Rams]] to Los Angeles and the then-103,000-seat [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]].<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16.">MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16.</ref> Reeves threatened to end his relationship with the NFL and get out of the professional football business altogether unless the Rams transfer to Los Angeles was permitted.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16."/><ref name="Littlewood, 1990, p. 160.">Littlewood, 1990, p. 160.</ref><ref name="Lyons, 2010, p. 118.">Lyons, 2010, p. 118.</ref> A settlement was reached and, as a result, Reeves was allowed to move his team to Los Angeles.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16."/><ref name="Yost, 2006, p. 57–58.">Yost, 2006, p. 57–58.</ref><ref name="Davis, 2005 p. 201–202.">Davis writes Halas engineered the approval of the Rams move to Los Angeles, Davis, 2005, p. 201–202.</ref><ref name="Lyons, 2010, p. 117–118.">Lyons, 2010, p. 117–118.</ref> Consequently, the NFL became the first professional coast-to-coast sports entertainment industry.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16."/> |
|||
From 1933, when [[Joe Lillard]] left the [[Chicago Cardinals (NFL, 1920–59)|Chicago Cardinals]], through 1946, there were no [[Black players in American professional football]].<ref name="EbonyMagazine">{{cite web|title=Ebony Magazine May 1969|date = May 1969|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ltoDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA118|publisher=Ebony Magazine|access-date=January 25, 2015}}</ref> After the Rams had received approval to move to Los Angeles, the Rams entered into negotiations to lease the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum. The Rams were advised that a precondition to them getting a lease was that they would have to integrate the team with at least one African-American; the Rams agreed to this condition.<ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.">MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.</ref><ref name="Levy, 2003, p. 92–93.">Levy, 2003, p. 92–93.</ref><ref name="Davis, 2005 p. 202.">Davis, 2005, p. 202.</ref><ref name="Strode, 1996, p. 140">Strode, 1990, p. 140.</ref> Subsequently, the Rams signed [[Kenny Washington (American football)|Kenny Washington]] on March 21, 1946.<ref name="Coenen, 2005, p. 123.">Coenen, 2005, p. 123.</ref><ref name="MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19. WASHINGTON">MacCambridge writes he was signed on May 4, 1946. MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.</ref><ref name="Ross, 1999, p. 82.">Ross, 1999, p. 82.</ref> The signing of Washington caused "all hell to break loose" among the owners of the NFL franchises.<ref name="Rathet, 1984, p. 210.">Rathet, 1984, p. 210.</ref> The Rams added a second black player, [[Woody Strode]], on May 7, 1946, giving them two black players going into the 1946 season. |
|||
===1956–1962: Tanking out=== |
|||
The Rams suffered a down period on the field from 1956 until 1966, posting losing records in every season. However, the business side of the franchise was nurtured by a visionary executive in [[Pete Rozelle]]. During his time with Rams, Rozelle learned the value of television for the sport of pro football. Through Rozelle's savvy use of television, the Rams remained a glamor NFL franchise despite their poor record. In a 1957 game against the [[1957 San Francisco 49ers season|San Francisco 49ers]], the [[1957 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] set the all-time record for attendance for a regular season NFL game with 102,368. The Rams would draw over 100,000 fans twice the following year. |
|||
The Rams were the first team in the NFL to play in Los Angeles (the [[1926 Los Angeles Buccaneers season|1926 Los Angeles Buccaneers]] were strictly a road team), but they were not the only professional football team to play its home games in the Coliseum between 1946 and 1949. The upstart [[All-America Football Conference]] had the [[Los Angeles Dons]] compete there as well. Reeves was taking a gamble that Los Angeles was ready for its own professional football team – and suddenly there were two in the City of Angels. Reeves was proved to be correct when the Rams played their first pre-season game against the [[1946 Washington Redskins season|Washington Redskins]] in front of a crowd of 95,000 fans. The team finished their first season in L.A. with a 6–4–1 record, second place behind the [[1946 Chicago Bears season|Chicago Bears]]. At the end of the season Walsh was fired as head coach. The Coliseum would be the home of the Rams for more than 30 years (the Dons merged with them in late 1949),<ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=52HGfXAUdOAC&dq=%22miami+seahawks%22+owner+1946+aafc&pg=PA438 James P. Quirk and Rodney D. Fort, ''Pay Dirt: The Business of Professional Team Sports'', p. 438], {{ISBN|0-691-01574-0}}</ref> but the facility was already over 20 years old on the day of the first kickoff. In 1948, halfback [[Fred Gehrke]] painted horns on the Rams' helmets, making the first modern helmet emblem in pro football.<ref name="RamsFunFacts">{{cite web|title=Fun Facts|url=http://www.stlouisrams.com/history/fun-facts.htm|publisher=St. Louis Rams|access-date=December 5, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151208043205/http://www.stlouisrams.com/history/fun-facts.htm|archive-date=December 8, 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
===1963–69: The Fearsome Foursome=== |
|||
[[Image:Fearsome Foursome.jpg|frame|right|The Fearsome Foursome: (L to R) Lundy, Grier, Olsen, and Jones]] |
|||
The Rams' play-by-play announcer from 1937 through 1965 was Robert J. "Bob" Kelley, known as "The Voice of the Rams", also broadcast for NCAA teams Notre Dame and Michigan football as well as the Los Angeles Angels Pacific Coast League team and American League team. Kelley had an early evening talk show on L.A. radio station KMPC, that was considered by most sports enthusiasts as highly entertaining. Kelley was generally considered a Legend and a true professional, one of the great radio, play-by-play announcers of our time. At the beginning of the 1951 World Championship game after the kickoff, Kelley was able to cite every player on the field prior to the first snap from scrimmage, an 80-yard touchdown ("and I think he's going to go all the way"). |
|||
The 1960s were defined by the Rams great defensive line of [[Rosey Grier]], [[Merlin Olsen]], [[Deacon Jones]], and [[Lamar Lundy]], dubbed the "[[Fearsome Foursome (football)|Fearsome Foursome]]." It was this group of players who restored the on-field luster of the franchise in [[1967 NFL season|1967]] when the Rams reached (but lost) the conference championship under legendary coach [[George Allen (football)|George Allen]]. That [[1967 Los Angeles Rams season|1967 squad]] would become the first NFL team to surpass one million spectators in a season, a feat the [[1968 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] would repeat the [[1968 NFL season|following year]]. In each of those two years, the L.A. Rams drew roughly double the number of fans that could be accommodated by their current stadium for a full season. |
|||
==== 1949–1956: Three-end formation ==== |
|||
[[File:Elroy Hirsch.png|thumb|left|upright|[[Elroy Hirsch]] spent nine seasons with the Los Angeles Rams from 1949 to 1957.]] |
|||
The Rams' first heyday in [[Southern California]] was from 1949 to 1955, when they played in the pre-Super Bowl era [[NFL Championship Game]] four times, winning once in the [[1951 NFL Championship Game|1951]]. During this period, they had the best offense in the NFL, even though there was a quarterback change from [[Bob Waterfield]] to [[Norm Van Brocklin]] in [[1951 NFL season|1951]]. The defining Offensive players of this period were wide receiver [[Elroy Hirsch]], Van Brocklin and Waterfield. Teamed with fellow Hall of Famer [[Tom Fears]], Hirsch helped create the style of Rams football as one of the first big play receivers. During the 1951 Championship season, Hirsch posted a then stunning 1,495 receiving yards with 17 touchdowns. The popularity of this wide-open offense enabled the [[1950 Los Angeles Rams season|Los Angeles Rams]] to become the first pro football team to have all their games televised in [[1950 NFL season|1950]]. |
|||
==== 1957–1964: Newcomers to L.A. and record attendance ==== |
|||
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the Los Angeles Rams went from being the only major professional sports franchise in Southern California and Los Angeles to being one of five. The [[Los Angeles Dodgers]] moved from [[Brooklyn]] in 1958, the [[Los Angeles Chargers]] of the upstart [[American Football League|AFL]] was established in 1960, the [[Los Angeles Lakers]] moved from [[Minneapolis]] in 1960, and the [[Los Angeles Angels]] were awarded to [[Gene Autry]] in 1961. In spite of this, the Rams continued to thrive in Southern California. In the first two years after the Dodgers moved to California, the Rams drew an average of 83,681 in 1958 and 74,069 in 1959. The Rams were so popular in Los Angeles that the upstart Chargers chose to relocate to [[San Diego]] rather than attempt to compete with the immensely popular Rams. The ''[[Los Angeles Times]]'' put the Chargers plight as such: "Hilton [the Chargers owner at the time] quickly realized that taking on the Rams in L.A. was like beating his head against the wall."<ref>{{cite web|last=Dwyre|first=Bill|title=Barron Hilton's Chargers turned short stay into long-term success|url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-2009-nov-30-la-sp-dwyre30-2009nov30-story.html|work=[[Los Angeles Times]]|date=November 30, 2009|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
During this time, the Rams were not as successful on the field as they had been during their first decade. The team's combined record from 1957 to 1964 was 24–35–1 (.407), but the Rams continued to fill the cavernous Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum on a regular basis. While the National Football League's average attendance ranged from the low 30,000s to the low 40,000s during this time, the Rams were drawing anywhere from 10,000 to 40,000 fans more than the league average. In 1957, the Rams set the all-time NFL attendance record that stood until 2006 and broke the 100,000 mark twice during the 1958 campaign.<ref>{{cite web|last=Plaschke|first=Bill|title=Whether Rams return or not, they're still family|url=http://www.latimes.com/sports/la-sp-rams-plaschke-20150107-column.html|work=Los Angeles Times|date=January 6, 2015|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=RAMS STATISTICS-ATTENDANCE|url=http://www.losangelesrams.org/about/statistics/attendance.html|publisher=Bring Back the Los Angeles Rams|access-date=December 5, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151130011412/http://losangelesrams.org/about/statistics/attendance.html|archive-date=November 30, 2015|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
===== Tanking out ===== |
|||
The Rams posted losing records in all but two seasons between 1956 and 1966. In those two seasons, the club finished with a 6 and 6 record in 1957 followed by an 8 and 4 mark and a strong second place showing the next year. Led by business executive [[Pete Rozelle]]'s shrewd understanding of how to use television as a (then) revolutionary promotional device, the Rams remained a business success despite the team's poor record. In a 1957 game against the [[San Francisco 49ers]], the Rams set a record for attendance for a regular-season NFL game (102,368 people).{{Citation needed|date=December 2009}} The Rams drew over 100,000 fans twice the following year. |
|||
==== 1965–1969: The Fearsome Foursome ==== |
|||
The 1960s were defined by the Rams great defensive line of [[Rosey Grier]], [[Merlin Olsen]], [[Deacon Jones]], and [[Lamar Lundy]], dubbed the "[[Fearsome Foursome (football)|Fearsome Foursome]]." It was this group of players who restored the on-field luster of the franchise in [[1967 NFL season|1967]] when the Rams reached (but lost) the conference championship under legendary coach [[George Allen (American football coach)|George Allen]]. That [[1967 Los Angeles Rams season|1967 squad]] would become the first NFL team to surpass one million spectators in a season, a feat the [[1968 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] would repeat the [[1968 NFL season|following year]]. In each of those two years, the L.A. Rams drew roughly double the number of fans that could be accommodated by their current stadium for a full season. |
|||
George Allen led the Rams from 1966 to 1970 and introduced many innovations, including the hiring of a young [[Dick Vermeil]] as one of the first [[special teams]] coaches. Though Allen would enjoy five straight winning seasons and win two divisional titles in his time with the Rams he never won a playoff game with the team, losing in 1967 to [[1967 Green Bay Packers season|Green Bay]] 28–7 and in [[1969 NFL season|1969]] 23–20 to [[1969 Minnesota Vikings season|Minnesota]]. Allen would leave after the 1970 season to take the head coaching job for the Washington Redskins. |
George Allen led the Rams from 1966 to 1970 and introduced many innovations, including the hiring of a young [[Dick Vermeil]] as one of the first [[special teams]] coaches. Though Allen would enjoy five straight winning seasons and win two divisional titles in his time with the Rams he never won a playoff game with the team, losing in 1967 to [[1967 Green Bay Packers season|Green Bay]] 28–7 and in [[1969 NFL season|1969]] 23–20 to [[1969 Minnesota Vikings season|Minnesota]]. Allen would leave after the 1970 season to take the head coaching job for the Washington Redskins. |
||
=== |
==== 1970–1972: Changes ==== |
||
Quarterback [[Roman Gabriel]] played eleven seasons for the Rams dating from |
Quarterback [[Roman Gabriel]] played eleven seasons for the Rams dating from 1962 to 1972. From 1967 to 1971, Gabriel led the Rams to either a first- or second-place finish in their division every year. He was voted the MVP of the entire NFL in 1969, for a season in which he threw for 2,549 yards and 24 TDs while leading the Rams to the playoffs. During the [[1970 NFL season|1970 season]], Gabriel combined with his primary receiver [[Jack Snow (American football)|Jack Snow]] for 51 receptions totaling 859 yards. This would prove to be the best season of their eight seasons as teammates. |
||
In [[1972 NFL season|1972]], Chicago industrialist [[Robert Irsay]] purchased the Rams for $19 million and then traded the franchise to [[Carroll Rosenbloom]] for his [[History of the Indianapolis Colts|Baltimore Colts]] and cash. The Rams remained solid contenders in the 1970s, winning seven straight [[NFC West]] championships between |
In [[1972 NFL season|1972]], [[Chicago]] industrialist [[Robert Irsay]] purchased the Rams for $19 million and then traded the franchise to [[Carroll Rosenbloom]] for his [[History of the Indianapolis Colts|Baltimore Colts]] and cash. The Rams remained solid contenders in the 1970s, winning seven straight [[NFC West]] championships between 1973 and 1979. Though they clearly were the class of the [[National Football Conference|NFC]] in the 1970s along with the [[Dallas Cowboys]] and [[Minnesota Vikings]], they lost the first four conference championship games they played in that decade, losing twice each to Minnesota (1974, 1976) and Dallas (1975, 1978) and failing to win a league championship. |
||
=== |
==== 1973–1979: NFC West champions ==== |
||
===== Chuck Knox's first stint ===== |
|||
The Rams' coach for this run was [[Chuck Knox]], who led the team through 1977. The Chuck Knox-coached Rams featured an unremarkable offense carried into the playoffs annually by an elite defensive unit. The defining player of the 1970s L.A. Rams was [[Jack Youngblood]]. Youngblood was called the 'Perfect Defensive End' by fellow Hall of Famer Merlin Olsen. His toughness was legendary, notably playing on a broken leg during the Rams' run to the [[1980 Super Bowl]]. His blue-collar ethic stood in opposition to the perception that the Rams were a soft 'Hollywood' team. However, several Rams players from this period took advantage of their proximity to Hollywood and crossed over into acting after their playing careers ended. Most notable of these was [[Fred Dryer]], who starred in the TV series ''[[Hunter (U.S. TV series)|Hunter]]'' from 1984 to 1991, as well as Merlin Olson, who retired after 1976. During the 1977 offseason, the Rams, looking for a veteran quarterback, acquired [[Joe Namath]] from the Jets. In spite of a 2-1 start to the [[1977 NFL season|regular season]], Namath's bad knees rendered him nearly immobile and after a [[Monday Night Football|Monday night]] defeat in Chicago, he never played again. With [[Pat Haden]] at the helm, the [[1977 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] won the division and advanced to the [[NFL playoffs, 1977-78|playoffs]], but lost at home to Minnesota. Chuck Knox left for the Bills in [[1978 NFL season|1978]], after which [[Ray Malavasi]] became head coach. Going 12-4, the [[1978 Los Angeles Rams season|team]] won the NFC West for the sixth year in a row and defeated the [[1978 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]], thus avenging their earlier playoff defeat. However, success eluded them again as they were shut out in the NFC Championship by the [[1978 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]. |
|||
[[File:LA Rams Wordmark.gif|250px|thumb|upright|Wordmark logo, used by the Rams from 1973 to 1984]] |
|||
[[File:Jack5-1.jpg|thumb|left|[[Jack Youngblood]] giving his Pro Football Hall of Fame induction speech in 2001]] |
|||
The Rams' coach for this run was [[Chuck Knox]], who led the team through 1977. The Chuck Knox-coached Rams featured an unremarkable offense carried into the playoffs annually by an elite defensive unit. The defining player of the 1970s L.A. Rams was [[Jack Youngblood]]. Youngblood was called the 'Perfect Defensive End' by fellow Hall of Famer Merlin Olsen. His toughness was legendary, notably playing on a broken leg during the Rams' run to the [[1980 Super Bowl]]. His blue-collar ethic stood in opposition to the perception that the Rams were a soft 'Hollywood' team. However, several Rams players from this period took advantage of their proximity to Hollywood and crossed over into acting after their playing careers ended. Most notable of these was [[Fred Dryer]], who starred in the TV series ''[[Hunter (1984 U.S. TV series)|Hunter]]'' from 1984 to 1991, as well as Olsen, who retired after 1976. During the 1977 offseason, the Rams, looking for a veteran quarterback, acquired [[Joe Namath]] from the Jets. In spite of a 2–1 start to the [[1977 NFL season|regular season]], Namath's bad knees rendered him nearly immobile and after a [[Monday Night Football|Monday night]] defeat in Chicago, he never played again. With [[Pat Haden]] at the helm, the [[1977 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] won the division and advanced to the [[1977–78 NFL playoffs|playoffs]], but lost at home to Minnesota. Chuck Knox left for the Bills in [[1978 NFL season|1978]], after which [[Ray Malavasi]] became head coach. Going 12–4, the [[1978 Los Angeles Rams season|team]] won the NFC West for the sixth year in a row and defeated the [[1978 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]], thus avenging their earlier playoff defeat. However, success eluded them again as they were shut out in the [[NFC Championship]] by the [[1978 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]. |
|||
====1979: First Super Bowl appearance==== |
==== 1979: First Super Bowl appearance ==== |
||
{{main|1979 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
{{main article|1979 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
||
[[File:1986 Jeno's Pizza - 46 - Terry Bradshaw.jpg|thumb|right|The Rams lost to the Steelers 19–31 in Super Bowl XIV]] |
|||
Ironically, it was the Rams' weakest divisional winner (an aging [[1979 NFL season|1979]] team that only achieved a 9–7 record) that would achieve the team's greatest success in that period. Led by third-year quarterback [[Vince Ferragamo]], the Rams shocked the heavily favored and two-time defending NFC champion [[1979 Dallas Cowboys season|Dallas Cowboys]] 21–19 in the Divisional Playoffs, then shut out the upstart [[1979 Tampa Bay Buccaneers season|Tampa Bay Buccaneers]] 9–0 in the conference championship game to win the [[National Football Conference Championship Game|NFC]] and reach their first Super Bowl. Along with Ferragamo, key players for the Rams were halfback [[Wendell Tyler]], offensive lineman [[Jackie Slater]], and Pro Bowl defenders [[Jack Youngblood]] and [[Jack "Hacksaw" Reynolds]]. |
|||
The Rams' opponent in their first [[Super Bowl XIV|Super Bowl]] was the defending champion [[1979 Pittsburgh Steelers season|Pittsburgh Steelers]]. The game would be a virtual home game for the Rams as it was played in Pasadena at the [[Rose Bowl (stadium)|Rose Bowl]]. Although some oddsmakers set the Rams as a 10½ point underdog, the Rams played Pittsburgh very tough, leading at halftime 13–10 and at the end of the third quarter 19–17. In the end, however, the Steelers finally asserted themselves, scoring two touchdowns in the 4th quarter and completely shutting down the Rams offense to win their fourth Super Bowl, 31–19. |
|||
Ironically, it was the Rams' weakest divisional winner (an aging [[1979 NFL season|1979]] team that only achieved a 9-7 record) that would achieve the team's greatest success in that period. Led by third-year quarterback [[Vince Ferragamo]], the Rams shocked the heavily favored and two-time defending NFC champion [[1979 Dallas Cowboys season|Dallas Cowboys]] 21-19 in the Divisional Playoffs, then shut out the [[1979 Tampa Bay Buccaneers season|Tampa Bay Buccaneers]] 9-0 in the conference championship game to win the [[National Football Conference Championship Game|NFC]] and reach their first Super Bowl. Along with Ferragamo, key players for the Rams were halfback [[Wendell Tyler]], offensive lineman [[Jackie Slater]], and Pro Bowl defenders [[Jack Youngblood]] and [[Jack "Hacksaw" Reynolds]]. |
|||
==== 1980–1982: The move to Anaheim ==== |
|||
The Rams' opponent in their first [[Super Bowl XIV|Super Bowl]] was the defending champion [[1979 Pittsburgh Steelers season|Pittsburgh Steelers]]. The game would be a virtual home game for the Rams as it was played in Pasadena at the [[Rose Bowl (stadium)|Rose Bowl]]. Although some oddsmakers set the Rams as a 10½ point underdog, the Rams played Pittsburgh very tough, leading at halftime 13-10 and at the end of the third quarter 19-17. In the end, however, the Steelers finally asserted themselves, scoring two touchdowns in the 4th quarter and completely shutting down the Rams offense to win their fourth Super Bowl, 31-19. |
|||
[[File:Anaheim Stadium 1986.jpg|thumb|left|[[Anaheim Stadium]], the home of the Los Angeles Rams from 1980 to 1994]] |
|||
Prior to the [[1979 NFL season]], owner Carroll Rosenbloom died in a drowning accident, and his widow, [[Georgia Frontiere]], inherited 70 percent ownership of the team. Frontiere then fired stepson [[Steve Rosenbloom]] and assumed total control of Rams operations. As had been planned prior to Rosenbloom's death, the Rams moved from their longtime home at the Coliseum to [[Anaheim Stadium]] in nearby [[Orange County, California|Orange County]] in 1980. |
|||
The reason for the move was twofold. First, the NFL's [[NFL blackout#Blackout policies|blackout rule]] forbade games from being televised in the team's local market if 85% of the tickets are not sold out 72 hours prior to opening kickoff. As the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum seated 92,604 at the time, it was rarely possible to sell that many tickets even in the Rams' best years, and so most Rams home games were blacked out. Second, this move was following the population pattern in Southern California. During the 1970s and 1980s, the decline of manufacturing industries in the northeastern United States combined with the desire of many people to live in a warmer climate caused a large-scale population shift to the southern and western states. As a result, many affluent new suburbs were built in the Los Angeles area. Anaheim Stadium was originally built in 1966 to be the home of the [[California Angels]]. To accommodate the Rams' move, the ballpark was reconfigured and enclosed to accommodate a capacity of 69,008 in the football configuration. With their new, smaller home, the Rams had no problem selling out games. |
|||
==Los Angeles Rams: Anaheim era (1980-94)== |
|||
===1980–1982: Starting over in Anaheim=== |
|||
Prior to the 1979 Super Bowl season, owner Carroll Rosenbloom died in a drowning accident, and his widow, [[Georgia Frontiere]], inherited 70% ownership of the team. Frontiere then fired stepson Steve Rosenbloom and assumed total control of Rams operations. As had been planned prior to Rosenbloom's death, the Rams moved from their longtime home at the Coliseum to [[Angel Stadium of Anaheim|Anaheim Stadium]] in nearby Orange County in 1980. The reason for the move was twofold. First, the NFL's [[NFL_blackout#Blackout_policies|blackout rule]] forbade games from being shown on local television if they did not sell out within 72 hours of the opening kickoff. As the Los Angeles Coliseum seated 100,000 people, it was rarely possible to sell that many tickets, and so most Rams home games were blacked out. Second, this move was following the population pattern in Southern California. During the 1970s and 1980s, the decline of manufacturing industries in the northeastern United States combined with the desire of many young people to live in a warmer climate cause a large-scale population shift to the southern and western states. As a result, many affluent new suburbs were built in the Los Angeles area. Anaheim Stadium was originally built in 1965 to be the home of the [[Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim|California Angels]]. To accommodate the Rams' move, the ballpark was reconfigured and enclosed to accommodate crowds of almost 70,000 in football configuration. With their new, smaller home, the Rams had no problem selling out games. |
|||
[[File:1986 Jeno's Pizza - 25 - Archie Manning (cropped).jpg|thumb|right|The Rams playing in their inaugural season at Anaheim Stadium in 1980]] |
|||
In [[1980 NFL season|1980]], the [[1980 Los Angeles Rams season|team]] posted an 11-5 record, but only managed a wild card spot and were sent packing after a loss to the [[1980 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]. Age and injuries finally caught up with the [[1981 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] in [[1981 NFL season|1981]], as they only won six games and missed the playoffs for the first time in nine years. After the [[1982 NFL season|1982 season]] was shortened to nine games by a [[1982 NFL strike|strike]], the [[1982 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] went 2-7, the worst record in the NFC. |
|||
In [[1980 NFL season|1980]], the [[1980 Los Angeles Rams season|team]] posted an 11–5 record, but only managed a wild card spot and were sent packing after a loss to the [[1980 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]. Age and injuries finally caught up with the [[1981 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] in [[1981 NFL season|1981]], as they only won six games, were swept for the first time by the division rival [[New Orleans Saints]], and missed the playoffs for the first time in nine years. After the [[1982 NFL season|1982 season]] was shortened to nine games by a [[1982 NFL strike|strike]], the [[1982 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] went 2–7, the team's worst season since [[1962 Los Angeles Rams season|1962]], when they won only 1 game. |
|||
===== Competition with the Raiders ===== |
|||
In [[1982 NFL season|1982]], the Oakland Raiders moved to Los Angeles and made their home in the Coliseum. The combined effect of these two moves was to divide the Rams' traditional fanbase in two. This was coupled with the early 1980s being rebuilding years for the club, while the [[1983 Los Angeles Raiders season|Raiders]] were winners of [[Super Bowl XVIII]] in the [[1983 NFL season|1983 season]]. Meanwhile, the [[Los Angeles Lakers]] won [[NBA Finals|championships]] in [[1980 NBA Finals|1980]] and [[1982 NBA Finals|1982]] en route to winning five titles in that decade, the [[Los Angeles Dodgers]] won the [[World Series]] in [[1981 World Series|1981]] and [[1988 World Series|1988]], and even the [[Los Angeles Kings]] made a deep run in the playoffs in 1982. As a result, the Rams declined sharply in popularity during the 1980s. |
|||
In [[1982 NFL season|1982]], the [[Oakland Raiders]] moved to Los Angeles and took up residence in the Rams' then-former home, the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum. The combined effect of these two moves was to divide the Rams' traditional fanbase in two. This was coupled with the early 1980s being rebuilding years for the club, while the [[1983 Los Angeles Raiders season|Raiders]] were winners of [[Super Bowl XVIII]] in the [[1983 NFL season|1983 season]]. Meanwhile, the [[Los Angeles Lakers]] won [[NBA Finals|championships]] in [[1980 NBA Finals|1980]] and [[1982 NBA Finals|1982]] en route to winning five titles in that decade, the [[Los Angeles Dodgers]] won the [[World Series]] in [[1981 World Series|1981]] and [[1988 World Series|1988]], and even the [[Los Angeles Kings]] made a deep run in the playoffs in 1982. As a result, the Rams declined sharply in popularity during the 1980s even though the team remained a playoff contender during the decade. |
|||
===1983–1991: Robinson takes over the Rams=== |
==== 1983–1991: Robinson takes over the Rams and the Dickerson era ==== |
||
[[File:1985 Police Raiders-Rams - 20 Eric Dickerson (crop).jpg|thumb|left|[[Eric Dickerson]], one of the best [[running back]]s in history, was most famous for his time with the Los Angeles Rams. In 1984, Dickerson rushed for 2,105 yards in the season, a record that still stands today.]] |
|||
Therefore, the hiring of coach [[John Robinson (coach)|John Robinson]] in 1983 provided a needed boost for pro football in Orange County. The former [[USC Trojans football|USC]] coach began by cutting the aged veterans left over from the 1970s teams. His rebuilding program began to show results when the [[1983 Los Angeles Rams season|team]] rebounded to 9-7 in [[1983 NFL season|1983]] and defeated [[1983 Dallas Cowboys season|Dallas]] in the [[NFL playoffs, 1983-84|playoffs]]. However, the season ended after a rout at the hands of the soon-to-be champion Redskins. Another trip to the playoffs in [[NFL playoffs, 1984-85|1984]] saw them lose to the [[1984 New York Giants season|Giants]]. They made the NFC Championship Game in [[1985 NFL season|1985]] after winning the division, where they would be shut out by the eventual champion [[1985 Chicago Bears season|Chicago Bears]]. |
|||
The hiring of coach [[John Robinson (coach)|John Robinson]] in 1983 provided a needed boost for pro football in Orange County. The former [[USC Trojans football|USC]] coach began by cutting the aged veterans left over from the 1970s teams. His rebuilding program began to show results when the [[1983 Los Angeles Rams season|team]] rebounded to 9–7 in [[1983 NFL season|1983]] and defeated [[1983 Dallas Cowboys season|Dallas]] in the [[1983–84 NFL playoffs|playoffs]]. However, the season ended after a rout at the hands of the soon-to-be champion Redskins. Another trip to the playoffs in [[1984–85 NFL playoffs|1984]] saw them lose to the [[1984 New York Giants season|Giants]]. They made the NFC Championship Game in [[1985 NFL season|1985]] after winning the division, where they would be shut out by the eventual champion [[1985 Chicago Bears season|Chicago Bears]] 24–0. |
|||
The most notable player for the Rams during that period was running back [[Eric Dickerson]], who was drafted in 1983 out of [[SMU Mustangs football|SMU]] and won Rookie of the Year. In 1984, Dickerson rushed for 2,105 yards, setting a new NFL record. Dickerson would end his five hugely successful years for the Rams in 1987 by being traded to the [[Indianapolis Colts]] for a number of players and draft picks after a bitter contract dispute, shortly after the players' strike that year ended. Dickerson |
The most notable player for the Rams during that period was running back [[Eric Dickerson]], who was drafted in 1983 out of [[SMU Mustangs football|SMU]] and won Rookie of the Year. In 1984, Dickerson rushed for 2,105 yards, setting a new NFL record. Dickerson would end his five hugely successful years for the Rams in 1987 by being traded to the [[Indianapolis Colts]] for a number of players and draft picks after a bitter contract dispute, shortly after the players' strike that year ended. Dickerson was the Rams' career rushing leader until 2010, with 7,245 yards. Despite this trade, the Rams remained contenders due to the arrival of the innovative offensive leadership of [[Ernie Zampese]]. Zampese brought the intricate timing routes he had used in making the [[San Diego Chargers]] a state-of-the-art offense. Under Zampese, the Rams rose steadily from 28th rated offense in 1986 to 3rd in 1990. The late 1980s Rams featured a gifted young QB in [[Jim Everett]], a solid rushing attack and a fleet of talented WRs led by [[Henry Ellard]]. |
||
[[File:1986 Jeno's Pizza - 23 - Eric Dickerson and Barry Redden (cropped).jpg|thumb|right|Dickerson (''29'') rushing through the Cowboys' defense in the [[1985–86 NFL playoffs|1985 NFC Divisional Playoff]] game]] |
|||
The [[1988 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] managed to return in [[1988 NFL season|1988]] with a 10-6 record, but then were defeated by [[1988 Minnesota Vikings season|Minnesota]]. [[1989 Los Angeles Rams season|Los Angeles]] won the first five games of [[1989 NFL season|1989]], including a sensational defeat of the defending champion [[1989 San Francisco 49ers season|49ers]]. After eliminating the [[1989 Philadelphia Eagles season|Eagles]] in the [[NFL playoffs, 1989-90|playoffs]], they beat the [[1989 New York Giants season|Giants]] in overtime. In the NFC Championship, the Rams faced the 49ers again and were crushed 30-3. After that, the team crumbled to 5-11 in [[1990 NFL season|1990]], followed by a 3-13 season in [[1991 NFL season|1991]]. |
|||
After a 10–6 season in [[1986 NFL season|1986]], the [[1986 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] were booted from the [[1986–87 NFL playoffs|playoffs]] by the [[1986 Washington Redskins season|Washington Redskins]]. After one game of the [[1987 NFL season|1987 season]] was lost to the [[1987 NFL strike|players' strike]], the NFL employed substitutes, most of which were given derogatory nicknames (in this case the Los Angeles Shams). After a 1–2 record, the [[1987 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams']] regulars returned, but the team only went 6–9 and did not qualify for the [[1987–88 NFL playoffs|postseason]]. |
|||
The [[1988 Los Angeles Rams season|Rams]] managed to return in [[1988 NFL season|1988]] with a 10–6 record, but then were defeated by [[1988 Minnesota Vikings season|Minnesota]] in the wild card round. [[1989 Los Angeles Rams season|Los Angeles]] won the first five games of [[1989 NFL season|1989]], including a sensational defeat of the defending champion [[1989 San Francisco 49ers season|49ers]]. They beat the [[1989 Philadelphia Eagles season|Eagles]] in the [[1989–90 NFL playoffs|wild card game]], then beat the [[1989 New York Giants season|Giants]] in overtime before suffering a 30–3 flogging at the hands of the 49ers in the NFC Championship Game. |
|||
Despite this trade, the Rams remained contenders due to the arrival of the innovative offensive leadership of [[Ernie Zampese]]. Zampese brought the intricate timing routes he had used in making the [[San Diego Chargers]] a state-of-the-art offense. Under Zampese, the Rams rose steadily from 28th rated offense in 1986 to 3rd in 1990. The late 1980s Rams featured a gifted young QB in [[Jim Everett]], a solid rushing attack and a fleet of talented WRs led by [[Henry Ellard]]. After an 11–5 record during the 1989 regular season, it was a team that seemed destined for greater things, until a 'phantom sack' in the 1989 NFC Championship derailed those ambitions. This occurred during a humiliating 30–3 defeat by division-rival San Francisco, when Everett collapsed to the turf untouched by San Francisco defenders.<ref>Van Brocklin, Roman (April 24, 2000). [http://216.117.175.77/April2000/jimeverett.htm Jim Everett & the Phantom Sack]. ''The Herd's "E-Zine"''. Retrieved 14 September 2006.</ref> From then on he was perceived to shy away from hits by Rams fans. As a result of this reputation, Southern California sports talk host, [[Jim Rome]], would refer to Everett as "Chris Everett," referring to the female tennis player [[Chris Evert]], on his radio and television show. During a live interview on Rome's [[ESPN2]] show, [[Talk2]], Everett challenged Rome to call him "Chris" to his face. When Rome responded by calling him "Chris," the seated Everett abruptly stood up, overturned a table, and pushed the startled host to the floor.<ref> [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9HNgqQVHI_8 YouTube video of Jim Everett interview by Jim Rome] ''Jim Rome's ESPN2 show, Talk2 (1994)'' Retrieved 29 January 2007.</ref> Everett then walked off the set. |
|||
Although it wasn't apparent at the time, the 1989 NFC Championship Game was the end of an era. The Rams did not have another winning season in their first stint in Los Angeles. They crumbled to 5–11 in [[1990 NFL season|1990]], followed by a 3–13 season in [[1991 NFL season|1991]]. |
|||
===1992–94: The Demise of the LA Rams=== |
|||
The Rams never recovered from the humiliation. The first half of the 1990s featured losing records, no playoff appearances for the Rams and waning fan interest. The return of Chuck Knox as head coach, after Knox's successful stints as head coach of the [[Buffalo Bills]] and [[Seattle Seahawks]], would not boost the Rams' fortunes. His run-oriented offense marked the end of the Zampese tenure in 1993. The strategy was for the offense to be steady, if unspectacular. Unfortunately for the Rams, Knox's offense was not only aesthetically unpleasing, but dull as well, especially by 1990s standards. The continued losing and uninspired play of the Rams further reduced the Rams fan base, which by 1994 had withered to the point where they were barely part of the Los Angeles sports landscape. The NFL black-out rule, which prevented the broadcast of home games that were not sold out, also worked against the Rams as their frequent non-sellouts denied the team a chance to be shown on local broadcast TV. One of the few bright spots during this time was [[Jerome Bettis]], a bruising running back from Notre Dame. Bettis flourished in Knox' offense, running for 1,400 yards in each of his first two seasons. |
|||
==== 1992–1994: The end of the original Southern California team ==== |
|||
As became increasingly common with sports franchises, the Rams began to blame much of their misfortune on their stadium situation. With Orange County mired in a deep recession resulting largely from defense sector layoffs, the Rams were unable to secure a new or improved stadium in the Los Angeles area, which ultimately cast their future in Southern California into doubt. |
|||
[[File:Atlanta Falcons at Los Angeles Rams 1991-12-08 - 01 (Rams-Falcons crop).jpg|thumb|right|The Rams hosting the [[Atlanta Falcons]] at Anaheim Stadium in 1991]] |
|||
Robinson was fired at the end of the 1991 season. The return of Chuck Knox as head coach, after Knox’ successful stints as head coach of [[List of Buffalo Bills seasons|the Buffalo Bills]] and [[List of Seattle Seahawks seasons|Seattle Seahawks]], would not boost the Rams’ fortunes. His run-oriented offense marked the end of the Zampese tenure in 1993. Knox’ game plans called for an offense that would be steady, if unspectacular. Unfortunately for the Rams, Knox’ offense was not only aesthetically unpleasing but dull as well, especially by 1990s standards. The Rams finished last in the [[NFC West]] during all three years of Knox’ second stint, and were never a serious contender. |
|||
As the losses piled up and the team was seen as playing uninspired football, the Rams’ already dwindling fan base was reduced even further. By 1994, support for the Rams had withered to the point where they were barely part of the Los Angeles sports landscape. With sellouts becoming fewer and far between, the Rams saw more of their games blacked out in Southern California. One of the few bright spots during this time was [[Jerome Bettis]], a bruising running back from Notre Dame. Bettis flourished in Knox’ offense, running for 1,429 yards as a rookie, and 1,025 in his sophomore effort. |
|||
As has become increasingly common with sports franchises, the Rams began to blame much of their misfortune on their stadium situation. With [[Orange County, California|Orange County]] mired in a deep recession resulting largely from defense sector layoffs, the Rams were unable to secure a new or improved stadium in the [[Los Angeles area]], which ultimately cast their future in Southern California into doubt. |
|||
===== Georgia moves the Rams to St. Louis ===== |
|||
The first half of the 1990s featured four straight 10-loss seasons, no playoff appearances, and waning fan interest. The return of Chuck Knox as head coach (after his successful stints as head coach of the [[Buffalo Bills]] and [[Seattle Seahawks]]), would not boost the Rams' fortunes. His run-oriented offense brought the end of Zampese's tenure, in 1993. John Shaw, the team's general manager, was perceived by some to continually squander [[NFL Draft]] picks on sub-standard talent. The offensive scheme was not only unspectacular to watch, but dull by 1990s standards—further alienating fans. |
|||
Team management traded quarterback [[Jim Everett]], and released [[All-Pro]] linebacker [[Kevin Greene]], which set the once-proud franchise further back. At this point, Georgia Frontiere blamed the poor front office decisions on their stadium situation. However, neither Orange County nor the city of Los Angeles were prepared to build a taxpayer-financed stadium just for the Rams. Claiming that Southern California was so unprofitable that the Rams would go bankrupt without a new stadium, Mrs. Frontiere decided to move the team. |
|||
[[File:NFL Rams Classical Helmet.svg|thumb|200px|left|Rams helmet from 1989 to 1994]] |
|||
Georgia Frontiere initially attempted to relocate the Rams to Baltimore,<ref>‘Frontiere Might Move Rams to Baltimore’; ''[[Austin American-Statesman]]'', December 25, 1993, p. E3</ref> but her fellow owners turned that proposal down. Mrs. Frontiere then sought to relocate the team to [[St. Louis]]. This move was initially voted down as well.<ref>{{cite news| url=https://www.nytimes.com/1995/03/16/sports/pro-football-nfl-owners-reject-rams-bid-to-move-to-st-louis.html | work=The New York Times | first=Thomas | last=George | title=PRO FOOTBALL; N.F.L. Owners Reject Rams' Bid to Move To St. Louis | date=March 16, 1995}}</ref><ref>{{cite news| url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1995-03-16-mn-43466-story.html | work=Los Angeles Times | first1=T.J. | last1=Simers | first2=Bill | last2=Plaschke | title=League Owners Reject Rams' Move to St. Louis | date=March 16, 1995}}</ref> The other owners (led by Buffalo's [[Ralph Wilson]], the Jets’ [[Leon Hess]], the Giants' [[Wellington Mara]], Washington's [[Jack Kent Cooke]], Arizona's [[Bill Bidwill]] and Minnesota's John Skoglund) believed that the Rams’ financial problems were due to the Frontieres’ mismanagement.<ref>Hamelin, Joe; ‘Rams off to St. Louis after all’; ''The Press-Enterprise'' <nowiki>[</nowiki>[[Riverside, California|Riverside]], California]; April 13, 1995, p. 1</ref> When Georgia Frontiere threatened to sue the league, Commissioner Paul Tagliabue acquiesced to Frontiere's demands. |
|||
As part of the relocation deal, the city of St. Louis agreed to build a taxpayer-financed stadium, the Trans World Dome (now the [[The Dome at America's Center|Dome at America's Center]]) and guaranteed that the stadium's amenities would be maintained in the top 25 percent of all NFL stadiums. Frontiere waived the clause after a 10-year threshold period passed, as the city implemented a later plan to improve the stadium. |
|||
The move left many in the Los Angeles area, and many of those indifferent to the whole situation, embittered toward the NFL. That sentiment was best expressed by [[Fred Dryer]], who at the time said "I hate these people (the organization and its owner) for what they did, taking the Rams logo with them when they moved to St. Louis. That logo belonged to Southern California."{{citation needed|date=June 2016}} Steve Rosenbloom, the general manager of the team during Carroll Rosenbloom's tenure, opined that teams come and go, but for a team to leave Los Angeles—the second largest media market in America—for St. Louis (approximately the 18th-largest) was simply irresponsible and foolish, in spite of the notoriously fickle support of Los Angeles fans. With the Raiders moving from Los Angeles back to Oakland only a few months later, the NFL would have no franchise in Los Angeles for the first time in fifty seasons. |
|||
==== 1995: Departure ==== |
|||
By 1995, the Rams franchise had withered to a mere shadow of its former self. Accusations and excuses were constantly thrown back and forth between the Rams fan base, ownership, and local politicians. Many in the fan base blamed the ownership of [[Georgia Frontiere]] for the franchise's woes, while ownership cited the out-dated stadium and withering fan support. |
|||
Frontiere finally gave up and decided to move the Rams to St. Louis. However, on March 15, 1995, the other league owners rejected Frontiere's bid to move the franchise by a 21–3–6 vote. Then-Commissioner Paul Tagliabue stated after rejecting the move, "This was one of the most complex issues we have had to approach in years. We had to balance the interest of fans in Los Angeles and in St. Louis that we appreciate very much. In my judgment, they did not meet the guidelines we have in place for such a move." The commissioner also added: "Once the bridges have been burned and people get turned off on a sports franchise, years of loyalty is not respected and it is difficult to get it back. By the same token, there are millions of fans in that area who have supported the Rams in an extraordinary way. The Rams have 50 years of history and the last 5 or so years of difficult times can be corrected."<ref>{{cite web|last=George|first=Thomas|title=PRO FOOTBALL; N.F.L. Owners Reject Rams' Bid to Move To St. Louis|url=https://www.nytimes.com/1995/03/16/sports/pro-football-nfl-owners-reject-rams-bid-to-move-to-st-louis.html|work=[[The New York Times]]|date=March 16, 1995|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author1=T.J. Simers|author2=Bill Plaschke|title=League Owners Reject Rams' Move to St. Louis|url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1995-03-16-mn-43466-story.html|work=Los Angeles Times|date=March 16, 1995|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
Frontiere, however, responded with a thinly veiled threat at a lawsuit. On April 12, 1995 the owners acquiesced to her demands, wary of going through a long, protracted legal battle. Tagliabue simply stated that "The desire to have peace and not be at war was a big factor" in allowing the Rams move to go forward. In a matter of a month, the vote had gone from 21–6 opposed to 23–6 in favor. Jonathan Kraft, son of Patriots owner [[Robert Kraft]], elaborated on the commissioner's remarks by saying that "about five or six owners didn't want to get the other owners into litigation, so they switched their votes." Only six teams remained in opposition to the Rams move from Los Angeles: the Pittsburgh Steelers, New York Giants, New York Jets, Buffalo Bills, Arizona Cardinals, and Washington Redskins. After the vote was over, Steelers owner Dan Rooney publicly stated that he opposed the move of the Los Angeles Rams because "I believe we should support the fans who have supported us for years."<ref>{{cite web|last=Simers|first=T.J.|title=NFL Owners OK Rams' Move to St. Louis|url=https://www.latimes.com/archives/la-xpm-1995-04-13-mn-54268-story.html|work=Los Angeles Times|date=April 13, 1995|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
=== 1995–2015: St. Louis era === |
|||
==== Time in St. Louis ==== |
|||
{{main article|St. Louis Rams|1999 St. Louis Rams season}} |
|||
While in St. Louis, the Rams played their first few home games at [[Busch Memorial Stadium]] before the Trans World Dome (now known as the [[The Dome at America's Center|Dome at America's Center]]) was completed during the middle of the 1995 season. Aided by an offense nicknamed "[[The Greatest Show on Turf]]", a period of success occurred between 1999 and 2004 when the team qualified for the playoffs in five out of those six seasons, including a win in [[Super Bowl XXXIV]] against the [[Tennessee Titans]], and a loss to the [[New England Patriots]] in [[Super Bowl XXXVI]]. Other than that period of success, the St. Louis Rams repeatedly suffered losing seasons. |
|||
==== Attempts to move back to Los Angeles ==== |
|||
{{main article|History of the National Football League in Los Angeles}} |
|||
Within months of the moves of the Rams and Raiders, several NFL teams were rumored to be replacements. They included the [[Cleveland Browns]], the [[Cincinnati Bengals]], the [[Tampa Bay Buccaneers]], and the [[Seattle Seahawks]]. However, the [[Cleveland Browns|Browns]] moved to become the [[Baltimore Ravens]] in {{nfly|1996}} amid [[Cleveland Browns relocation controversy|major controversy]], and a new Browns team occupied a [[FirstEnergy Stadium (Cleveland)|new stadium]] in {{nfly|1999}}. The Bengals, Buccaneers and Seahawks, meanwhile, used L.A.'s vacancy as leverage to convince their cities to help finance new stadiums. Meanwhile, various entities [[Proposed Los Angeles NFL stadiums|proposed new stadiums in Los Angeles]] in an attempt to lure a team to the market. |
|||
===== Seattle Seahawks in Los Angeles ===== |
|||
The closest Los Angeles had come to getting a new NFL franchise prior to 2016 was the [[Seattle Seahawks]]. In March 1996, Seahawks owner [[Ken Behring]] moved office equipment and some athletic gear to the elementary school in Anaheim that once held Rams practices, hoping to get approval for a permanent move to Southern California.<ref>Nightengale, Bob – Without Disney, Angels could become X-rated. (sale of California Angels to Walt Disney Co in jeopardy). Sporting News, March 25, 1996</ref> He also had plans to change the team's name and colors if a move to Los Angeles was successful. Because of an owners' revolt, Behring halted the process and moved the equipment back to [[Seattle]]. Eventually, [[Paul Allen]] bought the team and kept it in Seattle by building Seahawks Stadium, now known as [[Lumen Field]]. |
|||
===== 1999 NFL expansion ===== |
|||
Los Angeles again came close to regaining an NFL team in 1999, when the NFL approved a new franchise, the league's 32nd, for Los Angeles, on the condition that the city and NFL agree on a stadium site and stadium financing.<ref>{{cite web|title=Texans Team History|url=http://www.houstontexans.com/team/history.html|publisher=[[Houston Texans]]|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref> Those agreements were never reached, and on October 6, 1999, the franchise was awarded to a [[Houston]] ownership group instead, which formed the [[Houston Texans]]. |
|||
===== Using Los Angeles as leverage ===== |
|||
During the Rams' 21-year absence from Los Angeles, the market had been used on many different occasions as leverage to finance new stadiums or upgrade existing venues. An excellent example of this was when [[Indianapolis Colts]] owner [[Jim Irsay]]'s airplane appeared at [[Van Nuys Airport]],<ref name="lat20150107">{{cite news|author1=Fenno, Nathan|author2=Farmer, Sam|title=NFL teams often use L.A. to get better deals to stay where they are|url=http://www.latimes.com/sports/nfl/la-sp-la-leverage-city-20150107-story.html|newspaper=Los Angeles Times|date=January 7, 2015|access-date=January 10, 2015}}</ref> presumably for meetings with local officials on moving his team to Los Angeles. He eventually signed a deal to build [[Lucas Oil Stadium|a new venue in Indianapolis]] and Los Angeles continued to be without representation in the National Football League. |
|||
===== City of Champions Revitalization Initiative; Los Angeles Entertainment Center ===== |
|||
{{main article|SoFi Stadium}} |
|||
On January 31, 2014, both the ''[[Los Angeles Times]]'' and the ''[[St. Louis Post-Dispatch]]'' reported that Rams owner [[Stan Kroenke]] had purchased approximately 60 acres of land adjacent to the [[The Forum (Inglewood)|Forum]] in [[Inglewood, California]]. The purchase price was rumored to have been between $90 million and $100 million. Commissioner Roger Goodell represented that Mr. Kroenke informed the league of the purchase. As an NFL owner, any purchase of land in which a potential stadium could be built must be disclosed to the league. Kroenke subsequently announced plans to build an NFL stadium on the site, in connection with the owners of the adjacent 238-acre Hollywood Park site, Stockbridge Capital Group.<ref name="Los Angeles Times"/> This development has further fueled rumors that the Rams intend to return its management and football operations to Southern California. The land was initially targeted for a Walmart Supercenter but [[Walmart]] could not get the necessary permits to build it. Kroenke is married to [[Ann Walton Kroenke]] who is a member of the [[Walton family]] and many of Kroenke's real estate deals have involved Walmart properties. |
|||
On January 5, 2015, the ''[[Los Angeles Times]]'' reported that [[Kroenke Sports & Entertainment]] and [[Stockbridge Capital Group]] were partnering up in developing a new NFL stadium on the [[Inglewood, California|Inglewood]] property owned by Kroenke. The project will include a stadium of 80,000 seats and a performance venue of 6,000 seats while reconfiguring the previously approved [[Hollywood Park Racetrack|Hollywood Park]] plan for up to 890,000 square feet of retail, 780,000 square feet of office space, 2,500 new residential units, a 300-room hotel and 25 acres of public parks, playgrounds, open space and pedestrian and bicycle access. The stadium would likely be ready by 2018.<ref name="Los Angeles Times">{{cite news|last1=Farmer|first1=Sam|last2=Vincent|first2=Roger|title=Owner of St. Louis Rams plans to build NFL stadium in Inglewood|url=http://www.latimes.com/sports/nfl/la-sp-0105-nfl-la-stadium-20150105-story.html#page=1|access-date=5 January 2015|work=Los Angeles Times|date=5 January 2015}}</ref> |
|||
In lieu of this, St. Louis countered with [[National Car Rental Field|a stadium plan for the north riverfront area of downtown]], with the hope of keeping the Rams in the city. On February 24, 2015, the Inglewood City Council approved the stadium plan and the initiative with construction on the stadium planned to begin in December 2015. On December 21, 2015, Construction was officially underway for the stadium on the Hollywood Park site.<ref>{{cite web|last=Wagoner|first=Nick|title=Stan Kroenke buys 60 acres in L.A.|url=https://www.espn.com/los-angeles/nfl/story/_/id/10380150/st-louis-rams-owner-stan-kroenke-buys-60-acres-land-los-angeles|publisher=[[ESPN]]|date=February 1, 2014|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Piper |first=Brandie |title=Report: Rams owner bought 60 acres of land in California |url=http://www.ksdk.com/story/sports/nfl/rams/2014/01/30/stan-kroenke-plot-of-land-california-st-louis-rams/5069985/ |archive-url=https://archive.today/20140221154310/http://www.ksdk.com/story/sports/nfl/rams/2014/01/30/stan-kroenke-plot-of-land-california-st-louis-rams/5069985/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=February 21, 2014 |publisher=[[KSDK]] |date=January 31, 2014 |access-date=December 5, 2015 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last=Farmer|first=Sam|title=A return of L.A. Rams? Owner is said to buy possible stadium site|url=https://www.latimes.com/sports/la-xpm-2014-jan-30-la-sp-nfl-la-rams-20140131-story.html|work=Los Angeles Times|date=January 30, 2014|access-date=December 5, 2015}}</ref> |
|||
===== Stadium issues in St. Louis ===== |
|||
{{main article|The Dome at America's Center#The loss of the Rams (2012–2016)}} |
|||
The Rams and the St. Louis CVC began negotiating deals to get the Rams home stadium, the [[The Dome at America's Center|Edward Jones Dome]] into the top 25 percent of stadiums in the league (i.e., top eight teams of the 32 NFL teams in reference to luxury boxes, amenities and overall fan experience). Under the terms of the lease agreement, the St. Louis CVC was required to make modifications to the Edward Jones Dome in 2005. However, then-owner, Georgia Frontiere, waived the provision in exchange for cash that served as a penalty for the city's noncompliance. The city of St. Louis, in subsequent years, made changes to the scoreboard and increased the natural lighting by replacing panels with windows, although the overall feel remains dark. The minor renovations which totaled about $70 million did not bring the stadium within the specifications required under the lease agreement; thus, keeping the Dome in a state of uncertainty. |
|||
On February 1, 2013, a 3-person panel selected to preside over the arbitration process found that the Edward Jones Dome was not in the top 25 percent of all NFL venues as required under the terms of the lease agreement between the Rams and the CVC. The arbitrator further found that the estimated $700 million in proposed renovations by the Rams was not unreasonable given the terms of the lease agreement. Finally, the city of St. Louis was ordered to pay the Rams attorneys' fees which totaled a reported $2 million. |
|||
Publicly, city, county and state officials expressed no interest in providing further funding to the Edward Jones Dome in light of those entities, as well as taxpayers, continuing to owe approximately $300 million more on that facility. As such, if a resolution was not reached by the end of the [[2014 NFL season]] and the city of St. Louis remained non-compliant in its obligations under the lease agreement, the Rams would be free to nullify their lease and go to a year-to-year lease. Months later, the Rams scheduled to play in London, which violates the Edward Jones Dome's terms of lease. |
|||
===== Filing for relocation; Houston meetings ===== |
|||
[[File:LA Rams Fans.jpg|thumb|250px|Rally held at the [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]] in support of the Rams moving back to Los Angeles]] |
|||
On January 4, 2016, the St. Louis Rams filed for relocation to move to the Los Angeles area for the [[2016 NFL season]]. They were among the three teams (the Rams, [[Oakland Raiders]], and the [[San Diego Chargers]]) that filed for relocation to Los Angeles. All three franchises previously played in the [[Los Angeles metropolitan area]]. Weeks later, the NFL owners gathered in Houston for a meeting on January 11 and January 12, a meeting that decided the end of the Los Angeles race. A few days before the scheduled owners meeting, [[Dallas Cowboys]] owner [[Jerry Jones]] suggested that the Rams and Chargers should share Stan Kroenke's [[SoFi Stadium]]. This suggestion was taken as a possible option discussed in the Houston meetings. During the Los Angeles meeting, the Committee on Los Angeles Opportunities, which consists of six NFL owners, favored the [[Carson Stadium|Carson project]] over the Rams' Inglewood project. Despite this, thanks to Jerry Jones' pitch, the first round of voting during the meeting, the Rams got the greater number of votes, conquering the Carson project 21–11.<ref name="The Wow Factor">{{cite web|last1=Wickersham|first1=Seth|last2=Van Natta Jr.|first2=Don|title=The Wow Factor: The Real Story of the NFL Owners Battle To Bring Football Back To Los Angeles|url=https://www.espn.com/espn/feature/story/_/id/14752649/the-real-story-nfl-owners-battle-bring-football-back-los-angeles|publisher=ESPN|work=[[ESPN The Magazine]]|date=February 11, 2016|access-date=June 26, 2016}}</ref> However, the Rams did not meet the required 24 votes in the second round of voting the Rams Inglewood project received 20 votes while the Chargers and Raiders Carson project received only 12 votes. After hours of searching to find a compromise, it was determined that the Rams would relocate to Los Angeles and the Chargers would have the option to join them, while the Raiders would have the option to join the Rams if the Chargers elected not to move.<ref>{{cite news|last=Hanzus|first=Dan|title=Rams to relocate to L.A.; Chargers first option to join|url=https://www.nfl.com/news/rams-to-relocate-to-l-a-chargers-first-option-to-join-0ap3000000621645|website=NFL.com|publisher=National Football League|date=January 12, 2016|access-date=January 13, 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Rams to Return to Los Angeles|url=http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/Rams-to-Return-to-Los-Angeles/802b4e16-671e-4864-97b6-943115cdc4cf|publisher=St. Louis Rams|date=January 12, 2016|access-date=January 13, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160120221040/http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/Rams-to-Return-to-Los-Angeles/802b4e16-671e-4864-97b6-943115cdc4cf|archive-date=January 20, 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
<ref>{{cite news|title=Rams headed back to Los Angeles; Chargers have option to join|url=https://www.espn.com/nfl/story/_/id/14558668/st-louis-rams-relocate-los-angeles|agency=Associated Press|publisher=ESPN|date=January 12, 2016|access-date=January 13, 2016}}</ref> The Chargers used their option in January 2017 becoming the [[Los Angeles Chargers]] (and returning to their original home where they played in their inaugural season of 1960). |
|||
=== 2016–present: Return to Los Angeles === |
|||
[[File:California_lutheran_university_los_angeles_rams.jpg|thumb|LA Rams banner at [[California Lutheran University]] in Thousand Oaks.]] |
|||
Upon relocating back to Los Angeles in 2016, the Rams initially played their home games at the [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]], which had been home to the team for 33 seasons (1946–1979), and is the home of the [[USC Trojans football|USC Trojans]] college football team, until [[SoFi Stadium]] was completed four years later in 2020.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nbclosangeles.com/news/sports/Inglewood-Stadium-Opening-Delayed-Till-2020-423012364.html|title=Rain Delay: Opening of Inglewood Stadium Pushed Back to 2020|date=May 18, 2017|website=NBC Sports|access-date=March 30, 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Rearden|first1=Tim|title=LA COLISEUM PREPARES TO HOST NFL GAMES IN 2016|url=http://abc7.com/sports/la-coliseum-prepares-to-host-nfl-games-in-2016/1158491/|website=abc7.com|publisher=[[American Broadcasting Company|ABC]]|access-date=January 18, 2016}}</ref> |
|||
During that time The Rams' return to Los Angeles was used to help expand the league's presence around the globe. In 2016, the Rams faced the [[New York Giants]] in London at [[Twickenham Stadium]], as part of the NFL's [[NFL International Series|International Series]].<ref name="Rams to Play at Twickenham">{{cite web|title=Rams to Play First Ever NFL Game at Twickenham Stadium|url=http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/Rams-to-Play-First-Ever-NFL-Game-at-Twickenham-Stadium/f638f81b-a7c4-49b3-ade4-2610cf4f5566|publisher=St. Louis Rams|date=November 25, 2015|access-date=June 26, 2016|archive-date=June 21, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160621162753/http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/Rams-to-Play-First-Ever-NFL-Game-at-Twickenham-Stadium/f638f81b-a7c4-49b3-ade4-2610cf4f5566|url-status=dead}}</ref> Kevin Demoff, the team's Executive Vice President of Football Operations/Chief Operating Officer, told ''[[The Guardian]]'' that he sees L.A. as a gateway to Asia and says being in L.A. will help sell the brand, more so, than in St. Louis.<ref name="Rams Global">{{cite news|last=Carpenter|first=Les|title=Could the LA Rams become the NFL's first truly global team?|url=https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2016/apr/08/los-angeles-nfl-global-team|website=Guardian|date=April 8, 2016|access-date=June 26, 2016|quote=We don't want to play games in just London; we want to explore the Asian opportunity", Demoff said. "We want to grow the brand internationally. I think there's an opportunity to grow the Rams brand and I think the league wants to grow their brand in that market.}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Los Angeles Rams wordmark.svg|200px|thumb|right|Los Angeles Rams wordmark, 2016–2019]] |
|||
On February 4, 2016, the Los Angeles Rams selected [[Oxnard, California]] to be the site of their minicamp, offseason team activities, and offseason program that began on April 18. In March, it was announced that the Rams would be featured on [[HBO]]'s ''[[Hard Knocks (documentary series)|Hard Knocks]]''.<ref>{{cite news|last=Wesseling|first=Chris|title=Los Angeles Rams will be featured on 'Hard Knocks'|url=https://www.nfl.com/news/los-angeles-rams-will-be-featured-on-hard-knocks-0ap3000000646684|publisher=National Football League|date=March 23, 2016|access-date=March 25, 2016}}</ref> On March 30, [[California Lutheran University]] and the Rams reached an agreement that allowed the team to have regular-season training operations at CLU's campus for the next two years. The Rams paid for two practice fields, paved parking, and modular buildings constructed on the northwestern corner of the campus.<ref name="RamsCLUAgreement">{{cite news|last=Sessler|first=Marc|title=Rams choose Cal Lutheran for temporary training site|url=https://www.nfl.com/news/rams-choose-cal-lutheran-for-temporary-training-site-0ap3000000648936|publisher=National Football League|website=NFL.com|date=March 30, 2016|access-date=March 30, 2016}}</ref><ref name="LARamsCalLutheran">{{cite news|title=L.A. Rams training moving to Cal Lutheran|url=http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/LA-Rams-training-moving-to-Cal-Lutheran/c0cd7402-d587-4c87-9ac1-5754557429dd|publisher=Los Angeles Rams|date=March 30, 2016|access-date=April 1, 2016|quote=The facility at Cal Lutheran is the home base for about 130 athletes, coaches, trainers and other staff members.|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160401144546/http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/LA-Rams-training-moving-to-Cal-Lutheran/c0cd7402-d587-4c87-9ac1-5754557429dd|archive-date=April 1, 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
==== 2016 season: Jared Goff era begins ==== |
|||
{{main|2016 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
[[File:Jared Goff.JPG|200px|thumb|left|[[Jared Goff]] in his 2016 rookie season]] |
|||
On April 13, 2016, the Los Angeles Rams traded their 2016 first-round pick, two second-round picks, a third-round pick, and their 2017 first-round and third-round picks to the [[Tennessee Titans]] in exchange for the [[List of first overall National Football League draft picks|number one pick]], alongside their fourth-round pick and a sixth-round pick. The Rams decided to wait until after [[Los Angeles Lakers|Lakers]] great [[Kobe Bryant]]'s last game before announcing the blockbuster trade.<ref name="Rams Acquire First Overall Pick">{{cite news|last=Orr|first=Conor|title=L.A. Rams trade up to acquire No. 1 pick from Titans|url=https://www.nfl.com/news/l-a-rams-trade-up-to-acquire-no-1-pick-from-titans-0ap3000000652822|publisher=National Football League|date=April 14, 2016|access-date=June 26, 2016}}</ref> |
|||
On April 28, 2016, the Rams drafted quarterback [[Jared Goff]] from California, with the 1st overall pick in the 1st round. The team also selected tight end [[Tyler Higbee]] and wide receiver [[Pharoh Cooper]] in the 4th round with the 110th and 117th picks, tight end [[Temarrick Hemingway]], linebacker [[Josh Forrest]], and wide receiver [[Mike Thomas (wide receiver, born 1994)|Mike Thomas]] in the 6th round with the 190th, 193rd, and 206th picks. In June 2016, it was reported that the Rams had sold 63,000 season tickets, which was short of their goal of 70,000. Later on July 12, 2016, it was reported that they had sold 70,000 [[ticket (admission)|ticket]]s, reaching their goal. In July 2016, the Rams signed a three-year agreement with [[UC Irvine]] to use the university's facilities for training camp, with an option to extend it to two more years. On July 29, 2016, the ''Los Angeles Times'' reported that the Rams would host their first training-camp practice and "Rams Family Day" on Saturday, August 6 at the [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]], which was open to the public.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Klein|first1=Gary|title=Rams will hold first training-camp practice Saturday|url=http://www.latimes.com/sports/rams/la-sp-rams-training-camp-20160729-snap-story.html|newspaper=Los Angeles Times|access-date=4 August 2016}}</ref> |
|||
The Rams played their first game in the Los Angeles area since 1994, a 22-year absence, with a preseason opener against the [[2016 Dallas Cowboys season|Dallas Cowboys]] at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum on August 13. The Rams defeated the Cowboys 28–24 in front of a crowd of 89,140, a record attendance for a pre-season game.<ref>{{cite news|last=Bain|first=Nate|title=Rams Victorious in Return to Los Angeles|url=http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/Rams-Victorious-in-Return-to-Los-Angeles/039fc607-24af-4e67-b693-27b008ab8230|publisher=Los Angeles Rams|date=August 13, 2016|access-date=August 14, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160818134605/http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/Rams-Victorious-in-Return-to-Los-Angeles/039fc607-24af-4e67-b693-27b008ab8230|archive-date=August 18, 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
On September 12, 2016, the Rams played their first regular season game since returning to Los Angeles, where they lost to the [[2016 San Francisco 49ers season|San Francisco 49ers]] 28–0 at [[Levi's Stadium]]. On September 18, in front of over 91,000 fans at the [[Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum]], The Rams played their first home game on September 18, 2016, defeating the [[2016 Seattle Seahawks season|Seattle Seahawks]] 9–3.<ref name="It wasn't pretty but Rams win home opener, 9-3, over Seahawks">{{cite web|last1=Klein|first1=Gary|title=It wasn't pretty but Rams win home opener, 9-3, over Seahawks|url=http://www.latimes.com/sports/rams/la-sp-rams-seahawks-20160918-snap-story.html|website=Los Angeles Times|date=September 18, 2016|access-date=September 19, 2016}}</ref> |
|||
===== Fisher's firing ===== |
|||
On December 12, 2016, the team fired head coach [[Jeff Fisher]] after starting the season with a 4−9 record.<ref>{{cite news|last=Orr|first=Conor|title=Los Angeles Rams fire head coach Jeff Fisher|url=https://www.nfl.com/news/los-angeles-rams-fire-head-coach-jeff-fisher-0ap3000000755854|publisher=National Football League|date=December 12, 2016|access-date=December 12, 2016}}</ref> The team announced later that day that [[John Fassel]] would be taking over as interim head coach.<ref>{{cite news|title=John Fassel Named Rams Interim Head Coach|url=http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/John-Fassel-Named-Rams-Interim-Head-Coach/45376efe-b1c2-4974-ba48-02f35044b3df|publisher=Los Angeles Rams|date=December 12, 2016|access-date=December 12, 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161212224755/http://www.therams.com/news-and-events/article-1/John-Fassel-Named-Rams-Interim-Head-Coach/45376efe-b1c2-4974-ba48-02f35044b3df|archive-date=December 12, 2016|url-status=dead}}</ref> Fassel is the son of former NFL head coach [[Jim Fassel]] and had been the Rams special teams coach since the 2012 season. |
|||
==== 2017 season: McVay's hiring and first winning season since 2003 ==== |
|||
{{main|2017 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
On January 12, 2017 (the same day the [[Los Angeles Chargers|Chargers]] moved to the [[Los Angeles area]] as the team did) the Rams hired [[Sean McVay]] for the team's head coaching vacancy. McVay, then 30, became the youngest head coach in NFL history. McVay was formerly the offensive coordinator of the Redskins, working under coach [[Jay Gruden]]. Quarterback [[Jared Goff]] had begun to come into his own as an elite quarterback under McVay and running back [[Todd Gurley]] had returned to dominance. On November 26, 2017, the Rams defeated the [[2017 New Orleans Saints season|New Orleans Saints]] 26–20. The win was their eighth of the season, which secured their first non-losing year since [[2006 St. Louis Rams season|2006]] (and first in Los Angeles since [[1989 Los Angeles Rams season|1989]]). A week later, the Rams would defeat the [[2017 Arizona Cardinals season|Arizona Cardinals]] 32–16 to secure a winning season for the first time since the [[2003 St. Louis Rams season|2003 season]]. On December 24, 2017, the Rams defeated the [[2017 Tennessee Titans season|Tennessee Titans]] 27–23 to clinch their first NFC West title since 2003 (and first in Los Angeles since [[1985 Los Angeles Rams season|1985]]). Following a lost to the [[2017 San Francisco 49ers season|San Francisco 49ers]], the Rams went 11-5 and won their first division title since 2003, as well as their first playoff berth since [[2004 St. Louis Rams season|2004]]. |
|||
The Rams would lose in the Wild Card game against the defending NFC champion [[2017 Atlanta Falcons season|Atlanta Falcons]] 26–13. |
|||
==== 2018 season: Super Bowl run ==== |
|||
{{main|2018 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
The 2018 off-season was highlighted with acquiring [[Marcus Peters]] from the [[Kansas City Chiefs]], signing [[Ndamukong Suh]] in free agency, and acquiring five-time Pro Bowler [[Aqib Talib]] and [[Brandin Cooks]] via trades. While also signing Brandin Cooks, [[Todd Gurley]], [[Rob Havenstein]] and [[Aaron Donald]] to long-term deals. |
|||
The Rams opened their 2018 season on September 10 by defeating the [[2018 Oakland Raiders season|Oakland Raiders]] 33–13 on ''[[Monday Night Football]]'', scoring 23 unanswered second half points in a game where head coach McVay took on his former mentor, [[Jon Gruden]], who was making his return to coaching. It was the first of two ''Monday Night Football'' appearances for the Rams in the season. The Rams continued their strong start throughout the season finishing the first half of the season 8–0, their best start since [[1969 Los Angeles Rams season|1969]]. The Rams were the only remaining undefeated team in the NFL in 2018 until losing on the road to the [[2018 New Orleans Saints season|New Orleans Saints]] in Week 9 at the [[Mercedes-Benz Superdome]]. The Rams bounced back with three straight wins, defeating the [[2018 Seattle Seahawks season|Seattle Seahawks]] 36–31, and then winning a wild [[2018 Kansas City Chiefs–Los Angeles Rams game|54–51 shootout]] against the [[2018 Kansas City Chiefs season|Kansas City Chiefs]] on ''Monday Night Football''. Following a bye week, the Rams beat the host [[2018 Detroit Lions season|Detroit Lions]] 30–16 in Week 13 to clinch both a playoff berth and their second straight NFC West title. Los Angeles stumbled with back-to-back losses to the [[2018 Chicago Bears season|Chicago Bears]] and [[2018 Philadelphia Eagles season|Philadelphia Eagles]], but finished strong with victories over the [[2018 Arizona Cardinals season|Arizona Cardinals]] and [[2018 San Francisco 49ers season|San Francisco 49ers]] to clinch a first round bye. The Rams' 13–3 record tied for the best record in the league, while having the second-most wins in a single season in franchise history and were the most ever for any NFL team in Los Angeles. |
|||
The Rams defeated the [[2018 Dallas Cowboys season|Dallas Cowboys]] 30–22 in the divisional round to head to the NFC Championship Game for the first time since [[2001 St. Louis Rams season|2001]]. It was also the Rams' first playoff win since 2004. The Rams would meet the Saints again, but this time beating the Saints on the road 26–23 to advance to the Super Bowl for the first time since 2001 and first appearance based in Los Angeles since [[1979 Los Angeles Rams season|1979]]. Their opponent in [[Super Bowl LIII]] was the [[2018 New England Patriots season|New England Patriots]], whom they had previously faced in [[Super Bowl XXXVI]] when they were based in St. Louis, but narrowly lost 20–17. Despite their immense talent, the Rams offense was stymied and ineffective throughout the game, being held to no touchdowns and only one field goal. They held the Patriots to a 3–3 tie after 3 quarters, but lost 13–3. The Rams joined the [[1971 Miami Dolphins season|1971 Miami Dolphins]] in [[Super Bowl VI]] to only score 3 points in the Super Bowl. |
|||
==== 2019 season: Post-Super Bowl slump and Last season at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum ==== |
|||
{{main|2019 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
The season was filled with injuries and setbacks, as Los Angeles narrowly missed the playoffs with a 9–7 record. It also marked the Rams' final year at the Coliseum. |
|||
==== 2020 season: Debut at SoFi Stadium and COVID-19 ==== |
|||
{{main|2020 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
The Rams and Chargers moved into the newly completed [[SoFi Stadium]], but due to the [[COVID-19 pandemic]], were forced to play there without spectators.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Rams, Chargers announce fans will not be allowed to attend games 'until further notice'|url=https://sports.yahoo.com/rams-chargers-announce-fans-will-not-be-allowed-to-attend-games-until-further-notice-190726680.html|access-date=2020-09-05|website=Yahoo! Sports|date=August 25, 2020 |language=en-US}}</ref> The Rams also cut oft-injured running back [[Todd Gurley]], who previously led the league in rushing three times, during the offseason.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Jackson |first=Stu |date=March 19, 2020 |title=Rams release RB Todd Gurley |url=https://www.therams.com/news/rams-release-rb-todd-gurley |access-date=March 19, 2020 |website=therams.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Patra |first=Kevin |date=March 19, 2020 |title=Rams release former OPOY, standout Todd Gurley |url=https://www.nfl.com/news/rams-release-former-opoy-standout-todd-gurley-0ap3000001107050 |access-date=March 19, 2020 |website=NFL.com}}</ref> Despite being the first team to lose to the [[2020 New York Jets season|New York Jets]] in week 15,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Costello |first=Brian |date=2020-12-21 |title=Jets stun Rams to win first game — damaging Trevor Lawrence hopes |url=https://nypost.com/2020/12/20/jets-stun-rams-to-win-first-game-damaging-trevor-lawrence-hopes/ |access-date=2020-12-26 |website=New York Post |language=en-US}}</ref> the Rams finished the season at 10–6, returning to the playoffs. They beat the rival [[2020 Seattle Seahawks season|Seattle Seahawks]] in the wild card round, with backup quarterback [[John Wolford]] starting in place of an injured Goff, though Wolford would leave the game with a neck injury.<ref>{{cite web |title=Jared Goff replaces injured John Wolford in Rams' win over Seahawks; Aaron Donald dealing with rib injury |url=https://www.nfl.com/news/rams-qb-john-wolford-exits-after-hit-to-head-jared-goff-in |website=NFL.com |access-date=9 January 2021}}</ref> The team would lose to the [[2020 Green Bay Packers season|Green Bay Packers]] the following week during the divisional round. |
|||
==== 2021 season: End of Jared Goff era, Arrival of Matthew Stafford, and Super Bowl win ==== |
|||
{{main|2021 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
On March 18, 2021, Los Angeles traded Jared Goff and several draft picks to the [[Detroit Lions]] in exchange for their longtime quarterback [[Matthew Stafford]].<ref name="Stafford Trade">{{Cite web |title=Rams trade Jared Goff, future draft picks to Lions for Matthew Stafford |url=https://www.therams.com/news/rams-trade-jared-goff-future-draft-picks-to-lions-for-matthew-stafford |publisher=therams.com |access-date=2021-03-18}}</ref> The Rams started off strongly by winning seven out of their first eight games, but a three-game losing streak in November dropped the team to 7-4. Wide receiver [[Robert Woods (wide receiver, born 1992)|Robert Woods]] was lost for the season, but the Rams bolstered their roster by signing free agent wide receiver [[Odell Beckham Jr.]] and trading for former [[Denver Broncos]] All-Pro linebacker [[Von Miller]]. Los Angeles won five straight games but lost at home to the [[San Francisco 49ers]] to finish the regular season at 12-5, which clinched the team's third NFC West Division title since head coach [[Sean McVay]]'s arrival. |
|||
In the playoffs, the Rams routed the division rival [[Arizona Cardinals]] 34-11 in the first playoff game played at SoFi Stadium. A week later in Tampa Bay, Los Angeles built a 27-3 lead, then withstood a rally led by [[Tom Brady]] to defeat the [[Tampa Bay Buccaneers|Buccaneers]] 30-27. The Rams returned home for the [[NFC Championship Game]] to face the 49ers, who had won six straight regular season meetings. Despite trailing by 10 points going into the fourth quarter, the Rams came back to win 20-17 to earn their second trip to the [[Super Bowl]] in four seasons. Playing at their home stadium for [[Super Bowl LVI]] as the 'away' team, the Rams again overcame a late deficit to defeat the AFC champion [[Cincinnati Bengals]] 23-20, winning the franchise's second Super Bowl championship, and first in Los Angeles. Wide receiver [[Cooper Kupp]] was named the game's [[Super Bowl MVP|Most Valuable Player]]. |
|||
==== 2022 season: Super Bowl hangover ==== |
|||
{{main|2022 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
In 2022, injuries and regression derailed the Rams' chances of repeating as Super Bowl champions. Most notably, core contributors to the 2021 Super Bowl-winning team, including [[Matthew Stafford]], [[Cooper Kupp]], and [[Aaron Donald]], missed significant parts of the season with injuries. Los Angeles also experienced a historic number of offensive line injuries that forced McVay to start eleven different offensive line combinations in the first eleven games of the season, something that no team had done since the 1970 AFL-NFL merger. The team began the season by losing in blowout fashion on national television to the Super Bowl-hopeful [[Buffalo Bills]], and the game seemingly set the tone for the 2022 Rams, who never looked like their 2021 selves during the season. Although Los Angeles managed to stay afloat with a 3-3 record through six games, the team endured a deep slump and lost their next six games en route to a 5-12 finish. The .294 win percentage was the worst ever for a defending Super Bowl champion. |
|||
==== 2023 season: Resurgence and return to the playoffs ==== |
|||
{{main|2023 Los Angeles Rams season}} |
|||
Following the team's disastrous 2022 season, the Rams parted ways with several defensive contributors, as the team traded cornerback [[Jalen Ramsey]] to the [[Miami Dolphins]], released edge rusher [[Leonard Floyd]], and released linebacker [[Bobby Wagner]]. McVay and general manager [[Les Snead]] also stockpiled several mid-to-late round draft picks in the upcoming [[2023 NFL draft]]. |
|||
With the aforementioned moves, many expected the Rams to enter into a rebuilding stage and struggle throughout the 2023 season. However, the Rams returned to the playoffs as a wild card team (despite struggling to a 3-6 record before the bye week) thanks to the resurgence of Stafford and strong play from rookies such as wide receiver [[Puka Nacua]], defensive tackle [[Kobie Turner]], and linebacker [[Byron Young (linebacker)|Byron Young]]. |
|||
In the wild card round of the [[2023-24 NFL playoffs]], the Rams faced off against the NFC North champion [[Detroit Lions]], led by former Rams quarterback Jared Goff. The game was also notable for being Stafford's first game in Detroit as an opposing player (Stafford spent his first twelve seasons playing for Detroit). In a game that was dominated by storylines about the Stafford-Goff trade and dubbed as a "revenge game" for quarterbacks Stafford and Goff, the Lions emerged victorious with a narrow 24-23 win. Los Angeles was undone by scoring zero touchdowns in three red zone trips, while Detroit converted all three of its own red zone trips into touchdowns. |
|||
==List of seasons== |
|||
{{dablink|This section only lists the Rams' seasons in Los Angeles. For list of seasons of the entire Rams franchise, see [[List of Los Angeles Rams seasons]].}} |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size: 95%" |
|||
|- |
|||
!rowspan="2"|[[List of NFL seasons|Season]] |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Team |
|||
!rowspan="2"|[[List of leagues of American football|League]] |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Conference |
|||
!rowspan="2"|Division |
|||
!colspan="4"|[[National Football League regular season|Regular Season]] |
|||
!colspan="2"|Attendance |
|||
!rowspan="2" style="width:29%;"|[[National Football League playoffs|Postseason]] Results |
|||
!rowspan="2" style="width:20%;"|Awards |
|||
|- |
|||
!Finish |
|||
!Wins |
|||
!Losses |
|||
!Ties |
|||
!style="width:10%;"|Rams Average |
|||
!style="width:10%;"|NFL Average |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" colspan="13" style="{{NFLPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams|year=1946|border=2}};"|'''Los Angeles Rams (1946–1994)'''<ref>[[Dan Reeves (NFL owner)|Dan Reeves]] moved the team due to poor attendance at and competing against the [[Cleveland Browns]], the Rams became the first NFL team based on the [[West Coast of the United States|West Coast]].</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1946}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1946 Los Angeles Rams season|1946]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|42,834 <small>(2/10)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|34,397 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1947}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1947 Los Angeles Rams season|1947]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|32,130 <small>(5/10)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|30,226 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1948}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1948 Los Angeles Rams season|1948]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|28,258 <small>(5/10)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|26,240 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1949}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1949 Los Angeles Rams season|1949]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|44,043 <small>(1/10)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|24,798 |
|||
| Lost [[1949 NFL Championship Game|NFL Championship]] ([[1949 Philadelphia Eagles season|Eagles]]) 14–0 |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1950}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1950 Los Angeles Rams season|1950]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''National''' |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|26,341 <small>(6/13)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|27,070 |
|||
|bgcolor="#ddffdd"|'''Won''' National Conference Playoff ([[1950 Chicago Bears season|Bears]]) 24–14<br>Lost [[1950 NFL Championship Game|NFL Championship]] ([[1950 Cleveland Browns season|Browns]]) 30–28 |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1951}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1951 Los Angeles Rams season|1951]] |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #FFE6BD;"|'''NFL''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''National''' |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|44,196 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|28,741 |
|||
|style="background: #FFE6BD;"|'''Won [[1951 NFL Championship Game|NFL Championship]] <small>(2)</small>''' ([[1951 Cleveland Browns season|Browns]]) 24–17 |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1952}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1952 Los Angeles Rams season|1952]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|National |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#CCFFFF"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|53,157 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|31,278 |
|||
|Lost National Conference Playoff ([[1952 Detroit Lions season|Lions]]) 31–21 |
|||
|[[Hamp Pool]] ([[NFL Coach of the Year|COY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1953}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1953 Los Angeles Rams season|1953]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|54,744 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|32,895 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1954}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1954 Los Angeles Rams season|1954]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|54,734 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|33,769 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1955}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1955 Los Angeles Rams season|1955]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''Western''' |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|66,159 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|37,796 |
|||
|bgcolor="#ddffdd"|Lost [[1955 NFL Championship Game|NFL Championship]] ([[1955 Cleveland Browns season|Browns]]) 38–14 |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1956}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1956 Los Angeles Rams season|1956]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|T-5th |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|61,190 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|38,293 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1957}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1957 Los Angeles Rams season|1957]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|74,296 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|42,160 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1958}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1958 Los Angeles Rams season|1958]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|T-2nd |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|83,681 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|44,690 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1959}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1959 Los Angeles Rams season|1959]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|6th |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|74,069 <small>(1/12)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|46,134 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1960}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1960 Los Angeles Rams season|1960]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|6th |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|61,724 <small>(1/21)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|32,150 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1961}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1961 Los Angeles Rams season|1961]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|6th |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|47,992 <small>(7/22)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|33,874 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1962}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1962 Los Angeles Rams season|1962]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|7th |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|41,572 <small>(9/22)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|35,355 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1963}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1963 Los Angeles Rams season|1963]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|6th |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|42,302 <small>(9/22)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|36,610 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1964}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1964 Los Angeles Rams season|1964]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|5th |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|55,764 <small>(5/22)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|40,636 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1965}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1965 Los Angeles Rams season|1965]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|7th |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|40,333 <small>(13/22)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|43,489 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1966}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1966 Los Angeles Rams season|1966]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|49,776 <small>(10/24)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|45,732 |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1967}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1967 Los Angeles Rams season|1967]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''[[NFL Coastal Division|Coastal]]''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|60,000 <small>(6/25)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|48,606 |
|||
|Lost [[NFL playoffs, 1967|Conference Playoff Game]] ([[1967 Green Bay Packers season|Packers]]) 28–7 |
|||
|[[George Allen (American football coach)|George Allen]] ([[NFL Coach of the Year|COY]])<br>[[Deacon Jones]] ([[NFL Defensive Player of the Year Award|DPOY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1968}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1968 Los Angeles Rams season|1968]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center"|Coastal |
|||
|align="center"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|65,127 <small>(4/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|48,777 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Deacon Jones]] ([[NFL Defensive Player of the Year|DPOY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1969}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1969 Los Angeles Rams season|1969]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|Western |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''Coastal''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|71,242 <small>(3/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|51,053 |
|||
|Lost [[NFL playoffs, 1969|Conference Playoff Game]] ([[1969 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]]) 23–20 |
|||
|[[Roman Gabriel]] ([[NFL MVP|MVP]])/([[St Louis Rams awards#Daniel F. Reeves Memorial Award|Rams MVP]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1970}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1970 Los Angeles Rams season|1970]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|[[National Football Conference|NFC]] |
|||
|align="center"|[[NFC West|West]] |
|||
|align="center"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|71,242 <small>(2/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|54,375 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Merlin Olsen]] (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1971}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1971 Los Angeles Rams season|1971]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|8 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|72,453 <small>(3/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|56,935 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Isiah Robertson]] ([[NFL Defensive Rookie of the Year Award|DROY]])<br>[[Marlin McKeever]] (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1972}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1972 Los Angeles Rams season|1972]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|72,461 <small>(4/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|58,416 |
|||
| |
|||
|Merlin Olsen (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1973}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1973 Los Angeles Rams season|1973]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|74,168 <small>(2/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|55,339 |
|||
|Lost [[1973–74 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1973 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 27–16 |
|||
|[[Chuck Knox]] ([[NFL Coach of the Year|COY]])<br>[[John Hadl]] ([[UPI NFC Player of the Year|NFC]])/(Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1974}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1974 Los Angeles Rams season|1974]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|75,492 <small>(2/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|52,098 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1974–75 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1974 Washington Redskins season|Redskins]]) 19–10<br>Lost [[1974–75 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1974 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]]) 14–10 |
|||
|[[Lawrence McCutcheon]] (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1975}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1975 Los Angeles Rams season|1975]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|65,284 <small>(4/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|52,754 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1975–76 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1975 St. Louis Cardinals (NFL) season|Cardinals]]) 35–23<br>Lost [[1975–76 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1975 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 37–7 |
|||
|[[Jack Youngblood]] ([[NFL Defensive Player of the Year|DPOY]])/(Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1976}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1976 Los Angeles Rams season|1976]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|1 |
|||
|align="center"|63,141 <small>(4/26)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|53,983 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1976–77 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1976 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 14–12<br>Lost [[1976–77 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1976 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]]) 24–13 |
|||
|Jack Youngblood (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1977}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1977 Los Angeles Rams season|1977]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|53,585 <small>(10/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|52,711 |
|||
|Lost [[1977–78 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1977 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]]) 14–7 |
|||
|Lawrence McCutcheon (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1978}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1978 Los Angeles Rams season|1978]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|53,388 <small>(14/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|53,983 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1978–79 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1978 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]]) 34–10<br>Lost [[1978–79 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1978 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 28–0 |
|||
|[[Jim Youngblood]] (Rams MVP) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1979}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1979 Los Angeles Rams season|1979]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''NFC''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|52,970 <small>(17/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|55,960 |
|||
|bgcolor="#ddffdd"|'''Won''' [[1979–80 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] (Cowboys) 21–19<br>'''Won '''[[1979–80 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1979 Tampa Bay Buccaneers season|Buccaneers]]) 9–0<br>Lost [[Super Bowl XIV]] ([[1979 Pittsburgh Steelers season|Steelers]]) 31–19 |
|||
|Jack Youngblood (Rams MVP)<br>[[Kent Hill]] ([[St Louis Rams awards#Carroll Rosenbloom Memorial Award|Rams ROY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1980}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1980 Los Angeles Rams season|1980]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|62,550 <small>(8/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|56,667 |
|||
|Lost [[1980–81 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[1980 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 34–13 |
|||
|[[Vince Ferragamo]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Johnnie Johnson (American football)|Johnnie Johnson]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1981}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1981 Los Angeles Rams season|1981]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|60,503 <small>(11/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|57,665 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Nolan Cromwell]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Jairo Penaranda]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1982}}<ref>1982 was a strike-shortened season so the league was divided up into two conferences instead of its normal divisional alignment.</ref> |
|||
|align="center"|[[1982 Los Angeles Rams season|1982]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"|14th |
|||
|align="center"|2 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|51,690 <small>(16/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|52,527 |
|||
| |
|||
|Vince Ferragamo (Rams MVP)<br>[[Barry Redden]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1983}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1983 Los Angeles Rams season|1983]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|52,780 <small>(15/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|54,364 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1983–84 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] (Cowboys) 24–17<br>Lost [[1983–84 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1983 Washington Redskins season|Redskins]]) 51–7 |
|||
|[[Eric Dickerson]] ([[NFL Offensive Rookie of the Year Award|OROY]])/NFC/Rams MVP/Rams ROY |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1984}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1984 Los Angeles Rams season|1984]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|54,455 <small>(17/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|55,528 |
|||
|Lost [[1984–85 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[1984 New York Giants season|Giants]]) 16–13 |
|||
|Eric Dickerson (NFC)/(Rams MVP)<br>[[Ron Brown (wide receiver)|Ron Brown]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1985}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1985 Los Angeles Rams season|1985]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|56,242 <small>(15/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|55,408 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1985–86 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1985 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 20–0<br>Lost [[1985–86 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1985 Chicago Bears season|Bears]]) 24–0 |
|||
|[[LeRoy Irvin]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Dale Hatcher]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1986}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1986 Los Angeles Rams season|1986]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|59,285 <small>(10/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|56,872 |
|||
|Lost [[1986–87 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[1986 Washington Redskins season|Redskins]]) 19–7 |
|||
|[[Eric Dickerson]] ([[NFL Offensive Player of the Year Award|OPOY]])(NFC)/(Rams MVP)<br>[[Jim Everett]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1987}}<ref>The strike of 1987 reduced the regular season schedule from sixteen to fifteen games.</ref> |
|||
|align="center"|[[1987 Los Angeles Rams season|1987]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|47,356 <small>(18/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|48,639 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Charles White (American football)|Charles White]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Cliff Hicks]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1988}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1988 Los Angeles Rams season|1988]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|54,469 <small>(17/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|56,727 |
|||
|Lost [[1988–89 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[1988 Minnesota Vikings season|Vikings]]) 28–17 |
|||
|[[Henry Ellard]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Robert Delpino]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1989}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1989 Los Angeles Rams season|1989]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|58,846 <small>(11/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|57,257 |
|||
|'''Won''' [[1989–90 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[1989 Philadelphia Eagles season|Eagles]]) 21–7<br>'''Won''' [[1989–90 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[1989 New York Giants season|Giants]]) 19–13<br>Lost [[1989–90 NFL playoffs|Conference Championship]] ([[1989 San Francisco 49ers season|49ers]]) 30–3 |
|||
|Jim Everett (Rams MVP)<br>[[Darryl Henley]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1990}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1990 Los Angeles Rams season|1990]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|59,920 <small>(12/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|59,665 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Buford McGee]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Bern Brostek]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1991}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1991 Los Angeles Rams season|1991]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|13 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|51,586 <small>(22/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|58,926 |
|||
| |
|||
|Robert Delpino (Rams MVP)<br>[[Todd Lyght]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1992}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1992 Los Angeles Rams season|1992]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|47,811 <small>(25/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|58,734 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Jackie Slater]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Sean Gilbert]](Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1993}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1993 Los Angeles Rams season|1993]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|45,401 <small>(25/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|59,352 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Jerome Bettis]] ([[NFL Rookie of the Year|OROY]])(Rams MVP)/(Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|1994}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[1994 Los Angeles Rams season|1994]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|4th |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|43,312 <small>(28/28)</small> |
|||
|align="center"|60,107 |
|||
| |
|||
|[[Shane Conlan]] (Rams MVP)<br>[[Isaac Bruce]] (Rams ROY) |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" colspan="13" style="{{NFLPrimaryStyle|St. Louis Rams|border=2}};|'''St. Louis Rams (1995–2015)''' |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" colspan="13" style="{{NFLPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams|border=2}};"|'''Los Angeles Rams (2016–present)''' |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2016}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2016 Los Angeles Rams season|2016]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|4 |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"|84,457 <small>(2/32)</small><!--The number on ESPN only uses the one figure from London, not the 7 games in Los Angeles—this is the correct average attendance of the 7 games at the Coliseum--> |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2017}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2017 Los Angeles Rams season|2017]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|11 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|Lost [[2017–18 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[2017 Atlanta Falcons season|Falcons]]) 26-13 |
|||
|[[Sean McVay]] ([[NFL Coach of the Year|COY]])<br>[[Todd Gurley]] ([[Associated Press NFL Defensive Player of the Year Award|OPOY]])<br> [[Aaron Donald]] ([[Associated Press NFL Defensive Player of the Year Award|DPOY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2018}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2018 Los Angeles Rams season|2018]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''NFC''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|13 |
|||
|align="center"|3 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|bgcolor="#ddffdd"|'''Won''' [[2018–19 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[2018 Dallas Cowboys season|Cowboys]]) 30–22<br>'''Won''' [[2018 NFC Championship Game|NFC Championship]] ([[2018 New Orleans Saints season|Saints]]) 26–23 (OT) <br>'''Lost''' [[Super Bowl LIII]] ([[2018 New England Patriots season|Patriots]]) 3–13 |
|||
| [[Aaron Donald]] ([[Associated Press NFL Defensive Player of the Year Award|DPOY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2019}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2019 Los Angeles Rams season|2019]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|9 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2020}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2020 Los Angeles Rams season|2020]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|6 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|'''Won''' [[2020–21 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[2020 Seattle Seahawks season|Seahawks]]) 30–20<br>Lost [[2020–21 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[2020 Green Bay Packers season|Packers]]) 18-32 |
|||
| [[Aaron Donald]] ([[Associated Press NFL Defensive Player of the Year Award|DPOY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2021}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2021 Los Angeles Rams season|2021]] |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #FFE6BD;"|'''NFL''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #ddffdd;"|'''NFC''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''West''' |
|||
|align="center" style="background: #D0E7FF;"|'''1st''' |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|style="background: #FFE6BD;"|'''Won''' [[2021–22 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] ([[2021 Arizona Cardinals season|Cardinals]]) 34–11<br>'''Won''' [[2021–22 NFL playoffs|Divisional Playoffs]] ([[2021 Tampa Bay Buccaneers season|Buccaneers]]) 30–27<br>'''Won''' [[2021–22 NFL playoffs|NFC Championship]] ([[2021 San Francisco 49ers season|49ers]]) 20–17<br>'''Won [[Super Bowl LVI]]''' ([[2021 Cincinnati Bengals season|Bengals]]) 23–20 |
|||
|[[Cooper Kupp]] ([[Super Bowl Most Valuable Player Award|SB MVP]], [[NFL Offensive Player of the Year|OPOY]])<br>[[Andrew Whitworth]] ([[Walter Payton NFL Man of the Year|WPMOY]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2022}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2022 Los Angeles Rams season|2022]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center"|3rd |
|||
|align="center"|5 |
|||
|align="center"|12 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|{{nfly|2023}} |
|||
|align="center"|[[2023 Los Angeles Rams season|2023]] |
|||
|align="center"|NFL |
|||
|align="center"|NFC |
|||
|align="center"|West |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#96CDCD"|2nd |
|||
|align="center"|10 |
|||
|align="center"|7 |
|||
|align="center"|0 |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|align="center"| |
|||
|Lost [[2023–24 NFL playoffs|Wild Card Playoffs]] (at [[2023 Detroit Lions season|Lions]]) 23–24 |
|||
| |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center" rowSpan="3" colSpan="6"|Total<br>2 NFL Titles (1951 and 2021)<br>6 Conference Titles<br>13 Division Titles<br>26 Playoff Appearances |
|||
|align="center"|'''438''' |
|||
|align="center"|'''354''' |
|||
|align="center"|'''18''' |
|||
|colSpan="4"|(regular season)<ref name="exclude">1946–1994</ref> |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center"|'''19''' |
|||
|align="center"|'''23''' |
|||
|align="center"|'''0''' |
|||
|colSpan="4"|(playoffs) |
|||
|- |
|||
!align="center"|'''457''' |
|||
!align="center"|'''377''' |
|||
!align="center"|'''18''' |
|||
|colSpan="4"|(regular season and playoffs)<ref name="exclude" /> |
|||
|} |
|||
''* Between 1946 and 1994, the Los Angeles Rams Played a total of 679 Regular Season Games and 32 Playoff Games (711 Games)'' |
|||
''* Between 1946 and 1994, the Los Angeles Rams had a total record of 364–297 (Regular), 12–20 (Postseason), and 376–317 (Total)'' |
|||
==Pro Football Hall of Famers== |
|||
{{dablink|This section only lists Pro Football Hall of Famers who were with the Rams when they played in Los Angeles. For a complete list of Rams Hall of Fame inductees (including those that only played when the team was in St. Louis), see [[Los Angeles Rams#Hall of Famers]].}} |
|||
Former Los Angeles Rams in the [[Pro Football Hall of Fame]] include [[Jerome Bettis]] (36), [[Joe Namath]] (12), [[Ollie Matson]] (33), [[Andy Robustelli]] (84), [[Dick "Night Train" Lane]] (81), and general manager [[Tex Schramm]]. GM and later NFL [[Commissioner]] [[Pete Rozelle]] and coach [[Sid Gillman]] are also members of the Hall of Fame, but were elected on the basis of their performances with other teams or (in the case of Rozelle) NFL administration. |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan="5" style="{{NFLPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|'''Los Angeles Rams Hall of Famers''' |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="width:40px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|No. |
|||
! style="width:150px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Player |
|||
! style="width:30px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Class |
|||
! style="width:40px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Position(s) |
|||
! style="width:90px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Tenure |
|||
|- |
|||
| — ||[[George Allen (American football coach)|George Allen]]||2002||Coach|| 1966–1970 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 36 ||[[Jerome Bettis]]||2015||[[Running back|RB]]|| 1993–1994 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 76 ||[[Bob Brown (offensive lineman)|Bob Brown]]||2004||[[Offensive tackle|OT]]|| 1969–1970 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 29 ||[[Eric Dickerson]]||1999||[[Running back|RB]]|| 1983–1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 55 ||[[Tom Fears]]||1970||[[End (football)|End]]|| 1948–1956 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 40 ||[[Elroy Hirsch|Elroy "Crazy Legs" Hirsch]]||1968||[[Running back|RB]], [[Wide receiver|WR]]|| 1949–1957 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 75 ||[[Deacon Jones]]||1980||[[Defensive end|DE]]|| 1961–1971 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 65 ||[[Tom Mack]]||1999||[[Offensive guard|G]]|| 1966–1978 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 74 ||[[Merlin Olsen]]||1982||[[Defensive tackle|DT]]|| 1962–1976 |
|||
|- |
|||
| – ||[[Dan Reeves (NFL owner)|Dan Reeves]]||1967||Owner|| 1946–1971 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 67, 48 ||[[Les Richter]]||2011||[[Linebacker|LB]], [[Placekicker|K]]|| 1954–1962 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 78 ||[[Jackie Slater]]||2001||[[Offensive tackle|OT]]|| 1976–1994 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 25 ||[[Norm Van Brocklin]]||1971||[[Quarterback|QB]], [[Punter (football position)|P]]|| 1949–1957 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 7 ||[[Bob Waterfield]]||1965||[[Quarterback|QB]], [[Defensive back|DB]], [[Placekicker|K]], [[Punter (football position)|P]]|| 1946–1952 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 85 ||[[Jack Youngblood]]||2001||[[Defensive end|DE]]|| 1971–1984 |
|||
|- |
|||
| 91 ||[[Kevin Greene]]||2016||[[Linebacker|LB]], [[Defensive end|DE]]|| 1985–1992 |
|||
|} |
|||
===Retired numbers=== |
|||
Numbers that have been retired by the Rams. This list includes players who have played most of their career in Los Angeles Only. |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="text-align:center" |
|||
|- |
|||
| colspan="4" style="{{NFLPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|'''Los Angeles Rams retired numbers''' |
|||
|- |
|||
! style="width:40px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|No. |
|||
! style="width:150px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Player |
|||
! style="width:40px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Position |
|||
! style="width:100px; {{NFLAltPrimaryStyle|Los Angeles Rams 73thru94}};"|Tenure |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''7''' || [[Bob Waterfield]] || [[Quarterback|QB]] || 1945–1952 |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''29''' || [[Eric Dickerson]] || [[Running back|RB]] || 1983–1987 |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''74''' || [[Merlin Olsen]] || [[Defensive tackle|DT]] || 1962–1976 |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''75''' || [[Deacon Jones]] || [[Defensive end|DE]] || 1961–1971 |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''78''' || [[Jackie Slater]] || [[Offensive tackle|OT]] || 1976–1995 |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''85''' || [[Jack Youngblood]] || [[Defensive end|DE]] || 1971–1984 |
|||
|} |
|||
* [[Bob Waterfield]] played his first season in Cleveland |
|||
* [[Jackie Slater]] played his last season in St. Louis |
|||
==Radio and television== |
|||
The Rams were the first NFL team to televise their home games; in a sponsorship arrangement with [[Admiral (electrical appliances)|Admiral]] television, all home games of the [[1950 NFL season]] were shown locally. The Rams also televised games in the early 1950s. The [[1951 NFL Championship Game]] was the first championship game televised coast-to-coast (via the [[DuMont Television Network|DuMont Network]]). During the team's years in Los Angeles all games were broadcast on [[KSPN (AM)|KMPC]] radio (710 AM); play-by-play announcers were [[Bob Kelley]] (who accompanied the team from Cleveland and worked until his death in 1966), [[Dick Enberg]] (1966–1977), Al Wisk (1978–1979), [[Bob Starr (sportscaster)|Bob Starr]] (1980–1989, 1993), [[Eddie Doucette]] (1990), [[Paul Olden]] (1991–1992), and [[Steve Physioc]] (1994). Analysts included [[Gil Stratton]], Steve Bailey, [[Dave Niehaus]] (1968–1972), [[Don Drysdale]] (1973–1976), [[Dick Bass]] (1977–1986), [[Jack Youngblood]] (1987–1991), [[Jack Snow (American football)|Jack Snow]] (1992–1994), and [[Deacon Jones]] (1994). Today, Pac-12 Network broadcaster [[J. B. Long (sportscaster)|J.B. Long]] is the current play-by-play announcer with former running back [[Maurice Jones-Drew]] as the side analyst. |
|||
==In popular culture== |
|||
* In the 1978 film ''[[Heaven Can Wait (1978 film)|Heaven Can Wait]]'', Joe Pendleton ([[Warren Beatty]]), a fictional quarterback for the Los Angeles Rams, is looking forward to leading his team to the [[Super Bowl]]. |
|||
==See also== |
|||
* [[History of the National Football League in Los Angeles]] |
|||
* [[History of the Los Angeles Chargers]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist|30em}} |
||
{{Los Angeles Rams}} |
{{Los Angeles Rams}} |
||
{{NFL team history}} |
|||
{{Greater Los Angeles Area Sports}} |
|||
{{1951 Los Angeles Rams}} |
|||
{{Orange County Sports}} |
|||
{{California sports}} |
|||
[[Category:Los Angeles Rams]] |
[[Category:History of the Los Angeles Rams| ]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:American football in Los Angeles]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:History of Los Angeles]] |
||
[[Category:National Football League in Los Angeles]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 23:43, 12 October 2024
| This article is part of series of |
| Los Angeles Rams history |
|---|
| Cleveland Rams (1936–1945) |
| Los Angeles Rams (1946–1994) |
| St. Louis Rams (1995–2015) |
| Los Angeles Rams (2016–present) |
| List of seasons |
The Los Angeles Rams are a professional American football team that plays and competes in the National Football League (NFL). The Rams franchise was founded in 1936 as the Cleveland Rams in the short-lived second American Football League before joining the NFL the next year. In 1946, the franchise moved to Los Angeles. The Rams franchise remained in the metro area until 1994, when they moved to St. Louis, and were known as the St. Louis Rams from 1995 to 2015. The Rams franchise returned to Los Angeles in 2016. This article chronicles the franchise's history during their time in Los Angeles, from playing at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum between 1946 and 1979, to playing at Anaheim Stadium (now known as Angel Stadium of Anaheim) in Anaheim from 1980 to 1994, and its return to Southern California beginning with the 2016 to 2019 seasons playing temporarily at their old home the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum before moving to SoFi Stadium in Inglewood in 2020 alongside the Los Angeles Chargers.
History
[edit]1946–1994: Origins in Los Angeles
[edit]1946–1948: Starting over in Los Angeles
[edit]On January 12, 1946, Dan Reeves was denied a request by the other National Football League (NFL) owners to move his team, the Cleveland Rams to Los Angeles and the then-103,000-seat Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum.[1] Reeves threatened to end his relationship with the NFL and get out of the professional football business altogether unless the Rams transfer to Los Angeles was permitted.[1][2][3] A settlement was reached and, as a result, Reeves was allowed to move his team to Los Angeles.[1][4][5][6] Consequently, the NFL became the first professional coast-to-coast sports entertainment industry.[1]
From 1933, when Joe Lillard left the Chicago Cardinals, through 1946, there were no Black players in American professional football.[7] After the Rams had received approval to move to Los Angeles, the Rams entered into negotiations to lease the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum. The Rams were advised that a precondition to them getting a lease was that they would have to integrate the team with at least one African-American; the Rams agreed to this condition.[8][9][10][11] Subsequently, the Rams signed Kenny Washington on March 21, 1946.[12][13][14] The signing of Washington caused "all hell to break loose" among the owners of the NFL franchises.[15] The Rams added a second black player, Woody Strode, on May 7, 1946, giving them two black players going into the 1946 season.
The Rams were the first team in the NFL to play in Los Angeles (the 1926 Los Angeles Buccaneers were strictly a road team), but they were not the only professional football team to play its home games in the Coliseum between 1946 and 1949. The upstart All-America Football Conference had the Los Angeles Dons compete there as well. Reeves was taking a gamble that Los Angeles was ready for its own professional football team – and suddenly there were two in the City of Angels. Reeves was proved to be correct when the Rams played their first pre-season game against the Washington Redskins in front of a crowd of 95,000 fans. The team finished their first season in L.A. with a 6–4–1 record, second place behind the Chicago Bears. At the end of the season Walsh was fired as head coach. The Coliseum would be the home of the Rams for more than 30 years (the Dons merged with them in late 1949),[16] but the facility was already over 20 years old on the day of the first kickoff. In 1948, halfback Fred Gehrke painted horns on the Rams' helmets, making the first modern helmet emblem in pro football.[17]
The Rams' play-by-play announcer from 1937 through 1965 was Robert J. "Bob" Kelley, known as "The Voice of the Rams", also broadcast for NCAA teams Notre Dame and Michigan football as well as the Los Angeles Angels Pacific Coast League team and American League team. Kelley had an early evening talk show on L.A. radio station KMPC, that was considered by most sports enthusiasts as highly entertaining. Kelley was generally considered a Legend and a true professional, one of the great radio, play-by-play announcers of our time. At the beginning of the 1951 World Championship game after the kickoff, Kelley was able to cite every player on the field prior to the first snap from scrimmage, an 80-yard touchdown ("and I think he's going to go all the way").
1949–1956: Three-end formation
[edit]
The Rams' first heyday in Southern California was from 1949 to 1955, when they played in the pre-Super Bowl era NFL Championship Game four times, winning once in the 1951. During this period, they had the best offense in the NFL, even though there was a quarterback change from Bob Waterfield to Norm Van Brocklin in 1951. The defining Offensive players of this period were wide receiver Elroy Hirsch, Van Brocklin and Waterfield. Teamed with fellow Hall of Famer Tom Fears, Hirsch helped create the style of Rams football as one of the first big play receivers. During the 1951 Championship season, Hirsch posted a then stunning 1,495 receiving yards with 17 touchdowns. The popularity of this wide-open offense enabled the Los Angeles Rams to become the first pro football team to have all their games televised in 1950.
1957–1964: Newcomers to L.A. and record attendance
[edit]In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the Los Angeles Rams went from being the only major professional sports franchise in Southern California and Los Angeles to being one of five. The Los Angeles Dodgers moved from Brooklyn in 1958, the Los Angeles Chargers of the upstart AFL was established in 1960, the Los Angeles Lakers moved from Minneapolis in 1960, and the Los Angeles Angels were awarded to Gene Autry in 1961. In spite of this, the Rams continued to thrive in Southern California. In the first two years after the Dodgers moved to California, the Rams drew an average of 83,681 in 1958 and 74,069 in 1959. The Rams were so popular in Los Angeles that the upstart Chargers chose to relocate to San Diego rather than attempt to compete with the immensely popular Rams. The Los Angeles Times put the Chargers plight as such: "Hilton [the Chargers owner at the time] quickly realized that taking on the Rams in L.A. was like beating his head against the wall."[18]
During this time, the Rams were not as successful on the field as they had been during their first decade. The team's combined record from 1957 to 1964 was 24–35–1 (.407), but the Rams continued to fill the cavernous Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum on a regular basis. While the National Football League's average attendance ranged from the low 30,000s to the low 40,000s during this time, the Rams were drawing anywhere from 10,000 to 40,000 fans more than the league average. In 1957, the Rams set the all-time NFL attendance record that stood until 2006 and broke the 100,000 mark twice during the 1958 campaign.[19][20]
Tanking out
[edit]The Rams posted losing records in all but two seasons between 1956 and 1966. In those two seasons, the club finished with a 6 and 6 record in 1957 followed by an 8 and 4 mark and a strong second place showing the next year. Led by business executive Pete Rozelle's shrewd understanding of how to use television as a (then) revolutionary promotional device, the Rams remained a business success despite the team's poor record. In a 1957 game against the San Francisco 49ers, the Rams set a record for attendance for a regular-season NFL game (102,368 people).[citation needed] The Rams drew over 100,000 fans twice the following year.
1965–1969: The Fearsome Foursome
[edit]The 1960s were defined by the Rams great defensive line of Rosey Grier, Merlin Olsen, Deacon Jones, and Lamar Lundy, dubbed the "Fearsome Foursome." It was this group of players who restored the on-field luster of the franchise in 1967 when the Rams reached (but lost) the conference championship under legendary coach George Allen. That 1967 squad would become the first NFL team to surpass one million spectators in a season, a feat the Rams would repeat the following year. In each of those two years, the L.A. Rams drew roughly double the number of fans that could be accommodated by their current stadium for a full season.
George Allen led the Rams from 1966 to 1970 and introduced many innovations, including the hiring of a young Dick Vermeil as one of the first special teams coaches. Though Allen would enjoy five straight winning seasons and win two divisional titles in his time with the Rams he never won a playoff game with the team, losing in 1967 to Green Bay 28–7 and in 1969 23–20 to Minnesota. Allen would leave after the 1970 season to take the head coaching job for the Washington Redskins.
1970–1972: Changes
[edit]Quarterback Roman Gabriel played eleven seasons for the Rams dating from 1962 to 1972. From 1967 to 1971, Gabriel led the Rams to either a first- or second-place finish in their division every year. He was voted the MVP of the entire NFL in 1969, for a season in which he threw for 2,549 yards and 24 TDs while leading the Rams to the playoffs. During the 1970 season, Gabriel combined with his primary receiver Jack Snow for 51 receptions totaling 859 yards. This would prove to be the best season of their eight seasons as teammates.
In 1972, Chicago industrialist Robert Irsay purchased the Rams for $19 million and then traded the franchise to Carroll Rosenbloom for his Baltimore Colts and cash. The Rams remained solid contenders in the 1970s, winning seven straight NFC West championships between 1973 and 1979. Though they clearly were the class of the NFC in the 1970s along with the Dallas Cowboys and Minnesota Vikings, they lost the first four conference championship games they played in that decade, losing twice each to Minnesota (1974, 1976) and Dallas (1975, 1978) and failing to win a league championship.
1973–1979: NFC West champions
[edit]Chuck Knox's first stint
[edit]

The Rams' coach for this run was Chuck Knox, who led the team through 1977. The Chuck Knox-coached Rams featured an unremarkable offense carried into the playoffs annually by an elite defensive unit. The defining player of the 1970s L.A. Rams was Jack Youngblood. Youngblood was called the 'Perfect Defensive End' by fellow Hall of Famer Merlin Olsen. His toughness was legendary, notably playing on a broken leg during the Rams' run to the 1980 Super Bowl. His blue-collar ethic stood in opposition to the perception that the Rams were a soft 'Hollywood' team. However, several Rams players from this period took advantage of their proximity to Hollywood and crossed over into acting after their playing careers ended. Most notable of these was Fred Dryer, who starred in the TV series Hunter from 1984 to 1991, as well as Olsen, who retired after 1976. During the 1977 offseason, the Rams, looking for a veteran quarterback, acquired Joe Namath from the Jets. In spite of a 2–1 start to the regular season, Namath's bad knees rendered him nearly immobile and after a Monday night defeat in Chicago, he never played again. With Pat Haden at the helm, the Rams won the division and advanced to the playoffs, but lost at home to Minnesota. Chuck Knox left for the Bills in 1978, after which Ray Malavasi became head coach. Going 12–4, the team won the NFC West for the sixth year in a row and defeated the Vikings, thus avenging their earlier playoff defeat. However, success eluded them again as they were shut out in the NFC Championship by the Cowboys.
1979: First Super Bowl appearance
[edit]
Ironically, it was the Rams' weakest divisional winner (an aging 1979 team that only achieved a 9–7 record) that would achieve the team's greatest success in that period. Led by third-year quarterback Vince Ferragamo, the Rams shocked the heavily favored and two-time defending NFC champion Dallas Cowboys 21–19 in the Divisional Playoffs, then shut out the upstart Tampa Bay Buccaneers 9–0 in the conference championship game to win the NFC and reach their first Super Bowl. Along with Ferragamo, key players for the Rams were halfback Wendell Tyler, offensive lineman Jackie Slater, and Pro Bowl defenders Jack Youngblood and Jack "Hacksaw" Reynolds.
The Rams' opponent in their first Super Bowl was the defending champion Pittsburgh Steelers. The game would be a virtual home game for the Rams as it was played in Pasadena at the Rose Bowl. Although some oddsmakers set the Rams as a 10½ point underdog, the Rams played Pittsburgh very tough, leading at halftime 13–10 and at the end of the third quarter 19–17. In the end, however, the Steelers finally asserted themselves, scoring two touchdowns in the 4th quarter and completely shutting down the Rams offense to win their fourth Super Bowl, 31–19.
1980–1982: The move to Anaheim
[edit]
Prior to the 1979 NFL season, owner Carroll Rosenbloom died in a drowning accident, and his widow, Georgia Frontiere, inherited 70 percent ownership of the team. Frontiere then fired stepson Steve Rosenbloom and assumed total control of Rams operations. As had been planned prior to Rosenbloom's death, the Rams moved from their longtime home at the Coliseum to Anaheim Stadium in nearby Orange County in 1980.
The reason for the move was twofold. First, the NFL's blackout rule forbade games from being televised in the team's local market if 85% of the tickets are not sold out 72 hours prior to opening kickoff. As the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum seated 92,604 at the time, it was rarely possible to sell that many tickets even in the Rams' best years, and so most Rams home games were blacked out. Second, this move was following the population pattern in Southern California. During the 1970s and 1980s, the decline of manufacturing industries in the northeastern United States combined with the desire of many people to live in a warmer climate caused a large-scale population shift to the southern and western states. As a result, many affluent new suburbs were built in the Los Angeles area. Anaheim Stadium was originally built in 1966 to be the home of the California Angels. To accommodate the Rams' move, the ballpark was reconfigured and enclosed to accommodate a capacity of 69,008 in the football configuration. With their new, smaller home, the Rams had no problem selling out games.

In 1980, the team posted an 11–5 record, but only managed a wild card spot and were sent packing after a loss to the Cowboys. Age and injuries finally caught up with the Rams in 1981, as they only won six games, were swept for the first time by the division rival New Orleans Saints, and missed the playoffs for the first time in nine years. After the 1982 season was shortened to nine games by a strike, the Rams went 2–7, the team's worst season since 1962, when they won only 1 game.
Competition with the Raiders
[edit]In 1982, the Oakland Raiders moved to Los Angeles and took up residence in the Rams' then-former home, the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum. The combined effect of these two moves was to divide the Rams' traditional fanbase in two. This was coupled with the early 1980s being rebuilding years for the club, while the Raiders were winners of Super Bowl XVIII in the 1983 season. Meanwhile, the Los Angeles Lakers won championships in 1980 and 1982 en route to winning five titles in that decade, the Los Angeles Dodgers won the World Series in 1981 and 1988, and even the Los Angeles Kings made a deep run in the playoffs in 1982. As a result, the Rams declined sharply in popularity during the 1980s even though the team remained a playoff contender during the decade.
1983–1991: Robinson takes over the Rams and the Dickerson era
[edit]
The hiring of coach John Robinson in 1983 provided a needed boost for pro football in Orange County. The former USC coach began by cutting the aged veterans left over from the 1970s teams. His rebuilding program began to show results when the team rebounded to 9–7 in 1983 and defeated Dallas in the playoffs. However, the season ended after a rout at the hands of the soon-to-be champion Redskins. Another trip to the playoffs in 1984 saw them lose to the Giants. They made the NFC Championship Game in 1985 after winning the division, where they would be shut out by the eventual champion Chicago Bears 24–0.
The most notable player for the Rams during that period was running back Eric Dickerson, who was drafted in 1983 out of SMU and won Rookie of the Year. In 1984, Dickerson rushed for 2,105 yards, setting a new NFL record. Dickerson would end his five hugely successful years for the Rams in 1987 by being traded to the Indianapolis Colts for a number of players and draft picks after a bitter contract dispute, shortly after the players' strike that year ended. Dickerson was the Rams' career rushing leader until 2010, with 7,245 yards. Despite this trade, the Rams remained contenders due to the arrival of the innovative offensive leadership of Ernie Zampese. Zampese brought the intricate timing routes he had used in making the San Diego Chargers a state-of-the-art offense. Under Zampese, the Rams rose steadily from 28th rated offense in 1986 to 3rd in 1990. The late 1980s Rams featured a gifted young QB in Jim Everett, a solid rushing attack and a fleet of talented WRs led by Henry Ellard.

After a 10–6 season in 1986, the Rams were booted from the playoffs by the Washington Redskins. After one game of the 1987 season was lost to the players' strike, the NFL employed substitutes, most of which were given derogatory nicknames (in this case the Los Angeles Shams). After a 1–2 record, the Rams' regulars returned, but the team only went 6–9 and did not qualify for the postseason.
The Rams managed to return in 1988 with a 10–6 record, but then were defeated by Minnesota in the wild card round. Los Angeles won the first five games of 1989, including a sensational defeat of the defending champion 49ers. They beat the Eagles in the wild card game, then beat the Giants in overtime before suffering a 30–3 flogging at the hands of the 49ers in the NFC Championship Game.
Although it wasn't apparent at the time, the 1989 NFC Championship Game was the end of an era. The Rams did not have another winning season in their first stint in Los Angeles. They crumbled to 5–11 in 1990, followed by a 3–13 season in 1991.
1992–1994: The end of the original Southern California team
[edit]
Robinson was fired at the end of the 1991 season. The return of Chuck Knox as head coach, after Knox’ successful stints as head coach of the Buffalo Bills and Seattle Seahawks, would not boost the Rams’ fortunes. His run-oriented offense marked the end of the Zampese tenure in 1993. Knox’ game plans called for an offense that would be steady, if unspectacular. Unfortunately for the Rams, Knox’ offense was not only aesthetically unpleasing but dull as well, especially by 1990s standards. The Rams finished last in the NFC West during all three years of Knox’ second stint, and were never a serious contender.
As the losses piled up and the team was seen as playing uninspired football, the Rams’ already dwindling fan base was reduced even further. By 1994, support for the Rams had withered to the point where they were barely part of the Los Angeles sports landscape. With sellouts becoming fewer and far between, the Rams saw more of their games blacked out in Southern California. One of the few bright spots during this time was Jerome Bettis, a bruising running back from Notre Dame. Bettis flourished in Knox’ offense, running for 1,429 yards as a rookie, and 1,025 in his sophomore effort.
As has become increasingly common with sports franchises, the Rams began to blame much of their misfortune on their stadium situation. With Orange County mired in a deep recession resulting largely from defense sector layoffs, the Rams were unable to secure a new or improved stadium in the Los Angeles area, which ultimately cast their future in Southern California into doubt.
Georgia moves the Rams to St. Louis
[edit]The first half of the 1990s featured four straight 10-loss seasons, no playoff appearances, and waning fan interest. The return of Chuck Knox as head coach (after his successful stints as head coach of the Buffalo Bills and Seattle Seahawks), would not boost the Rams' fortunes. His run-oriented offense brought the end of Zampese's tenure, in 1993. John Shaw, the team's general manager, was perceived by some to continually squander NFL Draft picks on sub-standard talent. The offensive scheme was not only unspectacular to watch, but dull by 1990s standards—further alienating fans.
Team management traded quarterback Jim Everett, and released All-Pro linebacker Kevin Greene, which set the once-proud franchise further back. At this point, Georgia Frontiere blamed the poor front office decisions on their stadium situation. However, neither Orange County nor the city of Los Angeles were prepared to build a taxpayer-financed stadium just for the Rams. Claiming that Southern California was so unprofitable that the Rams would go bankrupt without a new stadium, Mrs. Frontiere decided to move the team.

Georgia Frontiere initially attempted to relocate the Rams to Baltimore,[21] but her fellow owners turned that proposal down. Mrs. Frontiere then sought to relocate the team to St. Louis. This move was initially voted down as well.[22][23] The other owners (led by Buffalo's Ralph Wilson, the Jets’ Leon Hess, the Giants' Wellington Mara, Washington's Jack Kent Cooke, Arizona's Bill Bidwill and Minnesota's John Skoglund) believed that the Rams’ financial problems were due to the Frontieres’ mismanagement.[24] When Georgia Frontiere threatened to sue the league, Commissioner Paul Tagliabue acquiesced to Frontiere's demands.
As part of the relocation deal, the city of St. Louis agreed to build a taxpayer-financed stadium, the Trans World Dome (now the Dome at America's Center) and guaranteed that the stadium's amenities would be maintained in the top 25 percent of all NFL stadiums. Frontiere waived the clause after a 10-year threshold period passed, as the city implemented a later plan to improve the stadium.
The move left many in the Los Angeles area, and many of those indifferent to the whole situation, embittered toward the NFL. That sentiment was best expressed by Fred Dryer, who at the time said "I hate these people (the organization and its owner) for what they did, taking the Rams logo with them when they moved to St. Louis. That logo belonged to Southern California."[citation needed] Steve Rosenbloom, the general manager of the team during Carroll Rosenbloom's tenure, opined that teams come and go, but for a team to leave Los Angeles—the second largest media market in America—for St. Louis (approximately the 18th-largest) was simply irresponsible and foolish, in spite of the notoriously fickle support of Los Angeles fans. With the Raiders moving from Los Angeles back to Oakland only a few months later, the NFL would have no franchise in Los Angeles for the first time in fifty seasons.
1995: Departure
[edit]By 1995, the Rams franchise had withered to a mere shadow of its former self. Accusations and excuses were constantly thrown back and forth between the Rams fan base, ownership, and local politicians. Many in the fan base blamed the ownership of Georgia Frontiere for the franchise's woes, while ownership cited the out-dated stadium and withering fan support.
Frontiere finally gave up and decided to move the Rams to St. Louis. However, on March 15, 1995, the other league owners rejected Frontiere's bid to move the franchise by a 21–3–6 vote. Then-Commissioner Paul Tagliabue stated after rejecting the move, "This was one of the most complex issues we have had to approach in years. We had to balance the interest of fans in Los Angeles and in St. Louis that we appreciate very much. In my judgment, they did not meet the guidelines we have in place for such a move." The commissioner also added: "Once the bridges have been burned and people get turned off on a sports franchise, years of loyalty is not respected and it is difficult to get it back. By the same token, there are millions of fans in that area who have supported the Rams in an extraordinary way. The Rams have 50 years of history and the last 5 or so years of difficult times can be corrected."[25][26]
Frontiere, however, responded with a thinly veiled threat at a lawsuit. On April 12, 1995 the owners acquiesced to her demands, wary of going through a long, protracted legal battle. Tagliabue simply stated that "The desire to have peace and not be at war was a big factor" in allowing the Rams move to go forward. In a matter of a month, the vote had gone from 21–6 opposed to 23–6 in favor. Jonathan Kraft, son of Patriots owner Robert Kraft, elaborated on the commissioner's remarks by saying that "about five or six owners didn't want to get the other owners into litigation, so they switched their votes." Only six teams remained in opposition to the Rams move from Los Angeles: the Pittsburgh Steelers, New York Giants, New York Jets, Buffalo Bills, Arizona Cardinals, and Washington Redskins. After the vote was over, Steelers owner Dan Rooney publicly stated that he opposed the move of the Los Angeles Rams because "I believe we should support the fans who have supported us for years."[27]
1995–2015: St. Louis era
[edit]Time in St. Louis
[edit]While in St. Louis, the Rams played their first few home games at Busch Memorial Stadium before the Trans World Dome (now known as the Dome at America's Center) was completed during the middle of the 1995 season. Aided by an offense nicknamed "The Greatest Show on Turf", a period of success occurred between 1999 and 2004 when the team qualified for the playoffs in five out of those six seasons, including a win in Super Bowl XXXIV against the Tennessee Titans, and a loss to the New England Patriots in Super Bowl XXXVI. Other than that period of success, the St. Louis Rams repeatedly suffered losing seasons.
Attempts to move back to Los Angeles
[edit]Within months of the moves of the Rams and Raiders, several NFL teams were rumored to be replacements. They included the Cleveland Browns, the Cincinnati Bengals, the Tampa Bay Buccaneers, and the Seattle Seahawks. However, the Browns moved to become the Baltimore Ravens in 1996 amid major controversy, and a new Browns team occupied a new stadium in 1999. The Bengals, Buccaneers and Seahawks, meanwhile, used L.A.'s vacancy as leverage to convince their cities to help finance new stadiums. Meanwhile, various entities proposed new stadiums in Los Angeles in an attempt to lure a team to the market.
Seattle Seahawks in Los Angeles
[edit]The closest Los Angeles had come to getting a new NFL franchise prior to 2016 was the Seattle Seahawks. In March 1996, Seahawks owner Ken Behring moved office equipment and some athletic gear to the elementary school in Anaheim that once held Rams practices, hoping to get approval for a permanent move to Southern California.[28] He also had plans to change the team's name and colors if a move to Los Angeles was successful. Because of an owners' revolt, Behring halted the process and moved the equipment back to Seattle. Eventually, Paul Allen bought the team and kept it in Seattle by building Seahawks Stadium, now known as Lumen Field.
1999 NFL expansion
[edit]Los Angeles again came close to regaining an NFL team in 1999, when the NFL approved a new franchise, the league's 32nd, for Los Angeles, on the condition that the city and NFL agree on a stadium site and stadium financing.[29] Those agreements were never reached, and on October 6, 1999, the franchise was awarded to a Houston ownership group instead, which formed the Houston Texans.
Using Los Angeles as leverage
[edit]During the Rams' 21-year absence from Los Angeles, the market had been used on many different occasions as leverage to finance new stadiums or upgrade existing venues. An excellent example of this was when Indianapolis Colts owner Jim Irsay's airplane appeared at Van Nuys Airport,[30] presumably for meetings with local officials on moving his team to Los Angeles. He eventually signed a deal to build a new venue in Indianapolis and Los Angeles continued to be without representation in the National Football League.
City of Champions Revitalization Initiative; Los Angeles Entertainment Center
[edit]On January 31, 2014, both the Los Angeles Times and the St. Louis Post-Dispatch reported that Rams owner Stan Kroenke had purchased approximately 60 acres of land adjacent to the Forum in Inglewood, California. The purchase price was rumored to have been between $90 million and $100 million. Commissioner Roger Goodell represented that Mr. Kroenke informed the league of the purchase. As an NFL owner, any purchase of land in which a potential stadium could be built must be disclosed to the league. Kroenke subsequently announced plans to build an NFL stadium on the site, in connection with the owners of the adjacent 238-acre Hollywood Park site, Stockbridge Capital Group.[31] This development has further fueled rumors that the Rams intend to return its management and football operations to Southern California. The land was initially targeted for a Walmart Supercenter but Walmart could not get the necessary permits to build it. Kroenke is married to Ann Walton Kroenke who is a member of the Walton family and many of Kroenke's real estate deals have involved Walmart properties.
On January 5, 2015, the Los Angeles Times reported that Kroenke Sports & Entertainment and Stockbridge Capital Group were partnering up in developing a new NFL stadium on the Inglewood property owned by Kroenke. The project will include a stadium of 80,000 seats and a performance venue of 6,000 seats while reconfiguring the previously approved Hollywood Park plan for up to 890,000 square feet of retail, 780,000 square feet of office space, 2,500 new residential units, a 300-room hotel and 25 acres of public parks, playgrounds, open space and pedestrian and bicycle access. The stadium would likely be ready by 2018.[31]
In lieu of this, St. Louis countered with a stadium plan for the north riverfront area of downtown, with the hope of keeping the Rams in the city. On February 24, 2015, the Inglewood City Council approved the stadium plan and the initiative with construction on the stadium planned to begin in December 2015. On December 21, 2015, Construction was officially underway for the stadium on the Hollywood Park site.[32][33][34]
Stadium issues in St. Louis
[edit]The Rams and the St. Louis CVC began negotiating deals to get the Rams home stadium, the Edward Jones Dome into the top 25 percent of stadiums in the league (i.e., top eight teams of the 32 NFL teams in reference to luxury boxes, amenities and overall fan experience). Under the terms of the lease agreement, the St. Louis CVC was required to make modifications to the Edward Jones Dome in 2005. However, then-owner, Georgia Frontiere, waived the provision in exchange for cash that served as a penalty for the city's noncompliance. The city of St. Louis, in subsequent years, made changes to the scoreboard and increased the natural lighting by replacing panels with windows, although the overall feel remains dark. The minor renovations which totaled about $70 million did not bring the stadium within the specifications required under the lease agreement; thus, keeping the Dome in a state of uncertainty.
On February 1, 2013, a 3-person panel selected to preside over the arbitration process found that the Edward Jones Dome was not in the top 25 percent of all NFL venues as required under the terms of the lease agreement between the Rams and the CVC. The arbitrator further found that the estimated $700 million in proposed renovations by the Rams was not unreasonable given the terms of the lease agreement. Finally, the city of St. Louis was ordered to pay the Rams attorneys' fees which totaled a reported $2 million.
Publicly, city, county and state officials expressed no interest in providing further funding to the Edward Jones Dome in light of those entities, as well as taxpayers, continuing to owe approximately $300 million more on that facility. As such, if a resolution was not reached by the end of the 2014 NFL season and the city of St. Louis remained non-compliant in its obligations under the lease agreement, the Rams would be free to nullify their lease and go to a year-to-year lease. Months later, the Rams scheduled to play in London, which violates the Edward Jones Dome's terms of lease.
Filing for relocation; Houston meetings
[edit]
On January 4, 2016, the St. Louis Rams filed for relocation to move to the Los Angeles area for the 2016 NFL season. They were among the three teams (the Rams, Oakland Raiders, and the San Diego Chargers) that filed for relocation to Los Angeles. All three franchises previously played in the Los Angeles metropolitan area. Weeks later, the NFL owners gathered in Houston for a meeting on January 11 and January 12, a meeting that decided the end of the Los Angeles race. A few days before the scheduled owners meeting, Dallas Cowboys owner Jerry Jones suggested that the Rams and Chargers should share Stan Kroenke's SoFi Stadium. This suggestion was taken as a possible option discussed in the Houston meetings. During the Los Angeles meeting, the Committee on Los Angeles Opportunities, which consists of six NFL owners, favored the Carson project over the Rams' Inglewood project. Despite this, thanks to Jerry Jones' pitch, the first round of voting during the meeting, the Rams got the greater number of votes, conquering the Carson project 21–11.[35] However, the Rams did not meet the required 24 votes in the second round of voting the Rams Inglewood project received 20 votes while the Chargers and Raiders Carson project received only 12 votes. After hours of searching to find a compromise, it was determined that the Rams would relocate to Los Angeles and the Chargers would have the option to join them, while the Raiders would have the option to join the Rams if the Chargers elected not to move.[36][37] [38] The Chargers used their option in January 2017 becoming the Los Angeles Chargers (and returning to their original home where they played in their inaugural season of 1960).
2016–present: Return to Los Angeles
[edit]
Upon relocating back to Los Angeles in 2016, the Rams initially played their home games at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, which had been home to the team for 33 seasons (1946–1979), and is the home of the USC Trojans college football team, until SoFi Stadium was completed four years later in 2020.[39][40]
During that time The Rams' return to Los Angeles was used to help expand the league's presence around the globe. In 2016, the Rams faced the New York Giants in London at Twickenham Stadium, as part of the NFL's International Series.[41] Kevin Demoff, the team's Executive Vice President of Football Operations/Chief Operating Officer, told The Guardian that he sees L.A. as a gateway to Asia and says being in L.A. will help sell the brand, more so, than in St. Louis.[42]

On February 4, 2016, the Los Angeles Rams selected Oxnard, California to be the site of their minicamp, offseason team activities, and offseason program that began on April 18. In March, it was announced that the Rams would be featured on HBO's Hard Knocks.[43] On March 30, California Lutheran University and the Rams reached an agreement that allowed the team to have regular-season training operations at CLU's campus for the next two years. The Rams paid for two practice fields, paved parking, and modular buildings constructed on the northwestern corner of the campus.[44][45]
2016 season: Jared Goff era begins
[edit]
On April 13, 2016, the Los Angeles Rams traded their 2016 first-round pick, two second-round picks, a third-round pick, and their 2017 first-round and third-round picks to the Tennessee Titans in exchange for the number one pick, alongside their fourth-round pick and a sixth-round pick. The Rams decided to wait until after Lakers great Kobe Bryant's last game before announcing the blockbuster trade.[46]
On April 28, 2016, the Rams drafted quarterback Jared Goff from California, with the 1st overall pick in the 1st round. The team also selected tight end Tyler Higbee and wide receiver Pharoh Cooper in the 4th round with the 110th and 117th picks, tight end Temarrick Hemingway, linebacker Josh Forrest, and wide receiver Mike Thomas in the 6th round with the 190th, 193rd, and 206th picks. In June 2016, it was reported that the Rams had sold 63,000 season tickets, which was short of their goal of 70,000. Later on July 12, 2016, it was reported that they had sold 70,000 tickets, reaching their goal. In July 2016, the Rams signed a three-year agreement with UC Irvine to use the university's facilities for training camp, with an option to extend it to two more years. On July 29, 2016, the Los Angeles Times reported that the Rams would host their first training-camp practice and "Rams Family Day" on Saturday, August 6 at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, which was open to the public.[47]
The Rams played their first game in the Los Angeles area since 1994, a 22-year absence, with a preseason opener against the Dallas Cowboys at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum on August 13. The Rams defeated the Cowboys 28–24 in front of a crowd of 89,140, a record attendance for a pre-season game.[48]
On September 12, 2016, the Rams played their first regular season game since returning to Los Angeles, where they lost to the San Francisco 49ers 28–0 at Levi's Stadium. On September 18, in front of over 91,000 fans at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum, The Rams played their first home game on September 18, 2016, defeating the Seattle Seahawks 9–3.[49]
Fisher's firing
[edit]On December 12, 2016, the team fired head coach Jeff Fisher after starting the season with a 4−9 record.[50] The team announced later that day that John Fassel would be taking over as interim head coach.[51] Fassel is the son of former NFL head coach Jim Fassel and had been the Rams special teams coach since the 2012 season.
2017 season: McVay's hiring and first winning season since 2003
[edit]On January 12, 2017 (the same day the Chargers moved to the Los Angeles area as the team did) the Rams hired Sean McVay for the team's head coaching vacancy. McVay, then 30, became the youngest head coach in NFL history. McVay was formerly the offensive coordinator of the Redskins, working under coach Jay Gruden. Quarterback Jared Goff had begun to come into his own as an elite quarterback under McVay and running back Todd Gurley had returned to dominance. On November 26, 2017, the Rams defeated the New Orleans Saints 26–20. The win was their eighth of the season, which secured their first non-losing year since 2006 (and first in Los Angeles since 1989). A week later, the Rams would defeat the Arizona Cardinals 32–16 to secure a winning season for the first time since the 2003 season. On December 24, 2017, the Rams defeated the Tennessee Titans 27–23 to clinch their first NFC West title since 2003 (and first in Los Angeles since 1985). Following a lost to the San Francisco 49ers, the Rams went 11-5 and won their first division title since 2003, as well as their first playoff berth since 2004.
The Rams would lose in the Wild Card game against the defending NFC champion Atlanta Falcons 26–13.
2018 season: Super Bowl run
[edit]The 2018 off-season was highlighted with acquiring Marcus Peters from the Kansas City Chiefs, signing Ndamukong Suh in free agency, and acquiring five-time Pro Bowler Aqib Talib and Brandin Cooks via trades. While also signing Brandin Cooks, Todd Gurley, Rob Havenstein and Aaron Donald to long-term deals.
The Rams opened their 2018 season on September 10 by defeating the Oakland Raiders 33–13 on Monday Night Football, scoring 23 unanswered second half points in a game where head coach McVay took on his former mentor, Jon Gruden, who was making his return to coaching. It was the first of two Monday Night Football appearances for the Rams in the season. The Rams continued their strong start throughout the season finishing the first half of the season 8–0, their best start since 1969. The Rams were the only remaining undefeated team in the NFL in 2018 until losing on the road to the New Orleans Saints in Week 9 at the Mercedes-Benz Superdome. The Rams bounced back with three straight wins, defeating the Seattle Seahawks 36–31, and then winning a wild 54–51 shootout against the Kansas City Chiefs on Monday Night Football. Following a bye week, the Rams beat the host Detroit Lions 30–16 in Week 13 to clinch both a playoff berth and their second straight NFC West title. Los Angeles stumbled with back-to-back losses to the Chicago Bears and Philadelphia Eagles, but finished strong with victories over the Arizona Cardinals and San Francisco 49ers to clinch a first round bye. The Rams' 13–3 record tied for the best record in the league, while having the second-most wins in a single season in franchise history and were the most ever for any NFL team in Los Angeles.
The Rams defeated the Dallas Cowboys 30–22 in the divisional round to head to the NFC Championship Game for the first time since 2001. It was also the Rams' first playoff win since 2004. The Rams would meet the Saints again, but this time beating the Saints on the road 26–23 to advance to the Super Bowl for the first time since 2001 and first appearance based in Los Angeles since 1979. Their opponent in Super Bowl LIII was the New England Patriots, whom they had previously faced in Super Bowl XXXVI when they were based in St. Louis, but narrowly lost 20–17. Despite their immense talent, the Rams offense was stymied and ineffective throughout the game, being held to no touchdowns and only one field goal. They held the Patriots to a 3–3 tie after 3 quarters, but lost 13–3. The Rams joined the 1971 Miami Dolphins in Super Bowl VI to only score 3 points in the Super Bowl.
2019 season: Post-Super Bowl slump and Last season at the Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum
[edit]The season was filled with injuries and setbacks, as Los Angeles narrowly missed the playoffs with a 9–7 record. It also marked the Rams' final year at the Coliseum.
2020 season: Debut at SoFi Stadium and COVID-19
[edit]The Rams and Chargers moved into the newly completed SoFi Stadium, but due to the COVID-19 pandemic, were forced to play there without spectators.[52] The Rams also cut oft-injured running back Todd Gurley, who previously led the league in rushing three times, during the offseason.[53][54] Despite being the first team to lose to the New York Jets in week 15,[55] the Rams finished the season at 10–6, returning to the playoffs. They beat the rival Seattle Seahawks in the wild card round, with backup quarterback John Wolford starting in place of an injured Goff, though Wolford would leave the game with a neck injury.[56] The team would lose to the Green Bay Packers the following week during the divisional round.
2021 season: End of Jared Goff era, Arrival of Matthew Stafford, and Super Bowl win
[edit]On March 18, 2021, Los Angeles traded Jared Goff and several draft picks to the Detroit Lions in exchange for their longtime quarterback Matthew Stafford.[57] The Rams started off strongly by winning seven out of their first eight games, but a three-game losing streak in November dropped the team to 7-4. Wide receiver Robert Woods was lost for the season, but the Rams bolstered their roster by signing free agent wide receiver Odell Beckham Jr. and trading for former Denver Broncos All-Pro linebacker Von Miller. Los Angeles won five straight games but lost at home to the San Francisco 49ers to finish the regular season at 12-5, which clinched the team's third NFC West Division title since head coach Sean McVay's arrival.
In the playoffs, the Rams routed the division rival Arizona Cardinals 34-11 in the first playoff game played at SoFi Stadium. A week later in Tampa Bay, Los Angeles built a 27-3 lead, then withstood a rally led by Tom Brady to defeat the Buccaneers 30-27. The Rams returned home for the NFC Championship Game to face the 49ers, who had won six straight regular season meetings. Despite trailing by 10 points going into the fourth quarter, the Rams came back to win 20-17 to earn their second trip to the Super Bowl in four seasons. Playing at their home stadium for Super Bowl LVI as the 'away' team, the Rams again overcame a late deficit to defeat the AFC champion Cincinnati Bengals 23-20, winning the franchise's second Super Bowl championship, and first in Los Angeles. Wide receiver Cooper Kupp was named the game's Most Valuable Player.
2022 season: Super Bowl hangover
[edit]In 2022, injuries and regression derailed the Rams' chances of repeating as Super Bowl champions. Most notably, core contributors to the 2021 Super Bowl-winning team, including Matthew Stafford, Cooper Kupp, and Aaron Donald, missed significant parts of the season with injuries. Los Angeles also experienced a historic number of offensive line injuries that forced McVay to start eleven different offensive line combinations in the first eleven games of the season, something that no team had done since the 1970 AFL-NFL merger. The team began the season by losing in blowout fashion on national television to the Super Bowl-hopeful Buffalo Bills, and the game seemingly set the tone for the 2022 Rams, who never looked like their 2021 selves during the season. Although Los Angeles managed to stay afloat with a 3-3 record through six games, the team endured a deep slump and lost their next six games en route to a 5-12 finish. The .294 win percentage was the worst ever for a defending Super Bowl champion.
2023 season: Resurgence and return to the playoffs
[edit]Following the team's disastrous 2022 season, the Rams parted ways with several defensive contributors, as the team traded cornerback Jalen Ramsey to the Miami Dolphins, released edge rusher Leonard Floyd, and released linebacker Bobby Wagner. McVay and general manager Les Snead also stockpiled several mid-to-late round draft picks in the upcoming 2023 NFL draft.
With the aforementioned moves, many expected the Rams to enter into a rebuilding stage and struggle throughout the 2023 season. However, the Rams returned to the playoffs as a wild card team (despite struggling to a 3-6 record before the bye week) thanks to the resurgence of Stafford and strong play from rookies such as wide receiver Puka Nacua, defensive tackle Kobie Turner, and linebacker Byron Young.
In the wild card round of the 2023-24 NFL playoffs, the Rams faced off against the NFC North champion Detroit Lions, led by former Rams quarterback Jared Goff. The game was also notable for being Stafford's first game in Detroit as an opposing player (Stafford spent his first twelve seasons playing for Detroit). In a game that was dominated by storylines about the Stafford-Goff trade and dubbed as a "revenge game" for quarterbacks Stafford and Goff, the Lions emerged victorious with a narrow 24-23 win. Los Angeles was undone by scoring zero touchdowns in three red zone trips, while Detroit converted all three of its own red zone trips into touchdowns.
List of seasons
[edit]| Season | Team | League | Conference | Division | Regular Season | Attendance | Postseason Results | Awards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finish | Wins | Losses | Ties | Rams Average | NFL Average | |||||||
| Los Angeles Rams (1946–1994)[58] | ||||||||||||
| 1946 | 1946 | NFL | West | 2nd | 6 | 4 | 1 | 42,834 (2/10) | 34,397 | |||
| 1947 | 1947 | NFL | West | 4th | 6 | 6 | 0 | 32,130 (5/10) | 30,226 | |||
| 1948 | 1948 | NFL | West | 3rd | 6 | 5 | 1 | 28,258 (5/10) | 26,240 | |||
| 1949 | 1949 | NFL | West | 1st | 8 | 2 | 2 | 44,043 (1/10) | 24,798 | Lost NFL Championship (Eagles) 14–0 | ||
| 1950 | 1950 | NFL | National | 1st | 9 | 3 | 0 | 26,341 (6/13) | 27,070 | Won National Conference Playoff (Bears) 24–14 Lost NFL Championship (Browns) 30–28 |
||
| 1951 | 1951 | NFL | National | 1st | 8 | 4 | 0 | 44,196 (1/12) | 28,741 | Won NFL Championship (2) (Browns) 24–17 | ||
| 1952 | 1952 | NFL | National | 2nd | 9 | 3 | 0 | 53,157 (1/12) | 31,278 | Lost National Conference Playoff (Lions) 31–21 | Hamp Pool (COY) | |
| 1953 | 1953 | NFL | Western | 3rd | 8 | 3 | 1 | 54,744 (1/12) | 32,895 | |||
| 1954 | 1954 | NFL | Western | 4th | 6 | 5 | 1 | 54,734 (1/12) | 33,769 | |||
| 1955 | 1955 | NFL | Western | 1st | 8 | 3 | 1 | 66,159 (1/12) | 37,796 | Lost NFL Championship (Browns) 38–14 | ||
| 1956 | 1956 | NFL | Western | T-5th | 4 | 8 | 0 | 61,190 (1/12) | 38,293 | |||
| 1957 | 1957 | NFL | Western | 4th | 6 | 6 | 0 | 74,296 (1/12) | 42,160 | |||
| 1958 | 1958 | NFL | Western | T-2nd | 8 | 4 | 0 | 83,681 (1/12) | 44,690 | |||
| 1959 | 1959 | NFL | Western | 6th | 2 | 10 | 0 | 74,069 (1/12) | 46,134 | |||
| 1960 | 1960 | NFL | Western | 6th | 4 | 7 | 1 | 61,724 (1/21) | 32,150 | |||
| 1961 | 1961 | NFL | Western | 6th | 4 | 10 | 0 | 47,992 (7/22) | 33,874 | |||
| 1962 | 1962 | NFL | Western | 7th | 1 | 12 | 1 | 41,572 (9/22) | 35,355 | |||
| 1963 | 1963 | NFL | Western | 6th | 5 | 9 | 0 | 42,302 (9/22) | 36,610 | |||
| 1964 | 1964 | NFL | Western | 5th | 5 | 7 | 2 | 55,764 (5/22) | 40,636 | |||
| 1965 | 1965 | NFL | Western | 7th | 4 | 10 | 0 | 40,333 (13/22) | 43,489 | |||
| 1966 | 1966 | NFL | Western | 3rd | 8 | 6 | 0 | 49,776 (10/24) | 45,732 | |||
| 1967 | 1967 | NFL | Western | Coastal | 1st | 11 | 1 | 2 | 60,000 (6/25) | 48,606 | Lost Conference Playoff Game (Packers) 28–7 | George Allen (COY) Deacon Jones (DPOY) |
| 1968 | 1968 | NFL | Western | Coastal | 2nd | 10 | 3 | 1 | 65,127 (4/26) | 48,777 | Deacon Jones (DPOY) | |
| 1969 | 1969 | NFL | Western | Coastal | 1st | 11 | 3 | 0 | 71,242 (3/26) | 51,053 | Lost Conference Playoff Game (Vikings) 23–20 | Roman Gabriel (MVP)/(Rams MVP) |
| 1970 | 1970 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 9 | 4 | 1 | 71,242 (2/26) | 54,375 | Merlin Olsen (Rams MVP) | |
| 1971 | 1971 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 8 | 5 | 1 | 72,453 (3/26) | 56,935 | Isiah Robertson (DROY) Marlin McKeever (Rams MVP) | |
| 1972 | 1972 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 6 | 7 | 1 | 72,461 (4/26) | 58,416 | Merlin Olsen (Rams MVP) | |
| 1973 | 1973 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 12 | 2 | 0 | 74,168 (2/26) | 55,339 | Lost Divisional Playoffs (Cowboys) 27–16 | Chuck Knox (COY) John Hadl (NFC)/(Rams MVP) |
| 1974 | 1974 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 10 | 4 | 0 | 75,492 (2/26) | 52,098 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Redskins) 19–10 Lost Conference Championship (Vikings) 14–10 |
Lawrence McCutcheon (Rams MVP) |
| 1975 | 1975 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 12 | 2 | 0 | 65,284 (4/26) | 52,754 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Cardinals) 35–23 Lost Conference Championship (Cowboys) 37–7 |
Jack Youngblood (DPOY)/(Rams MVP) |
| 1976 | 1976 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 10 | 3 | 1 | 63,141 (4/26) | 53,983 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Cowboys) 14–12 Lost Conference Championship (Vikings) 24–13 |
Jack Youngblood (Rams MVP) |
| 1977 | 1977 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 10 | 4 | 0 | 53,585 (10/28) | 52,711 | Lost Divisional Playoffs (Vikings) 14–7 | Lawrence McCutcheon (Rams MVP) |
| 1978 | 1978 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 12 | 4 | 0 | 53,388 (14/28) | 53,983 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Vikings) 34–10 Lost Conference Championship (Cowboys) 28–0 |
Jim Youngblood (Rams MVP) |
| 1979 | 1979 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 9 | 7 | 0 | 52,970 (17/28) | 55,960 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Cowboys) 21–19 Won Conference Championship (Buccaneers) 9–0 Lost Super Bowl XIV (Steelers) 31–19 |
Jack Youngblood (Rams MVP) Kent Hill (Rams ROY) |
| 1980 | 1980 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 11 | 5 | 0 | 62,550 (8/28) | 56,667 | Lost Wild Card Playoffs (Cowboys) 34–13 | Vince Ferragamo (Rams MVP) Johnnie Johnson (Rams ROY) |
| 1981 | 1981 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 6 | 10 | 0 | 60,503 (11/28) | 57,665 | Nolan Cromwell (Rams MVP) Jairo Penaranda (Rams ROY) | |
| 1982[59] | 1982 | NFL | NFC | 14th | 2 | 7 | 0 | 51,690 (16/28) | 52,527 | Vince Ferragamo (Rams MVP) Barry Redden (Rams ROY) | ||
| 1983 | 1983 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 9 | 7 | 0 | 52,780 (15/28) | 54,364 | Won Wild Card Playoffs (Cowboys) 24–17 Lost Divisional Playoffs (Redskins) 51–7 |
Eric Dickerson (OROY)/NFC/Rams MVP/Rams ROY |
| 1984 | 1984 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 10 | 6 | 0 | 54,455 (17/28) | 55,528 | Lost Wild Card Playoffs (Giants) 16–13 | Eric Dickerson (NFC)/(Rams MVP) Ron Brown (Rams ROY) |
| 1985 | 1985 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 11 | 5 | 0 | 56,242 (15/28) | 55,408 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Cowboys) 20–0 Lost Conference Championship (Bears) 24–0 |
LeRoy Irvin (Rams MVP) Dale Hatcher (Rams ROY) |
| 1986 | 1986 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 10 | 6 | 0 | 59,285 (10/28) | 56,872 | Lost Wild Card Playoffs (Redskins) 19–7 | Eric Dickerson (OPOY)(NFC)/(Rams MVP) Jim Everett (Rams ROY) |
| 1987[60] | 1987 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 6 | 9 | 0 | 47,356 (18/28) | 48,639 | Charles White (Rams MVP) Cliff Hicks (Rams ROY) | |
| 1988 | 1988 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 10 | 6 | 0 | 54,469 (17/28) | 56,727 | Lost Wild Card Playoffs (Vikings) 28–17 | Henry Ellard (Rams MVP) Robert Delpino (Rams ROY) |
| 1989 | 1989 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 11 | 5 | 0 | 58,846 (11/28) | 57,257 | Won Wild Card Playoffs (Eagles) 21–7 Won Divisional Playoffs (Giants) 19–13 Lost Conference Championship (49ers) 30–3 |
Jim Everett (Rams MVP) Darryl Henley (Rams ROY) |
| 1990 | 1990 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 5 | 11 | 0 | 59,920 (12/28) | 59,665 | Buford McGee (Rams MVP) Bern Brostek (Rams ROY) | |
| 1991 | 1991 | NFL | NFC | West | 4th | 3 | 13 | 0 | 51,586 (22/28) | 58,926 | Robert Delpino (Rams MVP) Todd Lyght (Rams ROY) | |
| 1992 | 1992 | NFL | NFC | West | 4th | 6 | 10 | 0 | 47,811 (25/28) | 58,734 | Jackie Slater (Rams MVP) Sean Gilbert(Rams ROY) | |
| 1993 | 1993 | NFL | NFC | West | 4th | 5 | 11 | 0 | 45,401 (25/28) | 59,352 | Jerome Bettis (OROY)(Rams MVP)/(Rams ROY) | |
| 1994 | 1994 | NFL | NFC | West | 4th | 4 | 12 | 0 | 43,312 (28/28) | 60,107 | Shane Conlan (Rams MVP) Isaac Bruce (Rams ROY) | |
| St. Louis Rams (1995–2015) | ||||||||||||
| Los Angeles Rams (2016–present) | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 4 | 12 | 0 | 84,457 (2/32) | |||
| 2017 | 2017 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 11 | 5 | 0 | Lost Wild Card Playoffs (Falcons) 26-13 | Sean McVay (COY) Todd Gurley (OPOY) Aaron Donald (DPOY) | ||
| 2018 | 2018 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 13 | 3 | 0 | Won Divisional Playoffs (Cowboys) 30–22 Won NFC Championship (Saints) 26–23 (OT) Lost Super Bowl LIII (Patriots) 3–13 |
Aaron Donald (DPOY) | ||
| 2019 | 2019 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 9 | 7 | 0 | ||||
| 2020 | 2020 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 10 | 6 | 0 | Won Wild Card Playoffs (Seahawks) 30–20 Lost Divisional Playoffs (Packers) 18-32 |
Aaron Donald (DPOY) | ||
| 2021 | 2021 | NFL | NFC | West | 1st | 12 | 5 | 0 | Won Wild Card Playoffs (Cardinals) 34–11 Won Divisional Playoffs (Buccaneers) 30–27 Won NFC Championship (49ers) 20–17 Won Super Bowl LVI (Bengals) 23–20 |
Cooper Kupp (SB MVP, OPOY) Andrew Whitworth (WPMOY) | ||
| 2022 | 2022 | NFL | NFC | West | 3rd | 5 | 12 | 0 | ||||
| 2023 | 2023 | NFL | NFC | West | 2nd | 10 | 7 | 0 | Lost Wild Card Playoffs (at Lions) 23–24 | |||
| Total 2 NFL Titles (1951 and 2021) 6 Conference Titles 13 Division Titles 26 Playoff Appearances |
438 | 354 | 18 | (regular season)[61] | ||||||||
| 19 | 23 | 0 | (playoffs) | |||||||||
| 457 | 377 | 18 | (regular season and playoffs)[61] | |||||||||
* Between 1946 and 1994, the Los Angeles Rams Played a total of 679 Regular Season Games and 32 Playoff Games (711 Games)
* Between 1946 and 1994, the Los Angeles Rams had a total record of 364–297 (Regular), 12–20 (Postseason), and 376–317 (Total)
Pro Football Hall of Famers
[edit]Former Los Angeles Rams in the Pro Football Hall of Fame include Jerome Bettis (36), Joe Namath (12), Ollie Matson (33), Andy Robustelli (84), Dick "Night Train" Lane (81), and general manager Tex Schramm. GM and later NFL Commissioner Pete Rozelle and coach Sid Gillman are also members of the Hall of Fame, but were elected on the basis of their performances with other teams or (in the case of Rozelle) NFL administration.
| Los Angeles Rams Hall of Famers | ||||
| No. | Player | Class | Position(s) | Tenure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | George Allen | 2002 | Coach | 1966–1970 |
| 36 | Jerome Bettis | 2015 | RB | 1993–1994 |
| 76 | Bob Brown | 2004 | OT | 1969–1970 |
| 29 | Eric Dickerson | 1999 | RB | 1983–1987 |
| 55 | Tom Fears | 1970 | End | 1948–1956 |
| 40 | Elroy "Crazy Legs" Hirsch | 1968 | RB, WR | 1949–1957 |
| 75 | Deacon Jones | 1980 | DE | 1961–1971 |
| 65 | Tom Mack | 1999 | G | 1966–1978 |
| 74 | Merlin Olsen | 1982 | DT | 1962–1976 |
| – | Dan Reeves | 1967 | Owner | 1946–1971 |
| 67, 48 | Les Richter | 2011 | LB, K | 1954–1962 |
| 78 | Jackie Slater | 2001 | OT | 1976–1994 |
| 25 | Norm Van Brocklin | 1971 | QB, P | 1949–1957 |
| 7 | Bob Waterfield | 1965 | QB, DB, K, P | 1946–1952 |
| 85 | Jack Youngblood | 2001 | DE | 1971–1984 |
| 91 | Kevin Greene | 2016 | LB, DE | 1985–1992 |
Retired numbers
[edit]Numbers that have been retired by the Rams. This list includes players who have played most of their career in Los Angeles Only.
| Los Angeles Rams retired numbers | |||
| No. | Player | Position | Tenure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Bob Waterfield | QB | 1945–1952 |
| 29 | Eric Dickerson | RB | 1983–1987 |
| 74 | Merlin Olsen | DT | 1962–1976 |
| 75 | Deacon Jones | DE | 1961–1971 |
| 78 | Jackie Slater | OT | 1976–1995 |
| 85 | Jack Youngblood | DE | 1971–1984 |
- Bob Waterfield played his first season in Cleveland
- Jackie Slater played his last season in St. Louis
Radio and television
[edit]The Rams were the first NFL team to televise their home games; in a sponsorship arrangement with Admiral television, all home games of the 1950 NFL season were shown locally. The Rams also televised games in the early 1950s. The 1951 NFL Championship Game was the first championship game televised coast-to-coast (via the DuMont Network). During the team's years in Los Angeles all games were broadcast on KMPC radio (710 AM); play-by-play announcers were Bob Kelley (who accompanied the team from Cleveland and worked until his death in 1966), Dick Enberg (1966–1977), Al Wisk (1978–1979), Bob Starr (1980–1989, 1993), Eddie Doucette (1990), Paul Olden (1991–1992), and Steve Physioc (1994). Analysts included Gil Stratton, Steve Bailey, Dave Niehaus (1968–1972), Don Drysdale (1973–1976), Dick Bass (1977–1986), Jack Youngblood (1987–1991), Jack Snow (1992–1994), and Deacon Jones (1994). Today, Pac-12 Network broadcaster J.B. Long is the current play-by-play announcer with former running back Maurice Jones-Drew as the side analyst.
In popular culture
[edit]- In the 1978 film Heaven Can Wait, Joe Pendleton (Warren Beatty), a fictional quarterback for the Los Angeles Rams, is looking forward to leading his team to the Super Bowl.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d MacCambridge, 2005, pp. 15–16.
- ^ Littlewood, 1990, p. 160.
- ^ Lyons, 2010, p. 118.
- ^ Yost, 2006, p. 57–58.
- ^ Davis writes Halas engineered the approval of the Rams move to Los Angeles, Davis, 2005, p. 201–202.
- ^ Lyons, 2010, p. 117–118.
- ^ "Ebony Magazine May 1969". Ebony Magazine. May 1969. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.
- ^ Levy, 2003, p. 92–93.
- ^ Davis, 2005, p. 202.
- ^ Strode, 1990, p. 140.
- ^ Coenen, 2005, p. 123.
- ^ MacCambridge writes he was signed on May 4, 1946. MacCambridge, 2005, p. 19.
- ^ Ross, 1999, p. 82.
- ^ Rathet, 1984, p. 210.
- ^ James P. Quirk and Rodney D. Fort, Pay Dirt: The Business of Professional Team Sports, p. 438, ISBN 0-691-01574-0
- ^ "Fun Facts". St. Louis Rams. Archived from the original on December 8, 2015. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Dwyre, Bill (November 30, 2009). "Barron Hilton's Chargers turned short stay into long-term success". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Plaschke, Bill (January 6, 2015). "Whether Rams return or not, they're still family". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ "RAMS STATISTICS-ATTENDANCE". Bring Back the Los Angeles Rams. Archived from the original on November 30, 2015. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ ‘Frontiere Might Move Rams to Baltimore’; Austin American-Statesman, December 25, 1993, p. E3
- ^ George, Thomas (March 16, 1995). "PRO FOOTBALL; N.F.L. Owners Reject Rams' Bid to Move To St. Louis". The New York Times.
- ^ Simers, T.J.; Plaschke, Bill (March 16, 1995). "League Owners Reject Rams' Move to St. Louis". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ Hamelin, Joe; ‘Rams off to St. Louis after all’; The Press-Enterprise [Riverside, California]; April 13, 1995, p. 1
- ^ George, Thomas (March 16, 1995). "PRO FOOTBALL; N.F.L. Owners Reject Rams' Bid to Move To St. Louis". The New York Times. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ T.J. Simers; Bill Plaschke (March 16, 1995). "League Owners Reject Rams' Move to St. Louis". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Simers, T.J. (April 13, 1995). "NFL Owners OK Rams' Move to St. Louis". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Nightengale, Bob – Without Disney, Angels could become X-rated. (sale of California Angels to Walt Disney Co in jeopardy). Sporting News, March 25, 1996
- ^ "Texans Team History". Houston Texans. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Fenno, Nathan; Farmer, Sam (January 7, 2015). "NFL teams often use L.A. to get better deals to stay where they are". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ a b Farmer, Sam; Vincent, Roger (January 5, 2015). "Owner of St. Louis Rams plans to build NFL stadium in Inglewood". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved January 5, 2015.
- ^ Wagoner, Nick (February 1, 2014). "Stan Kroenke buys 60 acres in L.A." ESPN. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Piper, Brandie (January 31, 2014). "Report: Rams owner bought 60 acres of land in California". KSDK. Archived from the original on February 21, 2014. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Farmer, Sam (January 30, 2014). "A return of L.A. Rams? Owner is said to buy possible stadium site". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 5, 2015.
- ^ Wickersham, Seth; Van Natta Jr., Don (February 11, 2016). "The Wow Factor: The Real Story of the NFL Owners Battle To Bring Football Back To Los Angeles". ESPN The Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ Hanzus, Dan (January 12, 2016). "Rams to relocate to L.A.; Chargers first option to join". NFL.com. National Football League. Retrieved January 13, 2016.
- ^ "Rams to Return to Los Angeles". St. Louis Rams. January 12, 2016. Archived from the original on January 20, 2016. Retrieved January 13, 2016.
- ^ "Rams headed back to Los Angeles; Chargers have option to join". ESPN. Associated Press. January 12, 2016. Retrieved January 13, 2016.
- ^ "Rain Delay: Opening of Inglewood Stadium Pushed Back to 2020". NBC Sports. May 18, 2017. Retrieved March 30, 2019.
- ^ Rearden, Tim. "LA COLISEUM PREPARES TO HOST NFL GAMES IN 2016". abc7.com. ABC. Retrieved January 18, 2016.
- ^ "Rams to Play First Ever NFL Game at Twickenham Stadium". St. Louis Rams. November 25, 2015. Archived from the original on June 21, 2016. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ Carpenter, Les (April 8, 2016). "Could the LA Rams become the NFL's first truly global team?". Guardian. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
We don't want to play games in just London; we want to explore the Asian opportunity", Demoff said. "We want to grow the brand internationally. I think there's an opportunity to grow the Rams brand and I think the league wants to grow their brand in that market.
- ^ Wesseling, Chris (March 23, 2016). "Los Angeles Rams will be featured on 'Hard Knocks'". National Football League. Retrieved March 25, 2016.
- ^ Sessler, Marc (March 30, 2016). "Rams choose Cal Lutheran for temporary training site". NFL.com. National Football League. Retrieved March 30, 2016.
- ^ "L.A. Rams training moving to Cal Lutheran". Los Angeles Rams. March 30, 2016. Archived from the original on April 1, 2016. Retrieved April 1, 2016.
The facility at Cal Lutheran is the home base for about 130 athletes, coaches, trainers and other staff members.
- ^ Orr, Conor (April 14, 2016). "L.A. Rams trade up to acquire No. 1 pick from Titans". National Football League. Retrieved June 26, 2016.
- ^ Klein, Gary. "Rams will hold first training-camp practice Saturday". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved August 4, 2016.
- ^ Bain, Nate (August 13, 2016). "Rams Victorious in Return to Los Angeles". Los Angeles Rams. Archived from the original on August 18, 2016. Retrieved August 14, 2016.
- ^ Klein, Gary (September 18, 2016). "It wasn't pretty but Rams win home opener, 9-3, over Seahawks". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved September 19, 2016.
- ^ Orr, Conor (December 12, 2016). "Los Angeles Rams fire head coach Jeff Fisher". National Football League. Retrieved December 12, 2016.
- ^ "John Fassel Named Rams Interim Head Coach". Los Angeles Rams. December 12, 2016. Archived from the original on December 12, 2016. Retrieved December 12, 2016.
- ^ "Rams, Chargers announce fans will not be allowed to attend games 'until further notice'". Yahoo! Sports. August 25, 2020. Retrieved September 5, 2020.
- ^ Jackson, Stu (March 19, 2020). "Rams release RB Todd Gurley". therams.com. Retrieved March 19, 2020.
- ^ Patra, Kevin (March 19, 2020). "Rams release former OPOY, standout Todd Gurley". NFL.com. Retrieved March 19, 2020.
- ^ Costello, Brian (December 21, 2020). "Jets stun Rams to win first game — damaging Trevor Lawrence hopes". New York Post. Retrieved December 26, 2020.
- ^ "Jared Goff replaces injured John Wolford in Rams' win over Seahawks; Aaron Donald dealing with rib injury". NFL.com. Retrieved January 9, 2021.
- ^ "Rams trade Jared Goff, future draft picks to Lions for Matthew Stafford". therams.com. Retrieved March 18, 2021.
- ^ Dan Reeves moved the team due to poor attendance at and competing against the Cleveland Browns, the Rams became the first NFL team based on the West Coast.
- ^ 1982 was a strike-shortened season so the league was divided up into two conferences instead of its normal divisional alignment.
- ^ The strike of 1987 reduced the regular season schedule from sixteen to fifteen games.
- ^ a b 1946–1994