Adoniram Judson: Difference between revisions
BelgicHerald (talk | contribs) m Adding a link to Judson College at Southeastern |
|||
| (43 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|American missionary (1788–1850)}} |
|||
{{More citations needed|date=December 2022}} |
{{More citations needed|date=December 2022}} |
||
{{Use mdy dates|date=February 2013}} |
{{Use mdy dates|date=February 2013}} |
||
{{Infobox person |
{{Infobox person |
||
| name = Adoniram Judson |
| name = Adoniram Judson |
||
| image = Adoniram Judson 1846.jpg |
| image = Adoniram Judson 1846.jpg |
||
|image_size=250px |
| image_size = 250px |
||
|caption=Adoniram Judson by [[George Peter Alexander Healy]], 1846 |
| caption = Adoniram Judson by [[George Peter Alexander Healy]], 1846 |
||
| occupation = Missionary to [[Burma]] |
| occupation = Missionary to [[Burma]] |
||
| birth_date = {{Birth-date|August 9, 1788}} |
| birth_date = {{Birth-date|August 9, 1788}} |
||
| birth_place = [[Malden, Massachusetts]] |
| birth_place = [[Malden, Massachusetts]] |
||
| death_date = {{Death date and age|1850|04|12|1788|08|09}} |
| death_date = {{Death date and age|1850|04|12|1788|08|09}} |
||
| death_place = At sea in the [[Bay of Bengal]] |
| death_place = At sea in the [[Bay of Bengal]] |
||
| nationality = American |
| nationality = American |
||
| spouse = [[Ann Hasseltine]], 1812–26 (her death)<br />[[Sarah Hall Boardman]], 1834–45 (her death)<br />[[Emily Chubbuck]], 1846–50 (his death) |
| spouse = [[Ann Hasseltine]], 1812–26 (her death)<br />[[Sarah Hall Boardman]], 1834–45 (her death)<br />[[Emily Chubbuck]], 1846–50 (his death) |
||
| children = (1) Stillborn son, 1813 to Ann Judson; (2) Roger Williams Judson, 11/11/1814 to Ann Judson (lived only 2 wks); (3) Maria Elizabeth Butterworth Judson, 1/26/1825 - 4/26/1827 to Ann Judson; (4) Abigail Ann Judson, 10/31/1835 to Sarah Judson; (5) Adoniram Judson Jr., 4/7/1837 to Sarah Judson; (6) Elnathan Judson, 7/15/1838 to Sarah Judson; (7) Henry Judson, 12/31/1839 - 7/31/1841 to Sarah Judson; (8) Stillborn son named Luther in 1840 to Sarah Judson; (9) Henry Judson, July 1842 (named in honor of baby Henry who had passed the previous year) to Sarah Judson; (10) Charles Judson, 12/18/1843 - 8/1845 to Sarah Judson; (11) Edward Judson 12/27/1844 to Sarah Judson; (12) Emily Frances Judson, 12/26/1847 to Emily Judson; (13) Charles Judson, 4/13/1850 (passed the same day) to Emily Judson. |
|||
| children = [[Edward Judson]], several others |
|||
| alma mater = [[Brown University]] and [[Andover Theological Seminary]] |
| alma mater = [[Brown University]] and [[Andover Theological Seminary]] |
||
| signature = Appletons' Judson Adoniram signature.jpg |
| signature = Appletons' Judson Adoniram signature.jpg |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Adoniram Judson ''' (August 9, 1788 – April 12, 1850) was an American [[Congregationalism in the United States|Congregationalist]] and later [[Particular Baptist]]<ref>{{ |
'''Adoniram Judson ''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|æ|d|ə|'|n|aɪ|r|ə|m}}; August 9, 1788 – April 12, 1850) was an American [[Congregationalism in the United States|Congregationalist]] and later [[Particular Baptist]]<ref>{{cite book|title=The Life of Adoniram Judson|url=https://archive.org/details/adoniramjudsond00judsgoog|last=Judson|first=Edward|year=1883|publisher=New York, A. D. F. Randolph & Company}}</ref> missionary, who worked in [[Burma]] for almost forty years. At the age of 25, Judson was sent from [[North America]] to preach in Burma. His mission and work with [[Luther Rice]] led to the formation of the first Baptist association in America to support missionaries. |
||
Judson was one of the first Protestant missionaries to Burma. He translated the [[Bible]] into [[Burmese language|Burmese]] and established a number of Baptist churches in Burma. |
Judson was one of the first Protestant missionaries to Burma. He translated the [[Bible]] into [[Burmese language|Burmese]] and established a number of Baptist churches in Burma. |
||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
==Early life== |
==Early life== |
||
[[File:Adoniram Judson birthplace.jpg|thumb|left|200px|House where Judson was born]] |
[[File:Adoniram Judson birthplace.jpg|thumb|left|200px|House where Judson was born]] |
||
| ⚫ | Judson was born on August 9, 1788, in [[Malden, Massachusetts|Malden]], [[Middlesex County, Massachusetts]].<ref |
||
| ⚫ | Judson was born on August 9, 1788, in [[Malden, Massachusetts|Malden]], [[Middlesex County, Massachusetts]].<ref name="William H. Brackney 2021, p. 332">William H. Brackney, ''Historical Dictionary of the Baptists'', Rowman & Littlefield, USA, 2021, p. 332</ref> He was born to Adoniram Judson Sr., a [[Congregationalism in the United States|Congregational]] minister, and Abigail (née Brown). Judson entered the College of Rhode Island & Providence Plantations (now [[Brown University]]) when he was sixteen, and graduated as valedictorian of his class at the age of nineteen.<ref name="William H. Brackney 2021, p. 332"/> While studying at college, he met a young man named Jacob Eames, a devout [[deist]] and [[skeptic]]. Judson and Eames developed a strong friendship, leading to Judson's abandonment of his childhood faith and parents' religious instruction. During this time, Judson embraced the writings of the French [[philosophe]]s. After graduating from college, Judson opened a school and wrote an English grammar and mathematics textbook for girls. |
||
| ⚫ | Judson's deist views were shaken when his friend Eames fell violently ill and died. Both had been sleeping in separate rooms at an inn, and Judson heard the death throes of the person next door, only to learn from the clerk the next morning that his anonymous neighbor had been Mr. Eames, who had indeed died. The shock of learning the dying neighbor's identity – and that Eames had led Judson away from the Christian faith into skepticism, but was now dead – returned Judson back to the faith of his youth, although he was already attending the [[Andover Theological Seminary]].<ref name=EB1911>{{cite EB1911 |
||
| ⚫ | Judson's deist views were shaken when his friend Eames fell violently ill and died. Both had been sleeping in separate rooms at an inn, and Judson heard the death throes of the person next door, only to learn from the clerk the next morning that his anonymous neighbor had been Mr. Eames, who had indeed died. The shock of learning the dying neighbor's identity – and that Eames had led Judson away from the Christian faith into skepticism, but was now dead – returned Judson back to the faith of his youth, although he was already attending the [[Andover Theological Seminary]].<ref name=EB1911>{{cite EB1911|wstitle=Judson, Adoniram|volume=15|page=534}}</ref> In 1808, Judson "made a solemn dedication of himself to God".<ref>Courtney Anderson (1987) ''To the Golden Shore: The Life of Adoniram Judson''. Judson Pr. {{ISBN|0817011218}}. p. 50</ref> During his final year at the school, Judson decided upon a missionary career. |
||
| ⚫ | In 1810, Judson joined a group of mission-minded students who called themselves " |
||
| ⚫ | In 1810, Judson joined a group of mission-minded students who called themselves "The Brethren"; the students inspired the establishment of America's first organized missionary society.<ref>[https://www.thetravelingteam.org/articles/ann-judson The Traveling Team website, ''History of Mission: Ann Judson'']</ref> Eager to serve abroad, Judson became convinced that "Asia with its idolatrous myriads, was the most important field in the world for missionary effort". He, and three other students from the seminary, appeared before the Congregationalists' General Association to appeal for support. In 1810, the elders voted to form the [[American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions]]. |
||
===Marriage=== |
===Marriage=== |
||
[[File:Salem Harbor Caravan.jpg|thumb|left|220px|Sailing from Salem on the "Caravan"]] |
[[File:Salem Harbor Caravan.jpg|thumb|left|220px|Sailing from Salem on the "Caravan"]] |
||
On September 19, Judson was appointed by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions as a missionary to the East. Judson was also commissioned by the Congregational Church, and married [[Ann Hasseltine]] on February 5, 1812. He was ordained the next day at the [http://www.tabernaclechurch.org Tabernacle Church] in Salem. On February 19, he set sail aboard the brig ''Caravan'' with [[Luther Rice]]; [[Samuel Newell |
On September 19, Judson was appointed by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions as a missionary to the East. Judson was also commissioned by the Congregational Church, and married [[Ann Hasseltine]] on February 5, 1812. He was ordained the next day at the [http://www.tabernaclechurch.org Tabernacle Church] in Salem. On February 19, he set sail aboard the brig ''Caravan'' with [[Luther Rice]]; [[Samuel Newell]] and [[Harriet Newell]]; and his wife, Ann (known as "Nancy") Judson. |
||
==Ministry background== |
==Ministry background== |
||
===Voyage to India=== |
===Voyage to India=== |
||
The Judsons arrived in [[Calcutta]] on June 17, 1812. While aboard ship en route to India, he did a focused study on the theology of baptism. He came to the position that [[believer's baptism]] was theologically valid and should be done as a matter of obedience to the command of Jesus ({{bibleref |
The Judsons arrived in [[Calcutta]] on June 17, 1812. While aboard ship en route to India, he did a focused study on the theology of baptism. He came to the position that [[believer's baptism]] was theologically valid and should be done as a matter of obedience to the command of Jesus ({{bibleref|Matthew|28:19–20}}).<ref name="William H. Brackney 2021, p. 332"/> |
||
On September 6, 1812, he switched to the [[Baptist]] denomination along with his wife and they were [[Baptism|baptized]] by immersion in Calcutta by an English missionary associate of [[William Carey (missionary)|William Carey]] named [[William Ward (missionary)|William Ward]].<ref |
On September 6, 1812, he switched to the [[Baptist]] denomination along with his wife and they were [[Baptism|baptized]] by immersion in Calcutta by an English missionary associate of [[William Carey (missionary)|William Carey]] named [[William Ward (missionary)|William Ward]].<ref name="William H. Brackney 2021, p. 332"/> |
||
Both the local and British authorities did not want Americans evangelizing [[Hindus]] in the area, so the group of missionaries separated and sought other mission fields. They were ordered out of India by the [[British East India Company]], to whom American missionaries were even less welcome than British (they were baptized in September, and already in June, the United States had declared war on |
Both the local and British authorities did not want Americans evangelizing [[Hindus]] in the area, so the group of missionaries separated and sought other mission fields. They were ordered out of India by the [[British East India Company]], to whom American missionaries were even less welcome than British (they were baptized in September, and already in June, the United States had [[War of 1812#Declaration of war|declared war on Great Britain]]). The following year, on July 13, 1813, he moved to Burma, and en route his wife miscarried their first child aboard ship. |
||
Judson offered to Baptists in the United States to serve as their missionary. [[Luther Rice]], who had also converted, was in poor health and returned to America where his work and William Carey's urging resulted in the 1814 formation of the first national Baptist denomination in the United States for Foreign Missions (commonly called the [[Triennial Convention]]) and its offshoot the [[American Baptist Missionary Union]]. |
Judson offered to Baptists in the United States to serve as their missionary. [[Luther Rice]], who had also converted, was in poor health and returned to America where his work and William Carey's urging resulted in the 1814 formation of the first national Baptist denomination in the United States for Foreign Missions (commonly called the [[Triennial Convention]]) and its offshoot the [[American Baptist Missionary Union]]. |
||
===Missionaries in Burma=== |
===Missionaries in Burma=== |
||
It was another difficult year before the Judsons finally reached their intended destination, Burma. Buddhist Burma, Judson was told by the [[Serampore]] Baptists, was impermeable to Christian evangelism. Judson, who already knew Latin, Greek, and Hebrew, immediately began studying |
It was another difficult year before the Judsons finally reached their intended destination, Burma. Buddhist Burma, Judson was told by the [[Serampore]] Baptists, was impermeable to Christian evangelism. Judson, who already knew Latin, Greek, and Hebrew, immediately began studying Burmese grammar but took over three years to learn to speak it. This was due, in part, to the radical difference in structure between Burmese and Western languages. He found a tutor and spent twelve hours per day studying the language. He and his wife firmly dedicated themselves to understanding it. |
||
| ⚫ | During this time they were almost entirely isolated from contact with any European or American. Four years passed before Judson dared even to hold a semi-public service. At first, he tried adapting to Burmese customs by wearing a yellow robe to mark himself as a teacher of religion, but he soon changed to white to show he was not a [[Buddhist]]. Then, he gave up the whole attempt as artificial and decided that, regardless of his dress, no Burmese would identify him as anything but a foreigner. |
||
| ⚫ | During this time they were almost entirely isolated from contact with any European or American. Four years passed before Judson dared even to hold a semi-public service. At first, he tried adapting to Burmese customs by wearing a yellow robe to mark himself as a teacher of religion, but he soon changed to white to show he was not a [[Buddhist]]. Then, he gave up the whole attempt as artificial and decided that, regardless of his dress, no Burmese would identify him as anything but a foreigner. |
||
[[File:Burmese Zayat.jpg|thumb|220px|A Burmese Zayat]] |
[[File:Burmese Zayat.jpg|thumb|220px|A Burmese Zayat]] |
||
| ⚫ | He accommodated |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | First attempts by the Judsons to interest the natives of Rangoon with the Gospel of Jesus met with almost total indifference. [[Buddhist]] traditions and the Burmese |
||
| ⚫ | He accommodated some Burmese customs and built a ''[[zayat]]'', the customary bamboo and thatch reception shelter, on the street near his home as a reception room and meeting place for Burmese men. Fifteen men came to his first public meeting in April 1819. He was encouraged but suspected they had come more out of curiosity than anything else. Their attention wandered, and they soon seemed uninterested. Two months later, he baptized his first Burmese convert, Maung Naw, a 35-year-old timber worker from the hill tribes. "Burma Baptist Chronicle" stated that Maung Naw ([[Burmese name#Honorifics|Nai]] Naw) was an ethnic [[Mon people|Mon]].<ref>Maung Shwe Wa & Sowards, Burma Baptist Chronicle, 1963, Board of Publications Burma Baptist Convention Rangoon, p. 66</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | Judson completed translation of the ''Grammatical Notices of the Burman Language'' the following July and the ''[[Gospel of Matthew]]'', in 1817. Judson began public [[evangelism]] in 1818 sitting in a [[zayat]] by the roadside calling out "Ho! |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | In 1820, Judson and a fellow missionary named Colman petitioned the Emperor of Burma, King [[Bagyidaw]], in the hope that he would grant freedom for the missionaries to preach and teach throughout the country, as well as remove the sentence of death that was given for those Burmese who changed religion. |
||
| ⚫ | First attempts by the Judsons to interest the natives of Rangoon with the Gospel of Jesus met with almost total indifference. [[Buddhist]] traditions and the Burmese worldview at that time led many to disregard the pleadings of Adoniram and his wife to believe in one living and all-powerful God. Their second child, Roger William Judson, died at almost eight months of age. |
||
| ⚫ | Judson completed the translation of the ''Grammatical Notices of the Burman Language'' the following July and the ''[[Gospel of Matthew]]'', in 1817. Judson began public [[evangelism]] in 1818 sitting in a [[zayat]] by the roadside calling out "Ho! Every one that thirsteth for knowledge!"<ref name=MB>[https://missionsbox.org/missionary-bio/adoniram-judson-1788-1850/ Missions Box website, ''Adoniram Judson (1788-1850)'']</ref> The first believer was baptized in 1819, and there were 18 believers by 1822.<ref>{{cite book|title=Adoniram Judson: Bound for Burma|last1=Benge|first1=Janet|first2=Geoff|last2=Benge}}.</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | In 1820, Judson and a fellow missionary named Colman petitioned the Emperor of Burma, King [[Bagyidaw]], in the hope that he would grant freedom for the missionaries to preach and teach throughout the country, as well as remove the sentence of death that was given for those Burmese who changed religion. |
||
[[File:Moung Shway Moung.jpg|thumb|upright|left|Moung Shway Moung, an early convert to Christianity]] |
[[File:Moung Shway Moung.jpg|thumb|upright|left|Moung Shway Moung, an early convert to Christianity]] |
||
Bagyidaw disregarded their appeal and threw one of their Gospel tracts to the ground after reading a few lines. The missionaries returned to Rangoon and met with the fledgling church there to consider what to do next. The progress of Christianity would continue to be slow with much risk of endangerment and death in the Burmese Empire. |
Bagyidaw disregarded their appeal and threw one of their Gospel tracts to the ground after reading a few lines. The missionaries returned to Rangoon and met with the fledgling church there to consider what to do next. The progress of Christianity would continue to be slow with much risk of endangerment and death in the Burmese Empire. |
||
It took Judson 12 years to make 18 converts. His wife, Ann, was even more fluent in the spoken language of the people than her more academically literate husband. She befriended the wife of the viceroy of [[Rangoon]], as quickly as she did illiterate workers and women.{{ |
It took Judson 12 years to make 18 converts. His wife, Ann, was even more fluent in the spoken language of the people than her more academically literate husband. She befriended the wife of the viceroy of [[Rangoon]], as quickly as she did illiterate workers and women.{{citation needed|date=December 2022}} |
||
| ⚫ | A printing press had been sent from Serampore, and a missionary printer, George H. Hough, who arrived from America with his wife in 1817, produced the first printed materials in Burmese ever printed in Burma, which included 800 copies of Judson's translation of the ''[[Gospel of Matthew]]''. The chronicler of the church, Maung Shwe Wa, concludes this part of the story, "So was born the church in Rangoon–logger and fisherman, the poor and the rich, men and women. One traveled the whole path to Christ in three days; another took two years. But once they had decided for Christ they were his for all time."<ref>{{cite book|title=A History of Christianity in Asia, Vol. II: 1500-1900 - Volume 2|last1=Moffett|first1=Samuel Hugh}}.</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | A printing press had been sent from Serampore, and a missionary printer, George H. Hough, who arrived from America with his wife in 1817, produced the first printed materials in Burmese ever printed in Burma, which included 800 copies of Judson's translation of the ''[[Gospel of Matthew]]''. The chronicler of the church, Maung Shwe Wa, concludes this part of the story, "So was born the church in Rangoon–logger and fisherman, the poor and the rich, men and women. One traveled the whole path to Christ in three days; another took two years. But once they had decided for Christ they were his for all time."<ref>{{ |
||
[[File:Judson Burmese Bible.jpg|thumb|The Bible in Burmese translated by Judson]] |
[[File:Judson Burmese Bible.jpg|thumb|The Bible in Burmese translated by Judson]] |
||
One of the early disciples was U Shwe Ngong, a teacher and leader of a group of intellectuals dissatisfied with Buddhism, who were attracted to the new faith. He was a [[Deist]] skeptic to whose mind the preaching of Judson, once a college skeptic himself, was singularly challenging. After consideration, he assured Judson that he was ready to believe in God, Jesus Christ, and the atonement. |
One of the early disciples was U Shwe Ngong, a teacher and leader of a group of intellectuals dissatisfied with Buddhism, who were attracted to the new faith. He was a [[Deist]] skeptic to whose mind the preaching of Judson, once a college skeptic himself, was singularly challenging. After consideration, he assured Judson that he was ready to believe in God, Jesus Christ, and the atonement. |
||
Judson, instead of welcoming him to the faith, pressed him further asking if he believed what he had read in the gospel of Matthew that [[Jesus]] the son of God died on the cross. U Shwe Ngong shook his head and said, "Ah, you have caught me now. I believe that he suffered death, but I cannot believe he suffered the shameful death on the cross." |
Judson, instead of welcoming him to the faith, pressed him further asking if he believed what he had read in the gospel of Matthew that [[Jesus]] the son of God died on the cross. U Shwe Ngong shook his head and said, "Ah, you have caught me now. I believe that he suffered death, but I cannot believe he suffered the shameful death on the cross."<ref>[https://www.fieldpartner.org/4-lessons-from-adoniram-judson/ Field Partner website, ''Four Lessons From the Life Of Adoniram Judson - Pt 3'']</ref> Not long after, he came back to tell Judson, "I have been trusting in my own reason, not the word of God…. I now believe the crucifixion of Christ because it is contained in scripture." |
||
The essence of Judson's preaching was a combination of conviction of the truth with the rationality of the Christian faith, a firm belief in the authority of the Bible, and a determination to make Christianity relevant to the Burmese mind without violating the integrity of Christian truth, or as he put it, "to preach the gospel, not anti-Buddhism." |
The essence of Judson's preaching was a combination of conviction of the truth with the rationality of the Christian faith, a firm belief in the authority of the Bible, and a determination to make Christianity relevant to the Burmese mind without violating the integrity of Christian truth, or as he put it, "to preach the gospel, not anti-Buddhism." |
||
| Line 73: | Line 83: | ||
===Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826)=== |
===Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826)=== |
||
[[File:Judson imprisoned.jpg|thumb|left|upright|Judson imprisoned at Ava]] |
[[File:Judson imprisoned.jpg|thumb|left|upright|Judson imprisoned at Ava]] |
||
Two opposite hungers triggered the [[First Anglo-Burmese War]] of 1824: Burma's desire for more territory, and Britain's desire for more trade. Burma threatened [[Assam]] and [[Bengal]]; Britain responded by attacking and absorbing two Burmese provinces into her India holdings to broaden her trade routes to East Asia. The war was a rough interruption of the Baptists' missionary work. English-speaking Americans were too easily confused with the enemy and suspected of spying. |
Two opposite hungers triggered the [[First Anglo-Burmese War]] of 1824: Burma's desire for more territory, and Britain's desire for more trade. Burma threatened [[Assam]] and [[Bengal]]; Britain responded by attacking and absorbing two Burmese provinces into her India holdings to broaden her trade routes to East Asia. The war was a rough interruption of the Baptists' missionary work. English-speaking Americans were too easily confused with the enemy and suspected of spying. |
||
Judson was imprisoned for 17 months during the war between the [[United Kingdom]] and Burma, first at [[Inwa|Ava]] and then at Aung Pinle. Judson and Price were violently arrested. Officers led by an official executioner burst into the Judson home, threw Judson to the ground in front of his wife, bound him with torture thongs, and dragged him off to the prison of Ava. |
Judson was imprisoned for 17 months during the war between the [[United Kingdom]] and Burma, first at [[Inwa|Ava]] and then at Aung Pinle. Judson and Price were violently arrested. Officers led by an official executioner burst into the Judson home, threw Judson to the ground in front of his wife, bound him with torture thongs, and dragged him off to the prison of Ava. |
||
Twelve months later, Judson and Price, along with a small group of surviving Western prisoners, were marched overland for six more months of misery in a primitive village near [[Mandalay]]. Of the [[sepoy]] British prisoners-of-war imprisoned with them, all but one died. He spent 20 months in prison. |
Twelve months later, Judson and Price, along with a small group of surviving Western prisoners, were marched overland for six more months of misery in a primitive village near [[Mandalay]]. Of the [[sepoy]] British prisoners-of-war imprisoned with them, all but one died. He spent 20 months in prison. |
||
[[File:Nancy visits Adoniram.jpg|thumb|Ann visits Adoniram in prison]] |
[[File:Nancy visits Adoniram.jpg|thumb|Ann visits Adoniram in prison]] |
||
| Line 83: | Line 95: | ||
On October 24, 1826, Ann died at Amherst (now [[Kyaikkami]]), Burma. Their third child died six months later. She died while her husband was out exploring the ceded province of [[Tanintharyi Region|Tenasserim]]. Within a few years of the end of the war, Baptist membership doubled on an average of every eight years for the 32 years between 1834 and 1866. |
On October 24, 1826, Ann died at Amherst (now [[Kyaikkami]]), Burma. Their third child died six months later. She died while her husband was out exploring the ceded province of [[Tanintharyi Region|Tenasserim]]. Within a few years of the end of the war, Baptist membership doubled on an average of every eight years for the 32 years between 1834 and 1866. |
||
[[File:Ko Thah A.jpg|thumb|left|140px|Ko-Thah-a]] |
[[File:Ko Thah A.jpg|thumb|left|140px|Ko-Thah-a]] |
||
The collapse of Burma's armies brought Judson out of prison, but his release was not complete freedom. In 1826, several months after the surrender, Burma pressed Judson into service as a translator for the peace negotiations. |
|||
Most of the growth of Baptist churches in Burma was in British-ruled territory, rather than the Burmese-ruled kingdom. Most of the growth came from animist tribes, rather than from the major population group, the Buddhist Burmese. The first Burmese pastor Judson ordained was |
The collapse of Burma's armies brought Judson out of prison, but his release was not complete freedom. In 1826, several months after the surrender, Burma pressed Judson into service as a translator for the peace negotiations. |
||
Most of the growth of Baptist churches in Burma was in British-ruled territory, rather than the Burmese-ruled kingdom. Most of the growth came from animist tribes, rather than from the major population group, the Buddhist Burmese. The first Burmese pastor Judson ordained was Ko-Thah-a, one of the original group of converts, who refounded the church at [[Rangoon]]. |
|||
===Karen apostle=== |
===Karen apostle=== |
||
| Line 93: | Line 107: | ||
The Karen people were a hunted minority group of ancient [[Tibeto-Burman]] ancestry scattered in the forests and jungles of the [[Salween River]] and in the hills along the southeast coast. Judson was the first missionary to make contact with them in 1827, when he ransomed and freed a debt-slave from one of his early converts. The freed slave, Ko Tha Byu, was an illiterate, surly man who spoke almost no Burmese and was reputed to be not only a thief, but also a murderer who admitted killing at least 30 men, but could not remember exactly how many more. |
The Karen people were a hunted minority group of ancient [[Tibeto-Burman]] ancestry scattered in the forests and jungles of the [[Salween River]] and in the hills along the southeast coast. Judson was the first missionary to make contact with them in 1827, when he ransomed and freed a debt-slave from one of his early converts. The freed slave, Ko Tha Byu, was an illiterate, surly man who spoke almost no Burmese and was reputed to be not only a thief, but also a murderer who admitted killing at least 30 men, but could not remember exactly how many more. |
||
In 1828, the former Karen bandit, "whose rough, undisciplined genius, energy and zeal for Christ" (Sarah B Judson) had caught the notice of the missionaries, was sent south with a new missionary couple, the Boardmans, into the territory of the strongly animistic, non-Buddhist Karen. Ko Tha Byu was no sooner baptized, when he set off into the jungle alone to preach to his fellow tribe members. Astonishingly, he found them prepared for his preaching. Their ancient oracle traditions, handed down for centuries, contained some startling echoes of the [[Old Testament]] that some scholars conjecture a linkage with Jewish communities (or possibly even [[ |
In 1828, the former Karen bandit, "whose rough, undisciplined genius, energy and zeal for Christ" (Sarah B Judson) had caught the notice of the missionaries, was sent south with a new missionary couple, the Boardmans, into the territory of the strongly animistic, non-Buddhist Karen. Ko Tha Byu was no sooner baptized, when he set off into the jungle alone to preach to his fellow tribe members. Astonishingly, he found them prepared for his preaching. Their ancient oracle traditions, handed down for centuries, contained some startling echoes of the [[Old Testament]] that some scholars conjecture a linkage with Jewish communities (or possibly even [[Church of the East|Nestorians]]), before their migrations from western China into Burma perhaps as early as the 12th century. |
||
The core of what they called their "Tradition of the Elders" was a belief in an unchangeable, eternal, all-powerful God, creator of heaven and earth, of man, and of woman formed from a rib taken from the man (Genesis). They believed in humanity's temptation by a devil, and its fall, and that some day a Great Messiah would come to its rescue. They lived in expectation of a prophecy that white foreigners would bring them a sacred parchment roll. |
The core of what they called their "Tradition of the Elders" was a belief in an unchangeable, eternal, all-powerful God, creator of heaven and earth, of man, and of woman formed from a rib taken from the man (Genesis). They believed in humanity's temptation by a devil, and its fall, and that some day a Great Messiah would come to its rescue. They lived in expectation of a prophecy that white foreigners would bring them a sacred parchment roll. |
||
While the Boardmans and Ko Tha Byu were penetrating the jungles to the south, Judson shook off a paralyzing year-long siege of depression that overcame him after the death of his wife and set out alone on long canoe trips up the Salween River into the [[tiger]]-infested jungles to evangelize the northern Karen. Between trips, he worked unceasingly at his lifelong goal of translating the entire Bible into Burmese. When he finished it at last in 1834, he had been labouring on it for 24 years. |
While the Boardmans and Ko Tha Byu were penetrating the jungles to the south, Judson shook off a paralyzing year-long siege of depression that overcame him after the death of his wife and set out alone on long canoe trips up the Salween River into the [[tiger]]-infested jungles to evangelize the northern Karen. Between trips, he worked unceasingly at his lifelong goal of translating the entire Bible into Burmese. When he finished it at last in 1834, he had been labouring on it for 24 years.<ref>Gerald H. Anderson, ''Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions'', Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, USA, 1999, p. 346</ref> It was printed and published in 1835. |
||
In April of that same year, he married [[Sarah Hall Boardman]], widow of fellow missionary [[George Boardman (missionary)|George Boardman]]. They had eight children, five of whom survived to adulthood. Sarah's health began failing and physicians recommended a return to America. Sarah died en route at [[St. Helena]] on September 1, 1845. He continued home, where he was greeted as a celebrity and toured the eastern seaboard raising the profile of and money for missionary activity. Because he could barely speak above a whisper, due to pulmonary illness, his public addresses were made by speaking to an assistant, who would then address the audience.<ref>{{ |
In April of that same year, he married [[Sarah Hall Boardman]], widow of fellow missionary [[George Boardman (missionary)|George Boardman]]. They had eight children, five of whom survived to adulthood. Sarah's health began failing and physicians recommended a return to America. Sarah died en route at [[St. Helena]] on September 1, 1845. He continued home, where he was greeted as a celebrity and toured the eastern seaboard raising the profile of and money for missionary activity. Because he could barely speak above a whisper, due to pulmonary illness, his public addresses were made by speaking to an assistant, who would then address the audience.<ref>{{cite web|title=Abraham Judson, Burma's First Missionary|work=Burmese Bible|last=Barlow|first=Fred|url=http://www.burmesebible.com/b/adoniram_judson_by_fred_barlow.htm|access-date=2006-06-04}} (English text is at the bottom.)</ref> |
||
On June 2, 1846, Judson married for the third time, to writer [[Emily Chubbuck]],<ref name=EB1911/> who he had commissioned to write memoirs for Sarah Hall Boardman. They had a daughter born in 1847. |
On June 2, 1846, Judson married for the third time, to writer [[Emily Chubbuck]],<ref name=EB1911/> who he had commissioned to write memoirs for Sarah Hall Boardman. They had a daughter born in 1847. |
||
| Line 107: | Line 121: | ||
In 1835, a second single woman, [[Eleanor Macomber]], after five years of mission to the [[Ojibway]] Indians in [[Michigan]], joined the mission in Burma. Alone, with the help of Karen evangelistic assistants, she planted a church in a remote Karen village and nurtured it to the point where it could be placed under the care of an ordinary missionary. She lived there five years and died of jungle fever. |
In 1835, a second single woman, [[Eleanor Macomber]], after five years of mission to the [[Ojibway]] Indians in [[Michigan]], joined the mission in Burma. Alone, with the help of Karen evangelistic assistants, she planted a church in a remote Karen village and nurtured it to the point where it could be placed under the care of an ordinary missionary. She lived there five years and died of jungle fever. |
||
Judson developed a serious lung disease and doctors prescribed a sea voyage as a cure. On April 12, 1850, he died at age 61 on board ship in the [[Bay of Bengal]] and was buried at sea, having spent 37 years abroad with only one trip back home to America. A memorial to Judson was built on [[Burial Hill]] in Plymouth, Massachusetts.<ref>{{cite web|title= |
Judson developed a serious lung disease and doctors prescribed a sea voyage as a cure. On April 12, 1850, he died at age 61 on board ship in the [[Bay of Bengal]] and was buried at sea, having spent 37 years abroad with only one trip back home to America. A memorial to Judson was built on [[Burial Hill]] in Plymouth, Massachusetts.<ref>{{cite web|title=The First Baptist Missionary|url=http://fbcplymouth.com/the-first-baptist-missionary/|website=FBC Plymouth|date= March 2014|access-date=28 November 2014}}</ref> |
||
==Legacy== |
==Legacy== |
||
[[File:YU Judson Church.JPG|thumb|left|160px|Judson Church, Yangon University]] |
[[File:YU Judson Church.JPG|thumb|left|160px|Judson Church, Yangon University]] |
||
[[File: Judson Memorial Baptist Church, Mandalay, Myanmar.JPG|left|thumb|160px| Judson Memorial Baptist Church, in [[Mandalay]], Myanmar.]] |
[[File: Judson Memorial Baptist Church, Mandalay, Myanmar.JPG|left|thumb|160px| Judson Memorial Baptist Church, in [[Mandalay]], Myanmar.]] |
||
| ⚫ | By the time of Judson's death, he had translated the Bible into Burmese as well as a half-completed Burmese-English dictionary. Burma at the time had 100 churches, and over 8,000 believers |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Judson compiled the first ever Burmese-[[English language|English]] dictionary; missionary E. A. Steven completed the English-Burmese half. Every dictionary and grammar written in Burma in the last two centuries has been based on ones originally created by Judson.{{ |
||
By 2006, [[Myanmar]] had the third largest number of Baptists worldwide,<ref>[https://christianhistoryinstitute.org/magazine/article/unforgettable Christian History Institute website, ''Unforgettable'', article by Rosalie Hall Hunt published in #90 in 2006]</ref> behind the United States and India. The majority of adherents are [[Karen people|Karen]], [[Kachin people|Kachin]] and Chin. |
|||
| ⚫ | Each July, Baptist churches in Myanmar celebrate "Judson Day," commemorating his arrival as a missionary. |
||
| ⚫ | Judson compiled the first ever Burmese-[[English language|English]] dictionary; missionary E. A. Steven completed the English-Burmese half. Every dictionary and grammar written in Burma in the last two centuries has been based on ones originally created by Judson.{{citation needed|date=December 2022}} Judson "became a symbol of the preeminence of Bible translation for" Protestant missionaries.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Richard V. Pierard|title=The Man Who Gave the Bible to the Burmese|url=http://www.christianitytoday.com/ch/2006/issue90/6.16.html|journal=Christian History & Biography|date=Spring 2006|volume=90|pages=16–21}}</ref> In the 1950s, Burma's Buddhist prime minister [[U Nu]] told the Burma Christian Council "Oh no, a new translation is not necessary. Judson's captures the language and idiom of Burmese perfectly and is very clear and understandable."<ref name="Rosalie Hall Hunt Spring 2006 39–41"/> Though the Bible has been translated [[Bible translations into Burmese|numerous times]] into Burmese, Judson's translation remains the most popular version in Myanmar.{{citation needed|date=October 2018}} |
||
| ⚫ | Judson's change to the validity of [[believer's baptism]], and subsequent need of support, led to the founding of the first national Baptist organization in the United States and subsequently to all American Baptist associations, including the [[Southern Baptist Convention|Southern Baptists]] that were the first to break off from the national organization. Publication of his wife Ann's letters about their mission inspired many Americans to become or support Christian missionaries.{{ |
||
| ⚫ | Each July, Baptist churches in Myanmar celebrate "Judson Day," commemorating his arrival as a missionary.<ref>[https://www.baptistpress.com/resource-library/news/adoniram-judsons-spiritual-descendants-in-massachusetts/ Baptist Press website, ''Adoniram Judson’s spiritual descendants in Massachusetts'', article by Tobin Perry, published December 9, 2019]</ref> Inside the campus of [[Yangon University]] is Judson Church, named in his honor, and in 1920 Judson College, named in his honor, merged into Rangoon College, which has since been renamed Yangon University.<ref name="Rosalie Hall Hunt Spring 2006 39–41">{{cite journal|author=Rosalie Hall Hunt |title=Unforgettable|url=http://www.christianitytoday.com/ch/2006/issue90/14.39.html|journal=Christian History & Biography|date=Spring 2006|volume=90|pages=39–41}}</ref> The American University named in his honor, [[Judson University]] was founded in [[Elgin, Illinois]], in 1963, as the liberal arts Judson College was separated from the [[Northern Baptist Theological Seminary]], which moved from [[Chicago]] to [[Lombard, Illinois]]. This American Judson College became Judson University in 2007 and now also has a campus in [[Rockford, Illinois]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Judson's change to the validity of [[believer's baptism]], and subsequent need of support, led to the founding of the first national Baptist organization in the United States and subsequently to all American Baptist associations, including the [[Southern Baptist Convention|Southern Baptists]] that were the first to break off from the national organization. Publication of his wife Ann's letters about their mission inspired many Americans to become or support Christian missionaries.{{citation needed|date=December 2022}} At least 36 Baptist churches in the United States are named after Judson. In 2024 [[Southeastern Baptist Theological Seminary]] renamed its undergraduate program to [[Judson College at Southeastern|Judson College.]] |
||
[[Judson Deland Cominskie]], first son of renowned [[Free Will Baptist]] minister [[Devin Lyle Cominskie]], derives his name from Adoniram. |
|||
The town of [[Judsonia]], Arkansas is named after Judson along with [[Judson College (Alabama)|Judson College in Alabama]] which was named after his wife Ann and a dormitory at Maranatha Baptist University carries his name.<ref name="Rosalie Hall Hunt Spring 2006 39–41" /> Christian Union owns and operates a ministry center named after him at his undergraduate alma mater, Brown University. His seminary alma mater, [[Andover Theological Seminary]], (now [[Andover Newton Theological School]]), gives out an annual The Judson Award.{{citation needed|date=December 2022}} |
|||
{{Libship honor|name=Adoniram Judson|type=his}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
In World War II, the United States liberty ship SS ''Adoniram Judson'' was named in his honor.<ref>[https://vesselhistory.marad.dot.gov/ShipHistory/Detail/42 U.S. Department of Transportation website, ''Adoniram Judson'']</ref> |
|||
==Published works== |
==Published works== |
||
| Line 134: | Line 151: | ||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{Portal|Biography|United States|Saints}} |
{{Portal|Biography|United States|Saints}} |
||
* [[John Alexander Stewart (scholar)]], another first compiler (with C.W. Dunn) of a Burmese-English dictionary |
* [[John Alexander Stewart (scholar)]], another first compiler (with C. W. Dunn) of a Burmese-English dictionary |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 143: | Line 160: | ||
* Brackney, William H. "The Legacy of Adoniram Judson." ''International Bulletin of Missionary Research'' 22.3 (1998): 122+ [http://www.wmcarey.edu/carey/electronic-books/articles/legacy-judson.pdf online] |
* Brackney, William H. "The Legacy of Adoniram Judson." ''International Bulletin of Missionary Research'' 22.3 (1998): 122+ [http://www.wmcarey.edu/carey/electronic-books/articles/legacy-judson.pdf online] |
||
* Bradshaw, Robert I. "the life and Work of Adoniram Judson, Missionary to Burma." (1992). [http://www.theologicalstudies.org.uk/article_judson.html online] |
* Bradshaw, Robert I. "the life and Work of Adoniram Judson, Missionary to Burma." (1992). [http://www.theologicalstudies.org.uk/article_judson.html online] |
||
* {{cite book |
* {{cite book|last=Clement|first=Jesse|title=Memoir of Adoniram Judson|url=https://archive.org/details/memoirofadoniram00clem|access-date=October 21, 2016|year=1852|publisher=Derby and Miller|location=Auburn, NY}} |
||
* |
* Duesing, Jason G. 2012. ''Adoniram Judson: A Bicentennial Appreciation of the Pioneer American Missionary''. B & H Academic. |
||
* James, Helen. "Adoniram Judson and the Creation of a Missionary Discourse in Pre-Colonial Burma." ''Journal of Burma Studies'' 7.1 (2002): 1-28. [https://muse.jhu.edu/article/411092/summary online] |
* James, Helen. "Adoniram Judson and the Creation of a Missionary Discourse in Pre-Colonial Burma." ''Journal of Burma Studies'' 7.1 (2002): 1-28. [https://muse.jhu.edu/article/411092/summary online] |
||
* Judson, Edward. ''The Life of Adoniram Judson'' (1883) [https://books.google.com/books? |
* Judson, Edward. ''The Life of Adoniram Judson'' (1883) [https://books.google.com/books?id=ZItUAAAAYAAJ&dq=%27%27Adoniram+Judson:+%27%27&pg=PA1 online]. |
||
* Neill, Stephen. ''A History of Christian Missions'' (Penguin Books, 1986) pp 293–95 |
* Neill, Stephen. ''A History of Christian Missions'' (Penguin Books, 1986) pp 293–95 |
||
* Wayland, Francis. 1853. ''A memoir of the Life and Labors of the Rev. Adoniram Judson'' |
* Wayland, Francis. 1853. ''A memoir of the Life and Labors of the Rev. Adoniram Judson'' |
||
* Torbet, Robert. 1955. ''Venture of Faith: The Story of the American Baptist Missionary Society'' |
* Torbet, Robert. 1955. ''Venture of Faith: The Story of the American Baptist Missionary Society'' |
||
* Leonard, Bill J., editor. 1994.''Dictionary of Baptists in America'' |
* Leonard, Bill J., editor. 1994.''Dictionary of Baptists in America'' |
||
* ''Encyclopedia of Southern Baptists,'' Norman W. Cox, editor |
* ''Encyclopedia of Southern Baptists,'' Norman W. Cox, editor |
||
* ''Burmese Encyclopedia: Vol 12, p-444,'' printed in 1966 |
* ''Burmese Encyclopedia: Vol 12, p-444,'' printed in 1966 |
||
| Line 164: | Line 181: | ||
{{Wikisourceauthor}} |
{{Wikisourceauthor}} |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080220131745/http://www.wholesomewords.org/missions/ijudson.html Adoniram Judson biographies] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080220131745/http://www.wholesomewords.org/missions/ijudson.html Adoniram Judson biographies] |
||
* [http://www.robibrad.demon.co.uk/Judson.htm Life and Work of Judson] {{ |
* [http://www.robibrad.demon.co.uk/Judson.htm Life and Work of Judson] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060411203028/http://www.robibrad.demon.co.uk/Judson.htm|date=April 11, 2006}} |
||
* [http://www.sbhla.org/bio_adoniramjudson.htm SBHLA bio of Judson] |
* [http://www.sbhla.org/bio_adoniramjudson.htm SBHLA bio of Judson] |
||
* [https://archive.org/details/amemoirlifeandl04waylgoog/page/n56 <!-- pg=1 quote=adoniram-judson/. --> Google E-text of an 1853 Biography Volume One] |
* [https://archive.org/details/amemoirlifeandl04waylgoog/page/n56 <!-- pg=1 quote=adoniram-judson/. --> Google E-text of an 1853 Biography Volume One] |
||
* [https://books.google.com/books? |
* [https://books.google.com/books?id=zov4cpqZlF4C&dq=adoniram-judson/&pg=PR1 Google E-text of an 1853 Biography Volume Two] |
||
* [http://www.judsonmemorial.org/ A memorial church to Adoniram and Ann Judson] |
* [http://www.judsonmemorial.org/ A memorial church to Adoniram and Ann Judson] |
||
* [http://www.burmesebible.com/ Online Burmese Bible] |
* [http://www.burmesebible.com/ Online Burmese Bible] |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20060615170340/http://www.myanmarbible.com/bible/Judson/html/ Online Burmese Bible (Compatible with Burmese Wikipedia)] — Translated from The Original Tongues by Rev. A. Judson, D.D. |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20060615170340/http://www.myanmarbible.com/bible/Judson/html/ Online Burmese Bible (Compatible with Burmese Wikipedia)] — Translated from The Original Tongues by Rev. A. Judson, D.D. |
||
* {{Find a Grave|11609|access-date=2009-02-26}} |
* {{Find a Grave|11609|access-date=2009-02-26}} |
||
* [http://www.hymntime.com/tch/htm/c/o/m/e/comehsdd.htm Hymn: "Come, Holy Spirit, Dove Divine"] |
* [http://www.hymntime.com/tch/htm/c/o/m/e/comehsdd.htm Hymn: "Come, Holy Spirit, Dove Divine"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303235713/http://www.hymntime.com/tch/htm/c/o/m/e/comehsdd.htm|date=March 3, 2016 }} |
||
* Judson, Edward. ''The Life of Adoniram Judson.'' New York: Anson D. F. Randolph & Company, 1883 |
* Judson, Edward. ''The Life of Adoniram Judson.'' New York: Anson D. F. Randolph & Company, 1883 |
||
* [https://archive.org/details/1528288.0001.001.umich.edu ''Judson's Burmese-English dictionary''], revised and enlarged by Robert C. Stevenson, Rangoon: Government Printing, Burma, 1893. |
* [https://archive.org/details/1528288.0001.001.umich.edu ''Judson's Burmese-English dictionary''], revised and enlarged by Robert C. Stevenson, Rangoon: Government Printing, Burma, 1893. |
||
* [https://archive.org/details/judsonburmeseeng00judsrich ''The Judson Burmese-English dictionary''], revised and enlarged by Robert C. Stevenson, revised and edited by F.H. Eveleth, Rangoon: American Baptist Mission Press, 1921. |
* [https://archive.org/details/judsonburmeseeng00judsrich ''The Judson Burmese-English dictionary''], revised and enlarged by Robert C. Stevenson, revised and edited by F. H. Eveleth, Rangoon: American Baptist Mission Press, 1921. |
||
* [https://bethanygu.edu/blog/stories/adoniram-and-ann-judson/ ''Adoniram and Ann Judson''] |
* [https://bethanygu.edu/blog/stories/adoniram-and-ann-judson/ ''Adoniram and Ann Judson''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210416140736/https://bethanygu.edu/blog/stories/adoniram-and-ann-judson/|date=April 16, 2021}} |
||
* [https://missiology.org.uk/pdf/e-books/grose/judson-centennial.pdf Missiology website, ''The Judson Centennial, 1814-1914'', edited by Howard B. Grose and Fred P. Haggard] (online copy) |
|||
* [https://missiology.org.uk/pdf/e-books/titterington-s-p/century-of-baptist-missions.pdf Missiology website, ''A Century of Baptist Foreign Missions; An Outline Sketch'', by Sophie Bronson Titterington, published by the American Baptist Publication Society (1891)] (online copy) |
|||
{{Christianity in Myanmar}} |
{{Christianity in Myanmar}} |
||
{{Protestant missions to Southeast Asia}} |
{{Protestant missions to Southeast Asia}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
| Line 185: | Line 204: | ||
[[Category:1788 births]] |
[[Category:1788 births]] |
||
[[Category:1850 deaths]] |
[[Category:1850 deaths]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:19th-century American male writers]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:American lexicographers]] |
[[Category:American lexicographers]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:American prisoners of war]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Baptist missionaries from the United States]] |
[[Category:Baptist missionaries from the United States]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Baptist writers]] |
|||
[[Category:Brown University alumni]] |
[[Category:Brown University alumni]] |
||
[[Category:Burials at sea]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:People from Malden, Massachusetts]] |
|||
[[Category:People of the First Anglo-Burmese War]] |
[[Category:People of the First Anglo-Burmese War]] |
||
[[Category:Translators of the Bible into Burmese]] |
|||
[[Category:People who died at sea]] |
[[Category:People who died at sea]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Translators of the Bible into Burmese]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 14:16, 16 October 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2022) |
Adoniram Judson | |
|---|---|
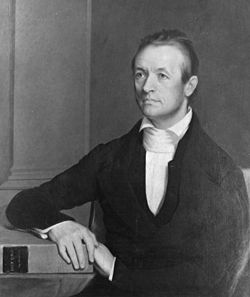 Adoniram Judson by George Peter Alexander Healy, 1846 | |
| Born | August 9, 1788 |
| Died | April 12, 1850 (aged 61) At sea in the Bay of Bengal |
| Nationality | American |
| Alma mater | Brown University and Andover Theological Seminary |
| Occupation | Missionary to Burma |
| Spouse(s) | Ann Hasseltine, 1812–26 (her death) Sarah Hall Boardman, 1834–45 (her death) Emily Chubbuck, 1846–50 (his death) |
| Children | (1) Stillborn son, 1813 to Ann Judson; (2) Roger Williams Judson, 11/11/1814 to Ann Judson (lived only 2 wks); (3) Maria Elizabeth Butterworth Judson, 1/26/1825 - 4/26/1827 to Ann Judson; (4) Abigail Ann Judson, 10/31/1835 to Sarah Judson; (5) Adoniram Judson Jr., 4/7/1837 to Sarah Judson; (6) Elnathan Judson, 7/15/1838 to Sarah Judson; (7) Henry Judson, 12/31/1839 - 7/31/1841 to Sarah Judson; (8) Stillborn son named Luther in 1840 to Sarah Judson; (9) Henry Judson, July 1842 (named in honor of baby Henry who had passed the previous year) to Sarah Judson; (10) Charles Judson, 12/18/1843 - 8/1845 to Sarah Judson; (11) Edward Judson 12/27/1844 to Sarah Judson; (12) Emily Frances Judson, 12/26/1847 to Emily Judson; (13) Charles Judson, 4/13/1850 (passed the same day) to Emily Judson. |
| Signature | |
Adoniram Judson (/ˌædəˈnaɪrəm/; August 9, 1788 – April 12, 1850) was an American Congregationalist and later Particular Baptist[1] missionary, who worked in Burma for almost forty years. At the age of 25, Judson was sent from North America to preach in Burma. His mission and work with Luther Rice led to the formation of the first Baptist association in America to support missionaries.
Judson was one of the first Protestant missionaries to Burma. He translated the Bible into Burmese and established a number of Baptist churches in Burma.
Early life
[edit]
Judson was born on August 9, 1788, in Malden, Middlesex County, Massachusetts.[2] He was born to Adoniram Judson Sr., a Congregational minister, and Abigail (née Brown). Judson entered the College of Rhode Island & Providence Plantations (now Brown University) when he was sixteen, and graduated as valedictorian of his class at the age of nineteen.[2] While studying at college, he met a young man named Jacob Eames, a devout deist and skeptic. Judson and Eames developed a strong friendship, leading to Judson's abandonment of his childhood faith and parents' religious instruction. During this time, Judson embraced the writings of the French philosophes. After graduating from college, Judson opened a school and wrote an English grammar and mathematics textbook for girls.
Judson's deist views were shaken when his friend Eames fell violently ill and died. Both had been sleeping in separate rooms at an inn, and Judson heard the death throes of the person next door, only to learn from the clerk the next morning that his anonymous neighbor had been Mr. Eames, who had indeed died. The shock of learning the dying neighbor's identity – and that Eames had led Judson away from the Christian faith into skepticism, but was now dead – returned Judson back to the faith of his youth, although he was already attending the Andover Theological Seminary.[3] In 1808, Judson "made a solemn dedication of himself to God".[4] During his final year at the school, Judson decided upon a missionary career.
In 1810, Judson joined a group of mission-minded students who called themselves "The Brethren"; the students inspired the establishment of America's first organized missionary society.[5] Eager to serve abroad, Judson became convinced that "Asia with its idolatrous myriads, was the most important field in the world for missionary effort". He, and three other students from the seminary, appeared before the Congregationalists' General Association to appeal for support. In 1810, the elders voted to form the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions.
Marriage
[edit]
On September 19, Judson was appointed by the American Board of Commissioners for Foreign Missions as a missionary to the East. Judson was also commissioned by the Congregational Church, and married Ann Hasseltine on February 5, 1812. He was ordained the next day at the Tabernacle Church in Salem. On February 19, he set sail aboard the brig Caravan with Luther Rice; Samuel Newell and Harriet Newell; and his wife, Ann (known as "Nancy") Judson.
Ministry background
[edit]Voyage to India
[edit]The Judsons arrived in Calcutta on June 17, 1812. While aboard ship en route to India, he did a focused study on the theology of baptism. He came to the position that believer's baptism was theologically valid and should be done as a matter of obedience to the command of Jesus (Matthew 28:19–20).[2]
On September 6, 1812, he switched to the Baptist denomination along with his wife and they were baptized by immersion in Calcutta by an English missionary associate of William Carey named William Ward.[2]
Both the local and British authorities did not want Americans evangelizing Hindus in the area, so the group of missionaries separated and sought other mission fields. They were ordered out of India by the British East India Company, to whom American missionaries were even less welcome than British (they were baptized in September, and already in June, the United States had declared war on Great Britain). The following year, on July 13, 1813, he moved to Burma, and en route his wife miscarried their first child aboard ship.
Judson offered to Baptists in the United States to serve as their missionary. Luther Rice, who had also converted, was in poor health and returned to America where his work and William Carey's urging resulted in the 1814 formation of the first national Baptist denomination in the United States for Foreign Missions (commonly called the Triennial Convention) and its offshoot the American Baptist Missionary Union.
Missionaries in Burma
[edit]It was another difficult year before the Judsons finally reached their intended destination, Burma. Buddhist Burma, Judson was told by the Serampore Baptists, was impermeable to Christian evangelism. Judson, who already knew Latin, Greek, and Hebrew, immediately began studying Burmese grammar but took over three years to learn to speak it. This was due, in part, to the radical difference in structure between Burmese and Western languages. He found a tutor and spent twelve hours per day studying the language. He and his wife firmly dedicated themselves to understanding it.
During this time they were almost entirely isolated from contact with any European or American. Four years passed before Judson dared even to hold a semi-public service. At first, he tried adapting to Burmese customs by wearing a yellow robe to mark himself as a teacher of religion, but he soon changed to white to show he was not a Buddhist. Then, he gave up the whole attempt as artificial and decided that, regardless of his dress, no Burmese would identify him as anything but a foreigner.

He accommodated some Burmese customs and built a zayat, the customary bamboo and thatch reception shelter, on the street near his home as a reception room and meeting place for Burmese men. Fifteen men came to his first public meeting in April 1819. He was encouraged but suspected they had come more out of curiosity than anything else. Their attention wandered, and they soon seemed uninterested. Two months later, he baptized his first Burmese convert, Maung Naw, a 35-year-old timber worker from the hill tribes. "Burma Baptist Chronicle" stated that Maung Naw (Nai Naw) was an ethnic Mon.[6]

First attempts by the Judsons to interest the natives of Rangoon with the Gospel of Jesus met with almost total indifference. Buddhist traditions and the Burmese worldview at that time led many to disregard the pleadings of Adoniram and his wife to believe in one living and all-powerful God. Their second child, Roger William Judson, died at almost eight months of age.
Judson completed the translation of the Grammatical Notices of the Burman Language the following July and the Gospel of Matthew, in 1817. Judson began public evangelism in 1818 sitting in a zayat by the roadside calling out "Ho! Every one that thirsteth for knowledge!"[7] The first believer was baptized in 1819, and there were 18 believers by 1822.[8]
In 1820, Judson and a fellow missionary named Colman petitioned the Emperor of Burma, King Bagyidaw, in the hope that he would grant freedom for the missionaries to preach and teach throughout the country, as well as remove the sentence of death that was given for those Burmese who changed religion.

Bagyidaw disregarded their appeal and threw one of their Gospel tracts to the ground after reading a few lines. The missionaries returned to Rangoon and met with the fledgling church there to consider what to do next. The progress of Christianity would continue to be slow with much risk of endangerment and death in the Burmese Empire.
It took Judson 12 years to make 18 converts. His wife, Ann, was even more fluent in the spoken language of the people than her more academically literate husband. She befriended the wife of the viceroy of Rangoon, as quickly as she did illiterate workers and women.[citation needed]
A printing press had been sent from Serampore, and a missionary printer, George H. Hough, who arrived from America with his wife in 1817, produced the first printed materials in Burmese ever printed in Burma, which included 800 copies of Judson's translation of the Gospel of Matthew. The chronicler of the church, Maung Shwe Wa, concludes this part of the story, "So was born the church in Rangoon–logger and fisherman, the poor and the rich, men and women. One traveled the whole path to Christ in three days; another took two years. But once they had decided for Christ they were his for all time."[9]

One of the early disciples was U Shwe Ngong, a teacher and leader of a group of intellectuals dissatisfied with Buddhism, who were attracted to the new faith. He was a Deist skeptic to whose mind the preaching of Judson, once a college skeptic himself, was singularly challenging. After consideration, he assured Judson that he was ready to believe in God, Jesus Christ, and the atonement.
Judson, instead of welcoming him to the faith, pressed him further asking if he believed what he had read in the gospel of Matthew that Jesus the son of God died on the cross. U Shwe Ngong shook his head and said, "Ah, you have caught me now. I believe that he suffered death, but I cannot believe he suffered the shameful death on the cross."[10] Not long after, he came back to tell Judson, "I have been trusting in my own reason, not the word of God…. I now believe the crucifixion of Christ because it is contained in scripture."
The essence of Judson's preaching was a combination of conviction of the truth with the rationality of the Christian faith, a firm belief in the authority of the Bible, and a determination to make Christianity relevant to the Burmese mind without violating the integrity of Christian truth, or as he put it, "to preach the gospel, not anti-Buddhism."
By 1823, ten years after his arrival, membership of the little church had grown to 18, and Judson finished the first draft of his translation of the New Testament in Burmese.
Anglo-Burmese War (1824–1826)
[edit]
Two opposite hungers triggered the First Anglo-Burmese War of 1824: Burma's desire for more territory, and Britain's desire for more trade. Burma threatened Assam and Bengal; Britain responded by attacking and absorbing two Burmese provinces into her India holdings to broaden her trade routes to East Asia. The war was a rough interruption of the Baptists' missionary work. English-speaking Americans were too easily confused with the enemy and suspected of spying.
Judson was imprisoned for 17 months during the war between the United Kingdom and Burma, first at Ava and then at Aung Pinle. Judson and Price were violently arrested. Officers led by an official executioner burst into the Judson home, threw Judson to the ground in front of his wife, bound him with torture thongs, and dragged him off to the prison of Ava.
Twelve months later, Judson and Price, along with a small group of surviving Western prisoners, were marched overland for six more months of misery in a primitive village near Mandalay. Of the sepoy British prisoners-of-war imprisoned with them, all but one died. He spent 20 months in prison.

After her husband was released by the Burmese, Ann wrote that one good result of the war could be that terms of the treaty which ceded Burmese provinces to the British might provide opportunity to expand the witness of the mission into unreached parts of the country.
On October 24, 1826, Ann died at Amherst (now Kyaikkami), Burma. Their third child died six months later. She died while her husband was out exploring the ceded province of Tenasserim. Within a few years of the end of the war, Baptist membership doubled on an average of every eight years for the 32 years between 1834 and 1866.

The collapse of Burma's armies brought Judson out of prison, but his release was not complete freedom. In 1826, several months after the surrender, Burma pressed Judson into service as a translator for the peace negotiations.
Most of the growth of Baptist churches in Burma was in British-ruled territory, rather than the Burmese-ruled kingdom. Most of the growth came from animist tribes, rather than from the major population group, the Buddhist Burmese. The first Burmese pastor Judson ordained was Ko-Thah-a, one of the original group of converts, who refounded the church at Rangoon.
Karen apostle
[edit]
The Karen people were a hunted minority group of ancient Tibeto-Burman ancestry scattered in the forests and jungles of the Salween River and in the hills along the southeast coast. Judson was the first missionary to make contact with them in 1827, when he ransomed and freed a debt-slave from one of his early converts. The freed slave, Ko Tha Byu, was an illiterate, surly man who spoke almost no Burmese and was reputed to be not only a thief, but also a murderer who admitted killing at least 30 men, but could not remember exactly how many more.
In 1828, the former Karen bandit, "whose rough, undisciplined genius, energy and zeal for Christ" (Sarah B Judson) had caught the notice of the missionaries, was sent south with a new missionary couple, the Boardmans, into the territory of the strongly animistic, non-Buddhist Karen. Ko Tha Byu was no sooner baptized, when he set off into the jungle alone to preach to his fellow tribe members. Astonishingly, he found them prepared for his preaching. Their ancient oracle traditions, handed down for centuries, contained some startling echoes of the Old Testament that some scholars conjecture a linkage with Jewish communities (or possibly even Nestorians), before their migrations from western China into Burma perhaps as early as the 12th century.
The core of what they called their "Tradition of the Elders" was a belief in an unchangeable, eternal, all-powerful God, creator of heaven and earth, of man, and of woman formed from a rib taken from the man (Genesis). They believed in humanity's temptation by a devil, and its fall, and that some day a Great Messiah would come to its rescue. They lived in expectation of a prophecy that white foreigners would bring them a sacred parchment roll.
While the Boardmans and Ko Tha Byu were penetrating the jungles to the south, Judson shook off a paralyzing year-long siege of depression that overcame him after the death of his wife and set out alone on long canoe trips up the Salween River into the tiger-infested jungles to evangelize the northern Karen. Between trips, he worked unceasingly at his lifelong goal of translating the entire Bible into Burmese. When he finished it at last in 1834, he had been labouring on it for 24 years.[11] It was printed and published in 1835.
In April of that same year, he married Sarah Hall Boardman, widow of fellow missionary George Boardman. They had eight children, five of whom survived to adulthood. Sarah's health began failing and physicians recommended a return to America. Sarah died en route at St. Helena on September 1, 1845. He continued home, where he was greeted as a celebrity and toured the eastern seaboard raising the profile of and money for missionary activity. Because he could barely speak above a whisper, due to pulmonary illness, his public addresses were made by speaking to an assistant, who would then address the audience.[12]
On June 2, 1846, Judson married for the third time, to writer Emily Chubbuck,[3] who he had commissioned to write memoirs for Sarah Hall Boardman. They had a daughter born in 1847.
Sarah Cummings and Jason Tuma arrived in 1832. Cummings proved her mettle at once, choosing to work alone with Karen evangelists in the malaria-ridden Salween River valley north of Moulmein, but within two years she died of fever.
In 1835, a second single woman, Eleanor Macomber, after five years of mission to the Ojibway Indians in Michigan, joined the mission in Burma. Alone, with the help of Karen evangelistic assistants, she planted a church in a remote Karen village and nurtured it to the point where it could be placed under the care of an ordinary missionary. She lived there five years and died of jungle fever.
Judson developed a serious lung disease and doctors prescribed a sea voyage as a cure. On April 12, 1850, he died at age 61 on board ship in the Bay of Bengal and was buried at sea, having spent 37 years abroad with only one trip back home to America. A memorial to Judson was built on Burial Hill in Plymouth, Massachusetts.[13]
Legacy
[edit]

By the time of Judson's death, he had translated the Bible into Burmese as well as a half-completed Burmese-English dictionary.[7] Burma at the time had 100 churches, and over 8,000 believers.
By 2006, Myanmar had the third largest number of Baptists worldwide,[14] behind the United States and India. The majority of adherents are Karen, Kachin and Chin.
Judson compiled the first ever Burmese-English dictionary; missionary E. A. Steven completed the English-Burmese half. Every dictionary and grammar written in Burma in the last two centuries has been based on ones originally created by Judson.[citation needed] Judson "became a symbol of the preeminence of Bible translation for" Protestant missionaries.[15] In the 1950s, Burma's Buddhist prime minister U Nu told the Burma Christian Council "Oh no, a new translation is not necessary. Judson's captures the language and idiom of Burmese perfectly and is very clear and understandable."[16] Though the Bible has been translated numerous times into Burmese, Judson's translation remains the most popular version in Myanmar.[citation needed]
Each July, Baptist churches in Myanmar celebrate "Judson Day," commemorating his arrival as a missionary.[17] Inside the campus of Yangon University is Judson Church, named in his honor, and in 1920 Judson College, named in his honor, merged into Rangoon College, which has since been renamed Yangon University.[16] The American University named in his honor, Judson University was founded in Elgin, Illinois, in 1963, as the liberal arts Judson College was separated from the Northern Baptist Theological Seminary, which moved from Chicago to Lombard, Illinois. This American Judson College became Judson University in 2007 and now also has a campus in Rockford, Illinois.
Judson's change to the validity of believer's baptism, and subsequent need of support, led to the founding of the first national Baptist organization in the United States and subsequently to all American Baptist associations, including the Southern Baptists that were the first to break off from the national organization. Publication of his wife Ann's letters about their mission inspired many Americans to become or support Christian missionaries.[citation needed] At least 36 Baptist churches in the United States are named after Judson. In 2024 Southeastern Baptist Theological Seminary renamed its undergraduate program to Judson College.
The town of Judsonia, Arkansas is named after Judson along with Judson College in Alabama which was named after his wife Ann and a dormitory at Maranatha Baptist University carries his name.[16] Christian Union owns and operates a ministry center named after him at his undergraduate alma mater, Brown University. His seminary alma mater, Andover Theological Seminary, (now Andover Newton Theological School), gives out an annual The Judson Award.[citation needed]
Judson Harmon, a former Governor of Ohio, was named after him.[citation needed]
In World War II, the United States liberty ship SS Adoniram Judson was named in his honor.[18]
Published works
[edit]- Burmese Bible, as well as portions published before the entire text was translated
- A Burmese-English dictionary (English-Burmese portion completed posthumously, see below)
- A Burmese Grammar
- Two hymns: Our Father, God, Who art in Heaven and Come Holy Spirit, Dove Divine
See also
[edit]- John Alexander Stewart (scholar), another first compiler (with C. W. Dunn) of a Burmese-English dictionary
References
[edit]- ^ Judson, Edward (1883). The Life of Adoniram Judson. New York, A. D. F. Randolph & Company.
- ^ a b c d William H. Brackney, Historical Dictionary of the Baptists, Rowman & Littlefield, USA, 2021, p. 332
- ^ a b Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 534.
- ^ Courtney Anderson (1987) To the Golden Shore: The Life of Adoniram Judson. Judson Pr. ISBN 0817011218. p. 50
- ^ The Traveling Team website, History of Mission: Ann Judson
- ^ Maung Shwe Wa & Sowards, Burma Baptist Chronicle, 1963, Board of Publications Burma Baptist Convention Rangoon, p. 66
- ^ a b Missions Box website, Adoniram Judson (1788-1850)
- ^ Benge, Janet; Benge, Geoff. Adoniram Judson: Bound for Burma..
- ^ Moffett, Samuel Hugh. A History of Christianity in Asia, Vol. II: 1500-1900 - Volume 2..
- ^ Field Partner website, Four Lessons From the Life Of Adoniram Judson - Pt 3
- ^ Gerald H. Anderson, Biographical Dictionary of Christian Missions, Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, USA, 1999, p. 346
- ^ Barlow, Fred. "Abraham Judson, Burma's First Missionary". Burmese Bible. Retrieved June 4, 2006. (English text is at the bottom.)
- ^ "The First Baptist Missionary". FBC Plymouth. March 2014. Retrieved November 28, 2014.
- ^ Christian History Institute website, Unforgettable, article by Rosalie Hall Hunt published in #90 in 2006
- ^ Richard V. Pierard (Spring 2006). "The Man Who Gave the Bible to the Burmese". Christian History & Biography. 90: 16–21.
- ^ a b c Rosalie Hall Hunt (Spring 2006). "Unforgettable". Christian History & Biography. 90: 39–41.
- ^ Baptist Press website, Adoniram Judson’s spiritual descendants in Massachusetts, article by Tobin Perry, published December 9, 2019
- ^ U.S. Department of Transportation website, Adoniram Judson
Further reading
[edit]- Anderson, Courtney. To the golden shore: The life of Adoniram Judson (Little, Brown, 1956), The standard biography
- Brackney, William H. "The Legacy of Adoniram Judson." International Bulletin of Missionary Research 22.3 (1998): 122+ online
- Bradshaw, Robert I. "the life and Work of Adoniram Judson, Missionary to Burma." (1992). online
- Clement, Jesse (1852). Memoir of Adoniram Judson. Auburn, NY: Derby and Miller. Retrieved October 21, 2016.
- Duesing, Jason G. 2012. Adoniram Judson: A Bicentennial Appreciation of the Pioneer American Missionary. B & H Academic.
- James, Helen. "Adoniram Judson and the Creation of a Missionary Discourse in Pre-Colonial Burma." Journal of Burma Studies 7.1 (2002): 1-28. online
- Judson, Edward. The Life of Adoniram Judson (1883) online.
- Neill, Stephen. A History of Christian Missions (Penguin Books, 1986) pp 293–95
- Wayland, Francis. 1853. A memoir of the Life and Labors of the Rev. Adoniram Judson
- Torbet, Robert. 1955. Venture of Faith: The Story of the American Baptist Missionary Society
- Leonard, Bill J., editor. 1994.Dictionary of Baptists in America
- Encyclopedia of Southern Baptists, Norman W. Cox, editor
- Burmese Encyclopedia: Vol 12, p-444, printed in 1966
Primary sources
[edit]- Knowles, James D. 1829. Memoir of Mrs Ann H. Judson, 252–259
- Mason, Francis. 1843. The Karen Apostle, or, Memoir of Ko tha Byu, the First Karen convert
- H. P. Cochrane, Among the Burmans: A Record of Fifteen Years
- Judson, Emily C. 1848. Memoir of Sarah Boardman Judson, Member of the American mission to Burma. New York: Sheldon, Lamport & Blakeman.
External links
[edit]- Adoniram Judson biographies
- Life and Work of Judson Archived April 11, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- SBHLA bio of Judson
- Google E-text of an 1853 Biography Volume One
- Google E-text of an 1853 Biography Volume Two
- A memorial church to Adoniram and Ann Judson
- Online Burmese Bible
- Online Burmese Bible (Compatible with Burmese Wikipedia) — Translated from The Original Tongues by Rev. A. Judson, D.D.
- "Adoniram Judson". Find a Grave. Retrieved February 26, 2009.
- Hymn: "Come, Holy Spirit, Dove Divine" Archived March 3, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- Judson, Edward. The Life of Adoniram Judson. New York: Anson D. F. Randolph & Company, 1883
- Judson's Burmese-English dictionary, revised and enlarged by Robert C. Stevenson, Rangoon: Government Printing, Burma, 1893.
- The Judson Burmese-English dictionary, revised and enlarged by Robert C. Stevenson, revised and edited by F. H. Eveleth, Rangoon: American Baptist Mission Press, 1921.
- Adoniram and Ann Judson Archived April 16, 2021, at the Wayback Machine
- Missiology website, The Judson Centennial, 1814-1914, edited by Howard B. Grose and Fred P. Haggard (online copy)
- Missiology website, A Century of Baptist Foreign Missions; An Outline Sketch, by Sophie Bronson Titterington, published by the American Baptist Publication Society (1891) (online copy)
- 1788 births
- 1850 deaths
- 19th-century American male writers
- 19th-century American non-fiction writers
- 19th-century American translators
- 19th-century Baptist ministers from the United States
- 19th-century lexicographers
- American evangelicals
- American expatriates in India
- American expatriates in Myanmar
- American lexicographers
- American male non-fiction writers
- American prisoners of war
- American religious writers
- Andover Theological Seminary alumni
- Baptist missionaries from the United States
- Baptist missionaries in India
- Baptist missionaries in Myanmar
- Baptist writers
- Brown University alumni
- Burials at sea
- American missionary linguists
- People from Malden, Massachusetts
- People of the First Anglo-Burmese War
- People who died at sea
- Translators of the Bible into Burmese

