Hel Peninsula: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Add: date, title. Changed bare reference to CS1/2. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by BrownHairedGirl | Linked from User:BrownHairedGirl/Articles_with_bare_links | #UCB_webform_linked 180/594 |
|||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Sand bar peninsula in northern Poland}} |
{{Short description|Sand bar peninsula in northern Poland}} |
||
{{More citations needed|date=July 2018}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
| name = Hel |
| name = Hel |
||
| settlement_type = Peninsula |
| settlement_type = Peninsula |
||
| image_skyline = File:Hel peninsula landsat.jpg |
| image_skyline = File:Hel peninsula landsat.jpg |
||
| image_caption = Hel Peninsula as seen from [[Landsat]] satellite in 2000 |
| image_caption = Hel Peninsula as seen from [[Landsat]] satellite in 2000 |
||
| image_flag = |
| image_flag = |
||
| image_shield = |
| image_shield = |
||
| image_map = |
| image_map = |
||
| subdivision_type = [[Countries of the world|Country]] |
| subdivision_type = [[Countries of the world|Country]] |
||
| subdivision_name = [[Poland]] |
| subdivision_name = [[Poland]] |
||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Voivodeships of Poland|Voivodeship]] |
| subdivision_type1 = [[Voivodeships of Poland|Voivodeship]] |
||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Pomeranian Voivodeship|Pomeranian]] |
| subdivision_name1 = [[Pomeranian Voivodeship|Pomeranian]] |
||
| subdivision_type2 = [[Powiat|County]] |
| subdivision_type2 = [[Powiat|County]] |
||
| subdivision_name2 = [[Puck County|Puck]] |
| subdivision_name2 = [[Puck County|Puck]] |
||
| subdivision_type3 |
| subdivision_type3 = |
||
| subdivision_name3 |
| subdivision_name3 = |
||
| coordinates = {{coord|54|38|30|N|18|46|53|E|region:PL|display=inline,title}} |
| coordinates = {{coord|54|38|30|N|18|46|53|E|region:PL|display=inline,title}} |
||
| pushpin_map = Poland |
| pushpin_map = Poland |
||
| pushpin_label_position = right |
| pushpin_label_position = right |
||
| elevation_m = |
| elevation_m = |
||
| population_total = |
| population_total = |
||
| website = |
| website = |
||
}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Hel |
[[File:Hel Flugzeug.JPG|thumb|Hel Peninsula]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Maszoperia Hel.jpg|thumb|Wooden house from circa 1850, now a restaurant]] |
[[File:Maszoperia Hel.jpg|thumb|Wooden house from circa 1850, now a restaurant]] |
||
[[File:Kite Poland 4.JPG|thumb|[[Kitesurfing]], Hel Peninsula]] |
[[File:Kite Poland 4.JPG|thumb|[[Kitesurfing]], Hel Peninsula]] |
||
[[File:Hel fokarium.jpg|thumb|[[Pinniped|Seal]] at the Oceanography Institute]] |
|||
'''Hel Peninsula''' ({{ |
'''Hel Peninsula''' ({{IPA|pl|xɛl|-|Pl-Hel.ogg}}; {{langx|pl|Mierzeja Helska, Półwysep Helski}}; {{langx|csb|Hélskô Sztremlëzna}}; {{langx|de|Halbinsel Hela}} or ''Putziger [[Spit (landform)|Nehrung]]'') is a {{convert|35|km|mi|adj=mid|-long}} [[sand bar]] [[peninsula]] in northern Poland separating the [[Bay of Puck]] from the open [[Baltic Sea]]. It is located in [[Puck County]] of the [[Pomeranian Voivodeship]]. |
||
==Name== |
== Name == |
||
The name of the peninsula |
The name of the peninsula might come from either the [[Old Polish]] word ''hyl''/''hel'', meaning "empty or exposed place", or the [[Germanic languages|Germanic]] word ''heel'', which is derived from the form of the peninsula and the fact that the area was first settled by the [[Goths]], an [[East Germanic]] tribe.<ref>{{Cite dictionary |url=https://pl.wikisource.org/wiki/S%C5%82ownik_etymologiczny_j%C4%99zyka_polskiego/hyl |first=Aleksander |last=Brückner |dictionary=Słownik etymologiczny języka polskiego |title=hyl |publisher=Krakowska Spółka Wydawnicza |year=1927 |location=Kraków |via=Wikisource}}</ref> |
||
==Geography== |
== Geography == |
||
The width of the peninsula varies from approximately {{convert|300|m}} near [[Jurata]] |
The width of the peninsula varies from approximately {{convert|300|m}} near [[Jurata]] to {{convert|100|m}} in the most narrow part to over {{convert|3|km}} at the tip. Since the peninsula is formed entirely of [[sand]], it is frequently turned into an island by winter storms. Until the 17th century, the peninsula was a chain of islands that formed a strip of land only in the summer. |
||
A road and a railroad run along the peninsula from the mainland to the town |
A road and a railroad run along the peninsula from the mainland to the town at the furthest point, [[Hel, Poland|Hel]], a popular tourist destination. Other towns, ports, and tourist resorts are [[Jurata]], [[Jastarnia]], [[Kuźnica, Pomeranian Voivodeship|Kuźnica]], [[Chałupy]], and [[Władysławowo]]. |
||
Bus transport on the peninsula consists of only one route, the 669. The |
|||
Bus transport on peninsula consists of only one route – 666.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.pksgdynia.pl/rozklad_jazdy2/linia/666.html|title = Rozkład jazdy - PKS GDYNIA}}</ref> <ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.trojmiasto.pl/wiadomosci/Linia-666-do-Helu-wzbudza-kontrowersje-n125920.html|title = Linia 666 do Helu wzbudza kontrowersje|date = 26 July 2018}}</ref> |
|||
route was originally numbered 666, which played on the biblical [[number of the beast]] and the similarity of the name "Hel" to the English word "hell". This raised complaints from Catholic groups which found the numbering blasphemous.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.pksgdynia.pl/rozklad_jazdy2/linia/666.html |title=Rozkład jazdy |website=PKS GDYNIA}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.trojmiasto.pl/wiadomosci/Linia-666-do-Helu-wzbudza-kontrowersje-n125920.html |title=Linia 666 do Helu wzbudza kontrowersje |website=trojmiasto.pl |date=26 July 2018}}</ref> The number was changed in 2023.<ref>{{cite news |last1=O'Carroll |first1=Lisa |title=No 666 to Hel: Polish bus route drops 'devil’s number' after Christian protests |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2023/jun/14/bus-666-to-hel-poland-devils-number-transport-route-protest |access-date=15 June 2023 |work=[[The Guardian]] |date=14 June 2023}}</ref> |
|||
==Military importance== |
== Military importance == |
||
The Hel |
The Hel Peninsula was part of [[Prussia]] and then [[Germany]] from 1772 to 1919, during which time it was known by its German name {{lang|de|Hela}}. After the peninsula became part of the [[Second Polish Republic]] after [[World War I]], it acquired considerable military significance as part of the [[Polish Corridor]] and was turned into a [[Hel Fortified Region|fortified region]], with a garrison of about 3,000. In the course of the [[Battle of Hel]] in 1939, Polish forces [[dynamite]]d the peninsula at one point and turned it into an island. |
||
During the years of [[ |
During the years of [[German occupation of Poland]] (1939–1945), Hel's defenses were further expanded, and a battery of three [[40.6 cm SK C/34 gun]] was constructed, but the guns were soon moved to the [[Atlantic Wall]] in [[occupied France]]. Hel peninsula remained in German hands until the end of [[World War II]], when the defending forces surrendered on 14 May 1945, six days after Germany capitulated. |
||
After the war, when |
After the war, when the peninsula again became part of Poland, it continued to have military significance, with much of its area reserved for military use. Additional gun batteries were built in the 1940s and the 1950s. Many of the fortifications and batteries are open to tourists today, but some areas of the peninsula still belong to the [[Polish Armed Forces]]. |
||
== Gallery == |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
File:HEL%2C_AB._018.JPG|[[Hel, Poland|Hel]] |
|||
File:Jastarnia_Stefa%C5%84skiego-8.jpg|[[Jastarnia]] |
|||
File:Stacja_ku%C5%BAnica.jpg|[[Kuźnica, Pomeranian Voivodeship|Kuźnica]] |
|||
File:Cha%C5%82upy_train_station.jpg|[[Chałupy|Chalupy]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
* [[Hel Fortified Area]] |
* [[Hel Fortified Area]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Lighthouse in Hel|Hel lighthouse]] |
* [[Lighthouse in Hel|Hel lighthouse]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Vistula Spit]] |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
| Line 56: | Line 67: | ||
{{Commons category|Hel Peninsula}} |
{{Commons category|Hel Peninsula}} |
||
{{Pomerania}} |
{{Pomerania}} |
||
{{Polish coast|state=autocollapse}} |
{{Polish coast|state=autocollapse}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Peninsulas of Poland]] |
[[Category:Peninsulas of Poland]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Spits of Europe]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 07:33, 21 October 2024
Hel | |
|---|---|
Peninsula | |
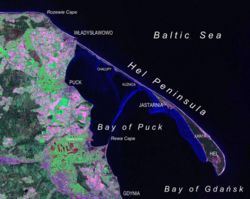 Hel Peninsula as seen from Landsat satellite in 2000 | |
| Coordinates: 54°38′30″N 18°46′53″E / 54.64167°N 18.78139°E | |
| Country | Poland |
| Voivodeship | Pomeranian |
| County | Puck |





Hel Peninsula (Polish pronunciation: [xɛl] ; Polish: Mierzeja Helska, Półwysep Helski; Kashubian: Hélskô Sztremlëzna; German: Halbinsel Hela or Putziger Nehrung) is a 35-kilometre-long (22 mi) sand bar peninsula in northern Poland separating the Bay of Puck from the open Baltic Sea. It is located in Puck County of the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Name
[edit]The name of the peninsula might come from either the Old Polish word hyl/hel, meaning "empty or exposed place", or the Germanic word heel, which is derived from the form of the peninsula and the fact that the area was first settled by the Goths, an East Germanic tribe.[1]
Geography
[edit]The width of the peninsula varies from approximately 300 metres (980 ft) near Jurata to 100 metres (330 ft) in the most narrow part to over 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) at the tip. Since the peninsula is formed entirely of sand, it is frequently turned into an island by winter storms. Until the 17th century, the peninsula was a chain of islands that formed a strip of land only in the summer.
A road and a railroad run along the peninsula from the mainland to the town at the furthest point, Hel, a popular tourist destination. Other towns, ports, and tourist resorts are Jurata, Jastarnia, Kuźnica, Chałupy, and Władysławowo.
Bus transport on the peninsula consists of only one route, the 669. The route was originally numbered 666, which played on the biblical number of the beast and the similarity of the name "Hel" to the English word "hell". This raised complaints from Catholic groups which found the numbering blasphemous.[2][3] The number was changed in 2023.[4]
Military importance
[edit]The Hel Peninsula was part of Prussia and then Germany from 1772 to 1919, during which time it was known by its German name Hela. After the peninsula became part of the Second Polish Republic after World War I, it acquired considerable military significance as part of the Polish Corridor and was turned into a fortified region, with a garrison of about 3,000. In the course of the Battle of Hel in 1939, Polish forces dynamited the peninsula at one point and turned it into an island.
During the years of German occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Hel's defenses were further expanded, and a battery of three 40.6 cm SK C/34 gun was constructed, but the guns were soon moved to the Atlantic Wall in occupied France. Hel peninsula remained in German hands until the end of World War II, when the defending forces surrendered on 14 May 1945, six days after Germany capitulated.
After the war, when the peninsula again became part of Poland, it continued to have military significance, with much of its area reserved for military use. Additional gun batteries were built in the 1940s and the 1950s. Many of the fortifications and batteries are open to tourists today, but some areas of the peninsula still belong to the Polish Armed Forces.
Gallery
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Brückner, Aleksander (1927). "hyl". Słownik etymologiczny języka polskiego. Kraków: Krakowska Spółka Wydawnicza – via Wikisource.
- ^ "Rozkład jazdy". PKS GDYNIA.
- ^ "Linia 666 do Helu wzbudza kontrowersje". trojmiasto.pl. 26 July 2018.
- ^ O'Carroll, Lisa (14 June 2023). "No 666 to Hel: Polish bus route drops 'devil's number' after Christian protests". The Guardian. Retrieved 15 June 2023.