Pella (regional unit): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Other uses|Pella (disambiguation)}} |
||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox Greece place |
||
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> |
|||
| name = Pella |
| name = Pella |
||
| |
| name_local = <small>Περιφερειακή ενότητα</small><br>Πέλλας |
||
| |
| type = regional unit |
||
| settlement_type = [[regional units of Greece|Regional unit]] |
|||
| image_skyline = 2010 Dimi Pellas numbered.svg |
| image_skyline = 2010 Dimi Pellas numbered.svg |
||
| |
| caption_skyline = Municipalities of Pella |
||
| image_caption = Municipalities of Pella |
|||
| imagesize = 150px |
|||
| image_flag = |
|||
| flag_alt = |
|||
| image_seal = |
|||
| seal_alt = |
|||
| image_shield = |
|||
| shield_alt = |
|||
| nickname = |
|||
| motto = |
|||
| image_map = Nomos Pellas.png |
| image_map = Nomos Pellas.png |
||
| map_alt = |
|||
| map_caption = Pella within Greece |
| map_caption = Pella within Greece |
||
| |
| coordinates = {{coord|40|55|N|22|05|E|display=inline,title}} |
||
| periph = [[Central Macedonia]] |
|||
| pushpin_label_position = |
|||
| pushpin_map_alt = |
|||
| pushpin_map_caption = |
|||
| latd = 40|latm = 55|lats = |latNS = N |
|||
| longd = 22 |longm = 05|longs = |longEW = E |
|||
| coor_pinpoint = |
|||
| coordinates_type = |
|||
| coordinates_display = inline,title |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type = Country |
|||
| subdivision_name = [[Greece]] |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Modern regions of Greece|Region]] |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Central Macedonia]] |
|||
| established_title = |
|||
| established_date = 2011 |
|||
| founder = |
|||
| seat_type = Capital |
|||
| seat = [[Edessa, Greece|Edessa]] |
| seat = [[Edessa, Greece|Edessa]] |
||
| |
| area = 2506 |
||
| |
| elevation = |
||
| |
| population = 126740 |
||
| |
| population_as_of = 2021 |
||
| |
| demonym = |
||
| area_footnotes = |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 2506 |
|||
| area_land_km2 = |
|||
| area_water_km2 = |
|||
| area_water_percent = |
|||
| area_note = |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| population_footnotes = |
|||
| population_total = 139680 |
|||
| population_as_of = 2011 |
|||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
|||
| population_demonym = |
|||
| population_note = |
|||
| time_zone = [[Eastern European Time|EET]] |
|||
| utc_offset = +2 |
|||
| timezone1_DST = [[EEST]] |
|||
| utc_offset1_DST = +3 |
|||
| postal_code_type = [[Postal codes in Greece|Postal codes]] |
|||
| postal_code = 58x xx |
| postal_code = 58x xx |
||
| area_code_type = [[Telephone numbers in Greece|Area codes]] |
|||
| area_code = 238x0 |
| area_code = 238x0 |
||
| |
| licence = ΕΕ |
||
| blank_info = ΕΕ |
|||
| iso_code = GR-59 |
|||
| website = {{URL|www.pella.gr}} |
| website = {{URL|www.pella.gr}} |
||
| footnotes = |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Pella''' ({{ |
'''Pella''' ({{langx|el|Περιφερειακή ενότητα Πέλλας}}) is one of the [[regional units of Greece]], in the geographic [[Geographic regions of Greece|region]] of [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]]. It is part of the [[Modern regions of Greece|Region]] of [[Central Macedonia]]. It is named after the ancient city of [[Pella]], the capital of [[ancient Macedonia]] and the birthplace of [[Alexander the Great]].<ref name="Establishment">{{cite book | title=Administrative subdivisions of countries: a comprehensive world reference, 1900 through 1998 | first=Gwillim | last=Law | publisher=McFarland | year=1999 | isbn=978-0-7864-0729-3 | page=[https://archive.org/details/administrativesu0000lawg/page/152 152] | url=https://archive.org/details/administrativesu0000lawg/page/152 }}</ref> The capital of Pella is [[Edessa, Greece|Edessa]] with a population of 19,036 inhabitants according to the census of 2021, while the largest town is [[Giannitsa]]. Other towns include [[Aridaia]], [[Skydra]], [[Arnissa]], [[Exaplatanos]] and [[Krya Vrysi, Pella|Krya Vrysi]]. |
||
==Administration== |
==Administration== |
||
According to the [[2011 Greek census|2011 census]] the population of the regional unit of Pella was 139,680.<ref name=Kallikratis/> It is subdivided into 4 municipalities. These are:<ref name=Kallikratis>{{cite web|url=http://www.et.gr/idocs-nph/search/pdfViewerForm.html?args=5C7QrtC22wGYK2xFpSwMnXdtvSoClrL8-SrPzKAEPjjtIl9LGdkF53UIxsx942CdyqxSQYNuqAGCF0IfB9HI6hq6ZkZV96FIukI0UzcPsWCK0LpLhpa7rhiWB4R5ntTnoWw7U8E1Amg.|title=ΦΕΚ A 87/2010, Kallikratis reform law text|language=el|publisher=[[Government Gazette (Greece)|Government Gazette]]}}</ref> |
|||
The regional unit Pella is subdivided into 4 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox):<ref name=Kallikratis>{{PDFlink|1=[http://www.kedke.gr/uploads2010/FEKB129211082010_kallikratis.pdf Kallikratis reform law text]}}</ref> |
|||
*[[Almopia]] (2) |
*[[Almopia]] (2) |
||
*[[Edessa, Greece|Edessa]] (1) |
*[[Edessa, Greece|Edessa]] (1) |
||
*[[Pella, Greece|Pella]] (3) |
*[[Pella, Greece|Pella]] (3) |
||
*[[ |
*[[Skydra]] (4) |
||
===Prefecture=== |
===Prefecture=== |
||
[[File:Edessa Waterfall.jpg|thumb|Edessa Waterfall]] |
|||
[[File:Statue of Alexander the Great riding Bucephalus and carrying a winged statue of Nike (square of Alexander the Great) in Pella city (6914694770).jpg|thumb|Statue of [[Alexander the Great]] in [[Pella (municipality)]].]] |
[[File:Statue of Alexander the Great riding Bucephalus and carrying a winged statue of Nike (square of Alexander the Great) in Pella city (6914694770).jpg|thumb|Statue of [[Alexander the Great]] in [[Pella (municipality)]].]] |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Πύργος του ρολογιού.jpg|thumb|Clocktower of [[Giannitsa]]]] |
||
As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit of Pella was created out of the former [[prefectures of Greece|prefecture]] Pella ({{langx|el|Νομός Πέλλας}}). The prefecture had the same territory as the present regional unit. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below.<ref name=Kallikratis/> |
|||
The region covers an area of 2.505,8 Km2 the majority of which is covered by arable land, forests and pastures. The mountains that surround the county is Mount Vora (2,524 m), Mount Vermion (2,027 m), mount Paiko (1,458 m), Mount Jenna (2,182 m) and Mount Pinovo (2,154 m .). The main plains of the prefecture is plain of Pozar in the north and the vast plain of Giannitsà in the southeastern part of the county. Of particular interest is the natural environment and ecosystems of the prefecture (the mountains, lakes Vegoritida Agra, rivers Loudias, Edessian). The county is rich in surface and groundwater resources also in the district identified archaeological sites of great value which attract large numbers of visitors. |
|||
Administratively, the Pella divided into 4 municipalities (Kallikratis). The population is according to the latest census of the Hellenic Statistical Authority (2011) to 139,680 inhabitants...<ref name=Kallikratis/> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|||
! New municipality !! Old municipalities !! Seat |
! New municipality !! Old municipalities !! Seat |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Line 112: | Line 60: | ||
| [[Megas Alexandros, Pella|Megas Alexandros]] |
| [[Megas Alexandros, Pella|Megas Alexandros]] |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| rowspan=2|[[ |
| rowspan=2|[[Skydra]]|| [[Skydra]] || rowspan=2|Skydra |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Meniida]] |
| [[Meniida]] |
||
| Line 118: | Line 66: | ||
=== Provinces === |
=== Provinces === |
||
The former prefecture of Pella was subdivided into the following [[Provinces of Greece|provinces]]:<ref name=census91>{{cite web|url= http://dlib.statistics.gr/Book/GRESYE_02_0101_00086.pdf |title=Detailed census results 1991 }} {{small|(39 MB)}} {{in lang|el|fr}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|||
! [[Provinces of Greece|Provinces]] of Pella Prefecture !! Seat (if different) |
|||
! Provinces of Pella Prefecture !! Seat (if different) |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| Province of [[Almopia]] || [[Aridaia]] |
| Province of [[Almopia]] || [[Aridaia]] |
||
| Line 131: | Line 81: | ||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
The regional unit covers an area of {{convert|2,505.8|km2|sqmi|frac=8}}, the majority of which is covered by arable land, forests and pastures. Mountainous areas surrounding Pella are the [[Voras Mountains]] (with [[Kaimaktsalan]] reaching a height of 2,524{{nbsp}}m), [[Mount Vermion]] (2,027{{nbsp}}m), [[Mount Paiko]] (1,458{{nbsp}}m), [[Mount Tzenna]] (2,182{{nbsp}}m) and [[Mount Pinovo]] (2,154{{nbsp}}m). The main plains are Pozar in the north and the vast plain of [[Giannitsa|Giannitsà]] in the southeastern part. Other natural features of the area include Lakes [[Lake Vegoritida|Vegoritida]] and Agra, and Rivers [[Loudias River|Loudias]] and Edessian. Pella's southernmost portion is flat and in ancient times, it was a gulf connected to the [[Aegean Sea]]. The elevation in the south does not exceed about {{convert|5|to|10|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} above sea level. Pella has surface and groundwater resources. There are a number of archaeological sites in the area. |
|||
The mountains lie to the north and the southwest especially the [[Vermio Mountains|Vermio]] mountains, the [[Voras]] mountains to the northwest and the [[Mount Paiko|Paiko]] mountains to the northeast. The southernmost portion is flat and in the ancient times, it was a gulf connected with the [[Aegean Sea]], the elevation does not succeed about {{convert|5|to|10|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} above sea level. Pella is bounded by the prefectures of [[Kilkis (regional unit)|Kilkis]] to the northeast, [[Thessaloniki (regional unit)|Thessaloniki]] to the east, [[Imathia]] to the south, [[Kozani (regional unit)|Kozani]] to the southwest, by Lake [[Vegoritida]] to the southwest, and by [[Florina (regional unit)|Florina]] to the west. On the north, it is bounded by the national border between Greece and the [[Republic of Macedonia]]. |
|||
Pella borders the regional units of [[Kilkis (regional unit)|Kilkis]] to the northeast, [[Thessaloniki (regional unit)|Thessaloniki]] to the east, [[Imathia]] to the south, [[Kozani (regional unit)|Kozani]] to the southwest, by Lake Vegoritida to the southwest, and by [[Florina (regional unit)|Florina]] to the west. To the north, it is bounded by the national border between Greece and [[North Macedonia]]. |
|||
==Tourism and sightseeing== |
|||
{{tone|date=September 2015}} |
|||
[[File:The big antechamber paved with white and black pebbles forming lozenges from the House of Dionysos, built in 325-300 BC, Ancient Pella (7060158217).jpg|thumb|[[Pella]] archaeological site.]] |
|||
[[File:Pojar waterfall.jpg|thumb|Pozar thermal baths]] |
|||
[[File:Kaimaktsalan 2009 SL training.jpg|thumb|Kaimaktsalan ski resort.]] |
|||
==History== |
|||
*'''Ancient [[Pella]] and [[Archaeological Museum of Pella]]''': The capital of ancient Macedonia and birthplace of [[Alexander the Great]] and King Phillip II left a lot of ancient findings and attractions in the place of ''Palace'' and the New Museum. |
|||
[[File:Pella Banner.jpg|750px|Pella Banner]] |
|||
[[File:20090711 Aridaia Loutra 1.jpg|thumb|Pozar Thermal Baths]] |
|||
[[File:Kaimaktsalan 2009 SL training.jpg|thumb|Kaimaktsalan Ski Area]] |
|||
In antiquity, the area around the modern Pella regional unit was part of the ancient Greek [[Macedon|Kingdom of Macedon]]. It later became part of the [[Roman Empire]] and later the [[Byzantine]] and the [[Ottoman Empire]]s. Following approximately 500 years of Ottoman rule, it rejoined [[Greece]] in 1913, following the [[Balkan Wars]]. |
|||
==Tourism== |
|||
*'''Loudias River''': A river 7 km from [[Giannitsa]] where there is a canoe, kayak and rowing center |
|||
*'''Ancient [[Pella]] and [[Archaeological Museum of Pella]]''': The capital of ancient Macedonia and birthplace of Alexander the Great. A number of archaeological findings are housed in the Palace and the New Museum.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.pella-museum.gr/ |title=Αρχαιολογικό Μουσείο Πέλλας | Αρχαιολογικό Μουσείο Πέλλας - Πέλλα |language=el |publisher=Pella-museum.gr |date=2022-03-31 |accessdate=2022-04-14}}</ref> |
|||
*''' |
*'''[[Loudias River]]''' |
||
*'''Waterfalls in the city of [[Edessa, Greece|Edessa]]''' <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.europeanwaterfalls.com/waterfalls/edessa-waterfalls-2/|title = Edessa waterfalls - European waterfalls}}</ref> |
|||
*'''Pozar thermal baths''': The hot springs are located in a mountainous area (altitude 360–390 m) and occupy an area of 75 |
*'''Pozar thermal baths''': The hot springs are located in a mountainous area (altitude 360–390 m) and occupy an area of {{convert|75|acre|ha|order=flip}}. Five spa gush along the warm river, which continues to flow in the basin of Almopia. |
||
*'''[[Kaimakchalan]] ski resort''': Mount Kaimakchalan or Vorras is the third largest in height mount in Greece (altitude 2,524 m). There is a ski area with 16 ski slopes. At the foot of the mountain there is the village of Agios Athanasios. |
|||
*'''[[Giannitsa]] Ottoman monuments''': At the city of Giannitsa there are a lot of buildings from the Ottoman period like the Clock Tower, Mausoleum and baths of Gazi Evrenos, House of Emin Bey, The Baths and the mausoleum of Ahmet Bey, Mosque of Sheikh Ilachi, Mosque of Iskender Bey.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.kaimaktsalan-voras.com/en/monument/giannitsa-clock-tower-12/|title=Giannitsa Clock Tower}}</ref> |
|||
*'''[[Kaimaktsalan]] ski resort''': Mount Kaimaktsalan or Vorras is the third largest in height mount in Greece (altitude 2524 mtr). There is a famous ski area with 16 ski slopes and the view from the mountain is excellent and when the weather permits one can observe the Thermaikos Gulf and [[Mount Olympus]]. At the foot of the mountain there is the picturesque village of Agios Athanasios. |
|||
*'''[[Giannitsa]] Ottoman monuments''': At the city of Giannitsa there are a lot of buildings from the Ottoman period like The Clock Tower, Mausoleum and baths of Gazi Evrenos, House of Emin Bey, The Baths and the mausoleum of Ahmet Bey, Mosque of Sheikh Ilachi, Mosque of Iskender Bey. |
|||
==History== |
|||
In antiquity, the area around the modern Pella regional unit was part of the ancient [[Macedon|Kingdom of Macedon]]. It later became part of the [[Roman Empire]] and later the [[Byzantine]] and the [[Ottoman Empire]]s. Following approximately 500 years of Ottoman rule, it joined [[Greece]] in 1913, following the [[Balkan Wars]]. |
|||
==Agriculture== |
==Agriculture== |
||
The southern part of the regional unit has |
The southern part of the regional unit has a number of [[orchard]]s. While agriculture once represented its main industry, today, manufacturing, services and other businesses dominate about 70% of its industry. |
||
==Transport== |
==Transport== |
||
| Line 164: | Line 109: | ||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[List of settlements in the Pella regional unit]] |
*[[List of settlements in the Pella regional unit]] |
||
*[[Former toponyms of places in Pella Prefecture]] |
*[[Former toponyms of places in Pella Prefecture]] |
||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist}} |
||
==External links== |
|||
{{commonscat|Pella Regional Unit}} |
|||
*[http://www.napella.gr/ Official website of the prefecture of Pella] |
|||
*[https://www.avenzamaps.com/maps/815748 Tzena - Pinovo - East Voras terrain map] by Geopsis |
|||
{{Kallikratis-Central Macedonia}} |
{{Kallikratis-Central Macedonia}} |
||
{{Prefectures of Greece}} |
{{Prefectures of Greece}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
*[http://www.napella.gr/ Official website of the prefecture of Pella] |
|||
*[http://www.gtp.gr/LocPage.asp?id=7289 Map & info of Pella Prefecture] |
|||
[[Category:Pella (regional unit)| ]] |
[[Category:Pella (regional unit)| ]] |
||
[[Category:Prefectures of Greece]] |
[[Category:Prefectures of Greece]] |
||
[[Category:Regional units of Greece]] |
|||
[[Category:1930 establishments in Greece]] |
[[Category:1930 establishments in Greece]] |
||
[[Category:Regional units of Central Macedonia]] |
[[Category:Regional units of Central Macedonia]] |
||
[[nn:Pélla]] |
[[nn:Pélla]] |
||
Latest revision as of 03:28, 23 October 2024
Pella
Περιφερειακή ενότητα Πέλλας | |
|---|---|
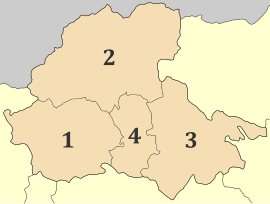 Municipalities of Pella | |
| Coordinates: 40°55′N 22°05′E / 40.917°N 22.083°E | |
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | Central Macedonia |
| Seat | Edessa |
| Area | |
• Total | 2,506 km2 (968 sq mi) |
| Population (2021)[1] | |
• Total | 126,740 |
| • Density | 51/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 58x xx |
| Area code(s) | 238x0 |
| Vehicle registration | ΕΕ |
| Website | www |
Pella (Greek: Περιφερειακή ενότητα Πέλλας) is one of the regional units of Greece, in the geographic region of Macedonia. It is part of the Region of Central Macedonia. It is named after the ancient city of Pella, the capital of ancient Macedonia and the birthplace of Alexander the Great.[2] The capital of Pella is Edessa with a population of 19,036 inhabitants according to the census of 2021, while the largest town is Giannitsa. Other towns include Aridaia, Skydra, Arnissa, Exaplatanos and Krya Vrysi.
Administration
[edit]According to the 2011 census the population of the regional unit of Pella was 139,680.[3] It is subdivided into 4 municipalities. These are:[3]
Prefecture
[edit]


As a part of the 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the regional unit of Pella was created out of the former prefecture Pella (Greek: Νομός Πέλλας). The prefecture had the same territory as the present regional unit. At the same time, the municipalities were reorganised, according to the table below.[3]
| New municipality | Old municipalities | Seat |
|---|---|---|
| Almopia | Aridaia | Aridaia |
| Exaplatanos | ||
| Edessa | Edessa | Edessa |
| Vegoritida | ||
| Pella | Pella | Giannitsa |
| Giannitsa | ||
| Krya Vrysi | ||
| Kyrros | ||
| Megas Alexandros | ||
| Skydra | Skydra | Skydra |
| Meniida |
Provinces
[edit]The former prefecture of Pella was subdivided into the following provinces:[4]
| Provinces of Pella Prefecture | Seat (if different) |
|---|---|
| Province of Almopia | Aridaia |
| Province of Edessa | |
| Province of Giannitsa |
Note: Provinces no longer hold any legal status in Greece.
Geography
[edit]The regional unit covers an area of 2,505.8 square kilometres (967+1⁄2 sq mi), the majority of which is covered by arable land, forests and pastures. Mountainous areas surrounding Pella are the Voras Mountains (with Kaimaktsalan reaching a height of 2,524 m), Mount Vermion (2,027 m), Mount Paiko (1,458 m), Mount Tzenna (2,182 m) and Mount Pinovo (2,154 m). The main plains are Pozar in the north and the vast plain of Giannitsà in the southeastern part. Other natural features of the area include Lakes Vegoritida and Agra, and Rivers Loudias and Edessian. Pella's southernmost portion is flat and in ancient times, it was a gulf connected to the Aegean Sea. The elevation in the south does not exceed about 5 to 10 m (16 to 33 ft) above sea level. Pella has surface and groundwater resources. There are a number of archaeological sites in the area.
Pella borders the regional units of Kilkis to the northeast, Thessaloniki to the east, Imathia to the south, Kozani to the southwest, by Lake Vegoritida to the southwest, and by Florina to the west. To the north, it is bounded by the national border between Greece and North Macedonia.
History
[edit]

In antiquity, the area around the modern Pella regional unit was part of the ancient Greek Kingdom of Macedon. It later became part of the Roman Empire and later the Byzantine and the Ottoman Empires. Following approximately 500 years of Ottoman rule, it rejoined Greece in 1913, following the Balkan Wars.
Tourism
[edit]- Ancient Pella and Archaeological Museum of Pella: The capital of ancient Macedonia and birthplace of Alexander the Great. A number of archaeological findings are housed in the Palace and the New Museum.[5]
- Loudias River
- Waterfalls in the city of Edessa [6]
- Pozar thermal baths: The hot springs are located in a mountainous area (altitude 360–390 m) and occupy an area of 30 hectares (75 acres). Five spa gush along the warm river, which continues to flow in the basin of Almopia.
- Kaimakchalan ski resort: Mount Kaimakchalan or Vorras is the third largest in height mount in Greece (altitude 2,524 m). There is a ski area with 16 ski slopes. At the foot of the mountain there is the village of Agios Athanasios.
- Giannitsa Ottoman monuments: At the city of Giannitsa there are a lot of buildings from the Ottoman period like the Clock Tower, Mausoleum and baths of Gazi Evrenos, House of Emin Bey, The Baths and the mausoleum of Ahmet Bey, Mosque of Sheikh Ilachi, Mosque of Iskender Bey.[7]
Agriculture
[edit]The southern part of the regional unit has a number of orchards. While agriculture once represented its main industry, today, manufacturing, services and other businesses dominate about 70% of its industry.
Transport
[edit]- GR-1 (old highway), SE
- GR-2/E90, W, SW, Cen., E, SE
- Edessa - Verroia road, S
- Thessaloniki-Giannitsa-Edessa
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Αποτελέσματα Απογραφής Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2021, Μόνιμος Πληθυσμός κατά οικισμό" [Results of the 2021 Population - Housing Census, Permanent population by settlement] (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority. 29 March 2024.
- ^ Law, Gwillim (1999). Administrative subdivisions of countries: a comprehensive world reference, 1900 through 1998. McFarland. p. 152. ISBN 978-0-7864-0729-3.
- ^ a b c "ΦΕΚ A 87/2010, Kallikratis reform law text" (in Greek). Government Gazette.
- ^ "Detailed census results 1991" (PDF). (39 MB) (in Greek and French)
- ^ "Αρχαιολογικό Μουσείο Πέλλας | Αρχαιολογικό Μουσείο Πέλλας - Πέλλα" (in Greek). Pella-museum.gr. 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-04-14.
- ^ "Edessa waterfalls - European waterfalls".
- ^ "Giannitsa Clock Tower".