Propiomazine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Cats. |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Chemical compound}} |
|||
{{Unreferenced|date=December 2009}} |
|||
{{Refimprove|date=February 2020}} |
|||
{{Drugbox |
{{Drugbox |
||
| Verifiedfields = |
| Verifiedfields = verified |
||
| verifiedrevid = 464216628 |
| verifiedrevid = 464216628 |
||
| IUPAC_name = 1-[10-(2-dimethylaminopropyl)-10''H''-phenothiazin-2-yl]propan-1-one |
| IUPAC_name = 1-[10-(2-dimethylaminopropyl)-10''H''-phenothiazin-2-yl]propan-1-one |
||
| image = Propiomazine.svg |
| image = Propiomazine.svg |
||
| width = |
| width = 225px |
||
<!--Clinical data--> |
<!--Clinical data--> |
||
| tradename = |
| tradename = Propavan, others |
||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CONS|propiomazine}} |
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|CONS|propiomazine}} |
||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> |
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> |
||
| pregnancy_US = <!-- A / B / C / D / X --> |
| pregnancy_US = <!-- A / B / C / D / X --> |
||
| legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S4 / S8 --> |
| legal_AU = <!-- Unscheduled / S2 / S4 / S8 --> |
||
| legal_BR = C1 |
|||
| legal_BR_comment = <ref>{{Cite web |author=Anvisa |author-link=Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency |date=2023-03-31 |title=RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial |trans-title=Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control|url=https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-rdc-n-784-de-31-de-marco-de-2023-474904992 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230803143925/https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-rdc-n-784-de-31-de-marco-de-2023-474904992 |archive-date=2023-08-03 |access-date=2023-08-16 |publisher=[[Diário Oficial da União]] |language=pt-BR |publication-date=2023-04-04}}</ref> |
|||
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> |
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL / P / POM / CD --> |
||
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only --> |
| legal_US = <!-- OTC / Rx-only --> |
||
| legal_status = Rx-only |
|||
| routes_of_administration = [[ |
| routes_of_administration = [[Oral administration|Oral]], [[intramuscular injection|IM]], [[intravenous therapy|IV]] |
||
<!-- Pharmacokinetic data --> |
|||
| bioavailability = [[Oral administration|Oral]]: 33%<ref name="pmid9327191" /> |
|||
| protein_bound = 81%<ref name="DrugBank">{{cite web | url=https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00777 | title=Propiomazine }}</ref> |
|||
| metabolism = |
|||
| metabolites = |
|||
| onset = |
|||
| elimination_half-life = 9 hours<ref name="pmid9327191">{{cite journal | vauthors = Dehlin O, Bengtsson C, Rubin B | title = A comparison of zopiclone and propiomazine as hypnotics in outpatients: a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group comparison of zopiclone and propiomazine in insomniacs | journal = Curr Med Res Opin | volume = 13 | issue = 10 | pages = 565–72 | date = 1997 | pmid = 9327191 | doi = 10.1185/03007999709113330 | url = }}</ref> |
|||
| duration_of_action = |
|||
| excretion = |
|||
<!--Identifiers--> |
<!--Identifiers--> |
||
| Line 34: | Line 48: | ||
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
| ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
||
| ChEBI = 8491 |
| ChEBI = 8491 |
||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite| |
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
||
| ChEMBL = 1201210 |
| ChEMBL = 1201210 |
||
| synonyms = Propionylpromethazine; CB-1678; Wy-1359; NSC-169450 |
|||
<!--Chemical data--> |
<!--Chemical data--> |
||
| C=20 | H=24 | N=2 | O=1 | S=1 |
| C=20 | H=24 | N=2 | O=1 | S=1 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| molecular_weight = 340.483 g/mol |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} |
||
| StdInChI = 1S/C20H24N2OS/c1-5-18(23)15-10-11-20-17(12-15)22(13-14(2)21(3)4)16-8-6-7-9-19(16)24-20/h6-12,14H,5,13H2,1-4H3 |
| StdInChI = 1S/C20H24N2OS/c1-5-18(23)15-10-11-20-17(12-15)22(13-14(2)21(3)4)16-8-6-7-9-19(16)24-20/h6-12,14H,5,13H2,1-4H3 |
||
| Line 47: | Line 61: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Propiomazine |
'''Propiomazine''', sold under the brand name '''Propavan''' among others, is an [[antihistamine]] which is used to treat [[insomnia]] and to produce [[sedation]] and relieve [[anxiety]] before or during [[surgery]] or other procedures and in combination with [[analgesic]]s as well as during [[childbirth|labor]].<ref name="MortonHall2012">{{cite book | vauthors= Morton IK, Hall JM | date = 6 December 2012 | title = Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms | publisher = Springer Science & Business Media | pages = 234– | isbn = 9789401144391 | oclc = 1243535030 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=tsjrCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA234}}</ref>{{Additional citation needed|date=July 2022}} Propiomazine is a [[phenothiazine]],<ref name="MortonHall2012" /> but is not used therapeutically as a [[neuroleptic]] because it does not block [[dopamine receptors]] well.{{Citation needed|date=July 2022}} |
||
== |
==Medical uses== |
||
Propiomazine has been used in the treatment of [[insomnia]]. |
|||
Propiomazine is an antagonist at types 1, 2, and 4 dopamine receptors, serotonin (5-HT) receptor types 2A and 2C, muscarinic receptors 1 through 5, alpha(1)-receptors, and histamine H1-receptors. Propiomazine's antipsychotic effect is due to antagonism at dopamine and serotonin type 2 receptors, with greater activity at serotonin 5-HT2 receptors than at dopamine type-2 receptors. This may explain the lack of extrapyramidal effects. Propiomazine does not appear to block dopamine within the tubero-infundibular tract, explaining the lower incidence of hyperprolactinemia than with typical antipsychotic agents or risperidone. |
|||
==Side effects== |
==Side effects== |
||
Rare, serious side effects include convulsions (seizures); difficult or unusually fast breathing; fast or irregular heartbeat or pulse; fever (high); high or low blood pressure; loss of bladder control; muscle stiffness (severe); unusual increase in sweating; unusually pale skin; and unusual tiredness or weakness. |
Drowsiness is a usual side effect. Rare, serious side effects include convulsions (seizures); difficult or unusually fast breathing; fast or irregular heartbeat or pulse; fever (high); high or low blood pressure; loss of bladder control; muscle stiffness (severe); unusual increase in sweating; unusually pale skin; and unusual tiredness or weakness.{{Citation needed|date=July 2022}} |
||
==Pharmacology== |
|||
Drowsiness is a usual side effect. |
|||
===Pharmacodynamics=== |
|||
==See also== |
|||
Propiomazine is an [[receptor antagonist|antagonist]] of the [[dopamine]] [[D1 receptor|D<sub>1</sub>]], [[D2 receptor|D<sub>2</sub>]], and [[D4 receptor|D<sub>4</sub> receptor]]s, the [[serotonin]] [[5-HT2A receptor|5-HT<sub>2A</sub>]] and [[5-HT2C receptor|5-HT<sub>2C</sub> receptor]]s, the [[muscarinic acetylcholine receptor]]s [[muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1|M<sub>1</sub>]], [[muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2|M<sub>2</sub>]], [[muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3|M<sub>3</sub>]], [[muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4|M<sub>4</sub>]], and [[muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M5|M<sub>5</sub> receptor]]s, [[alpha-1 adrenergic receptor|α<sub>1</sub>-adrenergic receptor]], and [[histamine]] [[H1 receptor|H<sub>1</sub> receptor]].{{Citation needed|date=July 2022}} |
|||
* [[Promethazine]] |
|||
The [[antipsychotic]] effect of propiomazine is thought to be due to antagonism of the dopamine D<sub>2</sub> receptor and serotonin 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> receptor,<ref>{{cite web |title=NCI Thesaurus |url=https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&ns=NCI_Thesaurus&code=C66486 |website=ncit.nci.nih.gov |access-date=29 February 2020}}</ref> with greater activity at the 5-HT<sub>2A</sub> receptor than at the D<sub>2</sub> receptor. This may explain the lack of [[extrapyramidal effects]] with propiomazine. Propiomazine does not appear to block dopamine within the [[tuberoinfundibular pathway]], which may explain its lower incidence of [[hyperprolactinemia]] than with [[typical antipsychotic]]s or [[risperidone]].{{Additional citations needed|date=July 2022}} |
|||
==Chemistry== |
|||
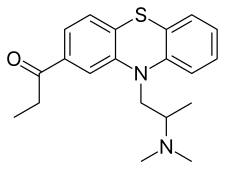
Propiomazine, also known as 10-(2-dimethylaminopropyl)-2-propionylphenothiazine or as propionylpromethazine, is a [[phenothiazine]] [[chemical derivative|derivative]]<ref name="MortonHall2012" /> and is [[structural analog|structurally related]] to [[promethazine]]. The compound is provided medically as the [[hydrochloride]] and [[maleate]] [[salt (chemistry)|salt]]s.<ref name="SwissPharmaceuticalSociety2000" /><ref name="MortonHall2012" /><ref name="Negwer2001" /> |
|||
==Society and culture== |
|||
===Brand names=== |
|||
Propiomazine has been sold under the brand names Dorevan, Dorévane, Indorm, Largon, Phenoctyl, Propavan, Propial, and Serentin.<ref name="Negwer2001">{{cite book | vauthors = Negwer M | date = 2001 | title = Organic-chemical Drugs and Their Synonyms: An International Survey, Volume 3 | edition = 8 | publisher = Wiley-VCH | page = 1946 | isbn = 978-3-527-30247-5 | oclc = 50441207 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=zmpqAAAAMAAJ | quote = Propiomazine**, Propionylpromethazine ... 9600-02 (7787-02) R Maleate (1:1) S 1678 C.B., Dorevan, Dorévane, Indorm, Phenoctyl, Propavan, Propial, Serentin, Wy-1359 U Sedative (pre-anesthetic), hypnotic ...}}</ref><ref name="SwissPharmaceuticalSociety2000">{{cite book | author = Swiss Pharmaceutical Society | date = 2000 | title = Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory | publisher = Taylor & Francis | pages = 887– | isbn = 978-3-88763-075-1 | url = https://books.google.com/books?id=5GpcTQD_L2oC&pg=PA887}}</ref> |
|||
===Availability=== |
|||
In 2000, propiomazine continued to be marketed only in [[Sweden]].<ref name="SwissPharmaceuticalSociety2000" /> |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{Reflist |
{{Reflist}} |
||
{{Hypnotics}} |
{{Hypnotics}} |
||
{{Antipsychotics}} |
{{Antipsychotics}} |
||
{{Navboxes |
|||
| title = [[Pharmacodynamics]] |
|||
| titlestyle = background:#ccccff |
|||
| list1 = |
|||
{{Adrenergic receptor modulators}} |
|||
{{Dopamine receptor modulators}} |
|||
{{Histamine receptor modulators}} |
{{Histamine receptor modulators}} |
||
{{Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulators}} |
{{Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor modulators}} |
||
{{Serotonin receptor modulators}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Tricyclics}} |
{{Tricyclics}} |
||
| Line 72: | Line 107: | ||
[[Category:Hypnotics]] |
[[Category:Hypnotics]] |
||
[[Category:Ketones]] |
[[Category:Ketones]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:M1 receptor antagonists]] |
||
[[Category:M2 receptor antagonists]] |
|||
[[Category:M3 receptor antagonists]] |
|||
[[Category:M4 receptor antagonists]] |
|||
[[Category:M5 receptor antagonists]] |
|||
[[Category:Phenothiazines]] |
[[Category:Phenothiazines]] |
||
[[Category:Sedatives]] |
[[Category:Sedatives]] |
||
{{sedative-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 05:57, 26 October 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2020) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Propavan, others |
| Other names | Propionylpromethazine; CB-1678; Wy-1359; NSC-169450 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IM, IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 33%[2] |
| Protein binding | 81%[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 9 hours[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.043 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H24N2OS |
| Molar mass | 340.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Propiomazine, sold under the brand name Propavan among others, is an antihistamine which is used to treat insomnia and to produce sedation and relieve anxiety before or during surgery or other procedures and in combination with analgesics as well as during labor.[4][additional citation(s) needed] Propiomazine is a phenothiazine,[4] but is not used therapeutically as a neuroleptic because it does not block dopamine receptors well.[citation needed]
Medical uses
[edit]Propiomazine has been used in the treatment of insomnia.
Side effects
[edit]Drowsiness is a usual side effect. Rare, serious side effects include convulsions (seizures); difficult or unusually fast breathing; fast or irregular heartbeat or pulse; fever (high); high or low blood pressure; loss of bladder control; muscle stiffness (severe); unusual increase in sweating; unusually pale skin; and unusual tiredness or weakness.[citation needed]
Pharmacology
[edit]Pharmacodynamics
[edit]Propiomazine is an antagonist of the dopamine D1, D2, and D4 receptors, the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors M1, M2, M3, M4, and M5 receptors, α1-adrenergic receptor, and histamine H1 receptor.[citation needed]
The antipsychotic effect of propiomazine is thought to be due to antagonism of the dopamine D2 receptor and serotonin 5-HT2A receptor,[5] with greater activity at the 5-HT2A receptor than at the D2 receptor. This may explain the lack of extrapyramidal effects with propiomazine. Propiomazine does not appear to block dopamine within the tuberoinfundibular pathway, which may explain its lower incidence of hyperprolactinemia than with typical antipsychotics or risperidone.[additional citation(s) needed]
Chemistry
[edit]Propiomazine, also known as 10-(2-dimethylaminopropyl)-2-propionylphenothiazine or as propionylpromethazine, is a phenothiazine derivative[4] and is structurally related to promethazine. The compound is provided medically as the hydrochloride and maleate salts.[6][4][7]
Society and culture
[edit]Brand names
[edit]Propiomazine has been sold under the brand names Dorevan, Dorévane, Indorm, Largon, Phenoctyl, Propavan, Propial, and Serentin.[7][6]
Availability
[edit]In 2000, propiomazine continued to be marketed only in Sweden.[6]
References
[edit]- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ a b Dehlin O, Bengtsson C, Rubin B (1997). "A comparison of zopiclone and propiomazine as hypnotics in outpatients: a multicentre, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group comparison of zopiclone and propiomazine in insomniacs". Curr Med Res Opin. 13 (10): 565–72. doi:10.1185/03007999709113330. PMID 9327191.
- ^ "Propiomazine".
- ^ a b c d Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 234–. ISBN 9789401144391. OCLC 1243535030.
- ^ "NCI Thesaurus". ncit.nci.nih.gov. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- ^ a b c Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. pp. 887–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b Negwer M (2001). Organic-chemical Drugs and Their Synonyms: An International Survey, Volume 3 (8 ed.). Wiley-VCH. p. 1946. ISBN 978-3-527-30247-5. OCLC 50441207.
Propiomazine**, Propionylpromethazine ... 9600-02 (7787-02) R Maleate (1:1) S 1678 C.B., Dorevan, Dorévane, Indorm, Phenoctyl, Propavan, Propial, Serentin, Wy-1359 U Sedative (pre-anesthetic), hypnotic ...
