JAITS: Difference between revisions
| (8 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| formation = {{start date and age|1977|11|04|df=y}} |
| formation = {{start date and age|1977|11|04|df=y}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Japanese Association of Independent Television Stations''' ('''JAITS'''; {{ |
The '''Japanese Association of Independent Television Stations''' ('''JAITS'''; {{Langx|ja|全国独立放送協議会|Zenkoku Dokuritsu Hōsō Kyōgi-kai|National Independent Broadcasting Forum}}) is a group of [[Japan]]'s reception fee-free [[commercial broadcasting|commercial]] [[terrestrial television]] stations which are not members of [[Japanese media#TV networks|the major national television networks]]. The association was established on 4 November 1977.<ref>{{Cite book|url=http://worldcat.org/oclc/673870022|title=NHK年鑑 1978年版|publisher=NHK (Japan Broadcasting Corporation)|year=1978|language=ja|trans-title=NHK Yearbook 1978 Edition|oclc=673870022}}</ref>{{Rp|page=30}} |
||
Its members sell to, buy from, and co-produce programmes with other members. While a few of them, namely [[Tokyo MX]], [[Television Kanagawa|TVK]] and [[Sun Television|Sun TV]] and sell more than the others, it does not mean the former control the others in programming. Meanwhile, some JAITS members (GBS, MTV, BBC, TVN, WTV) broadcast a lot of TV Tokyo's programs. It forms a loose [[broadcast network]] without exclusivity. They form permanent and ''ad hoc'' subgroups for production and sales of advertising opportunity.<ref>[http://www.mietv.com/showq/net6.html Tokyo-Osaka-Nagoya Intermetropolitan Network] ({{ |
Its members sell to, buy from, and co-produce programmes with other members. While a few of them, namely [[Tokyo MX]], [[Television Kanagawa|TVK]] and [[Sun Television|Sun TV]] and sell more than the others, it does not mean the former control the others in programming. Meanwhile, some JAITS members (GBS, MTV, BBC, TVN, WTV) broadcast a lot of TV Tokyo's programs.{{cn|date=July 2023}} It forms a loose [[broadcast network]] without exclusivity. They form permanent and ''ad hoc'' subgroups for production and sales of advertising opportunity.<ref>[http://www.mietv.com/showq/net6.html Tokyo-Osaka-Nagoya Intermetropolitan Network] ({{Langx|ja|東・名・阪ネット6|Tō-Mei-Han Netto 6}}) {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070630091818/http://www.mietv.com/showq/net6.html |date=2007-06-30 }}</ref> |
||
==Name== |
==Name== |
||
The English name of the group is provisional. The Japanese documents for the association refer to the acronym JAITS but the fully spelled English name has not been disclosed yet. |
The English name of the group is provisional. The Japanese documents for the association refer to the acronym JAITS but the fully spelled English name has not been disclosed yet. |
||
In Japanese, the group was previously known as {{Transliteration|ja|hepburn|Zenkoku Dokuritsu Yū-eichi-efu Hōsō Kyōgi-kai}} ({{ |
In Japanese, the group was previously known as {{Transliteration|ja|hepburn|Zenkoku Dokuritsu Yū-eichi-efu Hōsō Kyōgi-kai}} ({{Langx|ja|全国独立UHF放送協議会||National Independent UHF Broadcasting Forum}}), bearing the term [[ultra high frequency|UHF]] as all of the member stations broadcast on the UHF band in analogue, in contrast to major networks that primarily broadcast on the [[very high frequency|VHF]] band in analogue. All the Japanese terrestrial television stations switched to UHF digital when all analogue television transmissions (both VHF and UHF) were shut down between 24 July 2011 and 31 March 2012. |
||
==List of members== |
==List of members== |
||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
| [[Gifu Prefecture|Gifu]] |
| [[Gifu Prefecture|Gifu]] |
||
| [[Chūbu region|Chūbu]] |
| [[Chūbu region|Chūbu]] |
||
! [[Gifu Broadcasting System|Gifu Hōsō]] |
! [[Gifu Broadcasting System|Gifu Hōsō / Gifu Chan]] |
||
| GBS |
| GBS |
||
| JOZF-DTV |
| JOZF-DTV |
||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
In the [[Independent station (North America)|strict (North American) definition]] of "not affiliated with any networks", the only independent terrestrial television station in Japan would be [[The Open University of Japan]], which produces almost all its programs in-house. In addition, most of the JAITS independent stations have investments from the [[Chunichi Shimbun|Chunichi Shimbun Co.]] |
In the [[Independent station (North America)|strict (North American) definition]] of "not affiliated with any networks", the only independent terrestrial television station in Japan would be [[The Open University of Japan]], which produces almost all its programs in-house. In addition, most of the JAITS independent stations have investments from the [[Chunichi Shimbun|Chunichi Shimbun Co.]] |
||
The JAITS and the Japanese public take "Independent UHF Station" ({{ |
The JAITS and the Japanese public take "Independent UHF Station" ({{Langx|ja|独立U(HF)局|dokuritsu Yū(-eichi-efu) kyoku}}) for not being members of large networks, in which the Tokyo's stations almost control other members' programming. Those networks are also affiliated with large national newspapers. On the other hands, the JAITS stations are often affiliated with [[prefecture#Japanese sense of prefecture|prefectural]] or metropolitan newspapers and prefectural governments, whose degree of influence may vary. |
||
MTV, GBS, BBC, TVN, and WTV broadcast certain programmes from [[TV Tokyo]]. |
MTV, GBS, BBC, TVN, and WTV broadcast certain programmes from [[TV Tokyo]].{{cn|date=July 2023}} |
||
Here is the description of characters of the independent commercial terrestrial television stations in Japan. Currently all such stations are members of the JAITS. |
Here is the description of characters of the independent commercial terrestrial television stations in Japan. Currently all such stations are members of the JAITS. |
||
===Market=== |
===Market=== |
||
Their areas of coverage are located in [[Kantō region|Kantō]], [[Chūkyō Metropolitan Area|Chūkyō]] and [[Kansai region|Kansai]] regions which are the most urbanised in Japan. Their reachable population is large. If the population was too small they could not have number of viewers and sponsorship to sustain the station. However their coverage are within major network stations' official coverage, except [[TX Network|TXN]] network members [[ |
Their areas of coverage are located in [[Kantō region|Kantō]], [[Chūkyō Metropolitan Area|Chūkyō]] and [[Kansai region|Kansai]] regions which are the most urbanised in Japan. Their reachable population is large. If the population was too small they could not have number of viewers and sponsorship to sustain the station. However their coverage are within major network stations' official coverage, except [[TX Network|TXN]] network members [[TV Osaka]]'s, [[TV Aichi]]'s and [[TV Setouchi]]'s which are adjacent to. Multi-channel [[cable television]] may cover significant parts of the areas. Externally sourced popular contents are often too expensive to buy therefore they are very difficult to beat major networks in viewing rates. |
||
===Programming=== |
===Programming=== |
||
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
* [[Independent station |
* [[Independent station]] |
||
* [[TV Azteca]] |
|||
* [[Grupo Imagen]] |
|||
* [[Grupo Multimedios]] |
|||
* [[Independent station]] ''(other parts of the world)'' |
|||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
Latest revision as of 15:04, 28 October 2024
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Japanese. (December 2009) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
全国独立放送協議会 | |
| Abbreviation | JAITS |
|---|---|
| Formation | 4 November 1977 |
| Location | |
Official language | Japanese |
The Japanese Association of Independent Television Stations (JAITS; Japanese: 全国独立放送協議会, romanized: Zenkoku Dokuritsu Hōsō Kyōgi-kai, lit. 'National Independent Broadcasting Forum') is a group of Japan's reception fee-free commercial terrestrial television stations which are not members of the major national television networks. The association was established on 4 November 1977.[1]: 30
Its members sell to, buy from, and co-produce programmes with other members. While a few of them, namely Tokyo MX, TVK and Sun TV and sell more than the others, it does not mean the former control the others in programming. Meanwhile, some JAITS members (GBS, MTV, BBC, TVN, WTV) broadcast a lot of TV Tokyo's programs.[citation needed] It forms a loose broadcast network without exclusivity. They form permanent and ad hoc subgroups for production and sales of advertising opportunity.[2]
Name
[edit]The English name of the group is provisional. The Japanese documents for the association refer to the acronym JAITS but the fully spelled English name has not been disclosed yet.
In Japanese, the group was previously known as Zenkoku Dokuritsu Yū-eichi-efu Hōsō Kyōgi-kai (Japanese: 全国独立UHF放送協議会, lit. 'National Independent UHF Broadcasting Forum'), bearing the term UHF as all of the member stations broadcast on the UHF band in analogue, in contrast to major networks that primarily broadcast on the VHF band in analogue. All the Japanese terrestrial television stations switched to UHF digital when all analogue television transmissions (both VHF and UHF) were shut down between 24 July 2011 and 31 March 2012.
List of members
[edit]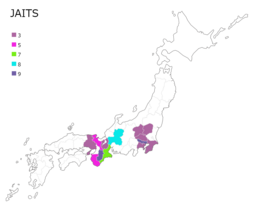
Stations are listed in Japanese order of prefectures which is mirrored in ISO 3166-2:JP.
| Broadcasting area(s) | Station | LCN | Start date of broadcast |
Note(s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefecture | Region | On air branding | Abbr. | Call sign | |||
| Tochigi | Kantō | Tochigi TV | GYT | JOGY-DTV | 3 | 1 April 1999 | |
| Gunma | Kantō | Gunma TV / GunTele | GTV | JOML-DTV | 3 | 16 April 1971 | |
| Saitama | Kantō | TV Saitama / Teletama | TVS | JOUS-DTV | 3 | 1 April 1979 | |
| Chiba | Kantō | Chiba TV | CTC | JOCL-DTV | 3 | 1 May 1971 | |
| Tokyo | Kantō | Tokyo MX | MX | JOMX-DTV | 9 | 1 November 1995 | |
| Kanagawa | Kantō | TV Kanagawa | tvk | JOKM-DTV | 3 | 1 April 1972 | |
| Gifu | Chūbu | Gifu Hōsō / Gifu Chan | GBS | JOZF-DTV | 8 | 12 August 1968 | |
| Mie | Kansai | Mie TV | MTV | JOMH-DTV | 7 | 1 December 1969 | |
| Shiga | Kansai | Biwako Hōsō | BBC | JOBL-DTV | 3 | 1 April 1972 | |
| Kyoto | Kansai | KBS Kyoto | KBS | JOBR-DTV | 5 | 1 April 1969 | |
| Hyōgo | Kansai | Sun TV | SUN | JOUH-DTV | 3 | 1 May 1969 | |
| Nara | Kansai | Nara TV | TVN | JONM-DTV | 9 | 1 April 1973 | |
| Wakayama | Kansai | TV Wakayama | WTV | JOOM-DTV | 5 | 1 April 1974 | |
Characteristics of the independent stations
[edit]Degree of independence
[edit]In the strict (North American) definition of "not affiliated with any networks", the only independent terrestrial television station in Japan would be The Open University of Japan, which produces almost all its programs in-house. In addition, most of the JAITS independent stations have investments from the Chunichi Shimbun Co.
The JAITS and the Japanese public take "Independent UHF Station" (Japanese: 独立U(HF)局, romanized: dokuritsu Yū(-eichi-efu) kyoku) for not being members of large networks, in which the Tokyo's stations almost control other members' programming. Those networks are also affiliated with large national newspapers. On the other hands, the JAITS stations are often affiliated with prefectural or metropolitan newspapers and prefectural governments, whose degree of influence may vary.
MTV, GBS, BBC, TVN, and WTV broadcast certain programmes from TV Tokyo.[citation needed]
Here is the description of characters of the independent commercial terrestrial television stations in Japan. Currently all such stations are members of the JAITS.
Market
[edit]Their areas of coverage are located in Kantō, Chūkyō and Kansai regions which are the most urbanised in Japan. Their reachable population is large. If the population was too small they could not have number of viewers and sponsorship to sustain the station. However their coverage are within major network stations' official coverage, except TXN network members TV Osaka's, TV Aichi's and TV Setouchi's which are adjacent to. Multi-channel cable television may cover significant parts of the areas. Externally sourced popular contents are often too expensive to buy therefore they are very difficult to beat major networks in viewing rates.
Programming
[edit]Compared with the major networks, the independent stations have a relatively smaller audience, but have a more flexible schedule due to their decentralized nature.
Short-running anime productions (as little as one episode) are often broadcast by the independent stations, a concept which has been referred to as "UHF anime". They also sometimes run shopping programming, along with brokered programming such as infomercials and televangelism. In 2000, All Japan Pro Wrestling moved to JAITS affiliates after it ended its run on Nippon TV.
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ NHK年鑑 1978年版 [NHK Yearbook 1978 Edition] (in Japanese). NHK (Japan Broadcasting Corporation). 1978. OCLC 673870022.
- ^ Tokyo-Osaka-Nagoya Intermetropolitan Network (Japanese: 東・名・阪ネット6, romanized: Tō-Mei-Han Netto 6) Archived 2007-06-30 at the Wayback Machine
