Steiner ellipse: Difference between revisions
Fgnievinski (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Circumellipse of a triangle whose center is the triangle's centroid}} |
|||
[[File:Steiner ellipse.svg|300px|thumb|right|The Steiner ellipse of an [[isosceles triangle]]. The three line segments inside the triangle are the triangle's [[median (geometry)|medians]], each [[bisection|bisecting]] a side. The medians coincide at the triangle's [[centroid]], which is also the center of the Steiner ellipse.]] |
[[File:Steiner ellipse.svg|300px|thumb|right|The Steiner ellipse of an [[isosceles triangle]]. The three line segments inside the triangle are the triangle's [[median (geometry)|medians]], each [[bisection|bisecting]] a side. The medians coincide at the triangle's [[centroid]], which is also the center of the Steiner ellipse.]] |
||
{{distinguish|Steiner conic}} |
{{distinguish|Steiner conic}} |
||
In [[geometry]], the '''Steiner ellipse''' of a [[triangle]] |
In [[geometry]], the '''Steiner ellipse''' of a [[triangle]] is the unique [[circumellipse]] (an [[ellipse]] that touches the triangle at its [[vertex (geometry)|vertices]]) whose center is the triangle's [[centroid]].<ref name="Weisstein">{{Cite web |last=Weisstein |first=Eric W. |title=Steiner Circumellipse |url=https://mathworld.wolfram.com/ |access-date=2024-07-22 |website=mathworld.wolfram.com |language=en}}</ref> It is also called the '''Steiner circumellipse''', to distinguish it from the [[Steiner inellipse]]. Named after [[Jakob Steiner]], it is an example of a [[circumconic]]. By comparison the [[circumcircle]] of a triangle is another circumconic that touches the triangle at its vertices, but is not centered at the triangle's centroid unless the triangle is [[equilateral triangle|equilateral]]. |
||
The area of the Steiner ellipse equals the area of the triangle times <math>\frac{4 \pi}{3\sqrt{3}},</math> and hence is 4 times the area of the Steiner inellipse. The Steiner ellipse has the least area of any ellipse circumscribed about the triangle.<ref name=Weisstein/> |
The area of the Steiner ellipse equals the area of the triangle times <math>\frac{4 \pi}{3\sqrt{3}},</math> and hence is 4 times the area of the Steiner inellipse. The Steiner ellipse has the least area of any ellipse circumscribed about the triangle.<ref name=Weisstein/> |
||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
== Properties == |
== Properties == |
||
[[File:Steiner-ellipse-12.svg|thumb|Steiner ellipse of an equilateral (left) and |
[[File:Steiner-ellipse-12.svg|thumb|Steiner ellipse of an equilateral (left) and isosceles triangle ]] |
||
* A Steiner ellipse is the only ellipse, whose center is the centroid <math>S</math> of a triangle <math>ABC</math> and contains the points <math>A,B,C</math>. The area of the Steiner ellipse is <math>\tfrac{4 \pi}{3\sqrt{3}}</math>-fold of the triangle's area. |
* A Steiner ellipse is the only ellipse, whose center is the centroid <math>S</math> of a triangle <math>ABC</math> and contains the points <math>A,B,C</math>. The area of the Steiner ellipse is <math>\tfrac{4 \pi}{3\sqrt{3}}</math>-fold of the triangle's area. |
||
;Proof: |
;Proof: |
||
'''A)''' For an |
'''A)''' For an equilateral triangle the Steiner ellipse is the [[circumcircle]], which is the only ellipse, that fulfills the preconditions. The desired ellipse has to contain the triangle reflected at the center of the ellipse. This is true for the circumcircle. A [[Conic section|conic]] is uniquely determined by 5 points. Hence the circumcircle is the only Steiner ellipse. |
||
'''B)''' Because an arbitrary triangle is the [[Affine map|affine image]] of an |
'''B)''' Because an arbitrary triangle is the [[Affine map|affine image]] of an equilateral triangle, an ellipse is the [[ellipse#Ellipse as an affine image of the unit circle x²+y²=1|affine image of the unit circle]] and the centroid of a triangle is mapped onto the centroid of the image triangle, the property (a unique circumellipse with the centroid as center) is true for any triangle. |
||
The area of the circumcircle of an |
The area of the circumcircle of an equilateral triangle is <math>\tfrac{4 \pi}{3\sqrt{3}}</math>-fold of the area of the triangle. An affine map preserves the ratio of areas. Hence the statement on the ratio is true for any triangle and its Steiner ellipse. |
||
== Determination of conjugate points == |
== Determination of conjugate points == |
||
| Line 30: | Line 31: | ||
2) determination of point <math>D</math> which is conjugate to <math>C</math> (steps 1–5)<br /> |
2) determination of point <math>D</math> which is conjugate to <math>C</math> (steps 1–5)<br /> |
||
3) drawing the ellipse with conjugate half diameters <math>SC, SD</math>]] |
3) drawing the ellipse with conjugate half diameters <math>SC, SD</math>]] |
||
Let be <math>ABC</math> a triangle and its centroid <math>S</math>. The shear mapping with axis <math>d</math> through <math>S</math> and parallel to <math> |
Let be <math>ABC</math> a triangle and its centroid <math>S</math>. The shear mapping with axis <math>d</math> through <math>S</math> and parallel to <math>AB</math> transforms the triangle onto the isosceles triangle <math>A'B'C'</math> (see diagram). Point <math>C'</math> is a vertex of the Steiner ellipse of triangle <math>A'B'C'</math>. A second vertex <math>D</math> of this ellipse lies on <math>d</math>, because <math>d</math> is perpendicular to <math>SC'</math> (symmetry reasons). This vertex can be determined from the data (ellipse with center <math>S</math> through <math>C'</math> and <math>B'</math>, <math>|A'B'|=c</math>) by ''calculation''. It turns out that |
||
:<math>|SD|=\frac{c}{\sqrt{3}}\ .</math> |
:<math>|SD|=\frac{c}{\sqrt{3}}\ .</math> |
||
Or by ''drawing'': Using [[ellipse#Parametric representation|de la Hire's method]] (see center diagram) vertex <math>D</math> of the Steiner ellipse of the isosceles triangle <math>A'B'C'</math> is determined.<br /> |
Or by ''drawing'': Using [[ellipse#Parametric representation|de la Hire's method]] (see center diagram) vertex <math>D</math> of the Steiner ellipse of the isosceles triangle <math>A'B'C'</math> is determined.<br /> |
||
| Line 38: | Line 39: | ||
With help of this pair of conjugate semi diameters the ellipse can be drawn, by hand or by computer. |
With help of this pair of conjugate semi diameters the ellipse can be drawn, by hand or by computer. |
||
== Parametric |
== Parametric representation and equation == |
||
[[File:Steiner-elli-3.svg|thumb|Steiner ellipse of a triangle including the axes and verices (purple)]] |
[[File:Steiner-elli-3.svg|thumb|Steiner ellipse of a triangle including the axes and verices (purple)]] |
||
Given: Triangle <math>\ A=(a_1,a_2),\; B=(b_1,b_2), \; C=(c_1,c_2)</math><br> |
Given: Triangle <math>\ A=(a_1,a_2),\; B=(b_1,b_2), \; C=(c_1,c_2)</math><br> |
||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
*<math>\ \vec x =\vec p(t)=\overrightarrow{OS}\; +\; \overrightarrow{SC}\; \cos t \;+\; \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\overrightarrow{AB}\; \sin t \; , \quad 0\le t <2\pi \; . </math> |
*<math>\ \vec x =\vec p(t)=\overrightarrow{OS}\; +\; \overrightarrow{SC}\; \cos t \;+\; \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\overrightarrow{AB}\; \sin t \; , \quad 0\le t <2\pi \; . </math> |
||
* The ''' |
* The '''four vertices''' of the ellipse are <math>\quad \vec p(t_0),\; \vec p(t_0\pm\frac{\pi}{2}),\; \vec p(t_0+\pi),\ </math> where <math>t_0</math> comes from |
||
:<math>\cot (2t_0)= \ |
:: <math>\cot (2t_0)= \frac{\vec f_1^{\, 2}-\vec f_2^{\, 2}}{2\vec f_1 \cdot \vec f_2}\quad</math> with <math>\quad \vec f_1=\vec{SC},\quad \vec f_2=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\vec{AB} \quad </math> (see [[ellipse#Ellipse as an affine image of the unit circle x²+y²=1|ellipse]]). |
||
The roles of the points for determining the parametric representation can be changed. |
The roles of the points for determining the parametric representation can be changed. |
||
| Line 61: | Line 62: | ||
'''Equation:''' |
'''Equation:''' |
||
If the origin is the centroid of the triangle (center of the Steiner ellipse) the equation corresponding to the parametric |
If the origin is the centroid of the triangle (center of the Steiner ellipse) the equation corresponding to the parametric representation <math display="inline">\vec x=\vec f_1 \cos t + \vec f_2 \sin t</math> is |
||
<math>\vec x=\vec f_1 \cos t + \vec f_2 \sin t</math> is |
|||
*<math>\ (xf_{2y} - yf_{2x})^2 + (yf_{1x} - xf_{1y})^2 - (f_{1x}f_{2y} - f_{1y}f_{2x})^2 =0 \ ,</math> |
*<math>\ (xf_{2y} - yf_{2x})^2 + (yf_{1x} - xf_{1y})^2 - (f_{1x}f_{2y} - f_{1y}f_{2x})^2 =0 \ ,</math> |
||
with <math>\ \vec f_i=(f_{ix},f_{iy})^T \ </math>.<ref>[http://www.mathematik.tu-darmstadt.de/~ehartmann/cdg-skript-1998.pdf CDKG: Computerunterstützte Darstellende und Konstruktive Geometrie (TU Darmstadt)] (PDF; 3,4 MB), p. 65.</ref> |
with <math>\ \vec f_i=(f_{ix},f_{iy})^T \ </math>.<ref>[http://www.mathematik.tu-darmstadt.de/~ehartmann/cdg-skript-1998.pdf CDKG: Computerunterstützte Darstellende und Konstruktive Geometrie (TU Darmstadt)] (PDF; 3,4 MB), p. 65.</ref> |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
Let be <math>a,b,\; a>b</math> the semi axes of the Steiner ellipse. From [[ellipse#Theorem of Apollonios on conjugate diameters|Apollonios theorem]] on properties of conjugate semi diameters of ellipses one gets: |
Let be <math>a,b,\; a>b</math> the semi axes of the Steiner ellipse. From [[ellipse#Theorem of Apollonios on conjugate diameters|Apollonios theorem]] on properties of conjugate semi diameters of ellipses one gets: |
||
: <math> a^2+b^2=\vec{SC}^2+\vec{SD}^2 \ , \quad a\cdot b=|\det(\vec{SC},\vec{SD})| \ .</math> |
: <math> a^2+b^2=\vec{SC}^2+\vec{SD}^2 \ , \quad a\cdot b= \left|\det(\vec{SC},\vec{SD})\right| \ .</math> |
||
Denoting the right hand sides of the equations by <math>M</math> and <math>N</math> respectively and transforming the non linear system (respecting <math>a>b>0</math>) leads to: |
Denoting the right hand sides of the equations by <math>M</math> and <math>N</math> respectively and transforming the non linear system (respecting <math>a>b>0</math>) leads to: |
||
:<math>a^2+b^2=M ,\ ab=N \quad \rightarrow \quad a^2+2ab+b^2=M+2N ,\ a^2-2ab+b^2=M-2N </math> |
:<math>a^2+b^2=M ,\ ab=N \quad \rightarrow \quad a^2+2ab+b^2=M+2N ,\ a^2-2ab+b^2=M-2N </math> |
||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
with <math>\qquad M= \vec{SC}^2+\frac{1}{3}\vec{AB}^2\ , \quad N= \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} |\det(\vec{SC},\vec{AB})|\qquad </math>. |
with <math>\qquad M= \vec{SC}^2+\frac{1}{3}\vec{AB}^2\ , \quad N= \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} |\det(\vec{SC},\vec{AB})|\qquad </math>. |
||
The '''linear eccentricity''' of the |
The '''linear eccentricity''' of the Steiner ellipse is |
||
* <math>c=\sqrt{a^2-b^2}=\cdots=\sqrt{\sqrt{M^2-4N^2}}\ .</math> |
* <math>c=\sqrt{a^2-b^2}=\cdots=\sqrt{\sqrt{M^2-4N^2}}\ .</math> |
||
and the '''area''' |
and the '''area''' |
||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
== Alternative calculation of the semi axes and linear eccentricity == |
== Alternative calculation of the semi axes and linear eccentricity == |
||
The semi-major and semi-minor axes have lengths<ref name=Weisstein/> |
The semi-major and semi-minor axes (of a triangle with sides of length a, b, c) have lengths<ref name=Weisstein/> |
||
:<math>\frac{1}{3}\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2 \pm 2Z},</math> |
:<math>\frac{1}{3}\sqrt{a^2+b^2+c^2 \pm 2Z},</math> |
||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
:<math>Z=\sqrt{a^4+b^4+c^4-a^2b^2-b^2c^2-c^2a^2}.</math> |
:<math>Z=\sqrt{a^4+b^4+c^4-a^2b^2-b^2c^2-c^2a^2}.</math> |
||
The foci are called the '''Bickart points''' of the triangle. |
The foci are called the '''[https://mathworld.wolfram.com/BickartPoints.html Bickart points]''' of the triangle. |
||
==See also== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Curves defined for a triangle]] |
|||
[[Category:Conic sections]] |
[[Category:Conic sections]] |
||
[[Category:Affine geometry]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 16:07, 28 October 2024

In geometry, the Steiner ellipse of a triangle is the unique circumellipse (an ellipse that touches the triangle at its vertices) whose center is the triangle's centroid.[1] It is also called the Steiner circumellipse, to distinguish it from the Steiner inellipse. Named after Jakob Steiner, it is an example of a circumconic. By comparison the circumcircle of a triangle is another circumconic that touches the triangle at its vertices, but is not centered at the triangle's centroid unless the triangle is equilateral.
The area of the Steiner ellipse equals the area of the triangle times and hence is 4 times the area of the Steiner inellipse. The Steiner ellipse has the least area of any ellipse circumscribed about the triangle.[1]
The Steiner ellipse is the scaled Steiner inellipse (factor 2, center is the centroid). Hence both ellipses are similar (have the same eccentricity).
Properties
[edit]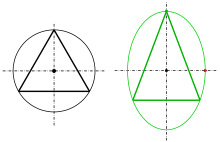
- A Steiner ellipse is the only ellipse, whose center is the centroid of a triangle and contains the points . The area of the Steiner ellipse is -fold of the triangle's area.
- Proof
A) For an equilateral triangle the Steiner ellipse is the circumcircle, which is the only ellipse, that fulfills the preconditions. The desired ellipse has to contain the triangle reflected at the center of the ellipse. This is true for the circumcircle. A conic is uniquely determined by 5 points. Hence the circumcircle is the only Steiner ellipse.
B) Because an arbitrary triangle is the affine image of an equilateral triangle, an ellipse is the affine image of the unit circle and the centroid of a triangle is mapped onto the centroid of the image triangle, the property (a unique circumellipse with the centroid as center) is true for any triangle.
The area of the circumcircle of an equilateral triangle is -fold of the area of the triangle. An affine map preserves the ratio of areas. Hence the statement on the ratio is true for any triangle and its Steiner ellipse.
Determination of conjugate points
[edit]An ellipse can be drawn (by computer or by hand), if besides the center at least two conjugate points on conjugate diameters are known. In this case
- either one determines by Rytz's construction the vertices of the ellipse and draws the ellipse with a suitable ellipse compass
- or uses an parametric representation for drawing the ellipse.
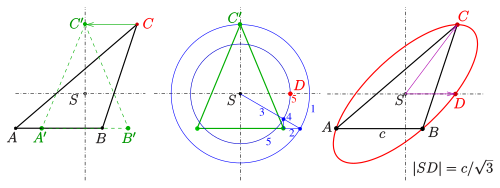
1) transformation of the triangle onto an isosceles triangle
2) determination of point which is conjugate to (steps 1–5)
3) drawing the ellipse with conjugate half diameters
Let be a triangle and its centroid . The shear mapping with axis through and parallel to transforms the triangle onto the isosceles triangle (see diagram). Point is a vertex of the Steiner ellipse of triangle . A second vertex of this ellipse lies on , because is perpendicular to (symmetry reasons). This vertex can be determined from the data (ellipse with center through and , ) by calculation. It turns out that
Or by drawing: Using de la Hire's method (see center diagram) vertex of the Steiner ellipse of the isosceles triangle is determined.
The inverse shear mapping maps back to and point is fixed, because it is a point on the shear axis. Hence semi diameter is conjugate to .
With help of this pair of conjugate semi diameters the ellipse can be drawn, by hand or by computer.
Parametric representation and equation
[edit]
Given: Triangle
Wanted: Parametric representation and equation of its Steiner ellipse
The centroid of the triangle is
Parametric representation:
From the investigation of the previous section one gets the following parametric representation of the Steiner ellipse:
- The four vertices of the ellipse are where comes from
- with (see ellipse).
The roles of the points for determining the parametric representation can be changed.
Example (see diagram): .

Equation:
If the origin is the centroid of the triangle (center of the Steiner ellipse) the equation corresponding to the parametric representation is
with .[2]
Example: The centroid of triangle is the origin. From the vectors one gets the equation of the Steiner ellipse:
Determination of the semi-axes and linear eccentricity
[edit]If the vertices are already known (see above), the semi axes can be determined. If one is interested in the axes and eccentricity only, the following method is more appropriate:
Let be the semi axes of the Steiner ellipse. From Apollonios theorem on properties of conjugate semi diameters of ellipses one gets:
Denoting the right hand sides of the equations by and respectively and transforming the non linear system (respecting ) leads to:
Solving for and one gets the semi axes:
with .
The linear eccentricity of the Steiner ellipse is
and the area
One should not confuse in this section with other meanings in this article !
Trilinear equation
[edit]The equation of the Steiner circumellipse in trilinear coordinates is[1]
for side lengths a, b, c.
Alternative calculation of the semi axes and linear eccentricity
[edit]The semi-major and semi-minor axes (of a triangle with sides of length a, b, c) have lengths[1]
and focal length
where
The foci are called the Bickart points of the triangle.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Weisstein, Eric W. "Steiner Circumellipse". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2024-07-22.
- ^ CDKG: Computerunterstützte Darstellende und Konstruktive Geometrie (TU Darmstadt) (PDF; 3,4 MB), p. 65.
- Georg Glaeser, Hellmuth Stachel, Boris Odehnal: The Universe of Conics, Springer 2016, ISBN 978-3-662-45449-7, p.383


















































