Bié Province: Difference between revisions
m + short description |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ |
{{Short description|Province of Angola}} |
||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> |
<!-- See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields and descriptions --> |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
| elevation_m = |
| elevation_m = |
||
| elevation_ft = |
| elevation_ft = |
||
| population_footnotes = <ref name |
| population_footnotes = <ref name="Censo2014">{{cite web |url=https://www.ine.gov.ao/images/Censo_2014/Bie_Final_DID_21.11.16_APJM_29.11.2016.pdf |title=Resultados Definitivos Recenseamento Geral da População e Habitação – 2014 Província do Bié |access-date=3 May 2020 |website=Instituto Nacional de Estatística, República de Angola |df=dmy-all}} {{dead link|date=February 2022 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes}}</ref> |
||
| population_total = 1455255 |
| population_total = 1455255 |
||
| population_as_of = 2014 census |
| population_as_of = 2014 census |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Bié''' is a [[Provinces of Angola|province]] of [[Angola]] located on the [[Bié Plateau]] in central part of country.<ref name="d"/> Its capital is [[Kuito]], which was called Silva Porto until independence from Portugal in 1975. The province has an area of {{convert|70,314|km2|mi2}} and a population of 1,455,255 in 2014.<ref name |
'''Bié''' is a [[Provinces of Angola|province]] of [[Angola]] located on the [[Bié Plateau]] in central part of country.<ref name="d"/> Its capital is [[Kuito]], which was called Silva Porto until independence from Portugal in 1975. The province has an area of {{convert|70,314|km2|mi2}} and a population of 1,455,255 in 2014.<ref name="Censo2014" /> The current governor of Bié is [[José Amaro Tati]]. |
||
==Geography== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Climate== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==History== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Bié province is perhaps best known as the place where the family of Angolan political leader [[Jonas Savimbi]] came from. Savimbi, although born in [[Moxico Province]] near Bié, was ethnically Bieno, i.e. of a subgroup of the [[Ovimbundu]]. He led the [[UNITA]] movement first in the anti-colonial war against the Portuguese, and then in the [[Civil War In Angola|Civil War]] against the ruling [[MPLA]] before he was killed in combat in 2002. Savimbi gained global notoriety as a [[United States]] ally during the [[Cold War]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Bié is one of the regions that was heavily affected by the Civil War. Agriculture came to a halt in several areas, and part of the rural population fled to the cities. The province capital Kuito was in part destroyed by bombing, as were roads and other infrastructures. Since 2002, reconstruction efforts have been important, but as of early 2011 much remained to be done. |
||
==Municipalities== |
==Municipalities== |
||
The province of Bié contains nine |
The province of Bié contains nine [[municipalities of Angola|municipalities]] ({{langx|pt|municípios}}): |
||
* [[Andulo]] |
* [[Andulo]] |
||
| Line 110: | Line 127: | ||
==Communes== |
==Communes== |
||
[[File:Cidade do kuito.jpg|300px|thumb|Kuito, Bié Province]] |
|||
The province of Bié contains the following [[communes of Angola|communes]] ( |
The province of Bié contains the following [[communes of Angola|communes]] ({{langx|pt|comunas}}); sorted by their respective municipalities: |
||
* |
* Andulo Municipality – [[Andulo]], [[Calucinga]], [[Cassumbe]], [[Chivaúlo]] |
||
* |
* Camacupa Municipality – [[Camacupa]], [[Cuanza, Angola|Cuanza]], [[Ringoma]], [[Santo António da Muinha]], [[Umpulo]] |
||
* |
* Catabola Municipality – [[Caivera|Caiuera]] (Caivera), [[Catabola]] [[Chipeta, Angola|Chipeta]], [[Chiuca]], [[Sande, Angola|Sande]] |
||
* |
* Chinguar Municipality – [[Kangote|Cangote]] (Kangote), [[Chinguar]], [[Kutato|Cutato]] (Kutato) |
||
* |
* Chitembo Municipality – [[Cachingues]], [[Chitembo]], [[Malengue]], [[Mumbué]], [[Matumbo, Angola|Mutumbo]] (Matumbo), [[Soma Cuanza]] |
||
* |
* Cuemba Municipality – [[Cuemba]], [[Luando]], [[Munhango]], [[Sachinemuna]] |
||
* |
* Kuito Municipality – [[Cambândua]], [[Chicala]], [[Cuíto]] (Kuito), [[Kunje|Cunje]] (Kunje), [[Trumba]] |
||
* |
* Cunhinga Municipality – [[Belo Horizonte, Angola|Belo Horizonte]], [[Cunhinga]] |
||
* |
* N'Harea Municipality – [[Calei]] (Caiei), [[Dando, Angola|Dando]], [[Gamba, Angola|Gamba]], [[Lúbia]], [[N'Harea]] (Nharea) |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Overview== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Bié province is perhaps best known as the place where the family of Angolan political leader [[Jonas Savimbi]] came from. Savimbi, although born in [[Moxico Province]] near Bié, was ethnically Bieno, i.e. of a subgroup of the [[Ovimbundu]]. He led the [[UNITA]] movement first in the anti-colonial war against the Portuguese, and then in the [[Civil War In Angola|Civil War]] against the ruling [[MPLA]] before he was killed in combat in 2002. Savimbi gained global notoriety as a [[United States]] ally during the [[Cold War]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Bié is one of the regions that was heavily affected by the Civil War. Agriculture came to a halt in several areas, and part of the rural population fled to the cities. The province capital Kuito was in part destroyed by bombing, as were roads and other infrastructures. Since 2002, reconstruction efforts have been important, but as of early 2011 much remained to be done. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | <ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.angop.ao/angola/pt_pt/noticias/politica/2018/8/37/Pereira-Alfredo-torna-governador-Bie,bb593e80-94f3-4b1a-8503-cdd1c5a91924.html |title=Pereira Alfredo torna-se no 10º governador do Bié |publisher=ANGOP Angolan News Agency |date=12 Sep 2018 | |
||
{| class="wikitable sortable |
{| class="wikitable sortable |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! Name !! Years in office |
! Name !! Years in office |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Amílcar Saraiva de Figueiredo |
| Amílcar Saraiva de Figueiredo|| data-sort-value="02"|1976–1977 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Fernando Faustino Muteka]] |
| [[Fernando Faustino Muteka]]|| data-sort-value="03"|1977–1979 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| João Baptista Jamba aka ''Jamba Ya Mina'' |
| João Baptista Jamba aka ''Jamba Ya Mina''|| data-sort-value="04"|1979–1982 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| João Marques Monocapui Bassovava |
| João Marques Monocapui Bassovava|| data-sort-value="05"|1982–1986 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| [[Marcolino Moco|Marcolino José Carlos Moco]] |
| [[Marcolino Moco|Marcolino José Carlos Moco]]|| data-sort-value="02"|1986–1987 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Luís Paulino dos Santos |
| Luís Paulino dos Santos|| data-sort-value="16"|1987–2002 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| José Amaro Tati || data-sort-value="07"| |
| José Amaro Tati || data-sort-value="07"|2002–2008 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Cândida Celeste da Silva || data-sort-value="02"| |
| Cândida Celeste da Silva || data-sort-value="02"|2008–2009 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Álvaro de Boavida Neto || data-sort-value="09"| |
| Álvaro de Boavida Neto || data-sort-value="09"|2009–2017 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Pereira Alfredo || data-sort-value="02"| |
| Pereira Alfredo || data-sort-value="02"|2018– |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| ⚫ | <ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.angop.ao/angola/pt_pt/noticias/politica/2018/8/37/Pereira-Alfredo-torna-governador-Bie,bb593e80-94f3-4b1a-8503-cdd1c5a91924.html |title=Pereira Alfredo torna-se no 10º governador do Bié |publisher=ANGOP Angolan News Agency |date=12 Sep 2018 |access-date=3 Mar 2019 |language=pt}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{ |
{{Reflist|2|refs= |
||
<ref name="d">{{cite book | last = Broadhead | first = Susan | title = Historical dictionary of Angola | publisher = Scarecrow Press | location = Metuchen, N.J | year = 1992 | isbn = 9780810825321 | page=47}}</ref> |
<ref name="d">{{cite book | last = Broadhead | first = Susan | title = Historical dictionary of Angola | publisher = Scarecrow Press | location = Metuchen, N.J | year = 1992 | isbn = 9780810825321 | page=47}}</ref> |
||
| Line 173: | Line 178: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://www.bie.gov.ao/ Official website of province governor] |
* [http://www.bie.gov.ao/ Official website of province governor] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141202194542/http://www.bie.gov.ao/ |date=2014-12-02 }} |
||
* [https://archive. |
* [https://archive.today/20121215202053/http://www.mat.gv.ao/portalmat/default.aspx?s=43 Information on this province at the Angolan ministry for territorial administration] |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20120831200402/http://www.info-angola.ao/index.php?option=com_content&view=section&layout=blog&id=10&Itemid=1198 Information on this province at ''Info Angola''] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20120831200402/http://www.info-angola.ao/index.php?option=com_content&view=section&layout=blog&id=10&Itemid=1198 Information on this province at ''Info Angola''] |
||
* [http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/angola/ao_appen.html US government statistics from 1988] |
* [http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/angola/ao_appen.html US government statistics from 1988] |
||
| Line 180: | Line 185: | ||
{{Provinces of Angola}} |
{{Provinces of Angola}} |
||
{{Municipalities of Angola}} |
|||
{{Bié Province}} |
{{Bié Province}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{ |
{{Coord|12|31|S|17|34|E|source:cawiki_type:adm1st_region:AO_scale:6000000|display=title}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bie Province}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Bie Province}} |
||
Latest revision as of 22:52, 1 November 2024
Bié | |
|---|---|
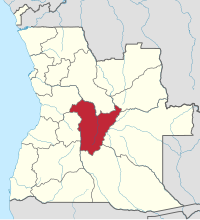 Bie, province of Angola | |
| Country | Angola |
| Capital | Kuito |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Pereira Alfredo |
| • Vice-Governor for the Political, Economic and Social Sector | Carlos Ulombe Esperança da Silva |
| • Vice-Governor for Technical Services and Infrastructures | José Fernando Tchatuvela |
| Area | |
• Total | 70,314 km2 (27,148 sq mi) |
| Population (2014 census)[1] | |
• Total | 1,455,255 |
| • Density | 21/km2 (54/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166 code | AO-BIE |
| HDI (2018) | 0.491[2] low · 17th |
| Website | www |
Bié is a province of Angola located on the Bié Plateau in central part of country.[3] Its capital is Kuito, which was called Silva Porto until independence from Portugal in 1975. The province has an area of 70,314 square kilometres (27,148 sq mi) and a population of 1,455,255 in 2014.[1] The current governor of Bié is José Amaro Tati.
Geography
[edit]Bié has boundaries with the province of Malanje, to the northeast with the province of Lunda Sul, to Moxico, to the south with Cuando Cubango and to the west with the provinces of Huila, Huambo and Cuanza Sul.
Climate
[edit]The climate of Bié is cool and abundant rainfall makes it possible to farm maize, sugar cane, rice, coffee and peanuts. Its ground is among the most fertile in Angola[citation needed].
History
[edit]The province was once an important commercial link between the Portuguese traders at the port of Benguela on the Atlantic Ocean and the Ovimbundu in the interior. The capital and other cities in the province remain important commercial centers in Angola.[3]
Origins of Jonas Savimbi
[edit]Bié province is perhaps best known as the place where the family of Angolan political leader Jonas Savimbi came from. Savimbi, although born in Moxico Province near Bié, was ethnically Bieno, i.e. of a subgroup of the Ovimbundu. He led the UNITA movement first in the anti-colonial war against the Portuguese, and then in the Civil War against the ruling MPLA before he was killed in combat in 2002. Savimbi gained global notoriety as a United States ally during the Cold War.
Civil War
[edit]Bié is one of the regions that was heavily affected by the Civil War. Agriculture came to a halt in several areas, and part of the rural population fled to the cities. The province capital Kuito was in part destroyed by bombing, as were roads and other infrastructures. Since 2002, reconstruction efforts have been important, but as of early 2011 much remained to be done.
Municipalities
[edit]The province of Bié contains nine municipalities (Portuguese: municípios):
Communes
[edit]
The province of Bié contains the following communes (Portuguese: comunas); sorted by their respective municipalities:
- Andulo Municipality – Andulo, Calucinga, Cassumbe, Chivaúlo
- Camacupa Municipality – Camacupa, Cuanza, Ringoma, Santo António da Muinha, Umpulo
- Catabola Municipality – Caiuera (Caivera), Catabola Chipeta, Chiuca, Sande
- Chinguar Municipality – Cangote (Kangote), Chinguar, Cutato (Kutato)
- Chitembo Municipality – Cachingues, Chitembo, Malengue, Mumbué, Mutumbo (Matumbo), Soma Cuanza
- Cuemba Municipality – Cuemba, Luando, Munhango, Sachinemuna
- Kuito Municipality – Cambândua, Chicala, Cuíto (Kuito), Cunje (Kunje), Trumba
- Cunhinga Municipality – Belo Horizonte, Cunhinga
- N'Harea Municipality – Calei (Caiei), Dando, Gamba, Lúbia, N'Harea (Nharea)
List of governors of Bié
[edit]| Name | Years in office |
|---|---|
| Amílcar Saraiva de Figueiredo | 1976–1977 |
| Fernando Faustino Muteka | 1977–1979 |
| João Baptista Jamba aka Jamba Ya Mina | 1979–1982 |
| João Marques Monocapui Bassovava | 1982–1986 |
| Marcolino José Carlos Moco | 1986–1987 |
| Luís Paulino dos Santos | 1987–2002 |
| José Amaro Tati | 2002–2008 |
| Cândida Celeste da Silva | 2008–2009 |
| Álvaro de Boavida Neto | 2009–2017 |
| Pereira Alfredo | 2018– |
Up to 1991, the official name was Provincial Commissioner.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Resultados Definitivos Recenseamento Geral da População e Habitação – 2014 Província do Bié" (PDF). Instituto Nacional de Estatística, República de Angola. Retrieved 3 May 2020. [permanent dead link]
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2020-02-27.
- ^ a b Broadhead, Susan (1992). Historical dictionary of Angola. Metuchen, N.J: Scarecrow Press. p. 47. ISBN 9780810825321.
- ^ "Pereira Alfredo torna-se no 10º governador do Bié" (in Portuguese). ANGOP Angolan News Agency. 12 Sep 2018. Retrieved 3 Mar 2019.
