Ćuprija: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Undid revision 1239555552 by 77.243.31.54 (talk) |
||
| (264 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox settlement |
|||
'''Ćuprija''' ([[Serbian language|Serbian]]: Ћуприја) is a city in [[Serbia and Montenegro]] at 43.93° North, 21.38° East. In [[2003]] its population was 20,000. |
|||
| native_name = {{native name|sr-Cyrl|Ћуприја|italics=off}} |
|||
| native_name_lang = sr |
|||
| official_name = Ćuprija |
|||
| other_name = |
|||
| settlement_type = [[List of cities in Serbia|Town]] and [[Municipalities and cities of Serbia|municipality]] |
|||
| image_shield = Cuprija-grb.png |
|||
| image_flag = |
|||
| image_skyline = Ћуприја главна улица.JPG |
|||
| image_caption = Main street, 2010 |
|||
| image_map = Municipalities of Serbia Ćuprija.png |
|||
| map_caption = Location of the municipality of Ćuprija within Serbia |
|||
| mapsize = |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|43|56|N|21|22|E|region:RS|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| subdivision_type = [[List of sovereign states|Country]] |
|||
| subdivision_name = {{flag|Serbia}} |
|||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Subdivisions of Serbia|Region]] |
|||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Šumadija and Western Serbia]] |
|||
| subdivision_type2 = [[Districts of Serbia|District]] |
|||
| subdivision_name2 = [[Pomoravlje District|Pomoravlje]] |
|||
| parts_type = Settlements |
|||
| parts_style = para |
|||
| p1 = 16 |
|||
| leader_title = Mayor |
|||
| leader_name = Jelena Đulinac ([[Serbian Progressive Party|SNS]]) |
|||
| area_blank1_title = Municipality |
|||
| area_blank1_km2 = 287 |
|||
| area_footnotes = <ref>{{Serbian municipalities 2006}}</ref> |
|||
| elevation_m = 124 |
|||
| population_footnotes = <ref>{{cite web|title=Census 2022: Total population, by municipalities and cities|url=https://popis2022.stat.gov.rs/media/31319/0_ukupan-broj-stanovnika-naselja.xlsx|website=popis2022.stat.gov.rs}}</ref> |
|||
| population_as_of = 2022 census |
|||
| population_blank1_title = Town |
|||
| population_blank1 = 16522 |
|||
| population_blank2_title = Municipality |
|||
| population_blank2 = 25325 |
|||
| timezone = [[Central European Time|CET]] |
|||
| utc_offset = +1 |
|||
| timezone_DST = [[Central European Summer Time|CEST]] |
|||
| utc_offset_DST = +2 |
|||
| postal_code_type = [[Postal codes in Serbia|Postal code]] |
|||
| postal_code = 35230<br />35231 |
|||
| area_code_type = [[Telephone numbers in Serbia|Area code]] |
|||
| area_code = +381(0)35 |
|||
| blank_name = [[Vehicle registration plates of Serbia|Car plates]] |
|||
| blank_info = ĆU |
|||
| website = {{url|www.cuprija.rs}} |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Ćuprija''' ([[Serbian Cyrillic]]: Ћуприја, {{IPA|sh|tɕǔprija|pron}}) is a town and municipality located in the [[Pomoravlje District]] of central Serbia. The population of the town is 16,522, while the municipality has 25,325 inhabitants (2022 census). |
|||
The city was founded as a military outpost on the road from [[Constantinople]] to [[Rome]] at a crossing of the river now known as [[Velika Morava]]. The city was first known as Ravanela, then by the Romans as Horeum Margi. When Serbs first moved into the area, it became known as Ravno ("flat"), since it is in a flat river valley. It became known as Ćuprija ([[Turkish language|Turkish]] "bridge") when it came under the control of the [[Ottoman Empire]]. |
|||
== History == |
|||
The town of Cuprija is localy known as "Cuprikovac" or "Cuprija je selo". |
|||
The Romans founded the town as a fort '''Horreum Margi''' (Horreum: ''Granary'', Margi: ''[[Great Morava|Morava]]'') on the road from [[Constantinople]] to [[Rome]], where it crosses the river now known as [[Velika Morava]]. It served as a Roman military base, had a <!-- arms<ref>{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=swAg9A3KCzUC&pg=PA268 | title=History of the Later Roman Empire: From the Death of Theodosius I.. | publisher=BiblioBazaar | last=Bury | first=John Bagnell | year=2009 | page=268 | isbn=978-1-113-20104-1}}</ref> -->shield factory<ref>{{cite book | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IiLtO4ZvTdEC | title=A Social Economic and Administrative Survey | publisher=Johns Hopkins University Press | last=Jones | first=Arnold Hugh Martin | series=The Later Roman Empire, 284-602 | year=1986 | volume=1 | isbn=978-0-8018-3353-3}}</ref> and gained the status of ''municipium'' before AD 224. In 505, the Romans were defeated by Goths and Huns under [[Mundo (Hun)|Mundo]], a descendant of [[Attila the Hun]].<ref>{{cite book|last=Jaques|first=Tony|title=Dictionary of Battles and Sieges: F-O|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Dh6jydKXikoC|year=2007|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=978-0-313-33538-9}}by Tony Jaques</ref> |
|||
Under Slavic rule, it became known as Ravno (literal translation to English would be "flat"), since it is in a flat river valley. Some local names (of the villages '''Paljane''' and '''Isakovo''', of the river '''Mirosava''') recall the major clash in autumn 1191 between the Serbs (under [[Stefan Nemanja]]) and the Byzantines (under Emperor [[Isaac II Angelos]]). |
|||
Notable People from this Town: |
|||
In the 15th century, Ćuprija became part of [[Ottoman Empire]]. After conquering this settlement, the Turks built a bridge or "''köprü''" in [[Turkish language|Turkish]] – hence the name of the town. Shortly after the [[First Serbian Uprising]] began, in 1805 one of the first and most important battles was won by Ivankovac, near Ćuprija. Serbian uprisers under the leadership of dukes Milenko Stojković, Petar Dobrnjac, and Stevan Sinđelić defeated a Turkish army which led to further spreading of the Uprising through all of Belgrade Pashaluk. Four years after that, in 1809, Ćuprija Elementary school was founded. |
|||
'''Dragana (Popadic) Bajevic''' |
|||
She immigrated to the United States when she was 29 years old. She currently lives in the Eastern Coast of the US at a city named Passaic, NJ. She is married to Branko Bajevic and have a well prominent associate named Ricky who loves to use profane language. Her success surpasses her in her career as a operating room assistant. She is the first one from the town Cuprija to take on this hard profession helping to save many lives everyday. |
|||
During the [[Second Serbian Uprising]], Serbian [[prince]] [[Miloš Obrenović]] made an oral agreement in Ćuprija which enabled [[Serbs]] in [[Belgrade Pashaluk]] to collect their own taxes, to participate in proceedings against Serbs and to establish a National Office composed of Serbian princes. After 1834, the town started to grow economically and eventually merged with the nearby villages of Mućava, Mrčajevci, and Žirovnica. In the Ottoman era, Ćuprija was the town of Smederevo with the highest concentration of Albanians. Contemporary Serb author [[Joakim Vujić]] recorded more "Turkish [[Arnauts]] than Serbs" in 1826 in the town. After the war, Obrenović began a campaign to buy out all Muslim Albanian households in the town.<ref name="Ceribasic201784">{{harvnb|Ceribašić-Begovac|2017|p=84}}</ref> In 1853, "Dobričevo" farm was founded. This led to the establishment of the Agricultural school in 1899. In 1911, a Sugar factory called "ŠELK 911" was founded. |
|||
During the 19th century, Ćuprija was the center of [[Nahiyah]]. After 1890, it was the seat of Morvaski okrug (Morava County). |
|||
Tha famous goalkeeper Mune is from Cuprija. |
|||
From 1929 to 1941, Ćuprija was part of the [[Morava Banovina]] of the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]]. |
|||
{{Serbia-geo-stub}} |
|||
In World War II, a special Ćuprija-Paraćin partisan troop was formed in order to fight against the German [[Wehrmacht]]. On September 26, 1941, 35 members of this troop were shot by German occupiers. The Second World War finally ended in Ćuprija on October 13, 1944, when town was liberated from the [[Wehrmacht]] during the so-called [[Belgrade Operation]]. |
|||
[[Category:Cities in Serbia and Montenegro]] |
|||
[[Category:Cities, towns and villages in Serbia]] |
|||
During the [[NATO bombing of Yugoslavia]] in 1999, the town's center was heavily damaged. Some buildings still remain in ruins. As of 2011 census, the municipality had 30,645 inhabitants. |
|||
[[Category:Šumadija]] |
|||
== Settlements == |
|||
Aside from the town of Ćuprija, the municipality includes the following 16 settlements: |
|||
{{div col}} |
|||
* [[Batinac]] |
|||
* [[Bigrenica]] |
|||
* [[Dobričevo, Ćuprija|Dobričevo]] |
|||
* [[Dvorica]] |
|||
* [[Isakovo, Serbia|Isakovo]] |
|||
* [[Ivankovac]] |
|||
* [[Jovac]] |
|||
* [[Kovanica]] |
|||
* [[Krušar]] |
|||
* [[Mijatovac]] |
|||
* [[Ostrikovac]] |
|||
* [[Paljane]] |
|||
* [[Senje]] |
|||
* [[Supska]] |
|||
* [[Virine]] |
|||
* [[Vlaška]] |
|||
{{col div end}} |
|||
== Demographics == |
|||
{{Historical populations |
|||
| type = |
|||
| percentages = pagr |
|||
|1948|28806 |1953|32313 |1961|34028 |1971|36529 |1981|38841 |1991|38747 |2002|33567 |2011|30645 |2022|25325 |
|||
| source = <ref>{{cite web | url=http://pod2.stat.gov.rs/ObjavljenePublikacije/Popis2011/Knjiga20.pdf | title=2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia | publisher=Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia | accessdate=11 January 2017 | website=stat.gov.rs}}</ref> |
|||
}} |
|||
The municipality of Ćuprija had a population of 30,645 inhabitants, according to the 2011 census results. All settlements in municipality have Serb ethnic majority except two villages, Bigrenica and Isakovo with Vlach ethnic majority. |
|||
== Economy == |
|||
The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):<ref name="stats18">{{cite web|title=MUNICIPALITIES AND REGIONS OF THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA, 2019.|url=https://publikacije.stat.gov.rs/G2019/PdfE/G201913046.pdf|website=stat.gov.rs|publisher=[[Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia]]|date=25 December 2019|accessdate=28 December 2019}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="font-size:95%;" |
|||
|- |
|||
! Activity |
|||
! Total |
|||
|- |
|||
|Agriculture, forestry and fishing||align="right"|42 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Mining and quarrying||align="right"|5 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Manufacturing||align="right"|1,462 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply||align="right"|62 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities||align="right"|231 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Construction||align="right"|577 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles||align="right"|1,129 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Transportation and storage||align="right"|218 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Accommodation and food services||align="right"|244 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Information and communication||align="right"|44 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Financial and insurance activities||align="right"|87 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Real estate activities||align="right"|5 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Professional, scientific and technical activities||align="right"|209 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Administrative and support service activities||align="right"|36 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Public administration and defense; compulsory social security||align="right"|477 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Education||align="right"|575 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Human health and social work activities||align="right"|1,291 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Arts, entertainment and recreation||align="right"|104 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Other service activities||align="right"|123 |
|||
|- |
|||
|Individual agricultural workers||align="right"|398 |
|||
|- class="sortbottom" |
|||
|'''Total'''||align="right"|'''7,320''' |
|||
|} |
|||
== Society and culture == |
|||
=== Education === |
|||
*Elementary school "[[Đura Jakšić]]" |
|||
*Elementary school "[[Vuk Stefanović Karadžić]]" |
|||
*Elementary school "13. Oktobar" |
|||
*High school in Ćuprija |
|||
*Medical High-School |
|||
*Technical School |
|||
*Medical College in Ćuprija |
|||
*Musical Elementary School "Dušan Skovran" |
|||
*School for musically gifted children |
|||
*Faculty for banking and trade, Alpha University |
|||
*College of Health Studies |
|||
=== Sports === |
|||
Sport activities in Ćuprija are developed. Thanks to many athletes and coaches (such as Vera Nikolić, Dragan Zdravković, Snežana Jolović-Pajkić, Zora Antić -Tomecić, Miroslav Pavlović, Vladan Đorđević, Dušan Košutić, Vlada Jovanović, Ljiljana Šušnjar and Aleksandar Petrović etc.) Ćuprija was well known as "the Athletics town". Beside athletic, soccer (football in Europe), basketball, handball, tennis and volleyball are extremely popular sports in Ćuprija. |
|||
Ćuprija's football club "Morava" was founded in 1918 and is currently competing in Pomoravsko-Timočka football zone. It has its own stadium with a capacity of 10,000 sport fans. |
|||
In Ćuprija, there could be found a dance club for those who love to dance. |
|||
=== Features === |
|||
Ćuprija lies on international road and railway links {{convert|150|km|0|abbr=off}} south of [[Belgrade]] and {{convert|90|km|0|abbr=on}} north of [[Niš]]. The main source of income is the College of Nursing and Agriculture. [[Ravanica Monastery]], built in 1381 by [[Lazar of Serbia]], is {{convert|8|km|0|abbr=on}} to the east. |
|||
== Climate == |
|||
Ćuprija has a [[humid subtropical climate]] ([[Köppen climate classification|Cfa]]) with hot summers coupled with cool nights and moderately cold, snowy, and very cloudy winters. Precipitation peaks during the month of June.{{Weather box |
|||
|width = auto |
|||
|location = Ćuprija (1991–2020, extremes 1961–2020) |
|||
|metric first = y |
|||
|single line = y |
|||
|Jan record high C = 20.6 |
|||
|Feb record high C = 25.5 |
|||
|Mar record high C = 29.0 |
|||
|Apr record high C = 33.8 |
|||
|May record high C = 35.4 |
|||
|Jun record high C = 40.1 |
|||
|Jul record high C = 44.6 |
|||
|Aug record high C = 42.7 |
|||
|Sep record high C = 38.3 |
|||
|Oct record high C = 33.2 |
|||
|Nov record high C = 28.0 |
|||
|Dec record high C = 21.4 |
|||
|year record high C = 44.6 |
|||
|Jan high C = 4.8 |
|||
|Feb high C = 7.7 |
|||
|Mar high C = 13.2 |
|||
|Apr high C = 18.9 |
|||
|May high C = 23.7 |
|||
|Jun high C = 27.5 |
|||
|Jul high C = 30.0 |
|||
|Aug high C = 30.4 |
|||
|Sep high C = 24.8 |
|||
|Oct high C = 18.7 |
|||
|Nov high C = 12.1 |
|||
|Dec high C = 5.8 |
|||
|year high C = 18.1 |
|||
|Jan mean C = 0.5 |
|||
|Feb mean C = 2.3 |
|||
|Mar mean C = 6.7 |
|||
|Apr mean C = 12.0 |
|||
|May mean C = 16.7 |
|||
|Jun mean C = 20.5 |
|||
|Jul mean C = 22.3 |
|||
|Aug mean C = 22.1 |
|||
|Sep mean C = 17.0 |
|||
|Oct mean C = 11.7 |
|||
|Nov mean C = 6.8 |
|||
|Dec mean C = 1.8 |
|||
|year mean C = 11.7 |
|||
|Jan low C = -3.1 |
|||
|Feb low C = -2.2 |
|||
|Mar low C = 1.0 |
|||
|Apr low C = 5.4 |
|||
|May low C = 10.0 |
|||
|Jun low C = 13.4 |
|||
|Jul low C = 14.7 |
|||
|Aug low C = 14.6 |
|||
|Sep low C = 10.7 |
|||
|Oct low C = 6.4 |
|||
|Nov low C = 2.7 |
|||
|Dec low C = -1.6 |
|||
|year low C = 6.0 |
|||
|Jan record low C = -27.1 |
|||
|Feb record low C = -25.8 |
|||
|Mar record low C = -17.3 |
|||
|Apr record low C = -8.1 |
|||
|May record low C = -3.2 |
|||
|Jun record low C = 1.0 |
|||
|Jul record low C = 4.1 |
|||
|Aug record low C = 3.6 |
|||
|Sep record low C = -3.3 |
|||
|Oct record low C = -8.0 |
|||
|Nov record low C = -18.6 |
|||
|Dec record low C = -20.8 |
|||
|year record low C = -27.1 |
|||
|precipitation colour = green |
|||
|Jan precipitation mm = 50.5 |
|||
|Feb precipitation mm = 47.8 |
|||
|Mar precipitation mm = 48.9 |
|||
|Apr precipitation mm = 61.9 |
|||
|May precipitation mm = 76.8 |
|||
|Jun precipitation mm = 74.5 |
|||
|Jul precipitation mm = 61.6 |
|||
|Aug precipitation mm = 45.3 |
|||
|Sep precipitation mm = 53.5 |
|||
|Oct precipitation mm = 57.4 |
|||
|Nov precipitation mm = 49.1 |
|||
|Dec precipitation mm = 58.4 |
|||
|year precipitation mm = 685.7 |
|||
|Jan humidity = 82.2 |
|||
|Feb humidity = 77.0 |
|||
|Mar humidity = 70.1 |
|||
|Apr humidity = 67.9 |
|||
|May humidity = 70.6 |
|||
|Jun humidity = 69.7 |
|||
|Jul humidity = 66.8 |
|||
|Aug humidity = 66.5 |
|||
|Sep humidity = 72.0 |
|||
|Oct humidity = 77.3 |
|||
|Nov humidity = 79.2 |
|||
|Dec humidity = 83.2 |
|||
|year humidity = 73.5 |
|||
|unit precipitation days = 0.1 mm |
|||
|Jan precipitation days = 14.7 |
|||
|Feb precipitation days = 13.6 |
|||
|Mar precipitation days = 12.6 |
|||
|Apr precipitation days = 13.6 |
|||
|May precipitation days = 14.3 |
|||
|Jun precipitation days = 11.5 |
|||
|Jul precipitation days = 10.0 |
|||
|Aug precipitation days = 8.0 |
|||
|Sep precipitation days = 10.3 |
|||
|Oct precipitation days = 10.6 |
|||
|Nov precipitation days = 11.4 |
|||
|Dec precipitation days = 15.3 |
|||
|year precipitation days = 145.9 |
|||
|Jan snow days = 8.9 |
|||
|Feb snow days = 7.7 |
|||
|Mar snow days = 3.7 |
|||
|Apr snow days = 0.8 |
|||
|May snow days = 0.0 |
|||
|Jun snow days = 0.0 |
|||
|Jul snow days = 0.0 |
|||
|Aug snow days = 0.0 |
|||
|Sep snow days = 0.0 |
|||
|Oct snow days = 0.2 |
|||
|Nov snow days = 2.3 |
|||
|Dec snow days = 6.9 |
|||
|year snow days = 30.5 |
|||
|Jan sun = 71.3 |
|||
|Feb sun = 95.4 |
|||
|Mar sun = 154.3 |
|||
|Apr sun = 190.0 |
|||
|May sun = 229.5 |
|||
|Jun sun = 265.3 |
|||
|Jul sun = 297.6 |
|||
|Aug sun = 285.1 |
|||
|Sep sun = 204.6 |
|||
|Oct sun = 151.4 |
|||
|Nov sun = 94.1 |
|||
|Dec sun = 59.8 |
|||
|year sun = 2098.4 |
|||
|source 1 = Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia<ref name = RHSS1991>{{cite web |
|||
| url = https://www.hidmet.gov.rs/ciril/meteorologija/stanica_sr_cuprija.php |
|||
| archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20220420200823/https://www.hidmet.gov.rs/ciril/meteorologija/stanica_sr_cuprija.php |
|||
| archive-date = 20 April 2022 |
|||
| title= Monthly and annual means, maximum and minimum values of meteorological elements for the period 1991–2020 |
|||
| language = sr |
|||
| publisher = Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia |
|||
| access-date = 20 April 2022}}</ref><ref name = RHSS1981>{{cite web |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210720080922/http://www.hidmet.gov.rs/eng/meteorologija/stanica_sr.php?moss_id=13384 |archive-date=20 July 2021 | url=http://www.hidmet.gov.rs/eng/meteorologija/stanica_sr.php?moss_id=13384 | title=Monthly and annual means, maximum and minimum values of meteorological elements for the period 1981–2010 | publisher=Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia | accessdate=February 25, 2017 | language=Serbian}}</ref> |
|||
|date=September 2012 |
|||
}} |
|||
== International relations == |
|||
{{See also|List of twin towns and sister cities in Serbia}} |
|||
=== Twin towns — Sister cities === |
|||
Ćuprija is [[Twin towns and sister cities|twinned]] with: |
|||
*{{flagicon|SVN}} '''[[Celje]]''', [[Slovenia]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|BIH}} '''[[Doboj]]''', [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]] |
|||
*{{flagicon|BIH}} '''[[Gradiška, Bosnia and Herzegovina|Gradiška]]''', [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], since 1994<ref>{{cite web |title=Побратимски градови|url=http://www.gradgradiska.com/medjunarodna-saradnja/|website=gradgradiska.com|publisher=Gradiška|language=sr|date=2021-04-24|access-date=2021-04-24}}</ref> |
|||
== Notable people == |
|||
* [[Dušan Matić]], poet |
|||
* [[Dragoslav Mihailović]], writer |
|||
* [[Filip Stojković]], professional footballer |
|||
* [[Snežana Pajkić]], middle-distance runner |
|||
* [[Vera Nikolić]], athlete and coach |
|||
== See also == |
|||
* [[List of places in Serbia]] |
|||
== References == |
|||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
== Sources == |
|||
*{{cite thesis|last=Ceribašić-Begovac|first=Anaid|year=2017|title=Die Muslime im Sandschak Smederevo am Übergang vom 18. ins 19. Jahrhundert - Ein Vergleich zwischen der serbischen und bosnischen wissenschaftlichen Literatur|publisher=University of Graz|url=https://unipub.uni-graz.at/obvugrhs/content/titleinfo/1883278/full.pdf}} |
|||
== External links == |
|||
{{Commons category|Ćuprija}} |
|||
* {{official website|http://www.cuprija.rs}} |
|||
{{Municipalities of Serbia}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cuprija}} |
|||
[[Category:Populated places in Pomoravlje District]] |
|||
[[Category:Municipalities and cities of Šumadija and Western Serbia]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 09:22, 2 November 2024
Ćuprija
Ћуприја (Serbian) | |
|---|---|
Town and municipality | |
 Main street, 2010 | |
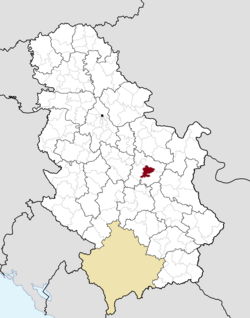 Location of the municipality of Ćuprija within Serbia | |
| Coordinates: 43°56′N 21°22′E / 43.933°N 21.367°E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Šumadija and Western Serbia |
| District | Pomoravlje |
| Settlements | 16 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Jelena Đulinac (SNS) |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 287 km2 (111 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 124 m (407 ft) |
| Population (2022 census)[2] | |
| • Town | 16,522 |
| • Municipality | 25,325 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 35230 35231 |
| Area code | +381(0)35 |
| Car plates | ĆU |
| Website | www |
Ćuprija (Serbian Cyrillic: Ћуприја, pronounced [tɕǔprija]) is a town and municipality located in the Pomoravlje District of central Serbia. The population of the town is 16,522, while the municipality has 25,325 inhabitants (2022 census).
History
[edit]The Romans founded the town as a fort Horreum Margi (Horreum: Granary, Margi: Morava) on the road from Constantinople to Rome, where it crosses the river now known as Velika Morava. It served as a Roman military base, had a shield factory[3] and gained the status of municipium before AD 224. In 505, the Romans were defeated by Goths and Huns under Mundo, a descendant of Attila the Hun.[4]
Under Slavic rule, it became known as Ravno (literal translation to English would be "flat"), since it is in a flat river valley. Some local names (of the villages Paljane and Isakovo, of the river Mirosava) recall the major clash in autumn 1191 between the Serbs (under Stefan Nemanja) and the Byzantines (under Emperor Isaac II Angelos).
In the 15th century, Ćuprija became part of Ottoman Empire. After conquering this settlement, the Turks built a bridge or "köprü" in Turkish – hence the name of the town. Shortly after the First Serbian Uprising began, in 1805 one of the first and most important battles was won by Ivankovac, near Ćuprija. Serbian uprisers under the leadership of dukes Milenko Stojković, Petar Dobrnjac, and Stevan Sinđelić defeated a Turkish army which led to further spreading of the Uprising through all of Belgrade Pashaluk. Four years after that, in 1809, Ćuprija Elementary school was founded.
During the Second Serbian Uprising, Serbian prince Miloš Obrenović made an oral agreement in Ćuprija which enabled Serbs in Belgrade Pashaluk to collect their own taxes, to participate in proceedings against Serbs and to establish a National Office composed of Serbian princes. After 1834, the town started to grow economically and eventually merged with the nearby villages of Mućava, Mrčajevci, and Žirovnica. In the Ottoman era, Ćuprija was the town of Smederevo with the highest concentration of Albanians. Contemporary Serb author Joakim Vujić recorded more "Turkish Arnauts than Serbs" in 1826 in the town. After the war, Obrenović began a campaign to buy out all Muslim Albanian households in the town.[5] In 1853, "Dobričevo" farm was founded. This led to the establishment of the Agricultural school in 1899. In 1911, a Sugar factory called "ŠELK 911" was founded.
During the 19th century, Ćuprija was the center of Nahiyah. After 1890, it was the seat of Morvaski okrug (Morava County).
From 1929 to 1941, Ćuprija was part of the Morava Banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
In World War II, a special Ćuprija-Paraćin partisan troop was formed in order to fight against the German Wehrmacht. On September 26, 1941, 35 members of this troop were shot by German occupiers. The Second World War finally ended in Ćuprija on October 13, 1944, when town was liberated from the Wehrmacht during the so-called Belgrade Operation.
During the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia in 1999, the town's center was heavily damaged. Some buildings still remain in ruins. As of 2011 census, the municipality had 30,645 inhabitants.
Settlements
[edit]Aside from the town of Ćuprija, the municipality includes the following 16 settlements:
Demographics
[edit]| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1948 | 28,806 | — |
| 1953 | 32,313 | +2.32% |
| 1961 | 34,028 | +0.65% |
| 1971 | 36,529 | +0.71% |
| 1981 | 38,841 | +0.62% |
| 1991 | 38,747 | −0.02% |
| 2002 | 33,567 | −1.30% |
| 2011 | 30,645 | −1.01% |
| 2022 | 25,325 | −1.72% |
| Source: [6] | ||
The municipality of Ćuprija had a population of 30,645 inhabitants, according to the 2011 census results. All settlements in municipality have Serb ethnic majority except two villages, Bigrenica and Isakovo with Vlach ethnic majority.
Economy
[edit]The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):[7]
| Activity | Total |
|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 42 |
| Mining and quarrying | 5 |
| Manufacturing | 1,462 |
| Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply | 62 |
| Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities | 231 |
| Construction | 577 |
| Wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles | 1,129 |
| Transportation and storage | 218 |
| Accommodation and food services | 244 |
| Information and communication | 44 |
| Financial and insurance activities | 87 |
| Real estate activities | 5 |
| Professional, scientific and technical activities | 209 |
| Administrative and support service activities | 36 |
| Public administration and defense; compulsory social security | 477 |
| Education | 575 |
| Human health and social work activities | 1,291 |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 104 |
| Other service activities | 123 |
| Individual agricultural workers | 398 |
| Total | 7,320 |
Society and culture
[edit]Education
[edit]- Elementary school "Đura Jakšić"
- Elementary school "Vuk Stefanović Karadžić"
- Elementary school "13. Oktobar"
- High school in Ćuprija
- Medical High-School
- Technical School
- Medical College in Ćuprija
- Musical Elementary School "Dušan Skovran"
- School for musically gifted children
- Faculty for banking and trade, Alpha University
- College of Health Studies
Sports
[edit]Sport activities in Ćuprija are developed. Thanks to many athletes and coaches (such as Vera Nikolić, Dragan Zdravković, Snežana Jolović-Pajkić, Zora Antić -Tomecić, Miroslav Pavlović, Vladan Đorđević, Dušan Košutić, Vlada Jovanović, Ljiljana Šušnjar and Aleksandar Petrović etc.) Ćuprija was well known as "the Athletics town". Beside athletic, soccer (football in Europe), basketball, handball, tennis and volleyball are extremely popular sports in Ćuprija.
Ćuprija's football club "Morava" was founded in 1918 and is currently competing in Pomoravsko-Timočka football zone. It has its own stadium with a capacity of 10,000 sport fans. In Ćuprija, there could be found a dance club for those who love to dance.
Features
[edit]Ćuprija lies on international road and railway links 150 kilometres (93 miles) south of Belgrade and 90 km (56 mi) north of Niš. The main source of income is the College of Nursing and Agriculture. Ravanica Monastery, built in 1381 by Lazar of Serbia, is 8 km (5 mi) to the east.
Climate
[edit]Ćuprija has a humid subtropical climate (Cfa) with hot summers coupled with cool nights and moderately cold, snowy, and very cloudy winters. Precipitation peaks during the month of June.
| Climate data for Ćuprija (1991–2020, extremes 1961–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.6 (69.1) |
25.5 (77.9) |
29.0 (84.2) |
33.8 (92.8) |
35.4 (95.7) |
40.1 (104.2) |
44.6 (112.3) |
42.7 (108.9) |
38.3 (100.9) |
33.2 (91.8) |
28.0 (82.4) |
21.4 (70.5) |
44.6 (112.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 4.8 (40.6) |
7.7 (45.9) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.9 (66.0) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.4 (86.7) |
24.8 (76.6) |
18.7 (65.7) |
12.1 (53.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
18.1 (64.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.5 (32.9) |
2.3 (36.1) |
6.7 (44.1) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.7 (62.1) |
20.5 (68.9) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.1 (71.8) |
17.0 (62.6) |
11.7 (53.1) |
6.8 (44.2) |
1.8 (35.2) |
11.7 (53.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −3.1 (26.4) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
1.0 (33.8) |
5.4 (41.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.4 (56.1) |
14.7 (58.5) |
14.6 (58.3) |
10.7 (51.3) |
6.4 (43.5) |
2.7 (36.9) |
−1.6 (29.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −27.1 (−16.8) |
−25.8 (−14.4) |
−17.3 (0.9) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
1.0 (33.8) |
4.1 (39.4) |
3.6 (38.5) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−18.6 (−1.5) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
−27.1 (−16.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 50.5 (1.99) |
47.8 (1.88) |
48.9 (1.93) |
61.9 (2.44) |
76.8 (3.02) |
74.5 (2.93) |
61.6 (2.43) |
45.3 (1.78) |
53.5 (2.11) |
57.4 (2.26) |
49.1 (1.93) |
58.4 (2.30) |
685.7 (27.00) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 14.7 | 13.6 | 12.6 | 13.6 | 14.3 | 11.5 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 10.3 | 10.6 | 11.4 | 15.3 | 145.9 |
| Average snowy days | 8.9 | 7.7 | 3.7 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 6.9 | 30.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82.2 | 77.0 | 70.1 | 67.9 | 70.6 | 69.7 | 66.8 | 66.5 | 72.0 | 77.3 | 79.2 | 83.2 | 73.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 71.3 | 95.4 | 154.3 | 190.0 | 229.5 | 265.3 | 297.6 | 285.1 | 204.6 | 151.4 | 94.1 | 59.8 | 2,098.4 |
| Source: Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia[8][9] | |||||||||||||
International relations
[edit]Twin towns — Sister cities
[edit]Ćuprija is twinned with:
 Celje, Slovenia
Celje, Slovenia Doboj, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Doboj, Bosnia and Herzegovina Gradiška, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 1994[10]
Gradiška, Bosnia and Herzegovina, since 1994[10]
Notable people
[edit]- Dušan Matić, poet
- Dragoslav Mihailović, writer
- Filip Stojković, professional footballer
- Snežana Pajkić, middle-distance runner
- Vera Nikolić, athlete and coach
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Municipalities of Serbia, 2006". Statistical Office of Serbia. Retrieved 2010-11-28.
- ^ "Census 2022: Total population, by municipalities and cities". popis2022.stat.gov.rs.
- ^ Jones, Arnold Hugh Martin (1986). A Social Economic and Administrative Survey. The Later Roman Empire, 284-602. Vol. 1. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-3353-3.
- ^ Jaques, Tony (2007). Dictionary of Battles and Sieges: F-O. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-33538-9.by Tony Jaques
- ^ Ceribašić-Begovac 2017, p. 84
- ^ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- ^ "MUNICIPALITIES AND REGIONS OF THE REPUBLIC OF SERBIA, 2019" (PDF). stat.gov.rs. Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. 25 December 2019. Retrieved 28 December 2019.
- ^ "Monthly and annual means, maximum and minimum values of meteorological elements for the period 1991–2020" (in Serbian). Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia. Archived from the original on 20 April 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ^ "Monthly and annual means, maximum and minimum values of meteorological elements for the period 1981–2010" (in Serbian). Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia. Archived from the original on 20 July 2021. Retrieved February 25, 2017.
- ^ "Побратимски градови". gradgradiska.com (in Serbian). Gradiška. 2021-04-24. Retrieved 2021-04-24.
Sources
[edit]- Ceribašić-Begovac, Anaid (2017). Die Muslime im Sandschak Smederevo am Übergang vom 18. ins 19. Jahrhundert - Ein Vergleich zwischen der serbischen und bosnischen wissenschaftlichen Literatur (PDF) (Thesis). University of Graz.