Celebic languages: Difference between revisions
Arianwen88 (talk | contribs) →top: Added image and caption #suggestededit-add-image-top Tags: Mobile edit Mobile app edit Android app edit |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|name=Celebic |
|name=Celebic |
||
|altname= |
|altname= |
||
|region=[[Sulawesi]] |
|region=[[Sulawesi]], [[Indonesia]] |
||
|familycolor=Austronesian |
|familycolor=Austronesian |
||
|fam2=[[Malayo-Polynesian languages|Malayo-Polynesian]] |
|fam2=[[Malayo-Polynesian languages|Malayo-Polynesian]] |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Celebic languages''' are a subgroup of the [[Austronesian languages]] spoken on the island of [[Sulawesi]], formerly |
[[File:Sulawesi_languages.jpg|thumb|right|alt=Map of the Sulawesi languages with Celebic depicted in red in the cencentrere. Celebic language is spoken a larger area than the other Sulawesi languages|Map of the Sulawesi languages with Celebic depicted in red (the map is in German)]] |
||
The '''Celebic languages''' are a subgroup of the [[Austronesian languages]] spoken on the [[Indonesia]]n island of [[Sulawesi]], formerly called ''Celebes.'' Almost all of the languages spoken in the provinces of [[Central Sulawesi]] and [[Southeast Sulawesi]] belong to the Celebic group. A few Celebic languages (e.g. [[Wotu language|Wotu]], [[Bonerate language|Bonerate]]) are located in [[South Sulawesi]] province. By number of languages (but not by number of speakers), Celebic is the largest subgroup of [[Austronesian languages]] on Sulawesi. |
|||
==Subgrouping== |
==Subgrouping== |
||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
David Mead (2003a:125) classifies the Celebic languages as follows.<ref name=Mead2003a>{{cite book |last=Mead |first=David |year=2003a |chapter=Evidence for a Celebic supergroup |title=Issues in Austronesian historical phonology |editor-first=John |editor-last=Lynch |pages=115-141 |series=Pacific Linguistics 550 |location=Canberra |publisher=Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University |chapter-url=https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/bitstream/1885/146173/1/PL-550.pdf#page=123}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Mead |first=David |year=2003b |chapter=The Saluan-Banggai microgroup of eastern Sulawesi |title=Issues in Austronesian historical phonology |editor-first=John |editor-last=Lynch |pages=65–86 |series=Pacific Linguistics 550 |location=Canberra |publisher=Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University |chapter-url=https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/bitstream/1885/146173/1/PL-550.pdf#page=73}}</ref> |
David Mead (2003a:125) classifies the Celebic languages as follows.<ref name=Mead2003a>{{cite book |last=Mead |first=David |year=2003a |chapter=Evidence for a Celebic supergroup |title=Issues in Austronesian historical phonology |editor-first=John |editor-last=Lynch |pages=115-141 |series=Pacific Linguistics 550 |location=Canberra |publisher=Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University |chapter-url=https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/bitstream/1885/146173/1/PL-550.pdf#page=123}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Mead |first=David |year=2003b |chapter=The Saluan-Banggai microgroup of eastern Sulawesi |title=Issues in Austronesian historical phonology |editor-first=John |editor-last=Lynch |pages=65–86 |series=Pacific Linguistics 550 |location=Canberra |publisher=Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University |chapter-url=https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/bitstream/1885/146173/1/PL-550.pdf#page=73}}</ref> |
||
{{tree list}} |
|||
*[[Tomini–Tolitoli languages|Tomini–Tolitoli]] |
|||
*'''Celebic''' |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[ |
**[[Tomini–Tolitoli languages|Tomini–Tolitoli]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
**[[ |
**[[Wotu–Wolio languages|Wotu–Wolio]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
***[[ |
***[[Saluan–Banggai languages|Saluan–Banggai]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
****[[Bungku–Tolaki languages|Bungku–Tolaki]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{tree list/end}} |
|||
More recently, Zobel (2020) proposed that [[Kaili–Pamona languages|Kaili–Pamona]] and [[Wotu–Wolio languages|Wotu–Wolio]] form a [[Kaili–Pamona languages|Kaili]]–[[Wotu–Wolio languages|Wolio]] group, which Zobel places as a primary subgroup of Celebic. Furthermore, in Zobel's (2020) classification, Kaili–Wolio is placed as a sister to group to Tominic–Eastern Celebic, which contains Mead's (2003) [[Tomini–Tolitoli languages|Tomini–Tolitoli]] and ''Eastern Celebic'' groups.<ref name="Zobel-2020">{{cite journal |last=Zobel |first=Erik |last2= |first2= |date=2020 |title=The Kaili–Wolio Branch of the Celebic Languages |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/article/782054 |journal=Oceanic Linguistics |volume=59 |issue=1/2 |pages=297-346 |doi=10.1353/ol.2020.0014 |publisher=University of Hawai'i Press}}</ref> |
|||
=== Position within Austronesian === |
=== Position within Austronesian === |
||
At the current |
At the current state of research, the Celebic languages are considered to make up a primary branch of the [[Malayo-Polynesian languages|Malayo-Polynesian]] subgroup within the [[Austronesian languages|Austronesian]] language family.<ref>{{cite journal| last=Smith |first=Alexander D. |title=The Western Malayo-Polynesian Problem |year=2017 |journal=Oceanic Linguistics |volume=56 |issue=2 |page=435–490|doi=10.1353/ol.2017.0021 }}</ref> |
||
==Proto-Celebic==<!---[[Proto-Celebic]] redirects here---> |
==Proto-Celebic==<!---[[Proto-Celebic]] redirects here---> |
||
| Line 49: | Line 55: | ||
David Mead (2003a:125) lists the following [[sound change]]s for Proto-Celebic and its subgroups.<ref name=Mead2003a /> |
David Mead (2003a:125) lists the following [[sound change]]s for Proto-Celebic and its subgroups.<ref name=Mead2003a /> |
||
# [[Proto-Malayo-Polynesian language|Proto-Malayo-Polynesian]] to Proto-Celebic |
|||
* *C<sub>1</sub>C<sub>2</sub> > *C<sub>2</sub> (C<sub>1</sub> not nasal) |
#* *C<sub>1</sub>C<sub>2</sub> > *C<sub>2</sub> (C<sub>1</sub> not nasal) |
||
* *h > Ø |
#* *h > Ø |
||
* *d > *r |
#* *d > *r |
||
* *ay, *-ey > *e |
#* *ay, *-ey > *e |
||
* *-aw, *-ew > *o |
#* *-aw, *-ew > *o |
||
* *j > *y, Ø |
#* *j > *y, Ø |
||
| ⚫ | |||
#* *e (schwa) > *o |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* * |
#* *-iq > *eq |
||
* * |
#*[[antepenultimate]] *a > *o |
||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[antepenultimate]] *a > *o |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* * |
#* *q > *ʔ |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* * |
#* *-w- > Ø |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* * |
#* *ñ > n |
||
* * |
#* *b > *b, *w |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* * |
#* *q > *ʔ |
||
* * |
#* *w- > *h |
||
| ⚫ | |||
# Proto-Southeastern Celebic to Proto-[[Muna–Buton languages|Muna–Buton]] |
|||
* * |
#* *w > Ø |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 92: | Line 93: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [https://www.ethnologue.com/subgroups/celebic Celebic languages] at ''[[Ethnologue]]'' ( |
* [https://www.ethnologue.com/subgroups/celebic Celebic languages] at ''[[Ethnologue]]'' (22nd ed., 2019). |
||
* [http://sulang.org/about/classification-sulawesi-languages Classification of Sulawesi languages] |
* [http://sulang.org/about/classification-sulawesi-languages Classification of Sulawesi languages] |
||
{{Celebic languages}} |
|||
{{Austronesian languages}} |
{{Austronesian languages}} |
||
{{Languages of Indonesia}} |
|||
[[Category:Celebic languages| ]] |
[[Category:Celebic languages| ]] |
||
Latest revision as of 10:20, 2 November 2024
| Celebic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Sulawesi, Indonesia |
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Celebic |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | cele1242 |
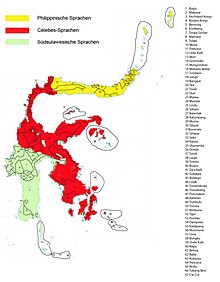
The Celebic languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, formerly called Celebes. Almost all of the languages spoken in the provinces of Central Sulawesi and Southeast Sulawesi belong to the Celebic group. A few Celebic languages (e.g. Wotu, Bonerate) are located in South Sulawesi province. By number of languages (but not by number of speakers), Celebic is the largest subgroup of Austronesian languages on Sulawesi.
Subgrouping
[edit]Internal classification
[edit]David Mead (2003a:125) classifies the Celebic languages as follows.[1][2]
- Celebic
- Tomini–Tolitoli
- Kaili–Pamona
- Wotu–Wolio
- Eastern
- Saluan–Banggai
- Southeastern
More recently, Zobel (2020) proposed that Kaili–Pamona and Wotu–Wolio form a Kaili–Wolio group, which Zobel places as a primary subgroup of Celebic. Furthermore, in Zobel's (2020) classification, Kaili–Wolio is placed as a sister to group to Tominic–Eastern Celebic, which contains Mead's (2003) Tomini–Tolitoli and Eastern Celebic groups.[3]
Position within Austronesian
[edit]At the current state of research, the Celebic languages are considered to make up a primary branch of the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup within the Austronesian language family.[4]
Proto-Celebic
[edit]| Proto-Celebic | |
|---|---|
| Reconstruction of | Celebic languages |
| Region | Sulawesi |
Reconstructed ancestors | |
| Lower-order reconstructions | |
David Mead (2003a:125) lists the following sound changes for Proto-Celebic and its subgroups.[1]
- Proto-Malayo-Polynesian to Proto-Celebic
- *C1C2 > *C2 (C1 not nasal)
- *h > Ø
- *d > *r
- *ay, *-ey > *e
- *-aw, *-ew > *o
- *j > *y, Ø
- Proto-Celebic to Proto-Eastern Celebic
- *e (schwa) > *o
- *-iq > *eq
- antepenultimate *a > *o
- Proto-Eastern Celebic to Proto-Saluan–Banggai
- *-awa- > *oa
- *-b, *-g > *p, *k
- *q > *ʔ
- Proto-Eastern Celebic to Proto-Southeastern Celebic
- *-w- > Ø
- *s > *s, *h
- *Z > *s
- *ñ > n
- *b > *b, *w
- Proto-Southeastern Celebic to Proto-Bungku–Tolaki
- *q > *ʔ
- *w- > *h
- *ʀ > Ø initially and contiguous to *i
- Proto-Southeastern Celebic to Proto-Muna–Buton
- *w > Ø
- final consonant loss (?)
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Mead, David (2003a). "Evidence for a Celebic supergroup" (PDF). In Lynch, John (ed.). Issues in Austronesian historical phonology. Pacific Linguistics 550. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. pp. 115–141.
- ^ Mead, David (2003b). "The Saluan-Banggai microgroup of eastern Sulawesi" (PDF). In Lynch, John (ed.). Issues in Austronesian historical phonology. Pacific Linguistics 550. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. pp. 65–86.
- ^ Zobel, Erik (2020). "The Kaili–Wolio Branch of the Celebic Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 59 (1/2). University of Hawai'i Press: 297–346. doi:10.1353/ol.2020.0014.
- ^ Smith, Alexander D. (2017). "The Western Malayo-Polynesian Problem". Oceanic Linguistics. 56 (2): 435–490. doi:10.1353/ol.2017.0021.
External links
[edit]- Celebic languages at Ethnologue (22nd ed., 2019).
- Classification of Sulawesi languages
