High-explosive incendiary/armor-piercing ammunition: Difference between revisions
m Typo fixing using AWB |
Updated reference link (old was 404) |
||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 38 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Multi-effect and multi-purpose ammuntion type}} |
|||
{{Multiple issues| |
|||
{{refimprove|date=September 2014}} |
|||
{{Unreliable sources|date=July 2023}} |
|||
}} |
|||
[[File:Raufoss NM140 MP (en).svg|thumb|[[Raufoss Mk 211]]]] |
[[File:Raufoss NM140 MP (en).svg|thumb|[[Raufoss Mk 211]]]] |
||
'''High |
'''High-explosive incendiary/armor-piercing ammunition (HEIAP)''' is a form of [[shell (projectile)|shell]] which combines armor-piercing capability and a [[high explosive|high-explosive]] effect. In this respect it is a modern version of an [[armor-piercing shell]]. The ammunition may also be called '''semi-armor-piercing high-explosive incendiary''' (SAPHEI).<ref>{{Cite web | title = PGU-27A/B TP/ PGU-28A/B SAPHEI / PGU-30A/B TP-T | accessdate = 2008-09-28 | url = http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/systems/munitions/pgu-28.htm }}</ref> |
||
Typical of a modern HEIAP shell is the [[Raufoss Mk 211]] |
Typical of a modern HEIAP shell is the [[Raufoss Mk 211]]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.nammo.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/nammo-handbook-2023.pdf|title=Nammo Ammunition Handbook}}</ref> designed for weapons such as [[heavy machine gun]]s and [[anti-materiel rifle]]s. |
||
The primary purpose of these munitions is armor penetration |
The primary purpose of these munitions is armor penetration with better beyond-armor effects.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/systems/munitions/mk211.htm|title=Mark 211 .50-caliber Multipurpose Ammunition|last=Pike|first=John|website=www.globalsecurity.org|access-date=2017-08-12}}</ref> Similarly to SLAP rounds ([[saboted light armor penetrator]]) which get their armor-piercing ability from the propulsion of a 7.62 mm [[tungsten]] heavy alloy [[bullet]] from a 12.7 mm barrel (.50 caliber) using a [[Sabot (firearms)|sabot]] with much more energy than is usually possible from a 7.62 mm round, HEIAP munitions utilize a similar theory with an added explosive effect at the end. The special effect is developed when the round strikes the target. The initial collision ignites the [[Incendiary device|incendiary]] material in the tip, triggering the [[detonation]] of the HE charge. The second ([[zirconium]] powder) incendiary charge will also ignite. This burns at a very high temperature, is not easily extinguished, and can last up to 15 minutes.{{Citation needed|date=August 2013}} |
||
| ⚫ | The remaining element of the round is the [[tungsten carbide]] penetrator. This has a large amount of [[kinetic energy]] and will penetrate the armor as a [[Shell (projectile)#Armour-piercing, composite rigid|solid-cored armor-piercing shot]] would. This takes the incendiary material and about 20 steel fragments (created by the explosives), delivering them in a 25–30 degree cone through the armor, increasing lethality.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
| ⚫ | The remaining element of the round is the [[tungsten carbide]] penetrator. This has a large amount of [[kinetic energy]] and will penetrate the armor as [[Shell (projectile)#Armour-piercing, composite rigid |
||
The triggering of the explosive charge is dependent upon the resistance of the target. If the target offers little resistance then the lack of [[friction]]al heating will prevent the incendiary from igniting and the high explosive from detonating. |
The triggering of the explosive charge is dependent upon the resistance of the target. If the target offers little resistance then the lack of [[friction]]al heating will prevent the incendiary from igniting and the high explosive from detonating. |
||
Exploding ammunition was used by both Allied and German forces during [[World War II]]. |
|||
Larger guns such as the British 30 mm [[RARDEN]] cannon fire APSE (Armour Piercing Special Effects) shells which are an armor-piercing round with added HE effect. |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
{{reflist}} |
|||
<references/> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
*[[High explosive incendiary]] |
*[[High explosive incendiary]] |
||
*[[Mine shell]] |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:High Explosive Incendiary Armor Piercing Ammunition}} |
|||
[[Category:Ammunition]] |
[[Category:Ammunition]] |
||
[[Category:High explosive and incendiary ammunition]] |
|||
[[Category:Explosive weapons]] |
|||
[[ja:HEIAP]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:00, 3 November 2024
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
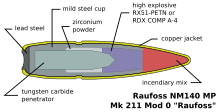
High-explosive incendiary/armor-piercing ammunition (HEIAP) is a form of shell which combines armor-piercing capability and a high-explosive effect. In this respect it is a modern version of an armor-piercing shell. The ammunition may also be called semi-armor-piercing high-explosive incendiary (SAPHEI).[1]
Typical of a modern HEIAP shell is the Raufoss Mk 211[2] designed for weapons such as heavy machine guns and anti-materiel rifles.
The primary purpose of these munitions is armor penetration with better beyond-armor effects.[3] Similarly to SLAP rounds (saboted light armor penetrator) which get their armor-piercing ability from the propulsion of a 7.62 mm tungsten heavy alloy bullet from a 12.7 mm barrel (.50 caliber) using a sabot with much more energy than is usually possible from a 7.62 mm round, HEIAP munitions utilize a similar theory with an added explosive effect at the end. The special effect is developed when the round strikes the target. The initial collision ignites the incendiary material in the tip, triggering the detonation of the HE charge. The second (zirconium powder) incendiary charge will also ignite. This burns at a very high temperature, is not easily extinguished, and can last up to 15 minutes.[citation needed]
The remaining element of the round is the tungsten carbide penetrator. This has a large amount of kinetic energy and will penetrate the armor as a solid-cored armor-piercing shot would. This takes the incendiary material and about 20 steel fragments (created by the explosives), delivering them in a 25–30 degree cone through the armor, increasing lethality.[3]
The triggering of the explosive charge is dependent upon the resistance of the target. If the target offers little resistance then the lack of frictional heating will prevent the incendiary from igniting and the high explosive from detonating.
Exploding ammunition was used by both Allied and German forces during World War II.
References
[edit]- ^ "PGU-27A/B TP/ PGU-28A/B SAPHEI / PGU-30A/B TP-T". Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ^ "Nammo Ammunition Handbook" (PDF).
- ^ a b Pike, John. "Mark 211 .50-caliber Multipurpose Ammunition". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved 2017-08-12.
