Kaniv Regiment: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Kaniv Regiment = |
|||
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
|||
{{Infobox military unit |
{{Infobox military unit |
||
| unit_name = Kaniv Regiment |
| unit_name = Kaniv Regiment |
||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
| size = 16 [[sotnia|sotnias]], 3167 Cossacks (1649) |
| size = 16 [[sotnia|sotnias]], 3167 Cossacks (1649) |
||
| garrison = [[Kaniv]], [[Right-bank Ukraine]] |
| garrison = [[Kaniv]], [[Right-bank Ukraine]] |
||
| battles = {{Tree list}} |
|||
*[[Khmelnytsky Uprising]] |
|||
**[[Battle of Pyliavtsi]], |
|||
**[[Battle of Zboriv (1649)]] |
|||
**[[Battle of Berestechko]] |
|||
**[[Battle of Batih]] |
|||
*[[Paliy uprising]] |
|||
{{tree list/end}} |
|||
| notable_commanders = [[Semen Paliy]], [[Petro Doroshenko]] |
| notable_commanders = [[Semen Paliy]], [[Petro Doroshenko]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Kaniv Regiment''' ({{ |
The '''Kaniv Regiment''' ({{Langx|uk|Канівський полк}}) was a regiment of the [[Registered Cossacks]] (1625–1638) and later also an administrative subdivision of the [[Cossack Hetmanate]] (1648–1678, 1702–1712). It was centred around the town of [[Kaniv]] in central Ukraine, on the banks of the [[Dnieper]] river. |
||
== History == |
== History == |
||
=== Early history === |
=== Early history === |
||
The Kaniv regiment was originally a unit of the Registered Cossacks, who were formally registered in the army of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] and received an annual salary from the government. Due to the strategic position of the unit, from which crossings over the Dnieper (at [[Trakhtemyriv]], [[Rzhyshchiv]] and Kaniv itself) could be controlled, it grew to become one of the largest Cossack units in employ of the Polish king by the 17th century. In early 1648, following the start of the [[Khmelnytsky Uprising]], the regiment became part of Hetman [[Bohdan Khmelnytsky]]'s army. It was subsequently reformed into an administrative unit of the early [[Cossack Hetmanate]] on 8 September, 1649 following the [[Treaty of Zboriv]], replacing the earlier [[Starostwo|starostwos]] of [[Pereiaslav]], [[Cherkasy]] and [[Kaniv]], as well as a part of the [[Kiev Voivodeship]]. |
The Kaniv regiment was originally formed in 1625 as a unit of the Registered Cossacks, who were formally registered in the army of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] and received an annual salary from the government. Due to the strategic position of the unit, from which crossings over the Dnieper (at [[Trakhtemyriv]], [[Rzhyshchiv]] and Kaniv itself) could be controlled, it grew to become one of the largest Cossack units in employ of the Polish king by the 17th century. In early 1648, following the start of the [[Khmelnytsky Uprising]], the regiment became part of Hetman [[Bohdan Khmelnytsky]]'s army. It was subsequently reformed into an administrative subdivision, also called a [[Regiment (administrative unit)|regiment]], of the early [[Cossack Hetmanate]] on 8 September, 1649 following the [[Treaty of Zboriv]], replacing the earlier [[Starostwo|starostwos]] of [[Pereiaslav]], [[Cherkasy]] and [[Kaniv]], as well as a part of the [[Kiev Voivodeship]].{{Efn|Military and civilian divisions were often united in the Zaporozhian Host, so that the commander of a regiment would also rule and govern the civilians around his garrison.}} |
||
By the register (or census) of 1649, the regiment as a whole had 3167 Cossacks and 19 [[Sotnia|sotnias]], while Kaniv itself hosted 2263 Cossacks and 10 sotnias, making it the 3rd largest in the Hetmanate, only behind the {{Interlanguage link|Korsun Regiment|uk|Корсунський полк}} and [[Chyhyryn Regiment]]. Between 18 September, 1651 and 8 January, 1654, the administrative divisions of the regiment were changed, as the Maslivka and Trakhtemyriv sotnias were disbanded and the number of Kaniv sotnias reduced to 5, while two new sotnias were formed at Bubniv and Konochan. By 1654, the regiment thus numbered 3152 Cossacks and 11 sotnias. |
By the register (or census) of 1649, the regiment as a whole had 3167 Cossacks and 19 [[Sotnia|sotnias]], while Kaniv itself hosted 2263 Cossacks and 10 sotnias, making it the 3rd largest in the Hetmanate, only behind the {{Interlanguage link|Korsun Regiment|uk|Корсунський полк}} and [[Chyhyryn Regiment]]. Between 18 September, 1651 and 8 January, 1654, the administrative divisions of the regiment were changed, as the Maslivka and Trakhtemyriv sotnias were disbanded and the number of Kaniv sotnias reduced to 5, while two new sotnias were formed at Bubniv and Konochan. By 1654, the regiment thus numbered 3152 Cossacks and 11 sotnias. |
||
During the [[Khmelnytsky Uprising]], the regiment was engaged in some battles against the Polish army, such as at the [[Battle of Pyliavtsi]], [[Battle of Zboriv (1649)]], [[Battle of Berestechko]] and [[Battle of Batih]].<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=КАНІВСЬКИЙ ПОЛК |url=http://resource.history.org.ua/cgi-bin/eiu/history.exe?&I21DBN=EIU&P21DBN=EIU&S21STN=1&S21REF=10&S21FMT=eiu_all&C21COM=S&S21CNR=20&S21P01=0&S21P02=0&S21P03=TRN=&S21COLORTERMS=0&S21STR=Kanivsky_polk |access-date=2024-10-21 |website=resource.history.org.ua}}</ref> |
|||
=== The Ruin === |
=== The Ruin === |
||
During [[The Ruin (Ukrainian history)|the Ruin]], when skirmishes and conflict between different Cossack factions was common, the regiment often changed hands between different hetmans. In 1667, as part of the [[Truce of Andrusovo]], the regiment became part of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] once more. However, only a year later, in 1668, [[Petro Doroshenko]] seized the regiment and incorporated it into the territory of [[Ottoman Ukraine]], in which it would remain part until its functional disbandment in 1676, as only 3 sotnias remained active. Eventually, after the [[Treaty of Bakhchisarai]] in 1681, the regiment was completely disbanded, after which its members settled in neighbouring regions, mostly in [[Left-bank Ukraine]]. |
During [[The Ruin (Ukrainian history)|the Ruin]], when skirmishes and conflict between different Cossack factions was common, the regiment often changed hands between different hetmans. In 1667, as part of the [[Truce of Andrusovo]], the regiment became part of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]] once more. However, only a year later, in 1668, [[Petro Doroshenko]] seized the regiment and incorporated it into the territory of [[Ottoman Ukraine]], in which it would remain part until its functional disbandment in 1676, as only 3 sotnias remained active. Eventually, after the [[Treaty of Bakhchisarai]] in 1681, the regiment was completely disbanded, after which its members settled in neighbouring regions, mostly in [[Left-bank Ukraine]]. |
||
=== Later revival === |
=== Later revival and end === |
||
Around the 1680's, the regiment was reformed by [[Semen Paliy]], although it was now based in [[Bohuslav]], and was thus sometimes referred to as the Bohuslav |
Around the 1680's, the regiment was reformed by [[Semen Paliy]], although it was now based in [[Bohuslav]], and was thus sometimes referred to as the Bohuslav |
||
{{Infobox former subdivision |
|||
| native_name = {{native name|uk|Канівський полк}} |
|||
| common_name = Kaniv |
|||
| capital = [[Kaniv]] |
|||
| event_start = [[Khmelnytsky Uprising]] |
|||
| event_end = [[Treaty of the Pruth]] |
|||
| year_end = 1712 |
|||
| year_start = 1648 |
|||
| nation = [[Cossack Hetmanate|the Cossack Hetmanate]] |
|||
| image_coat = Kaniv_polk.svg |
|||
| image_map = KanivRegiment 1660.svg |
|||
| today = {{Flag|Ukraine|name=Ukraine}} |
|||
| image_map_caption = The Kaniv Regiment (red) in the [[Cossack Hetmanate]] in 1660 |
|||
| subdivision = [[Regiment (administrative unit)|Regiment]] |
|||
| conventional_long_name = Kaniv Regiment |
|||
| p1 = Kiev Voivodeship |
|||
| s1 = Kiev Governorate |
|||
| image_s1 = [[Image:Coat_of_arms_of_the_Kiev_Governorate.png|20px]] |
|||
| image_p1 = [[Image:COA_of_Kiev_Voivodship_XVII.svg|20px]] |
|||
}} |
|||
regiment. In 1702, a new regiment now centred around Kaniv was formed and engaged in [[Paliy uprising]],<ref name=":0" /> but it was once again disbanded in 1712, as part of the conditions of the [[Treaty of the Pruth]]. |
|||
== Administrative divisions and commanders == |
== Administrative divisions and commanders == |
||
| Line 118: | Line 149: | ||
|[[Kaniv]] |
|[[Kaniv]] |
||
|} |
|} |
||
According to the Zboriv register of 1649, the regimental scribe ({{ |
According to the Zboriv register of 1649, the regimental scribe ({{Langx|uk|Писар}}) was Herasym Savych, while the [[Yesaul]] was Bohdan Shabelnychenko. |
||
== Notes == |
|||
{{reflist}}{{Notelist}} |
|||
== References == |
|||
* {{Cite book |last=Заруба |first=Віктор |title=Адміністративно-територіальний устрій та адміністрація Війська Запорозького у 1648-1782 рр. |year=2007 |isbn=978-966-383-095-7 |language=uk |trans-title=Administrative-territorial divisions and governance of the Zaporozhian Host, 1648-1782}} |
|||
{{Cossack Regiments}} |
{{Cossack Regiments}} |
||
Latest revision as of 23:47, 4 November 2024
| Kaniv Regiment | |
|---|---|
| Канівський полк | |
 Coat of arms of the Kaniv Regiment | |
| Active | 1648–1678 |
| Country | Cossack Hetmanate |
| Type | Cossack regiment |
| Size | 16 sotnias, 3167 Cossacks (1649) |
| Garrison/HQ | Kaniv, Right-bank Ukraine |
| Engagements | |
| Commanders | |
| Notable commanders | Semen Paliy, Petro Doroshenko |
The Kaniv Regiment (Ukrainian: Канівський полк) was a regiment of the Registered Cossacks (1625–1638) and later also an administrative subdivision of the Cossack Hetmanate (1648–1678, 1702–1712). It was centred around the town of Kaniv in central Ukraine, on the banks of the Dnieper river.
History
[edit]Early history
[edit]The Kaniv regiment was originally formed in 1625 as a unit of the Registered Cossacks, who were formally registered in the army of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and received an annual salary from the government. Due to the strategic position of the unit, from which crossings over the Dnieper (at Trakhtemyriv, Rzhyshchiv and Kaniv itself) could be controlled, it grew to become one of the largest Cossack units in employ of the Polish king by the 17th century. In early 1648, following the start of the Khmelnytsky Uprising, the regiment became part of Hetman Bohdan Khmelnytsky's army. It was subsequently reformed into an administrative subdivision, also called a regiment, of the early Cossack Hetmanate on 8 September, 1649 following the Treaty of Zboriv, replacing the earlier starostwos of Pereiaslav, Cherkasy and Kaniv, as well as a part of the Kiev Voivodeship.[a]
By the register (or census) of 1649, the regiment as a whole had 3167 Cossacks and 19 sotnias, while Kaniv itself hosted 2263 Cossacks and 10 sotnias, making it the 3rd largest in the Hetmanate, only behind the Korsun Regiment and Chyhyryn Regiment. Between 18 September, 1651 and 8 January, 1654, the administrative divisions of the regiment were changed, as the Maslivka and Trakhtemyriv sotnias were disbanded and the number of Kaniv sotnias reduced to 5, while two new sotnias were formed at Bubniv and Konochan. By 1654, the regiment thus numbered 3152 Cossacks and 11 sotnias.
During the Khmelnytsky Uprising, the regiment was engaged in some battles against the Polish army, such as at the Battle of Pyliavtsi, Battle of Zboriv (1649), Battle of Berestechko and Battle of Batih.[1]
The Ruin
[edit]During the Ruin, when skirmishes and conflict between different Cossack factions was common, the regiment often changed hands between different hetmans. In 1667, as part of the Truce of Andrusovo, the regiment became part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth once more. However, only a year later, in 1668, Petro Doroshenko seized the regiment and incorporated it into the territory of Ottoman Ukraine, in which it would remain part until its functional disbandment in 1676, as only 3 sotnias remained active. Eventually, after the Treaty of Bakhchisarai in 1681, the regiment was completely disbanded, after which its members settled in neighbouring regions, mostly in Left-bank Ukraine.
Later revival and end
[edit]Around the 1680's, the regiment was reformed by Semen Paliy, although it was now based in Bohuslav, and was thus sometimes referred to as the Bohuslav
| Kaniv Regiment Канівський полк (Ukrainian) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regiment of the Cossack Hetmanate | |||||||||
| 1648–1712 | |||||||||
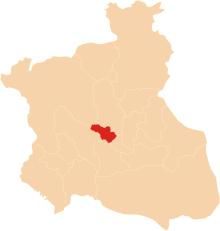 The Kaniv Regiment (red) in the Cossack Hetmanate in 1660 | |||||||||
| Capital | Kaniv | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 1648 | |||||||||
| 1712 | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
regiment. In 1702, a new regiment now centred around Kaniv was formed and engaged in Paliy uprising,[1] but it was once again disbanded in 1712, as part of the conditions of the Treaty of the Pruth.
Administrative divisions and commanders
[edit]| Sotnias of the regiment (1649) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Size (men) | Commander | Garrison |
| Starodub | Ivan Starodub | ||
| Volynets | Pavlo Volynets | ||
| Kulaha | Yakym Kulaha | ||
| Bohdanenko | Fesko Bohdanenko | ||
| Huniak | Fedir Huniak | ||
| Roshchenko | Petro Roshchenko | ||
| Klym | Klym Malashenko | ||
| Yukhymov | Yukhym Roshchenko | ||
| Andrii | Andrii | ||
| Mezhyrich | 147 | Suprun Mykhailovych | Mezhyrich, Cherkasy Oblast |
| Trakhtemyriv | 167 | Tsepkovskyi | Trakhtemyriv |
| Rzhyshchiv | 222 | Chuhui | Rzhyshchiv |
| Staiky | 170 | Taras Sheremet | Staiky, Kyiv Oblast |
| Mykhailiv | 98 | Danylo Yukhymovych | Mykhailivka, Cherkasy Oblast |
| Maslivka | 100 | Semen Yevlashenko | Maslivka, Kyiv Oblast |
| Kaniv | Ivan Holota | Kaniv | |
According to the Zboriv register of 1649, the regimental scribe (Ukrainian: Писар) was Herasym Savych, while the Yesaul was Bohdan Shabelnychenko.
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b "КАНІВСЬКИЙ ПОЛК". resource.history.org.ua. Retrieved 2024-10-21.
- ^ Military and civilian divisions were often united in the Zaporozhian Host, so that the commander of a regiment would also rule and govern the civilians around his garrison.
References
[edit]- Заруба, Віктор (2007). Адміністративно-територіальний устрій та адміністрація Війська Запорозького у 1648-1782 рр [Administrative-territorial divisions and governance of the Zaporozhian Host, 1648-1782] (in Ukrainian). ISBN 978-966-383-095-7.


