Hudson River Chains: Difference between revisions
Wikiuser100 (talk | contribs) Gen'l cleanup |
Quuxplusone (talk | contribs) restore section heading linked from Cheval de frise; also hyphenated just reads easier |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|River barriers used during the American Revolutionary War}} |
{{short description|River barriers used during the American Revolutionary War}} |
||
{{coord missing|Hudson Valley}} |
{{coord missing|Hudson Valley}} |
||
| ⚫ | The '''Hudson River Chains''' were a series of [[boom (navigational barrier)|chain booms]] constructed across the [[Hudson River]] at [[West Point, New York|West Point]] by [[Continental Army]] forces from 1776 to 1778 during the [[American Revolutionary War]]. These served as defenses preventing [[Kingdom of Great Britain|British]] naval vessels from sailing upriver and were overseen by the [[Departments of the Continental Army#Highlands Department|Highlands Department of the Continental Army]]. |
||
| ⚫ | The first chain was destroyed by British forces in the aftermath of the [[Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery]] in October 1777. The more significant and successful was the Great Chain, constructed in 1778 and used through war's end in 1782. Two other barriers across the river, referred to as ''[[Cheval de frise|chevaux-de-frise]]'', were undertaken by the Colonials; the first, between [[Fort Washington (Manhattan)|Fort Washington]] on the island of [[Manhattan]], and [[Fort Lee Historic Park|Fort Lee]] in [[Fort Lee, New Jersey|New Jersey]], was completed in 1776 and shortly seized by the British; another was started in 1776 between Plum Point on the east bank and [[Pollepel Island]] north of West Point but abandoned in 1777 in favor of completion of the Great Chain nearby the following year. |
||
| ⚫ | The |
||
The first was captured and destroyed by British forces during and in the aftermath of the [[Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery]] in October of 1777. The more significant and successful was the [[#Great Chain (1778–1782)|Great Chain]], constructed in 1778 and used through war's end in 1782. |
|||
| ⚫ | Two other barriers across the river, referred to as ''[[ |
||
[[File:West Point Fortifications.jpg|thumb|Map of West Point fortifications from 1778 to 1783, showing the Great Chain and a separate log boom placed downstream to absorb the momentum of any ship attempting to breach the chain]] |
[[File:West Point Fortifications.jpg|thumb|Map of West Point fortifications from 1778 to 1783, showing the Great Chain and a separate log boom placed downstream to absorb the momentum of any ship attempting to breach the chain]] |
||
==Background== |
==Background== |
||
Even before the April 1775 [[Battles of Lexington and Concord]] in Massachusetts both the Americans and British knew that passage on the Hudson River was strategically important to each sides’ war effort. The Americans were desperate to control the river, lest [[New England]] be divided from the rest of the colonies |
Even before the April 1775 [[Battles of Lexington and Concord]] in Massachusetts, both the Americans and British knew that passage on the Hudson River was strategically important to each sides’ war effort. The Americans were desperate to control the river, lest [[New England]] be divided from the rest of the colonies. The immediate American plan was to slow or block ship traffic on the river by attacking British vessels with cannon and [[mortar (weapon)|mortar]]s from both shores. This anticipated batteries at both existing and planned defensive fortifications. In late 1776 [[Henry Wisner]], a resident of [[Goshen, New York]], and one of New York's representatives to the [[Second Continental Congress|Continental Congress]], along with [[Gilbert Livingston (legislator)|Gilbert Livingston]], [[depth sounding|sounded]] the Hudson River and, as part of a Secret Committee of the "[[Committee of safety (American Revolution)|Committee of Safety]]," recommended the placement of chains in strategic locations along the Hudson.<ref>Letter from Henry Wisner and Gilbert Livingston to New-York Committee of Safety: Soundings of Hudson river in the Highlands American Archives Series 5, Volume 3, Page 0812 November 22, 1776. http://lincoln.lib.niu.edu/cgi-bin/amarch/getdoc.pl?/var/lib/philologic/databases/amarch/.27283 {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141204115143/http://lincoln.lib.niu.edu/cgi-bin/amarch/getdoc.pl?%2Fvar%2Flib%2Fphilologic%2Fdatabases%2Famarch%2F.27283 |date=2014-12-04 }} Accessed February 19, 2015.</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | Colonial forces eventually constructed three obstacles across the river: a ''[[cheval de frise#American Revolutionary War|chevaux-de-frise]]'' at northern Manhattan between Forts Washington and [[Fort Lee, New Jersey|Lee]] in 1776; at the lower entrance to the [[Hudson Highlands]], from newly constructed [[Fort Montgomery (Hudson River)|Fort Montgomery]] on the west bank at [[Popolopen#Popolopen Creek|Popolopen Creek]] just north of the modern-day [[Bear Mountain Bridge]] to [[Anthony's Nose (Westchester County, New York)|Anthony's Nose]] on the east bank in 1776–1777; and between [[West Point, New York|West Point]] and [[Constitution Island]] in 1778, known as the Great Chain. A fourth, a cheval-de-frise started in 1776 between Plum Point on the east bank and [[Pollepel Island]] north of West Point, was begun but abandoned. The first two were promptly captured by the British, while the Great Chain, the largest and most important of the projects, was reset each spring until the end of the war. Attention was concentrated on the West Point area because the river narrowed and curved so sharply there that ships slowed in navigating the passage by shifting winds, tides, and current made optimal targets. |
||
The immediate Americans plan was to slow or block ship traffic on the river by attacking British vessels with cannons and [[mortar (weapon)|mortar]]s from both shores. This anticipated batteries at both existing and planned defensive fortifications. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
In late 1776 [[Henry Wisner]], a resident of [[Goshen, New York]] and one of New York's representatives to the [[Second Continental Congress|Continental Congress]], along with [[Gilbert Livingston (legislator)|Gilbert Livingston]], [[depth sounding|sounded]] the Hudson River and, as part of a Secret Committee of the "[[Committees of safety (American Revolution)|Committee of Safety]]," recommended the placement of chains in strategic locations along the Hudson.<ref>Letter from Henry Wisner and Gilbert Livingston to New-York Committee of Safety: Soundings of Hudson river in the Highlands American Archives Series 5, Volume 3, Page 0812 November 22, 1776. http://lincoln.lib.niu.edu/cgi-bin/amarch/getdoc.pl?/var/lib/philologic/databases/amarch/.27283 {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141204115143/http://lincoln.lib.niu.edu/cgi-bin/amarch/getdoc.pl?%2Fvar%2Flib%2Fphilologic%2Fdatabases%2Famarch%2F.27283 |date=2014-12-04 }} Accessed February 19, 2015.</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | In 1776 the Continental Army constructed an array of logs sunk underwater between Fort Washington on the island of Manhattan and Fort Lee across the river in New Jersey. Built to a design of Scottish engineer turned Colonial sympathizer [[Robert Erskine (inventor)|Robert Erskine]], the logs were intended to pierce and sink any British ships that passed over them. An opening was left for the passage of American ships. |
||
| ⚫ | Colonial forces eventually constructed three obstacles across the river: a ''[[ |
||
| ⚫ | After the British learned of the opening from a local resident, they successfully passed through the barrier several times.<ref>Diamant, ''Chaining The Hudson'', 1989</ref> The British successfully captured both forts in the [[Battle of Fort Washington]] on November 16, 1776, and [[Fort Lee Historic Park|Battle of Fort Lee]] on November 20, putting the defensive barrier in their hands. This change had little impact, as the nascent [[Continental Navy]] lacked ships of the size and power of the British, leaving it to resort to small and more maneuverable vessels regardless. |
||
The first two were promptly captured by the British, while the Great Chain, the largest and most important of the projects, was reset each spring until the end of the war. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Attention was concentrated on the West Point area because the river narrowed and curved so sharply there that ships slowed in navigating the passage by shifting winds, tides, and current made optimal targets. |
|||
| ⚫ | In 1776 a chain and [[Boom (navigational barrier)|boom]] were stretched across the river from [[Fort Montgomery (Hudson River)|Fort Montgomery]] on the west bank, at the lower entrance to the Highlands just north of the modern-day Bear Mountain Bridge, to Anthony's Nose on the east bank. Captain Thomas Machin headed the chain effort. In November 1776, a faulty link broke under stress induced by the river current, highlighting some of the difficulties of trying to chain the Hudson.<ref>Diamant, ''Chaining the Hudson,'' 1989, p 105</ref> It was repaired and reset. |
||
| ⚫ | After the British [[Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery|captured forts Montgomery and Clinton]], a [[Fort Clinton (West Point)|second fortress]] built opposite it at the mouth of Popolopen's Kill (today's Popolopen Creek) on its south bank, on 6 October 6 1777, they dismantled the chain.<ref>[https://www.scribd.com/doc/279854/West-Point-Fortifications West Point Fortifications] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131103105206/http://www.scribd.com/doc/279854/West-Point-Fortifications |date=2013-11-03 }}</ref> Free to do so, they raided upriver as far as [[Kingston, New York|Kingston]], then the capitol of New York State, [[Burning of Kingston|putting the torch to it]] and burning all but several of its hundreds of buildings to the ground. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | [[File:A plan of the operations of the King's army, Chevaux de Frise between Fort Lee and Fort Washington, detail.jpg|thumb|400px|1777 map detail showing the '' |
||
| ⚫ | Governor [[George Clinton (vice president)|George Clinton]], a member of the committee assigned by the New York Convention to devise a means of defending the Hudson, was heartened as the British had never attempted to run ships through the chain.<ref>Diamant, ''Chaining the Hudson'', p. 122</ref> He concluded that the basic idea of obstructing the river seemed sound. After Captain Machin recovered from wounds from battle with the British, he began work on the stronger Great Chain at West Point, which was constructed and installed in 1778. |
||
| ⚫ | In 1776 the Continental Army constructed |
||
| ⚫ | After the British learned of the opening from a local resident they successfully passed through the barrier several times.<ref>Diamant, ''Chaining The Hudson'', 1989</ref> The British successfully captured both forts in the [[Battle of Fort Washington]] on November 16, 1776, and [[Battle of Fort Lee]] on November 20, putting the defensive barrier in their hands. |
||
{{-}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | In 1776 a chain and [[Boom (navigational barrier)|boom]] were stretched across the river from [[Fort Montgomery (Hudson River)|Fort Montgomery]] on the west bank, at the lower entrance to the Highlands just north of the modern-day |
||
Captain Thomas Machin headed the chain effort. In November 1776, a faulty link broke under stress induced by the river tides, highlighting some of the difficulties of trying to chain the Hudson.<ref>Diamant, ''Chaining the Hudson,'' 1989, p 105</ref> It was repaired and reset. |
|||
| ⚫ | After the British [[Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery|captured forts Montgomery and Clinton]], a [[Fort Clinton|second fortress]] built opposite it at the mouth of |
||
| ⚫ | [[George Clinton (vice president)| |
||
==Pollepel Island chevaux-de-frise (1776–1777)== |
==Pollepel Island chevaux-de-frise (1776–1777)== |
||
Another |
Another cheval-de-frise was undertaken across the Hudson between Plum Point on the east bank and Pollepel Island north of West Point. The defenses were never fully completed, and its importance was overshadowed by completion of the Great Chain at West Point the following year. |
||
==Great Chain (1778–1782)== |
=={{visible anchor|Great Chain}} (1778–1782)== |
||
{{redirect|Great Chain}} |
|||
[[File:Fields of Fire from Fort Constitution.jpg|thumb|"Fields of Fire" |
[[File:Fields of Fire from Fort Constitution.jpg|thumb|"Fields of Fire" from Fort Constitution on the [[Hudson River]] during the [[American Revolutionary War|Revolutionary War]]]] |
||
[[File:The Great Chain Sketch.jpg|thumb|Sketch of the Great Chain |
[[File:The Great Chain Sketch.jpg|thumb|Sketch of the Great Chain<br>and log boom]] |
||
[[File:Chain Battery.JPG|thumb|The remnants of the earthworks of Chain Battery on [[Flirtation Walk (West Point)|Flirtation Walk]]]] |
[[File:Chain Battery.JPG|thumb|The remnants of the earthworks of Chain Battery on [[Flirtation Walk (West Point)|Flirtation Walk]]]] |
||
In the spring of 1778 a heavy chain supported by huge log rafts was stretched across the Hudson from |
In the spring of 1778, a heavy chain supported by huge log rafts was stretched across the Hudson from West Point to Constitution Island to impede the movement of British ships north of West Point. A second log boom (resembling a ladder in construction) spanned the river about {{convert|100|yd|-1}} downstream to absorb the impact of any ship attempting to breach the barrier. |
||
| ⚫ | The Hudson River's changing tides, strong current, and frequently unfavorable winds created adverse sailing conditions at West Point. Compounding this, the river's narrow width and sharp "S-Curve" there forced any large ship to [[Tacking (sailing)|tack]] in order to navigate it. Cannon were placed in forts and artillery batteries on both sides of the river to attack ships when they were slowed to a halt by the Patriot barrier placed there. |
||
The chain was constructed over six weeks at the [[Sterling Iron Works]], in [[Warwick (village), New York|Warwick]], [[Orange County, New York|Orange County]], of chain links from Long Pond Iron Works in [[Ringwood, New Jersey]]. |
|||
The chain was constructed over six weeks at the [[Sterling Iron Works]] in [[Warwick (village), New York|Warwick]], [[Orange County, New York|Orange County]], of chain links from Long Pond Iron Works in [[Ringwood, New Jersey]]. When completed, the {{convert|600|yard|adj=on}} chain contained iron links {{convert|2|ft|1|spell=in}} in length, weighing {{convert|140|to|180|lb}}.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm |title="Explore the Hudson River's Rich History; A Chain Across the Hudson", Rebecca Haynes, hudsonriver.com |access-date=2008-04-19 |archive-date=2008-02-16 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080216045411/http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> The links were carted to [[New Windsor, New York|New Windsor]], where they were put together and floated down the river to West Point on logs late in April. |
|||
| ⚫ | The Hudson River's changing tides, strong current, and frequently unfavorable winds created adverse sailing conditions at West Point. Compounding this, the |
||
Including [[swivel]]s, [[Clevis fastener|clevise]]s, and anchors, the chain weighed 65 tons. For buoyancy, logs were cut into {{convert|16|ft|0|adj=on}} lengths, waterproofed, and joined by fours into rafts fastened to one another with {{convert|12|ft|adj=on}} timbers. Short sections of chain (10 links, a swivel, and a clevis) were attached across each raft then joined to create a continuous boom of chains and rafts once afloat. |
|||
Captain Thomas Machin, the artillery officer and engineer who had installed the chain at Fort Montgomery, directed installation across the river on 30 April 1778. Both ends were anchored to log cribs filled with rocks, the southern at a small cove on the west bank and northern at Constitution Island. The West Point side was protected by the Chain Battery and the Constitution Island side by the Marine Battery. |
Captain Thomas Machin, the artillery officer and engineer who had installed the chain at Fort Montgomery, directed installation across the river on 30 April 1778. Both ends were anchored to log cribs filled with rocks, the southern at a small cove on the west bank and the northern at Constitution Island. The West Point side was protected by the Chain Battery and the Constitution Island side by the Marine Battery. A system of pulleys, rollers, ropes, and mid-stream anchors were used to adjust the chain's tension to overcome the effects of river current and changing tide. Until 1783, the chain was removed each winter and reinstalled each spring to avoid destruction by ice. |
||
| ⚫ | The British never attempted to run the chain, in spite of [[Benedict Arnold]] claiming in correspondence with them that "a well-loaded ship could break the chain."<ref>[http://www.unc.edu/~chaos1/chain.html "The Great Chain"] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080907012534/http://www.unc.edu/~chaos1/chain.html |date=2008-09-07 }}, University of North Carolina</ref> Polish engineer and [[Patriot (American Revolution)|Patriot]] volunteer [[Tadeusz Kościuszko|Thaddeus Kościuszko]] contributed to the system of fortifications at West Point.<ref name="Storozynski">Storozynski, A., 2009, The Peasant Prince, New York: St. Martin's Press, {{ISBN|9780312388027}}</ref>{{rp|52–70}} |
||
A system of pulleys, rollers, ropes, and mid-stream anchors were used to adjust the chain's tension to overcome the effects of river current and changing tide. Until 1783 the chain was removed each winter and reinstalled each spring to avoid destruction by ice. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The British never attempted to run the chain, in spite of |
||
Polish engineer and Patriot volunteer [[Thaddeus Kościuszko]] contributed to the system of fortifications at West Point.<ref name=Storozynski>Storozynski, A., 2009, The Peasant Prince, New York: St. Martin's Press, {{ISBN|9780312388027}}</ref>{{rp|52–70}} |
|||
{{-}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Great Chain and Mortars.jpg|thumb|The Great Chain and mortars]] |
[[File:Great Chain and Mortars.jpg|thumb|The Great Chain and mortars]] |
||
[[File:The Great Chain Today.jpg|thumb|Part of The Great Chain at [[Trophy Point]] at West Point]] |
[[File:The Great Chain Today.jpg|thumb|Part of The Great Chain at [[Trophy Point]] at West Point]] |
||
After the |
After the war, part of the Great Chain was saved for posterity and the rest relegated to the West Point Foundry furnaces near [[Cold Spring, New York]], to be melted down.{{citation needed|reason=Not at the cite previously provided|date=August 2021}} A saved portion was first displayed at the West Point ordnance compound, along with a captured mortar, as shown in a 1905 drawing.<ref>West Point Museum e-mail correspondence</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | Thirteen links are displayed at [[Trophy Point]], one for each of the [[Thirteen Colonies]]. Also included are a swivel and clevis. The exhibit is maintained and preserved by the West Point Museum.<ref name="museum">{{cite web|url=http://www.usma.edu/museum|title=USMA: West Point Museum|access-date=2010-11-07}}</ref> A section of boom recovered from the river in 1855 is displayed at [[Washington's Headquarters State Historic Site]] in [[Newburgh, New York]]. |
||
| ⚫ | Two links of the original chain are also at [[Raynham Hall Museum|Raynham Hall]] in [[Oyster Bay (town), New York|Oyster Bay, New York]], the home of [[Robert Townsend (spy)|Robert Townsend]], a cousin of iron works owner Peter Townsend, and (as "Culper Jr") a member of [[George Washington]]’s [[Culper Ring|Culper spy ring]]. Bilking the gullible, John C. Abbey,{{who|date=August 2021}} and later Pollepel Island owner [[Pollepel Island#Bannerman's Castle|Francis Bannerman]], sold counterfeit chain links to collectors and museums.<ref>[http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm Diamant, ''The Chaining of the Hudson -- And Profiteering on History''] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080216045411/http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm |date=2008-02-16 }}, Hudson River{{clarify|“Hudson River” what?|date=August 2021}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Two links of the original chain are also |
Two links of the original chain are also displayed under a portrait of [[George Washington]] in the [[New York State Capitol]] [[File:Lansdowne portrait copy in New York State Capitol.jpg|thumb|Some of the Hudson River Chains located under a portrait of George Washington inside the New York State Capitol]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{-}} |
|||
==Bibliography== |
==Bibliography== |
||
*"Hudson River Chain", ''Harper's Encyclopedia of United States History'', Vol. IV, p. 447, Harper & Brothers Publishers, 1905. |
*"Hudson River Chain", ''Harper's Encyclopedia of United States History'', Vol. IV, p. 447, Harper & Brothers Publishers, 1905. |
||
| Line 89: | Line 73: | ||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20131103105206/http://www.scribd.com/doc/279854/West-Point-Fortifications West Point Fortifications] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20131103105206/http://www.scribd.com/doc/279854/West-Point-Fortifications West Point Fortifications] |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080907012534/http://www.unc.edu/~chaos1/chain.html The Great Chain] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080907012534/http://www.unc.edu/~chaos1/chain.html The Great Chain] |
||
* [http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm Chaining of the Hudson in 1778] |
* [http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm Chaining of the Hudson in 1778] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080216045411/http://www.hudsonriver.com/halfmoonpress/stories/0298link.htm |date=2008-02-16 }} |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080709042028/http://www.hhr.highlands.com/chain.htm The Great Chain] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080709042028/http://www.hhr.highlands.com/chain.htm The Great Chain] |
||
* [https://books.google.com/books?id=bkNjv-9mqocC&dq=hudson+river+chain&pg=PP1 |
* [https://books.google.com/books?id=bkNjv-9mqocC&dq=hudson+river+chain&pg=PP1 Chaining The Hudson] |
||
* [http://www.hudsonrivervalley.org/presscenter/newsLetters/gw2nypc.php George Washington's letter about the strategic importance of the Hudson]{{dead link|date=November 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
* [http://www.hudsonrivervalley.org/presscenter/newsLetters/gw2nypc.php George Washington's letter about the strategic importance of the Hudson]{{dead link|date=November 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
||
* [http://www.hudsonrivervalley.org/amerRevLesson/chainscript.php Contract for the forging of The Great Chain]{{dead link|date=November 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
* [http://www.hudsonrivervalley.org/amerRevLesson/chainscript.php Contract for the forging of The Great Chain]{{dead link|date=November 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
||
Latest revision as of 16:11, 11 November 2024
The Hudson River Chains were a series of chain booms constructed across the Hudson River at West Point by Continental Army forces from 1776 to 1778 during the American Revolutionary War. These served as defenses preventing British naval vessels from sailing upriver and were overseen by the Highlands Department of the Continental Army.
The first chain was destroyed by British forces in the aftermath of the Battle of Forts Clinton and Montgomery in October 1777. The more significant and successful was the Great Chain, constructed in 1778 and used through war's end in 1782. Two other barriers across the river, referred to as chevaux-de-frise, were undertaken by the Colonials; the first, between Fort Washington on the island of Manhattan, and Fort Lee in New Jersey, was completed in 1776 and shortly seized by the British; another was started in 1776 between Plum Point on the east bank and Pollepel Island north of West Point but abandoned in 1777 in favor of completion of the Great Chain nearby the following year.

Background
[edit]Even before the April 1775 Battles of Lexington and Concord in Massachusetts, both the Americans and British knew that passage on the Hudson River was strategically important to each sides’ war effort. The Americans were desperate to control the river, lest New England be divided from the rest of the colonies. The immediate American plan was to slow or block ship traffic on the river by attacking British vessels with cannon and mortars from both shores. This anticipated batteries at both existing and planned defensive fortifications. In late 1776 Henry Wisner, a resident of Goshen, New York, and one of New York's representatives to the Continental Congress, along with Gilbert Livingston, sounded the Hudson River and, as part of a Secret Committee of the "Committee of Safety," recommended the placement of chains in strategic locations along the Hudson.[1]
Colonial forces eventually constructed three obstacles across the river: a chevaux-de-frise at northern Manhattan between Forts Washington and Lee in 1776; at the lower entrance to the Hudson Highlands, from newly constructed Fort Montgomery on the west bank at Popolopen Creek just north of the modern-day Bear Mountain Bridge to Anthony's Nose on the east bank in 1776–1777; and between West Point and Constitution Island in 1778, known as the Great Chain. A fourth, a cheval-de-frise started in 1776 between Plum Point on the east bank and Pollepel Island north of West Point, was begun but abandoned. The first two were promptly captured by the British, while the Great Chain, the largest and most important of the projects, was reset each spring until the end of the war. Attention was concentrated on the West Point area because the river narrowed and curved so sharply there that ships slowed in navigating the passage by shifting winds, tides, and current made optimal targets.
Fort Lee to Fort Washington chevaux-de-frise (1776)
[edit]
In 1776 the Continental Army constructed an array of logs sunk underwater between Fort Washington on the island of Manhattan and Fort Lee across the river in New Jersey. Built to a design of Scottish engineer turned Colonial sympathizer Robert Erskine, the logs were intended to pierce and sink any British ships that passed over them. An opening was left for the passage of American ships.
After the British learned of the opening from a local resident, they successfully passed through the barrier several times.[2] The British successfully captured both forts in the Battle of Fort Washington on November 16, 1776, and Battle of Fort Lee on November 20, putting the defensive barrier in their hands. This change had little impact, as the nascent Continental Navy lacked ships of the size and power of the British, leaving it to resort to small and more maneuverable vessels regardless.
Fort Montgomery chain (1776–1777)
[edit]In 1776 a chain and boom were stretched across the river from Fort Montgomery on the west bank, at the lower entrance to the Highlands just north of the modern-day Bear Mountain Bridge, to Anthony's Nose on the east bank. Captain Thomas Machin headed the chain effort. In November 1776, a faulty link broke under stress induced by the river current, highlighting some of the difficulties of trying to chain the Hudson.[3] It was repaired and reset.
After the British captured forts Montgomery and Clinton, a second fortress built opposite it at the mouth of Popolopen's Kill (today's Popolopen Creek) on its south bank, on 6 October 6 1777, they dismantled the chain.[4] Free to do so, they raided upriver as far as Kingston, then the capitol of New York State, putting the torch to it and burning all but several of its hundreds of buildings to the ground.
Governor George Clinton, a member of the committee assigned by the New York Convention to devise a means of defending the Hudson, was heartened as the British had never attempted to run ships through the chain.[5] He concluded that the basic idea of obstructing the river seemed sound. After Captain Machin recovered from wounds from battle with the British, he began work on the stronger Great Chain at West Point, which was constructed and installed in 1778.
Pollepel Island chevaux-de-frise (1776–1777)
[edit]Another cheval-de-frise was undertaken across the Hudson between Plum Point on the east bank and Pollepel Island north of West Point. The defenses were never fully completed, and its importance was overshadowed by completion of the Great Chain at West Point the following year.
Great Chain (1778–1782)
[edit]
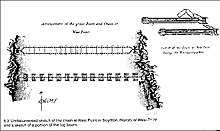
and log boom

In the spring of 1778, a heavy chain supported by huge log rafts was stretched across the Hudson from West Point to Constitution Island to impede the movement of British ships north of West Point. A second log boom (resembling a ladder in construction) spanned the river about 100 yards (90 m) downstream to absorb the impact of any ship attempting to breach the barrier.
The Hudson River's changing tides, strong current, and frequently unfavorable winds created adverse sailing conditions at West Point. Compounding this, the river's narrow width and sharp "S-Curve" there forced any large ship to tack in order to navigate it. Cannon were placed in forts and artillery batteries on both sides of the river to attack ships when they were slowed to a halt by the Patriot barrier placed there.
The chain was constructed over six weeks at the Sterling Iron Works in Warwick, Orange County, of chain links from Long Pond Iron Works in Ringwood, New Jersey. When completed, the 600-yard (550 m) chain contained iron links two feet (0.6 m) in length, weighing 140 to 180 pounds (64 to 82 kg).[6] The links were carted to New Windsor, where they were put together and floated down the river to West Point on logs late in April.
Including swivels, clevises, and anchors, the chain weighed 65 tons. For buoyancy, logs were cut into 16-foot (5 m) lengths, waterproofed, and joined by fours into rafts fastened to one another with 12-foot (3.7 m) timbers. Short sections of chain (10 links, a swivel, and a clevis) were attached across each raft then joined to create a continuous boom of chains and rafts once afloat.
Captain Thomas Machin, the artillery officer and engineer who had installed the chain at Fort Montgomery, directed installation across the river on 30 April 1778. Both ends were anchored to log cribs filled with rocks, the southern at a small cove on the west bank and the northern at Constitution Island. The West Point side was protected by the Chain Battery and the Constitution Island side by the Marine Battery. A system of pulleys, rollers, ropes, and mid-stream anchors were used to adjust the chain's tension to overcome the effects of river current and changing tide. Until 1783, the chain was removed each winter and reinstalled each spring to avoid destruction by ice.
The British never attempted to run the chain, in spite of Benedict Arnold claiming in correspondence with them that "a well-loaded ship could break the chain."[7] Polish engineer and Patriot volunteer Thaddeus Kościuszko contributed to the system of fortifications at West Point.[8]: 52–70
Memorials
[edit]

After the war, part of the Great Chain was saved for posterity and the rest relegated to the West Point Foundry furnaces near Cold Spring, New York, to be melted down.[citation needed] A saved portion was first displayed at the West Point ordnance compound, along with a captured mortar, as shown in a 1905 drawing.[9]
Thirteen links are displayed at Trophy Point, one for each of the Thirteen Colonies. Also included are a swivel and clevis. The exhibit is maintained and preserved by the West Point Museum.[10] A section of boom recovered from the river in 1855 is displayed at Washington's Headquarters State Historic Site in Newburgh, New York.
Two links of the original chain are also at Raynham Hall in Oyster Bay, New York, the home of Robert Townsend, a cousin of iron works owner Peter Townsend, and (as "Culper Jr") a member of George Washington’s Culper spy ring. Bilking the gullible, John C. Abbey,[who?] and later Pollepel Island owner Francis Bannerman, sold counterfeit chain links to collectors and museums.[11]
Two links of the original chain are also displayed under a portrait of George Washington in the New York State Capitol

Bibliography
[edit]- "Hudson River Chain", Harper's Encyclopedia of United States History, Vol. IV, p. 447, Harper & Brothers Publishers, 1905.
- Information plaques at Trophy Point at West Point, New York.
- "West Point Fortifications", Scribd
- U.S. Military Academy Department of History, West Point Fortifications Staff Ride Notecards, second edition (1998)
References
[edit]- ^ Letter from Henry Wisner and Gilbert Livingston to New-York Committee of Safety: Soundings of Hudson river in the Highlands American Archives Series 5, Volume 3, Page 0812 November 22, 1776. http://lincoln.lib.niu.edu/cgi-bin/amarch/getdoc.pl?/var/lib/philologic/databases/amarch/.27283 Archived 2014-12-04 at the Wayback Machine Accessed February 19, 2015.
- ^ Diamant, Chaining The Hudson, 1989
- ^ Diamant, Chaining the Hudson, 1989, p 105
- ^ West Point Fortifications Archived 2013-11-03 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Diamant, Chaining the Hudson, p. 122
- ^ ""Explore the Hudson River's Rich History; A Chain Across the Hudson", Rebecca Haynes, hudsonriver.com". Archived from the original on 2008-02-16. Retrieved 2008-04-19.
- ^ "The Great Chain" Archived 2008-09-07 at the Wayback Machine, University of North Carolina
- ^ Storozynski, A., 2009, The Peasant Prince, New York: St. Martin's Press, ISBN 9780312388027
- ^ West Point Museum e-mail correspondence
- ^ "USMA: West Point Museum". Retrieved 2010-11-07.
- ^ Diamant, The Chaining of the Hudson -- And Profiteering on History Archived 2008-02-16 at the Wayback Machine, Hudson River[clarification needed]
External links
[edit]- Merle Sheffield, The Chain and Boom, Hudson River Valley, official website
- West Point Fortifications
- The Great Chain
- Chaining of the Hudson in 1778 Archived 2008-02-16 at the Wayback Machine
- The Great Chain
- Chaining The Hudson
- George Washington's letter about the strategic importance of the Hudson[permanent dead link]
- Contract for the forging of The Great Chain[permanent dead link]
- New York Times Article about The Chain February 17, 1895
- Chain Salvaging Blurb
- "Revolutionary West Point: 'The Key to the Continent'",

