25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase: Difference between revisions
Artoria2e5 (talk | contribs) m Artoria2e5 moved page 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1-alpha-hydroxylase to 25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase: uniprot rename |
m →Further reading: task, replaced: Multiple Sclerosis (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) → Multiple Sclerosis |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Mammalian protein found in humans}} |
|||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase}} |
{{DISPLAYTITLE:25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase}} |
||
{{Infobox_gene}} |
{{Infobox_gene}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
'''25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase''' (VD 1A hydroxylase) also known as '''cytochrome p450 27B1''' (CYP27B1) or simply '''1-alpha-hydroxylase''' is a [[cytochrome P450]] [[enzyme]] that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP27B1'' [[gene]].<ref name="entrez">{{cite web | title = Entrez Gene: cytochrome P450| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1594 |
'''25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase''' (VD 1A hydroxylase) also known as '''calcidiol 1-monooxygenase''' <ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/25-hydroxyvitamin-d3-1-alpha-hydroxylase | title=25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1-Alpha-Hydroxylase - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics }}</ref> or '''cytochrome p450 27B1''' (CYP27B1) or simply '''1-alpha-hydroxylase''' is a [[cytochrome P450]] [[enzyme]] that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP27B1'' [[gene]].<ref name="entrez">{{cite web | title = Entrez Gene: cytochrome P450| url = https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1594}}</ref><ref name="pmid9295274">{{cite journal | vauthors = Takeyama K, Kitanaka S, Sato T, Kobori M, Yanagisawa J, Kato S | title = 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase and vitamin D synthesis | journal = Science | volume = 277 | issue = 5333 | pages = 1827–30 | date = Sep 1997 | pmid = 9295274 | doi = 10.1126/science.277.5333.1827 }}</ref><ref name="pmid9344864">{{cite journal | vauthors = Monkawa T, Yoshida T, Wakino S, Shinki T, Anazawa H, Deluca HF, Suda T, Hayashi M, Saruta T | title = Molecular cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA for human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1 alpha-hydroxylase | journal = Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications | volume = 239 | issue = 2 | pages = 527–33 | date = Oct 1997 | pmid = 9344864 | doi = 10.1006/bbrc.1997.7508 }}</ref> |
||
VD 1A hydroxylase is located in the [[proximal tubule]] of the [[kidney]] and a variety of other tissues, including skin ([[keratinocyte]]s), immune cells,<ref name="pmid17259988">{{cite journal | vauthors = Sigmundsdottir H, Pan J, Debes GF, Alt C, Habtezion A, Soler D, Butcher EC | s2cid = 9540123 | title = DCs metabolize sunlight-induced vitamin D3 to 'program' T cell attraction to the epidermal chemokine CCL27 | journal = Nature Immunology | volume = 8 | issue = 3 | pages = 285–93 | date = Mar 2007 | pmid = 17259988 | doi = 10.1038/ni1433 | url = http://www.biochem.wisc.edu/courses/biochem901/secure/materials/readings/08Sigmundsdottir_etal.pdf }}{{Dead link|date=April 2019 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> and bone ([[osteoblast]]s).<ref name="pmid20739402">{{cite journal | vauthors = Kogawa M, Findlay DM, Anderson PH, Ormsby R, Vincent C, Morris HA, Atkins GJ | title = Osteoclastic metabolism of 25(OH)-vitamin D3: a potential mechanism for optimization of bone resorption | journal = Endocrinology | volume = 151 | issue = 10 | pages = 4613–25 | date = Oct 2010 | pmid = 20739402 | doi = 10.1210/en.2010-0334 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
== Reactions == |
|||
The [[enzyme]] catalyzes the [[hydroxylation]] of [[calcifediol]] to [[calcitriol]] (the bioactive form of [[Vitamin D]]):<ref name="pmid4404596">{{cite journal | vauthors = Gray RW, Omdahl JL, Ghazarian JG, DeLuca HF | title = 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol-1-hydroxylase. Subcellular location and properties | journal = The Journal of Biological Chemistry | volume = 247 | issue = 23 | pages = 7528–32 | date = Dec 1972 | doi = 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)44557-2 | pmid = 4404596 | doi-access = free }}</ref> |
|||
:calcidiol + 2 reduced [[adrenodoxin reductase|adrenodoxin]] + 2 H<sup>+</sup> + O<sub>2</sub> {{eqm}} calcitriol + 2 oxidized adrenodoxin + H<sub>2</sub>O |
:calcidiol + 2 reduced [[adrenodoxin reductase|adrenodoxin]] + 2 H<sup>+</sup> + O<sub>2</sub> {{eqm}} calcitriol + 2 oxidized adrenodoxin + H<sub>2</sub>O |
||
The enzyme is also able to oxidize ercalcidiol (25-OH D2) to ercalcitriol, secalciferol to calcitetrol, and 25-hydroxy-24-oxocalciol to (1S)-1,25-dihydroxy-24-oxocalciol.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sawada |first1=N |last2=Sakaki |first2=T |last3=Kitanaka |first3=S |last4=Takeyama |first4=K |last5=Kato |first5=S |last6=Inouye |first6=K |title=Enzymatic properties of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase coexpression with adrenodoxin and NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase in Escherichia coli. |journal=European |
The enzyme is also able to oxidize ercalcidiol (25-OH D2) to ercalcitriol, secalciferol to calcitetrol, and 25-hydroxy-24-oxocalciol to (1S)-1,25-dihydroxy-24-oxocalciol.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sawada |first1=N |last2=Sakaki |first2=T |last3=Kitanaka |first3=S |last4=Takeyama |first4=K |last5=Kato |first5=S |last6=Inouye |first6=K |title=Enzymatic properties of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase coexpression with adrenodoxin and NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase in Escherichia coli. |journal=European Journal of Biochemistry |date=November 1999 |volume=265 |issue=3 |pages=950–6 |doi=10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00794.x |pmid=10518789|doi-access=free }}</ref> |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
| Line 15: | Line 28: | ||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== Clinical significance == |
|||
{| |
|||
Loss-of-function mutations in CYP27B1 cause [[Rickets#Types|Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type IA]].<ref>{{cite web |title=# 264700 - VITAMIN D HYDROXYLATION-DEFICIENT RICKETS, TYPE 1A; VDDR1A |url=https://www.omim.org/entry/264700 |website=www.omim.org |language=en-us}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| IUBMB_EC_number = 1/14/13/13 |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
|} |
|||
==Interactive pathway map== |
==Interactive pathway map== |
||
| Line 36: | Line 39: | ||
== Further reading == |
== Further reading == |
||
{{refbegin | 2}} |
{{refbegin | 2}} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Carr EJ, Niederer HA, Williams J, Harper L, Watts RA, Lyons PA, Smith KG | title = Confirmation of the genetic association of CTLA4 and PTPN22 with ANCA-associated vasculitis | journal = BMC Medical Genetics | volume = 10 | pages = 121 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19951419 | pmc = 3224698 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2350-10-121 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Carr EJ, Niederer HA, Williams J, Harper L, Watts RA, Lyons PA, Smith KG | title = Confirmation of the genetic association of CTLA4 and PTPN22 with ANCA-associated vasculitis | journal = BMC Medical Genetics | volume = 10 | pages = 121 | year = 2009 | pmid = 19951419 | pmc = 3224698 | doi = 10.1186/1471-2350-10-121 | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Alzahrani AS, Zou M, Baitei EY, Alshaikh OM, Al-Rijjal RA, Meyer BF, Shi Y | title = A novel G102E mutation of CYP27B1 in a large family with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1 | journal = The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism | volume = 95 | issue = 9 | pages = 4176–83 | date = Sep 2010 | pmid = 20534770 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2009-2278 | doi-access = free }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Alzahrani AS, Zou M, Baitei EY, Alshaikh OM, Al-Rijjal RA, Meyer BF, Shi Y | title = A novel G102E mutation of CYP27B1 in a large family with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1 | journal = The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism | volume = 95 | issue = 9 | pages = 4176–83 | date = Sep 2010 | pmid = 20534770 | doi = 10.1210/jc.2009-2278 | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Lagishetty V, Chun RF, Liu NQ, Lisse TS, Adams JS, Hewison M | title = 1alpha-hydroxylase and innate immune responses to 25-hydroxyvitamin D in colonic cell lines | journal = The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology | volume = 121 | issue = 1–2 | pages = 228–33 | date = Jul 2010 | pmid = 20152900 | pmc = 2891066 | doi = 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.02.004 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Lagishetty V, Chun RF, Liu NQ, Lisse TS, Adams JS, Hewison M | title = 1alpha-hydroxylase and innate immune responses to 25-hydroxyvitamin D in colonic cell lines | journal = The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology | volume = 121 | issue = 1–2 | pages = 228–33 | date = Jul 2010 | pmid = 20152900 | pmc = 2891066 | doi = 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.02.004 }} |
||
| Line 45: | Line 48: | ||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Shen H, Bielak LF, Ferguson JF, Streeten EA, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Liu J, Post W, O'Connell JR, Hixson JE, Kardia SL, Sun YV, Jhun MA, Wang X, Mehta NN, Li M, Koller DL, Hakonarson H, Keating BJ, Rader DJ, Shuldiner AR, Peyser PA, Reilly MP, Mitchell BD | title = Association of the vitamin D metabolism gene CYP24A1 with coronary artery calcification | journal = Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology | volume = 30 | issue = 12 | pages = 2648–54 | date = Dec 2010 | pmid = 20847308 | pmc = 2988112 | doi = 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.211805 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Shen H, Bielak LF, Ferguson JF, Streeten EA, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Liu J, Post W, O'Connell JR, Hixson JE, Kardia SL, Sun YV, Jhun MA, Wang X, Mehta NN, Li M, Koller DL, Hakonarson H, Keating BJ, Rader DJ, Shuldiner AR, Peyser PA, Reilly MP, Mitchell BD | title = Association of the vitamin D metabolism gene CYP24A1 with coronary artery calcification | journal = Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology | volume = 30 | issue = 12 | pages = 2648–54 | date = Dec 2010 | pmid = 20847308 | pmc = 2988112 | doi = 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.211805 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Sundqvist E, Bäärnhielm M, Alfredsson L, Hillert J, Olsson T, Kockum I | title = Confirmation of association between multiple sclerosis and CYP27B1 | journal = European Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 18 | issue = 12 | pages = 1349–52 | date = Dec 2010 | pmid = 20648053 | pmc = 3002863 | doi = 10.1038/ejhg.2010.113 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Sundqvist E, Bäärnhielm M, Alfredsson L, Hillert J, Olsson T, Kockum I | title = Confirmation of association between multiple sclerosis and CYP27B1 | journal = European Journal of Human Genetics | volume = 18 | issue = 12 | pages = 1349–52 | date = Dec 2010 | pmid = 20648053 | pmc = 3002863 | doi = 10.1038/ejhg.2010.113 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Fichna M, Zurawek M, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Gryczyñska M, Fichna P, Sowiñski J, Nowak J | title = Association of the CYP27B1 C(-1260)A polymorphism with autoimmune Addison's disease | journal = Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes | volume = 118 | issue = 8 | pages = 544–9 | date = Aug 2010 | pmid = 19998245 | doi = 10.1055/s-0029-1241206 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Fichna M, Zurawek M, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Gryczyñska M, Fichna P, Sowiñski J, Nowak J | title = Association of the CYP27B1 C(-1260)A polymorphism with autoimmune Addison's disease | journal = Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes | volume = 118 | issue = 8 | pages = 544–9 | date = Aug 2010 | pmid = 19998245 | doi = 10.1055/s-0029-1241206 | s2cid = 5609583 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Holt SK, Kwon EM, Koopmeiners JS, Lin DW, Feng Z, Ostrander EA, Peters U, Stanford JL | title = Vitamin D pathway gene variants and prostate cancer prognosis | journal = The Prostate | volume = 70 | issue = 13 | pages = 1448–60 | date = Sep 2010 | pmid = 20687218 | pmc = 2927712 | doi = 10.1002/pros.21180 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Holt SK, Kwon EM, Koopmeiners JS, Lin DW, Feng Z, Ostrander EA, Peters U, Stanford JL | title = Vitamin D pathway gene variants and prostate cancer prognosis | journal = The Prostate | volume = 70 | issue = 13 | pages = 1448–60 | date = Sep 2010 | pmid = 20687218 | pmc = 2927712 | doi = 10.1002/pros.21180 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Bu FX, Armas L, Lappe J, Zhou Y, Gao G, Wang HW, Recker R, Zhao LJ | s2cid = 5782938 | title = Comprehensive association analysis of nine candidate genes with serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels among healthy Caucasian subjects | journal = Human Genetics | volume = 128 | issue = 5 | pages = 549–56 | date = Nov 2010 | pmid = 20809279 | doi = 10.1007/s00439-010-0881-9 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Bu FX, Armas L, Lappe J, Zhou Y, Gao G, Wang HW, Recker R, Zhao LJ | s2cid = 5782938 | title = Comprehensive association analysis of nine candidate genes with serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels among healthy Caucasian subjects | journal = Human Genetics | volume = 128 | issue = 5 | pages = 549–56 | date = Nov 2010 | pmid = 20809279 | doi = 10.1007/s00439-010-0881-9 }} |
||
| Line 52: | Line 55: | ||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Liu CY, Wu MC, Chen F, Ter-Minassian M, Asomaning K, Zhai R, Wang Z, Su L, Heist RS, [[Matthew Kulke|Kulke MH]], Lin X, Liu G, Christiani DC | title = A Large-scale genetic association study of esophageal adenocarcinoma risk | journal = Carcinogenesis | volume = 31 | issue = 7 | pages = 1259–63 | date = Jul 2010 | pmid = 20453000 | pmc = 2893800 | doi = 10.1093/carcin/bgq092 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Liu CY, Wu MC, Chen F, Ter-Minassian M, Asomaning K, Zhai R, Wang Z, Su L, Heist RS, [[Matthew Kulke|Kulke MH]], Lin X, Liu G, Christiani DC | title = A Large-scale genetic association study of esophageal adenocarcinoma risk | journal = Carcinogenesis | volume = 31 | issue = 7 | pages = 1259–63 | date = Jul 2010 | pmid = 20453000 | pmc = 2893800 | doi = 10.1093/carcin/bgq092 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Sunyer J, Basagaña X, González JR, Júlvez J, Guerra S, Bustamante M, de Cid R, Antó JM, Torrent M | title = Early life environment, neurodevelopment and the interrelation with atopy | journal = Environmental Research | volume = 110 | issue = 7 | pages = 733–8 | date = Oct 2010 | pmid = 20701904 | doi = 10.1016/j.envres.2010.07.005 | bibcode = 2010ER....110..733S }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Sunyer J, Basagaña X, González JR, Júlvez J, Guerra S, Bustamante M, de Cid R, Antó JM, Torrent M | title = Early life environment, neurodevelopment and the interrelation with atopy | journal = Environmental Research | volume = 110 | issue = 7 | pages = 733–8 | date = Oct 2010 | pmid = 20701904 | doi = 10.1016/j.envres.2010.07.005 | bibcode = 2010ER....110..733S }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Simon KC, Munger KL, Ascherio A | title = Polymorphisms in vitamin D metabolism related genes and risk of multiple sclerosis | journal = Multiple Sclerosis |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Simon KC, Munger KL, Ascherio A | title = Polymorphisms in vitamin D metabolism related genes and risk of multiple sclerosis | journal = Multiple Sclerosis | volume = 16 | issue = 2 | pages = 133–8 | date = Feb 2010 | pmid = 20007432 | pmc = 2819633 | doi = 10.1177/1352458509355069 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hendrickson SL, Lautenberger JA, Chinn LW, Malasky M, Sezgin E, Kingsley LA, Goedert JJ, Kirk GD, Gomperts ED, Buchbinder SP, Troyer JL, O'Brien SJ | title = Genetic variants in nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes influence AIDS progression | journal = PLOS ONE | volume = 5 | issue = 9 | pages = e12862 | year = 2010 | pmid = 20877624 | pmc = 2943476 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0012862 | bibcode = 2010PLoSO...512862H | editor1-last = Badger | editor1-first = Jonathan H. }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Hendrickson SL, Lautenberger JA, Chinn LW, Malasky M, Sezgin E, Kingsley LA, Goedert JJ, Kirk GD, Gomperts ED, Buchbinder SP, Troyer JL, O'Brien SJ | title = Genetic variants in nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes influence AIDS progression | journal = PLOS ONE | volume = 5 | issue = 9 | pages = e12862 | year = 2010 | pmid = 20877624 | pmc = 2943476 | doi = 10.1371/journal.pone.0012862 | bibcode = 2010PLoSO...512862H | editor1-last = Badger | editor1-first = Jonathan H. | doi-access = free }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Dusso AS, Brown AJ, Slatopolsky E | title = Vitamin D | journal = American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology | volume = 289 | issue = 1 | pages = F8–28 | date = Jul 2005 | pmid = 15951480 | doi = 10.1152/ajprenal.00336.2004 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Dusso AS, Brown AJ, Slatopolsky E | title = Vitamin D | journal = American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology | volume = 289 | issue = 1 | pages = F8–28 | date = Jul 2005 | pmid = 15951480 | doi = 10.1152/ajprenal.00336.2004 }} |
||
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Bailey SD, Xie C, Do R, Montpetit A, Diaz R, Mohan V, Keavney B, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Engert JC, Anand S | title = Variation at the NFATC2 locus increases the risk of thiazolidinedione-induced edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) study | journal = Diabetes Care | volume = 33 | issue = 10 | pages = 2250–3 | date = Oct 2010 | pmid = 20628086 | pmc = 2945168 | doi = 10.2337/dc10-0452 }} |
* {{cite journal | vauthors = Bailey SD, Xie C, Do R, Montpetit A, Diaz R, Mohan V, Keavney B, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Engert JC, Anand S | title = Variation at the NFATC2 locus increases the risk of thiazolidinedione-induced edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) study | journal = Diabetes Care | volume = 33 | issue = 10 | pages = 2250–3 | date = Oct 2010 | pmid = 20628086 | pmc = 2945168 | doi = 10.2337/dc10-0452 }} |
||
Latest revision as of 18:21, 12 November 2024
| calcidiol 1-monooxygenase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.14.15.18 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9081-36-1 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase (VD 1A hydroxylase) also known as calcidiol 1-monooxygenase [5] or cytochrome p450 27B1 (CYP27B1) or simply 1-alpha-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP27B1 gene.[6][7][8]
VD 1A hydroxylase is located in the proximal tubule of the kidney and a variety of other tissues, including skin (keratinocytes), immune cells,[9] and bone (osteoblasts).[10]
Reactions
[edit]The enzyme catalyzes the hydroxylation of calcifediol to calcitriol (the bioactive form of Vitamin D):[11]
- calcidiol + 2 reduced adrenodoxin + 2 H+ + O2 ⇌ calcitriol + 2 oxidized adrenodoxin + H2O
The enzyme is also able to oxidize ercalcidiol (25-OH D2) to ercalcitriol, secalciferol to calcitetrol, and 25-hydroxy-24-oxocalciol to (1S)-1,25-dihydroxy-24-oxocalciol.[12]
Clinical significance
[edit]Loss-of-function mutations in CYP27B1 cause Vitamin D-dependent rickets, type IA.[13]
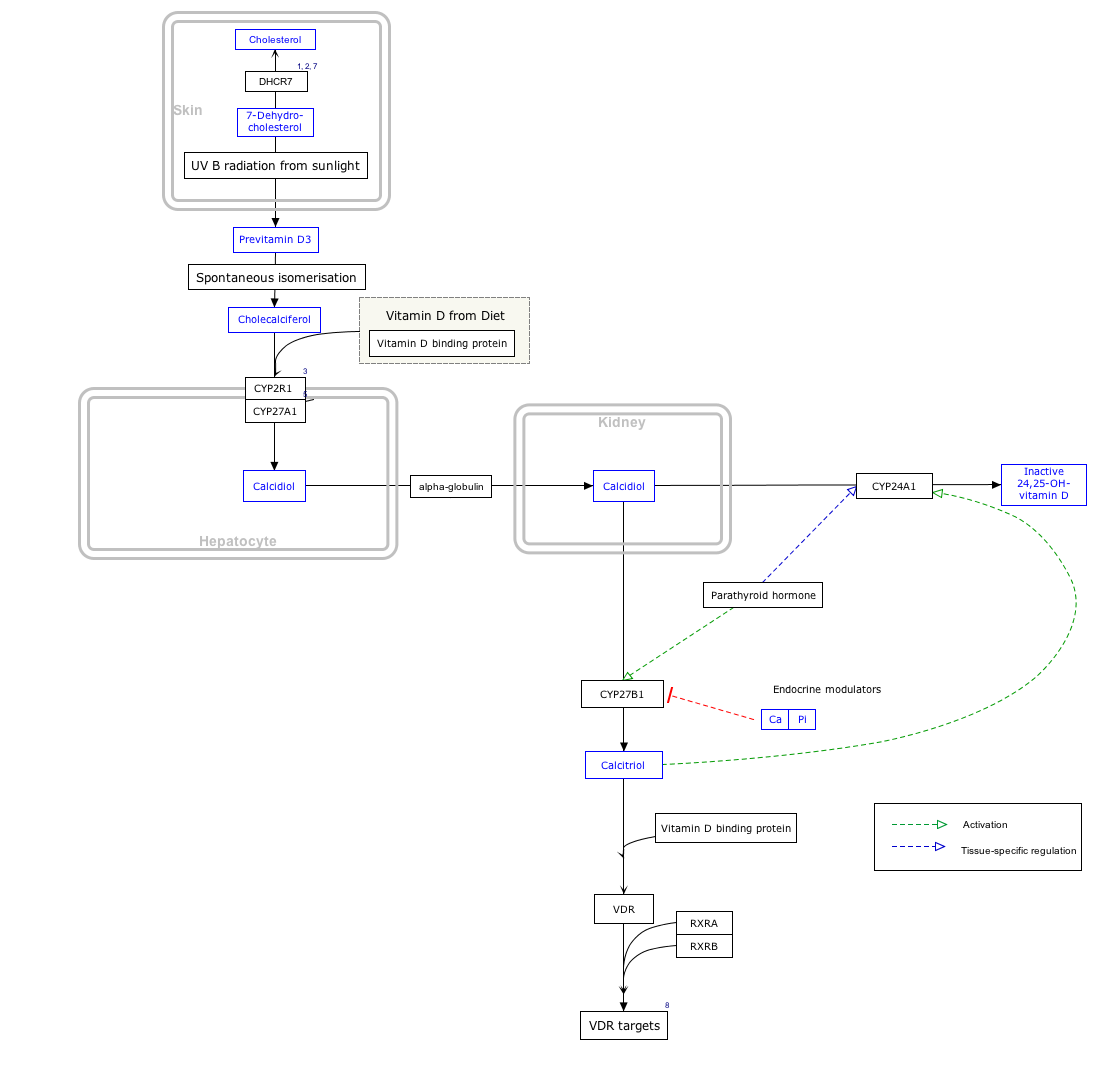
Interactive pathway map
[edit]Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000111012 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000006724 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1-Alpha-Hydroxylase - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics".
- ^ "Entrez Gene: cytochrome P450".
- ^ Takeyama K, Kitanaka S, Sato T, Kobori M, Yanagisawa J, Kato S (Sep 1997). "25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase and vitamin D synthesis". Science. 277 (5333): 1827–30. doi:10.1126/science.277.5333.1827. PMID 9295274.
- ^ Monkawa T, Yoshida T, Wakino S, Shinki T, Anazawa H, Deluca HF, Suda T, Hayashi M, Saruta T (Oct 1997). "Molecular cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA for human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1 alpha-hydroxylase". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 239 (2): 527–33. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7508. PMID 9344864.
- ^ Sigmundsdottir H, Pan J, Debes GF, Alt C, Habtezion A, Soler D, Butcher EC (Mar 2007). "DCs metabolize sunlight-induced vitamin D3 to 'program' T cell attraction to the epidermal chemokine CCL27" (PDF). Nature Immunology. 8 (3): 285–93. doi:10.1038/ni1433. PMID 17259988. S2CID 9540123.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Kogawa M, Findlay DM, Anderson PH, Ormsby R, Vincent C, Morris HA, Atkins GJ (Oct 2010). "Osteoclastic metabolism of 25(OH)-vitamin D3: a potential mechanism for optimization of bone resorption". Endocrinology. 151 (10): 4613–25. doi:10.1210/en.2010-0334. PMID 20739402.
- ^ Gray RW, Omdahl JL, Ghazarian JG, DeLuca HF (Dec 1972). "25-Hydroxycholecalciferol-1-hydroxylase. Subcellular location and properties". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 247 (23): 7528–32. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)44557-2. PMID 4404596.
- ^ Sawada, N; Sakaki, T; Kitanaka, S; Takeyama, K; Kato, S; Inouye, K (November 1999). "Enzymatic properties of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase coexpression with adrenodoxin and NADPH-adrenodoxin reductase in Escherichia coli". European Journal of Biochemistry. 265 (3): 950–6. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00794.x. PMID 10518789.
- ^ "# 264700 - VITAMIN D HYDROXYLATION-DEFICIENT RICKETS, TYPE 1A; VDDR1A". www.omim.org.
Further reading
[edit]- Carr EJ, Niederer HA, Williams J, Harper L, Watts RA, Lyons PA, Smith KG (2009). "Confirmation of the genetic association of CTLA4 and PTPN22 with ANCA-associated vasculitis". BMC Medical Genetics. 10: 121. doi:10.1186/1471-2350-10-121. PMC 3224698. PMID 19951419.
- Alzahrani AS, Zou M, Baitei EY, Alshaikh OM, Al-Rijjal RA, Meyer BF, Shi Y (Sep 2010). "A novel G102E mutation of CYP27B1 in a large family with vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 95 (9): 4176–83. doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2278. PMID 20534770.
- Lagishetty V, Chun RF, Liu NQ, Lisse TS, Adams JS, Hewison M (Jul 2010). "1alpha-hydroxylase and innate immune responses to 25-hydroxyvitamin D in colonic cell lines". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 121 (1–2): 228–33. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.02.004. PMC 2891066. PMID 20152900.
- Giroux S, Elfassihi L, Clément V, Bussières J, Bureau A, Cole DE, Rousseau F (Nov 2010). "High-density polymorphisms analysis of 23 candidate genes for association with bone mineral density". Bone. 47 (5): 975–81. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.06.030. PMID 20654748.
- Zhou S, LeBoff MS, Glowacki J (Jan 2010). "Vitamin D metabolism and action in human bone marrow stromal cells". Endocrinology. 151 (1): 14–22. doi:10.1210/en.2009-0969. PMC 2803155. PMID 19966181.
- Payne AH, Hales DB (Dec 2004). "Overview of steroidogenic enzymes in the pathway from cholesterol to active steroid hormones". Endocrine Reviews. 25 (6): 947–70. doi:10.1210/er.2003-0030. PMID 15583024.
- Maver A, Medica I, Salobir B, Tercelj M, Peterlin B (2010). "Lack of association of immune-response-gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to sarcoidosis in Slovenian patients". Genetics and Molecular Research. 9 (1): 58–68. doi:10.4238/vol9-1gmr682. PMID 20082271.
- Shen H, Bielak LF, Ferguson JF, Streeten EA, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Liu J, Post W, O'Connell JR, Hixson JE, Kardia SL, Sun YV, Jhun MA, Wang X, Mehta NN, Li M, Koller DL, Hakonarson H, Keating BJ, Rader DJ, Shuldiner AR, Peyser PA, Reilly MP, Mitchell BD (Dec 2010). "Association of the vitamin D metabolism gene CYP24A1 with coronary artery calcification". Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 30 (12): 2648–54. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.211805. PMC 2988112. PMID 20847308.
- Sundqvist E, Bäärnhielm M, Alfredsson L, Hillert J, Olsson T, Kockum I (Dec 2010). "Confirmation of association between multiple sclerosis and CYP27B1". European Journal of Human Genetics. 18 (12): 1349–52. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2010.113. PMC 3002863. PMID 20648053.
- Fichna M, Zurawek M, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Gryczyñska M, Fichna P, Sowiñski J, Nowak J (Aug 2010). "Association of the CYP27B1 C(-1260)A polymorphism with autoimmune Addison's disease". Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes. 118 (8): 544–9. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1241206. PMID 19998245. S2CID 5609583.
- Holt SK, Kwon EM, Koopmeiners JS, Lin DW, Feng Z, Ostrander EA, Peters U, Stanford JL (Sep 2010). "Vitamin D pathway gene variants and prostate cancer prognosis". The Prostate. 70 (13): 1448–60. doi:10.1002/pros.21180. PMC 2927712. PMID 20687218.
- Bu FX, Armas L, Lappe J, Zhou Y, Gao G, Wang HW, Recker R, Zhao LJ (Nov 2010). "Comprehensive association analysis of nine candidate genes with serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels among healthy Caucasian subjects". Human Genetics. 128 (5): 549–56. doi:10.1007/s00439-010-0881-9. PMID 20809279. S2CID 5782938.
- Fichna M, Zurawek M, Januszkiewicz-Lewandowska D, Fichna P, Nowak J (Oct 2010). "PTPN22, PDCD1 and CYP27B1 polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 1 diabetes in Polish patients". International Journal of Immunogenetics. 37 (5): 367–72. doi:10.1111/j.1744-313X.2010.00935.x. PMID 20518841. S2CID 19398299.
- Wjst M, Heimbeck I, Kutschke D, Pukelsheim K (Jul 2010). "Epigenetic regulation of vitamin D converting enzymes". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 121 (1–2): 80–3. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.056. PMID 20304056. S2CID 29338132.
- Liu CY, Wu MC, Chen F, Ter-Minassian M, Asomaning K, Zhai R, Wang Z, Su L, Heist RS, Kulke MH, Lin X, Liu G, Christiani DC (Jul 2010). "A Large-scale genetic association study of esophageal adenocarcinoma risk". Carcinogenesis. 31 (7): 1259–63. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq092. PMC 2893800. PMID 20453000.
- Sunyer J, Basagaña X, González JR, Júlvez J, Guerra S, Bustamante M, de Cid R, Antó JM, Torrent M (Oct 2010). "Early life environment, neurodevelopment and the interrelation with atopy". Environmental Research. 110 (7): 733–8. Bibcode:2010ER....110..733S. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2010.07.005. PMID 20701904.
- Simon KC, Munger KL, Ascherio A (Feb 2010). "Polymorphisms in vitamin D metabolism related genes and risk of multiple sclerosis". Multiple Sclerosis. 16 (2): 133–8. doi:10.1177/1352458509355069. PMC 2819633. PMID 20007432.
- Hendrickson SL, Lautenberger JA, Chinn LW, Malasky M, Sezgin E, Kingsley LA, Goedert JJ, Kirk GD, Gomperts ED, Buchbinder SP, Troyer JL, O'Brien SJ (2010). Badger JH (ed.). "Genetic variants in nuclear-encoded mitochondrial genes influence AIDS progression". PLOS ONE. 5 (9): e12862. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...512862H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012862. PMC 2943476. PMID 20877624.
- Dusso AS, Brown AJ, Slatopolsky E (Jul 2005). "Vitamin D". American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology. 289 (1): F8–28. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00336.2004. PMID 15951480.
- Bailey SD, Xie C, Do R, Montpetit A, Diaz R, Mohan V, Keavney B, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Engert JC, Anand S (Oct 2010). "Variation at the NFATC2 locus increases the risk of thiazolidinedione-induced edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) study". Diabetes Care. 33 (10): 2250–3. doi:10.2337/dc10-0452. PMC 2945168. PMID 20628086.
External links
[edit]- 25-Hydroxyvitamin+D3+1-alpha-Hydroxylase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human CYP27B1 genome location and CYP27B1 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Human VDR genome location and VDR gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.