Orange (fruit): Difference between revisions
rv, sub trivial |
m clean up, typo(s) fixed: onboard → on board |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Citrus fruit}} |
|||
{{taxobox |
|||
{{Redirect|Orange peel}} |
|||
|name = Orange |
|||
{{pp-semi-indef}} |
|||
|image = OrangeBloss_wb.jpg |
|||
{{pp-move}} |
|||
|image_caption = Orange blossoms and oranges on tree |
|||
{{good article}} |
|||
|image_width=250px |
|||
[[File:Oranges - whole-halved-segment.jpg|thumb|upright=1.35|Orange—whole, halved, and peeled segment]] |
|||
|regnum = [[Plantae]] |
|||
The '''orange''', also called '''sweet orange''' to distinguish it from the [[bitter orange]] (''Citrus × aurantium''), is the [[fruit]] of a tree in the [[family (biology)|family]] [[Rutaceae]]. Botanically, this is the hybrid [[Citrus × sinensis|''Citrus'' × ''sinensis'']], between the [[pomelo]] (''Citrus maxima'') and the [[mandarin orange]] (''Citrus reticulata''). The [[chloroplast]] [[genome]], and therefore the maternal line, is that of pomelo. There are many related hybrids including of mandarins and sweet orange. The sweet orange has had its full [[Whole genome sequencing|genome sequenced]]. |
|||
|unranked_divisio = [[Angiosperms]] |
|||
|unranked_classis = [[Eudicots]] |
|||
The orange originated in a region encompassing [[Southern China]], [[Northeast India]], and [[Myanmar]]; the earliest mention of the sweet orange was in [[Chinese literature]] in 314 BC. Orange trees are widely grown in tropical and subtropical areas for their sweet fruit. The fruit of the [[orange tree]] can be eaten fresh or processed for its juice or fragrant [[peel (fruit)|peel]]. In 2022, 76 million [[tonne]]s of oranges were grown worldwide, with [[Brazil]] producing 22% of the total, followed by [[India]] and [[China]]. |
|||
|unranked_ordo = [[Rosids]] |
|||
|ordo = [[Sapindales]] |
|||
Oranges, variously understood, have featured in human culture since ancient times. They first appear in Western art in the ''[[Arnolfini Portrait]]'' by [[Jan van Eyck]], but they had been depicted in Chinese art centuries earlier, as in Zhao Lingrang's [[Song dynasty]] fan painting ''Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines''. By the 17th century, an orangery had become an item of prestige in Europe, as seen at the [[Versailles Orangerie]]. More recently, artists such as [[Vincent van Gogh]], [[John Sloan]], and [[Henri Matisse]] included oranges in their paintings. |
|||
|familia = [[Rutaceae]] |
|||
|genus = ''[[Citrus]]'' |
|||
== Description == |
|||
|species = '''''C. ×sinensis''''' |
|||
|binomial = ''Citrus ×sinensis'' |
|||
The orange tree is a relatively small [[evergreen]], [[Flowering plant|flowering]] tree, with an average height of {{cvt|9|to|10|m}}, although some very old specimens can reach {{cvt|15|m}}.<ref name="webber4">{{cite book |editor-last1=Webber |editor-first1=Herbert John |editor-last2=''rev'' Walter Reuther and Harry W. Lawton |last=Hodgson |first=Willard |chapter=Chapter 4: Horticultural Varieties of Citrus |title=The Citrus Industry |publisher=University of California Division of Agricultural Sciences |year=1967–1989 |orig-year=1943 |location=Riverside, California |chapter-url=http://websites.lib.ucr.edu/agnic/webber/Vol1/Chapter4.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120205061009/http://websites.lib.ucr.edu/agnic/webber/Vol1/Chapter4.html |archive-date=2012-02-05}}</ref> Its oval [[leaf|leaves]], which are [[leaf arrangement|alternately arranged]], are {{convert|4|to|10|cm|in|abbr=on}} long and have [[crenulate]] margins.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.eol.org/pages/582206 |title=Sweet Orange – Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck (pro. sp.) – Overview – Encyclopedia of Life |website=[[Encyclopedia of Life]] |access-date=2011-01-18 |archive-date=2010-12-04 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101204135918/http://www.eol.org/pages/582206 |url-status=live }}</ref> Sweet oranges grow in a range of different sizes, and shapes varying from spherical to oblong. Inside and attached to the rind is a porous white tissue, the white, bitter [[mesocarp]] or albedo (''[[pith]]'').<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.yourdictionary.com/pith |title=Pith dictionary definition – pith defined |website=www.yourdictionary.com |access-date=2011-01-17 |archive-date=2011-05-12 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110512173111/http://www.yourdictionary.com/pith |url-status=live }}</ref> The orange contains a number of distinct ''[[carpel]]s'' (segments or pigs, botanically the fruits) inside, typically about ten, each delimited by a membrane and containing many [[Juice vesicles|juice-filled vesicles]] and usually a few [[seed|pips]]. When unripe, the fruit is green. The grainy irregular rind of the ripe fruit can range from bright orange to yellow-orange, but frequently retains green patches or, under warm climate conditions, remains entirely green. Like all other citrus fruits, the sweet orange is non-[[Climacteric (botany)|climacteric]], not ripening off the tree. The ''Citrus sinensis'' group is subdivided into four classes with distinct characteristics: common oranges, blood or pigmented oranges, navel oranges, and acidless oranges.<ref name=Kimball>{{cite book |last=Kimball |first=Dan A. |title=Citrus processing: a complete guide |publisher=Springer |edition=2d |date=June 30, 1999 |location=New York |page=450 |isbn=978-0-8342-1258-9}}</ref><ref name=Webber1>{{cite web |last1=Webber |first1=Herbert John |last2=Reuther |first2=Walter |last3=Lawton |first3=Harry W. |title=The Citrus Industry |publisher=[[University of California]] Division of Agricultural Sciences |year=1967–1989 |orig-year=1903 |location=Riverside, California |url=http://lib.ucr.edu/agnic/webber/ |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040604204203/http://lib.ucr.edu/agnic/webber/ |url-status=dead |archive-date=2004-06-04}}</ref><ref name=Sauls/> The fruit is a [[hesperidium]], a modified [[berry (botany)|berry]]; it is covered by a [[Peel (fruit)|rind]] formed by a rugged thickening of the [[Fruit anatomy#Pericarp layers|ovary wall]].<ref name="Bailey">Bailey, H. and Bailey, E. (1976). ''Hortus Third''. [[Cornell University]] MacMillan. N.Y. p. 275.</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.esu.edu/~milewski/intro_biol_two/lab_4_seeds_fruits/Seeds_and_Fruits.html |title=Seed and Fruits |website=esu.edu |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101114115047/http://www.esu.edu/~milewski/intro_biol_two/lab_4_seeds_fruits/Seeds_and_Fruits.html |archive-date=2010-11-14}}</ref> |
|||
|binomial_authority = ([[Carl Linnaeus|L.]]) [[Osbeck]]<ref> |
|||
{{cite web |
|||
<gallery mode=packed heights=155px> |
|||
|url=http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/taxon.pl?10782 |
|||
File:Orange Blossom.JPG|Flowers |
|||
|title=Citrus sinensis information from NPGS/GRIN |
|||
File:Orange tree fruiting.jpg|Fruit starting to develop |
|||
|publisher=www.ars-grin.gov |
|||
File:OrangeBloss wb.jpg|Flowers and fruit simultaneously |
|||
|accessdate=2008-03-17 |
|||
File:Laranxeira Naranjo GFDL.JPG|Mature tree in [[Galicia, Spain]], fruiting in November |
|||
|last= |
|||
File:Structure of an orange.svg|Structure of the botanical [[hesperidium]] |
|||
|first= |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== History == |
|||
<!--spaces left intentionally for maintainability--> |
|||
=== Hybrid origins === |
|||
''[[Citrus]]'' trees are [[angiosperms]], and most species are almost entirely [[Hybrid plant|interfertile]]. This includes [[grapefruit]]s, [[lemon]]s, [[lime (fruit)|limes]], oranges, and many [[citrus hybrids]]. As the interfertility of oranges and other citrus has produced numerous hybrids and [[cultivar]]s, and [[Sport (botany)|bud mutations]] have also been selected, [[citrus taxonomy]] has proven difficult.<ref name="Nicolosi">{{cite journal |doi=10.1007/s001220051419 |title=Citrus phylogeny and genetic origin of important species as investigated by molecular markers |year=2000 |last1=Nicolosi |first1=E. |last2=Deng |first2=Z. N. |last3=Gentile |first3=A. |last4=La Malfa |first4=S. |last5=Continella |first5=G. |last6=Tribulato |first6=E. |journal=[[Theoretical and Applied Genetics]] |volume=100 |issue=8 |pages=1155–1166 |s2cid=24057066 }}</ref> |
|||
The sweet orange, ''[[Citrus × sinensis|Citrus x sinensis]]'',<ref name="USDA">{{cite web |url=http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=CISI3 |title=Citrus ×sinensis (L.) Osbeck (pro sp.) (maxima × reticulata) sweet orange |work=Plants.USDA.gov |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110512023634/http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=CISI3 |archive-date=May 12, 2011 }}</ref> is not a wild fruit, but arose in [[domestication]] in East Asia. It originated in a region encompassing [[Southern China]], [[Northeast India]],<ref name="Morton 1987">{{cite book |title=Fruits of Warm Climates |last=Morton |first=Julia F. |year=1987 |pages=134–142 |url=https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/morton/orange.html |access-date=2020-05-05 |archive-date=2019-05-26 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190526032938/https://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/morton/orange.html |url-status=live }}</ref> and [[Myanmar]].<ref>{{cite book |title=The Genus Citrus |last1=Talon |first1=Manuel |last2=Caruso |first2=Marco |last3=Gmitter |first3=Fred G. Jr. |year=2020 |publisher=[[Woodhead Publishing]] |page=17 |isbn=978-0128122174 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dslaDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA17 |access-date=2020-05-05 |archive-date=2024-03-16 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240316051931/https://books.google.com/books?id=dslaDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA17#v=onepage&q&f=false |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The fruit was created as a cross between a non-pure [[mandarin orange]] and a hybrid [[pomelo]] that had a substantial mandarin component.<ref name=fullgenome>{{cite journal |doi=10.1038/ng.2472 |volume=45 |title=The draft genome of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) |journal=[[Nature Genetics]] |pages=59–66 |pmid=23179022 |date=Jan 2013 |last1=Xu |first1=Q. |last2=Chen |first2=L.L. |last3=Ruan |first3=X. |last4=Chen |first4=D. |last5=Zhu |first5=A. |last6=Chen |first6=C. |last7=Bertrand |first7=D. |last8=Jiao |first8=W.B. |last9=Hao |first9=B.H. |last10=Lyon |first10=M.P. |last11=Chen |first11=J. |last12=Gao |first12=S. |display-authors=6 |issue=1 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref name="AGLthesis">{{cite thesis |title=Organización de la diversidad genética de los cítricos |year=2013 |last=Andrés García Lor |url=https://riunet.upv.es/bitstream/handle/10251/31518/Versi%C3%B3n3.Tesis%20Andr%C3%A9s%20Garc%C3%ADa-Lor.pdf |page=79 |access-date=2015-04-24 |archive-date=2021-02-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210225034715/https://riunet.upv.es/bitstream/handle/10251/31518/Versi%C3%B3n3.Tesis%20Andr%C3%A9s%20Garc%C3%ADa-Lor.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Since its [[chloroplast DNA]] is that of pomelo, it was likely the hybrid pomelo, perhaps a pomelo [[backcrossing|BC1 backcross]], that was the maternal parent of the first orange.<ref name=genealogy_review>{{cite journal |doi=10.1038/nbt.2954 |volume=32 |issue=7 |title=A genealogy of the citrus family |journal=Nature Biotechnology |pages=640–642 |pmid=25004231 |last1=Velasco |first1=R. |last2=Licciardello |first2=C. |year=2014 |s2cid=9357494 |doi-access=free }}</ref><ref name=Wu>{{cite journal |title=Sequencing of diverse mandarin, pomelo and orange genomes reveals complex history of admixture during citrus domestication |journal=Nature Biotechnology |last=Wu |first=G. Albert |volume=32 |issue=7 |doi=10.1038/nbt.2906 |pages=656–662 |pmid=24908277 |pmc=4113729 |year=2014 }}</ref> Based on genomic analysis, the relative proportions of the ancestral species in the sweet orange are approximately 42% pomelo and 58% mandarin.<ref name="Wu Terol Ibanez 2018">{{cite journal |title=Genomics of the origin and evolution of ''Citrus'' |last1=Wu |first1=Guohong Albert |last2=Terol |first2=Javier |last3=Ibanez |first3=Victoria |last4=López-García |first4=Antonio |last5=Pérez-Román |first5=Estela |last6=Borredá |first6=Carles |last7=Domingo |first7=Concha |last8=Tadeo |first8=Francisco R. |last9=Carbonell-Caballero |first9=Jose |last10=Alonso |first10=Roberto |last11=Curk |first11=Franck |last12=Du |first12=Dongliang |last13=Ollitrault |first13=Patrick |last14=Roose |first14=Mikeal L. Roose |last15=Dopazo |first15=Joaquin |last16=Gmitter Jr |first16=Frederick G. |last17=Rokhsar |first17=Daniel |last18=Talon |first18=Manuel |display-authors=6 |journal=[[Nature (journal)|Nature]] |year=2018 |volume=554 |issue=7692 |pages=311–316 |doi=10.1038/nature25447 |pmid=29414943 |bibcode=2018Natur.554..311W |doi-access=free |hdl=20.500.11939/5741 |hdl-access=free}} and Supplement</ref> All varieties of the sweet orange descend from this prototype cross, differing only by mutations selected for during agricultural propagation.<ref name=Wu/> Sweet oranges have a distinct origin from the bitter orange, which arose independently, perhaps in the wild, from a cross between pure mandarin and pomelo parents.<ref name=Wu/> |
|||
Sweet oranges have in turn given rise to many further hybrids including the [[grapefruit]], which arose from a sweet orange x pomelo backcross. Spontaneous and engineered backcrosses between the sweet orange and mandarin oranges or tangerines have produced the [[clementine]] and [[murcott (fruit)|murcott]]<!--[[tangor]]s-->. The ambersweet is a complex sweet orange x (Orlando [[tangelo]] x clementine) hybrid.<ref name="Wu Terol Ibanez 2018"/><ref>{{cite journal |last1=Bai |first1=Jinhe |last2=Baldwin |first2=Elizabeth B. |last3=Hearn |first3=Jake |last4=Driggers |first4=Randy |last5=Stover |first5=Ed |title=Volatile Profile Comparison of USDA Sweet Orange-like Hybrids versus 'Hamlin' and 'Ambersweet' |year=2014 |journal=[[HortScience]] |volume=49 |issue=10 |pages=1262–1267 |url=http://hortsci.ashspublications.org/content/49/10/1262.full |doi=10.21273/HORTSCI.49.10.1262 |doi-access=free |access-date=2018-03-18 |archive-date=2016-07-21 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160721041615/http://hortsci.ashspublications.org/content/49/10/1262.full |url-status=live }}</ref> The [[citrange]]s are a group of sweet orange x [[trifoliate orange]] (''Citrus trifoliata'') hybrids.<ref>{{cite web |title=Trifoliate hybrids |url=http://citrusvariety.ucr.edu/citrus/trifoliatehybrids.html |website=University of California at Riverside, Givaudan Citrus Variety Collection |accessdate=15 March 2024 |archive-date=20 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220120113508/https://citrusvariety.ucr.edu/citrus/trifoliatehybrids.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Hybrid origins of orange.svg|thumb|center|upright=2|The orange is a [[Hybrid (biology)|hybrid]] of [[Mandarin orange|mandarin]] and [[pomelo]].<ref name="Wu Terol Ibanez 2018"/>]] |
|||
=== Arab Agricultural Revolution === |
|||
{{further|Arab Agricultural Revolution}} |
|||
[[File:Bayad-wa-riyadبياض-و-رياض-.jpg|thumb|upright|The [[Arab Agricultural Revolution]] spread citrus fruits as far as the Iberian Peninsula. Page from the ''[[Hadith Bayad wa Riyad]]'', 13th century]] |
|||
In Europe, the [[Moors]] introduced citrus fruits including the bitter orange, lemon, and lime to [[Al-Andalus]] in the [[Iberian Peninsula]] during the [[Arab Agricultural Revolution]].<ref name="Watson 1974">{{cite journal |last=Watson |first=Andrew M. |year=1974 |title=The Arab Agricultural Revolution and Its Diffusion, 700–1100 |journal=The Journal of Economic History |volume=34 |issue=1 |pages=8–35 |doi=10.1017/S0022050700079602 |jstor=2116954|s2cid=154359726 }}</ref> Large-scale cultivation started in the 10th century, as evidenced by complex irrigation techniques specifically adapted to support orange orchards.<ref>{{cite web |last=Trillo San José |first=Carmen |title=Water and landscape in Granada |url=http://canal.ugr.es/prensa-y-comunicacion/science-news-ugr/social-economic-and-legal-sciences/sugar-cane-cumin-and-orange-grove-crops-were-adapted-in-alandalus-from-the-10th-century/ |date=1 September 2003 |publisher=[[University of Granada]] |access-date=7 January 2017 |archive-date=8 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230308071051/http://canal.ugr.es/prensa-y-comunicacion/science-news-ugr/social-economic-and-legal-sciences/sugar-cane-cumin-and-orange-grove-crops-were-adapted-in-alandalus-from-the-10th-century/ |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Watson 1974"/> Citrus fruits—among them the bitter orange—were introduced to Sicily in the 9th century during the period of the [[Emirate of Sicily]], but the sweet orange was unknown there until the late 15th century or the beginnings of the 16th century, when Italian and Portuguese merchants brought orange trees into the Mediterranean area.<ref name="Morton 1987"/> |
|||
=== Spread across Europe === |
|||
Shortly afterward, the sweet orange quickly was adopted as an edible fruit. It was considered a luxury food grown by wealthy people in private conservatories, called [[orangerie]]s. By 1646, the sweet orange was well known throughout Europe; it went on to become the most often cultivated of all fruit trees.<ref name="Morton 1987"/> [[Louis XIV]] of France had a great love of orange trees and built the grandest of all royal [[Orangerie of Versailles|Orangeries]] at the [[Palace of Versailles]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Leroux |first=Jean-Baptiste |title=The Gardens of Versailles |publisher=[[Thames & Hudson]] |year=2002 |page=368}}</ref> At Versailles, potted orange trees in solid silver tubs were placed throughout the rooms of the palace, while the Orangerie allowed year-round cultivation of the fruit to supply the court. When Louis condemned his finance minister, [[Nicolas Fouquet]], in 1664, part of the treasures that he confiscated were over 1,000 orange trees from Fouquet's estate at [[Vaux-le-Vicomte]].<ref>{{cite book |last=Mitford |first=Nancy |author-link=Nancy Mitford |title=The Sun King |publisher=[[Sphere Books]] |year=1966 |page=11}}</ref> |
|||
=== To the Americas === |
|||
{{further|Columbian exchange}} |
|||
Spanish travelers introduced the sweet orange to the American continent. On his second voyage in 1493, [[Christopher Columbus]] may have planted the fruit on [[Hispaniola]].<ref name=Sauls>{{cite web |last=Sauls |first=Julian W. |title=Home Fruit Production – Oranges |url=http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/citrus/oranges.htm |publisher=[[Texas A&M University]] |access-date=30 November 2012 |date=December 1998 |archive-date=10 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230510155730/https://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/citrus/oranges.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Subsequent expeditions in the mid-1500s brought sweet oranges to South America and Mexico, and to Florida in 1565, when [[Pedro Menéndez de Avilés]] founded [[St. Augustine, Florida|St Augustine]]. [[Spanish missions in Arizona|Spanish missionaries]] brought orange trees to Arizona between 1707 and 1710, while the [[Spanish missions in California|Franciscans]] did the same in San Diego, California, in 1769.<ref name="Morton 1987"/> [[Archibald Menzies]], the botanist on the [[Vancouver Expedition]], collected orange seeds in South Africa, raised the seedlings on board, and gave them to several Hawaiian chiefs in 1792. The sweet orange came to be grown across the [[Hawaiian Islands]], but its cultivation stopped after the arrival of the [[Ceratitis capitata|Mediterranean fruit fly]] in the early 1900s.<ref name="Morton 1987"/><ref>{{cite web |last1=Mau |first1=Ronald |last2=Kessing |first2=Jayma Martin |title=Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) |url=http://www.extento.hawaii.edu/kbase/crop/Type/ceratiti.htm |publisher=[[University of Hawaii]] |access-date=5 December 2012 |date=April 2007 |archive-date=18 July 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120718012506/http://www.extento.hawaii.edu/kbase/crop/Type/ceratiti.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> [[Florida]] farmers obtained seeds from New Orleans around 1872, after which orange groves were established by grafting the sweet orange on to sour orange rootstocks.<ref name="Morton 1987"/> |
|||
=== Etymology === |
|||
{{main|Orange (word)|l1=''Orange'' (word)}} |
|||
The word "orange" derives ultimately from [[Proto-Dravidian]] or [[Tamil language|Tamil]] {{lang|ta|நாரம்}} ({{transliteration |ta|nāram}}). From there the word entered [[Sanskrit]] {{lang|sa|नारङ्ग}} ({{transliteration|sa|nāraṅga}}), meaning 'orange tree'. The Sanskrit word reached [[Languages of Europe|European languages]] through [[Persian language|Persian]] {{lang|fa|نارنگ}} ({{transliteration|fa|nārang}}) and its [[Arabic language|Arabic]] derivative {{lang|ar|نارنج}} ({{transliteration|ar|nāranj}}).<ref name="Online Etym">{{cite web |title=orange (n.) |url=https://www.etymonline.com/word/orange |publisher=[[Online Etymology Dictionary]] |access-date=15 March 2024 |archive-date=21 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240221041826/https://www.etymonline.com/word/orange |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The word entered [[Late Middle English]] in the 14th century via [[Old French]] {{lang|fro|pomme d'orenge}}.<ref>{{cite web |title=Definition of ''orange'' |url=http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/orange?q=orange |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130511044657/http://oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/orange?q=orange |url-status=dead |archive-date=May 11, 2013 |publisher=[[OED]] online (www.oxforddictionaries.com)}}</ref> Other forms include [[Old Provençal]] {{lang|pro|auranja}},<ref name="Collins">{{cite web |title=Definition of ''orange'' |url=http://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/orange?showCookiePolicy=true |publisher=[[Collins English Dictionary]] (collinsdictionary.com) |access-date=2012-12-05 |archive-date=2013-04-03 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130403180939/http://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/orange?showCookiePolicy=true |url-status=live }}</ref> Italian ''arancia'', formerly ''narancia''.<ref name="Online Etym"/> In several languages, the initial ''n'' present in earlier forms of the word dropped off because it may have been mistaken as part of an indefinite article ending in an ''n'' sound. In French, for example, {{lang|fr|une norenge}} may have been heard as {{lang|fr|une orenge}}. This linguistic change is called [[juncture loss]]. [[orange (color)|The color]] was named after the fruit,<ref>{{cite book |last=Paterson |first=Ian |title=A Dictionary of Colour: A Lexicon of the Language of Colour |edition=1st paperback |year=2003 |publication-date=2004 |publisher=Thorogood |location=London |isbn=978-1-85418-375-0 |oclc=60411025 |page=280}}</ref> with the first recorded use of ''orange'' as a color name in English in 1512.<ref>{{cite OED |term=orange colour |id=132168}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=Maerz |first=Aloys John |last2=Morris |first2=Rea Paul |title=A Dictionary of Color |location=New York |publisher=McGraw-Hill |year=1930 |page=200}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Orange etymology.svg|thumb|center|upright=2|Etymology of 'orange']] |
|||
== Composition == |
|||
=== Nutrition === |
|||
{{Infobox nutritional value |
|||
|name =Oranges, raw,<br/>all commercial varieties |
|||
|kJ =197 |
|||
|protein =0.94 g |
|||
|water =86.75 g |
|||
|fat =0.12 g |
|||
|carbs =11.75 g |
|||
|fiber =2.4 g |
|||
|sugars =9.35 g |
|||
|calcium_mg =40 |
|||
|iron_mg =0.1 |
|||
|magnesium_mg =10 |
|||
|phosphorus_mg=14 |
|||
|potassium_mg =181 |
|||
|zinc_mg =0.07 |
|||
|manganese_mg =0.025 |
|||
|vitC_mg =53.2 |
|||
|thiamin_mg =0.087 |
|||
|riboflavin_mg=0.04 |
|||
|niacin_mg =0.282 |
|||
|pantothenic_mg=0.25 |
|||
|vitB6_mg =0.06 |
|||
|folate_ug =30 |
|||
|choline_mg =8.4 |
|||
|vitA_ug =11 |
|||
|vitE_mg =0.18 |
|||
|source_usda =1 |
|||
|note =[https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169097/nutrients Link to USDA Database entry] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
</ref> |
|||
|}} |
|||
Orange flesh is 87% water, 12% [[carbohydrate]]s, 1% [[protein]], and contains negligible [[fat]] (see table). As a 100-gram reference amount, orange flesh provides 47 [[calorie]]s, and is a rich source of [[vitamin C]], providing 64% of the [[Daily Value]]. No other [[micronutrient]]s are present in significant amounts (see table). |
|||
An '''orange'''—specifically, the '''sweet orange'''—is the [[citrus]] ''Citrus ×sinensis'' ([[Synonymy|syn.]] ''Citrus aurantium'' [[Carl Linnaeus|L.]] [[var.]] ''dulcis'' [[Carl Linnaeus|L.]], or ''Citrus aurantium'' [[Antoine Risso|Risso]]) and its [[fruit]]. The orange is a [[Hybrid (biology)|hybrid]] of ancient cultivated origin, possibly between [[pomelo]] (''Citrus maxima'') and [[tangerine]] (''Citrus reticulata''). It is a small [[Flowering plant|flowering]] [[tree]] growing to about 10 m tall with [[evergreen]] [[leaf|leaves]], which are arranged alternately, of ovate shape with crenulate margins and 4–10 cm long. The orange [[fruit]] is a [[hesperidium]], a type of [[berry]]. |
|||
=== Phytochemicals === |
|||
Oranges originated in [[Southeast Asia]]. The fruit of ''Citrus sinensis'' is called ''sweet orange'' to distinguish it from ''Citrus aurantium'', the [[bitter orange]]. The name is thought to ultimately derive from the [[Dravidian languages|Dravidian]] and [[Telugu]] word for the orange tree, with its final form developing after passing through numerous intermediate languages. |
|||
Oranges contain diverse [[phytochemical]]s, including [[carotenoid]]s ([[beta-carotene]], [[lutein]] and [[beta-cryptoxanthin]]), [[flavonoid]]s (e.g. [[naringenin]])<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Aschoff |first1=Julian K. |last2=Kaufmann |first2=Sabrina |last3=Kalkan |first3=Onur |last4=Neidhart |first4=Sybille |last5=Carle |first5=Reinhold |last6=Schweiggert |first6=Ralf M. |title=In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids, Flavonoids, and Vitamin C from Differently Processed Oranges and Orange Juices [ Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck] |journal=Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry |volume=63 |issue=2 |date=2015-01-21 |issn=0021-8561 |doi=10.1021/jf505297t |pages=578–587}}</ref> and numerous [[volatile organic compounds]] producing orange [[aroma]], including [[aldehyde]]s, [[ester]]s, [[terpene]]s, [[Alcohol (chemistry)|alcohols]], and [[ketone]]s.<ref>{{cite journal |journal=Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr |year=2008 |volume=48 |issue=7 |pages=681–95 |doi=10.1080/10408390701638902 |title=Fresh squeezed orange juice odor: a review |last1=Perez-Cacho |first1=P.R. |last2=Rouseff |first2=R.L. |pmid=18663618 |s2cid=32567584}}</ref> Orange juice contains only about one-fifth the [[citric acid]] of [[Lime (fruit)|lime]] or [[lemon]] juice (which contain about 47 g/L).<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Penniston |first1=Kristina L. |last2=Nakada |first2=Stephen Y. |last3=Holmes |first3=Ross P. |last4=Assimos |first4=Dean G. |title=Quantitative Assessment of Citric Acid in Lemon Juice, Lime Juice, and Commercially-Available Fruit Juice Products |journal=Journal of Endourology |volume=22 |issue=3 |date=2008 |issn=0892-7790 |pmid=18290732 |pmc=2637791 |doi=10.1089/end.2007.0304 |pages=567–570}}</ref> |
|||
In a number of languages, it is known as a "Chinese apple" (e.g. [[Dutch language|Dutch]] ''Sinaasappel'', "China's apple", or "Apfelsine" in German). |
|||
== |
=== Taste === |
||
[[File:Orange and cross section.jpg|thumb|left|Orange fruit and cross section]] |
|||
All citrus trees are of the single [[genus]], ''Citrus'', and remain largely interbreedable; that is, there is only one "[[superspecies]]" which includes [[grapefruit]]s, [[lemon]]s, [[lime (fruit)|limes]], and oranges. Nevertheless, names have been given to the various members of the genus, oranges often being referred to as ''Citrus sinensis'' and ''[[bitter orange|Citrus aurantium]]''. Fruits of all members of the genus ''Citrus'' are considered [[berry|berries]] because they have many [[seed]]s, are fleshy and soft, and derive from a single [[ovary (plants)|ovary]]. An orange seed is called a [[pip]]. The white thread-like material attached to the inside of the peel is called [[pith]]. |
|||
[[File:Octyl acetate.svg|thumb|center|upright|[[Octyl acetate]], a volatile compound contributing to the fragrance of oranges]] |
|||
The taste of oranges is determined mainly by the ratio of sugars to acids, whereas orange aroma derives from [[volatile organic compound]]s, including [[Alcohol (chemistry)|alcohols]], [[aldehyde]]s, [[ketone]]s, [[terpene]]s, and [[ester]]s.<ref name="tietel">{{cite journal |last1=Tietel |first1=Z. |last2=Plotto |first2=A. |last3=Fallik |first3=E. |last4=Lewinsohn |first4=E. |last5=Porat |first5=R. |title=Taste and aroma of fresh and stored mandarins |journal=Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture |year=2011 |volume=91 |issue=1 |pages=14–23 |pmid=20812381 |doi=10.1002/jsfa.4146 |bibcode=2011JSFA...91...14T }}</ref><ref name="hadi">{{cite journal |pmid=23852166 |year=2013 |last1=El Hadi |first1=M. A. |title=Advances in fruit aroma volatile research |journal=[[Molecules (journal)|Molecules]] |volume=18 |issue=7 |pages=8200–29 |last2=Zhang |first2=F. J. |last3=Wu |first3=F. F. |last4=Zhou |first4=C. H. |last5=Tao |first5=J |doi=10.3390/molecules18078200 |pmc=6270112 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Bitter [[limonoid]] compounds, such as [[limonin]], decrease gradually during development, whereas volatile aroma compounds tend to peak in mid- to late-season development.<ref name="bai">{{cite journal |pmc=5224568 |year=2016 |last1=Bai |first1=J. |last2=Baldwin |first2=E. A. |last3=McCollum |first3=G. |last4=Plotto |first4=A. |last5=Manthey |first5=J. A. |last6=Widmer |first6=W. W. |last7=Luzio |first7=G. |last8=Cameron |first8=R. |title=Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of "Valencia" Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons |journal=[[Foods (journal)|Foods]] |volume=5 |issue=1 |pages=4 |doi=10.3390/foods5010004 |pmid=28231099 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Taste quality tends to improve later in harvests when there is a higher sugar/acid ratio with less bitterness.<ref name=bai/> As a citrus fruit, the orange is acidic, with [[pH]] levels ranging from 2.9<ref name="sinclair">{{cite journal |last1=Sinclair, Walton B. |last2=Bartholomew, E.T. |last3=Ramsey, R. C. |title=Analysis of the organic acids of orange juice |journal=Plant Physiology |year=1945 |volume=20 |pages=3–18 |url=http://www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/reprint/20/1/3.pdf |doi=10.1104/pp.20.1.3 |pmid=16653966 |issue=1 |pmc=437693}}</ref> to 4.0.<ref name=sinclair/><ref>{{cite journal |title=Outbreak of Salmonella Serotype Muenchen Infections Associated with Unpasteurized Orange Juice – United States and Canada, June 1999 |journal=Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report |date=July 16, 1999 |url=https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm4827a2.htm |volume=48 |issue=27 |pages=582–585 |pmid=10428096 |author=[[Centers for Disease Control and Prevention]] |access-date=September 10, 2017 |archive-date=November 1, 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211101165047/https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm4827a2.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Taste and aroma vary according to genetic background, environmental conditions during development, ripeness at harvest, postharvest conditions, and storage duration.<ref name=tietel/><ref name=hadi/> |
|||
== Cultivars == |
|||
=== Common === |
|||
Common oranges (also called "white", "round", or "blond" oranges) constitute about two-thirds of all orange production. The majority of this crop is used for juice.<ref name=Kimball/><ref name="Sauls"/> |
|||
=== Valencia === |
|||
{{main|Valencia orange}} |
|||
The Valencia orange is a late-season fruit; it is popular when navel oranges are out of season. [[Thomas Rivers (nurseryman)|Thomas Rivers]], an English nurseryman, imported this variety from the [[Azores]] and catalogued it in 1865 under the name Excelsior. Around 1870, he provided trees to S. B. Parsons, a [[Long Island]] nurseryman, who in turn sold them to E. H. Hart of [[Federal Point, Florida]].<ref name=coit>{{cite book |last=Coit |first=John Eliot |title=Citrus fruits: an account of the citrus fruit industry, with special reference to California requirements and practices and similar conditions |url=https://archive.org/details/citrusfruits00coit |access-date=2 October 2011 |year=1915 |publisher=[[Macmillan Publishers|Macmillan]] }}</ref> |
|||
=== Navel === |
|||
{{main|Navel orange}} |
|||
Navel oranges have a characteristic second fruit at the [[Apical meristems|apex]], which protrudes slightly like a human [[navel]]. They are mainly an eating fruit, as their thicker skin makes them easy to peel, they are less juicy and their bitterness makes them less suitable for juice.<ref name=Kimball/> The parent variety was probably the Portuguese navel orange or ''Umbigo''.<ref name="Washington on Citrus ID">{{cite web |title=Washington |url=https://idtools.org/citrus_id/index.cfm?packageID=1179&entityID=8903 |website=Citrus ID |access-date=14 March 2024 |archive-date=14 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240314221534/https://idtools.org/citrus_id/index.cfm?packageID=1179&entityID=8903 |url-status=live }}, citing amongst other sources {{cite book |last1=Risso |first1=A. |last2=Poiteau |first2=A. |title=Histoire Naturelle des Orangers |date=1819–1822 |publisher=Audot |location=Paris |url=https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k1512210b |access-date=2024-03-14 |archive-date=2023-12-10 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231210231146/https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k1512210b |url-status=live }}</ref> The cultivar rapidly spread to other countries, but being seedless it had to be propagated by [[cutting (plant)|cutting]] and [[grafting]].<ref name="cfaitc">{{cite web |title=Commodity Fact Sheet: Citrus Fruits |work=California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom |url=https://cdn.agclassroom.org/media/uploads/2017/12/07/citrus_fruit_commodity_fact_sheet.pdf |access-date=14 March 2024 |archive-date=16 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220816191813/https://cdn.agclassroom.org/media/uploads/2017/12/07/citrus_fruit_commodity_fact_sheet.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
The [[Cara cara orange]] is a type of navel orange grown mainly in [[Venezuela]], [[South Africa]] and California's [[San Joaquin Valley]]. It is sweet and low in acid,<ref name="UBC">{{cite web |url=http://www.ubcbotanicalgarden.org/potd/2007/02/citrus_sinensis_cara_cara.php |title=UBC Botanical Garden, Botany Photo of the Day |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100124174207/http://www.ubcbotanicalgarden.org/potd/2007/02/citrus_sinensis_cara_cara.php |archive-date=2010-01-24}}</ref> with distinctively pinkish red flesh. It was discovered at the [[Hacienda]] Cara Cara in [[Valencia, Venezuela|Valencia]], Venezuela, in 1976.<ref name=UCR>{{Cite web |url=http://www.citrusvariety.ucr.edu/citrus/caracara.html |title=Cara Cara navel orange |publisher=[[University of California, Riverside]] |access-date=2011-01-20 |archive-date=2019-04-25 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190425074600/https://citrusvariety.ucr.edu/citrus/caracara.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
=== Blood === |
|||
== Varieties == |
|||
=== Blood orange === |
|||
{{main|Blood orange}} |
{{main|Blood orange}} |
||
The [[blood orange]] has streaks of red in the fruit, and the juice is often a dark burgundy colour. The fruit has found a niche as an interesting ingredient variation on traditional Seville marmalade, with its striking red streaks and distinct flavour. The '''scarlet navel''' is a variety with the same dual-fruit mutation as the navel orange. |
|||
Blood oranges, with an intense red coloration inside, are widely grown around the Mediterranean; there are several cultivars.<ref name="Morton 1987"/> The development of the red color requires cool nights.<ref name="McGee 2004">{{cite book |last=McGee |first=Harold |title=On food and cooking: the science and lore of the kitchen |publisher=Scribner |year=2004 |isbn=0-684-80001-2 |location=New York |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bKVCtH4AjwgC |page=[https://books.google.com/books?id=bKVCtH4AjwgC&pg=PA376 376] |access-date=2024-03-15 |archive-date=2023-07-28 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230728202046/https://books.google.com/books?id=bKVCtH4AjwgC |url-status=live }}</ref> The redness is mainly due to the [[anthocyanin]] pigment [[chrysanthemin]] (cyanidin 3-''O''-glucoside).<ref>{{cite journal|title=Influence of glucose on cyanidin 3-glucoside absorption in rats |last1=Felgines |first1=C. |last2=Texier |first2=O. |last3=Besson |first3=C. |last4=Vitaglione |first4=P |last5=Lamaison |first5=J.-L. |last6=Fogliano |first6=V. |last7=Scalbert |first7=A. |last8=Vanella |first8=L. |last9=Galvano |first9=F. |display-authors=6 |journal=[[Molecular Nutrition & Food Research]] |date=2008 |volume=52 |issue=8 |pages=959–64 |doi=10.1002/mnfr.200700377 |pmid=18646002}}</ref> |
|||
=== Navel orange === |
|||
[[File:Navel orange sectioned.jpg|thumb|right|A peeled sectioned navel orange. The underdeveloped twin is located on the bottom right.]] |
|||
A single [[mutation]] in 1820 in an [[orchard]] of sweet oranges planted at a [[monastery]] in [[Brazil]] yielded the '''navel orange''', also known as the Washington, Riverside, or Bahie navel. The mutation causes the orange to develop a second orange at the base of the original fruit, opposite the stem, as a [[Conjoined twins|conjoined twin]] in a set of smaller segments embedded within the peel of the larger orange. From the outside, it looks similar to the human [[navel]], thus its name. |
|||
=== Acidless === |
|||
Because the mutation left the fruit seedless, and therefore sterile, the only means available to cultivate more of this new variety is to graft cuttings onto other varieties of citrus tree. Two such cuttings of the original tree were transplanted<ref>{{cite web|url=http://thegoldengecko.com/blog/?p=34 |title=Parent Navel Orange Tree in Riverside, CA |publisher=Thegoldengecko.com |date= |accessdate=2009-04-16}}</ref> to [[Riverside, California|Riverside]], [[California]] in 1870, which eventually led to worldwide popularity. |
|||
Acidless oranges are an early-season fruit with very low levels of acid. They also are called "sweet" oranges in the United States, with similar names in other countries: ''douce'' in France, ''sucrena'' in Spain, ''dolce'' or ''maltese'' in Italy, ''meski'' in North Africa and the Near East (where they are especially popular), ''succari'' in Egypt, and ''lima'' in Brazil.<ref name=Kimball/> The lack of acid, which protects orange juice against spoilage in other groups, renders them generally unfit for processing as juice, so they are primarily eaten. They remain profitable in areas of local consumption, but rapid spoilage renders them unsuitable for export to major population centres of Europe, Asia, or the United States.<ref name=Kimball/> |
|||
Today, navel oranges continue to be produced via [[cutting (plant)|cutting]] and [[grafting]]. This does not allow for the usual [[artificial selection|selective breeding]] methodologies, and so not only do the navel oranges of today have exactly the same genetic makeup as the original tree, and are therefore [[clones]], in a sense, all navel oranges can be considered to be the fruit of that single over-a-century-old tree. This is similar to the common yellow seedless banana, the [[Cavendish banana|Cavendish]]. On rare occasions, however, further mutations can lead to new varieties.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.citrusvariety.ucr.edu/citrus/sweet_oranges.html |title=Citrus Variety Collection |publisher=Citrusvariety.ucr.edu |date=2002-05-28 |accessdate=2009-04-16}}</ref> |
|||
<gallery mode=packed heights=155> |
|||
=== Persian orange === |
|||
File:Florida orange grove.JPG|A grove of [[Valencia orange]]s in [[Florida]] |
|||
The Persian orange, grown widely in [[southern Europe]] after its introduction to [[Italy]] in the 11th century, was bitter. Sweet oranges brought to Europe in the 15th century from [[India]] by [[Portugal|Portuguese]] traders, quickly displaced the bitter, and are now the most common variety of orange cultivated. The sweet orange will grow to different sizes and colours according to local conditions, most commonly with ten ''[[carpel]]s'', or segments, inside. |
|||
File:Cara cara orange cut in half.JPG|[[Cara cara navel orange]] |
|||
File:BloodOrange.jpg|[[Blood orange]] |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== Cultivation == |
|||
Some South East Indo-European tongues name orange after [[Portugal]], which was formerly the main source of imports of sweet oranges. Examples are [[Bulgarian language|Bulgarian]] ''portokal'' [портокал], [[Modern Greek|Greek]] ''portokali'' [πορτοκάλι], [[Persian language|Persian]] ''porteghal'' [پرتقال], [[Albanian language|Albanian]] "portokall", and [[Romanian language|Romanian]] ''portocală''. Also in [[Italian dialects|South Italian dialects]] ([[Neapolitan language|Neapolitan]]), orange is named ''portogallo'' or ''purtualle'', literally "the Portuguese ones". Related names can also be found in other languages: [[Turkish language|Turkish]] ''Portakal'', [[Arabic language|Arabic]] ''al-burtuqal'' [البرتقال], [[Amharic]] ''birtukan'', and [[Georgian language|Georgian]] ''phortokhali'' [ფორთოხალი]. |
|||
=== Climate === |
|||
[[Portuguese empire|Portuguese]], [[Spanish empire|Spanish]], [[Arab empire|Arab]], and [[Dutch empire|Dutch]] sailors planted citrus trees along trade routes to prevent [[scurvy]]. On his second voyage in 1493, Christopher Columbus brought the seeds of oranges, lemons and citrons to [[Haiti]] and the Caribbean. They were introduced in Florida (along with lemons) in 1513 by [[Spain|Spanish]] explorer [[Juan Ponce de Leon]], and were introduced to [[Hawaii]] in 1792. |
|||
Like most citrus plants, oranges do well under moderate temperatures—between {{cvt|15.5|and|29|C}}—and require considerable amounts of sunshine and water. They are principally grown in tropical and subtropical regions.<ref name=Sauls/> |
|||
=== Valencia orange === |
|||
{{main|Valencia orange}} |
|||
The [[Valencia orange|Valencia]] or [[Murcia]] orange is one of the sweet oranges used for juice extraction. It is a late-season fruit, and therefore a popular variety when the navel oranges are out of season. For this reason, the orange was chosen to be the official [[mascot]] of the [[1982 FIFA World Cup]], which was held in [[Spain]]. The mascot was called "[[Naranjito]]" ("little orange"), and wore the colours of the Spanish football team uniform. |
|||
As oranges are sensitive to [[frost]], farmers have developed methods to protect the trees from frost damage. A common process is to spray the trees with water so as to cover them with a thin layer of ice, insulating them even if air temperatures drop far lower. This practice, however, offers protection only for a very short time.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.newton.dep.anl.gov/askasci/gen01/gen01243.htm |title=How Cold Can Water Get? |publisher=[[Argonne National Laboratory]] |date=2002-09-08 |access-date=2009-04-16 |archive-date=2015-02-26 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150226033418/http://www.newton.dep.anl.gov/askasci/gen01/gen01243.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Another procedure involves burning fuel oil in [[smudge pot]]s put between the trees. These burn with a great deal of particulate emission, so condensation of water vapor on the particulate soot prevents condensation on plants and raises the air temperature very slightly. Smudge pots were developed after a disastrous freeze in southern California in January 1913 destroyed a whole crop.<ref name='moore'>{{cite book |last=Moore |first=Frank Ensor |title=Redlands Astride the Freeway: The Development of Good Automobile Roads |publisher=Moore Historical Foundation |location=Redlands, California |year=1995 |page=9 |isbn =978-0-914167-07-5}}</ref> |
|||
== Attributes == |
|||
=== Nutritional Value === |
|||
{| |
|||
|{{nutritionalvalue |
|||
| name=Orange, raw, Florida |
|||
| kJ=192 | protein=0.70 g |
|||
| fat=0.21 g |
|||
| carbs=11.54 g |
|||
| fiber=2.4 g |
|||
| sugars=9.14 g |
|||
| iron_mg=0.09 |
|||
| calcium_mg=43 |
|||
| magnesium_mg=10 |
|||
| phosphorus_mg=12 |
|||
| potassium_mg=169 |
|||
| zinc_mg=0.08 |
|||
| vitC_mg=45 |
|||
| pantothenic_mg=0.250 |
|||
| vitB6_mg=0.051 |
|||
| folate_ug=17 |
|||
| thiamin_mg=0.100 |
|||
| riboflavin_mg=0.040 |
|||
| niacin_mg=0.400 |
|||
| right=1 |
|||
| source_usda=1 |
|||
}} |
|||
|} |
|||
=== |
=== Propagation === |
||
Like all citrus fruits, the ''orange'' is acidic, with a pH level of around 2.5-3; depending on the age, size and variety of the fruit. Although this is not, on average, as strong as the [[lemon]], it is still quite strong on the pH scale – as strong as vinegar. |
|||
{{further|Fruit tree propagation|Citrus rootstock}} |
|||
Commercially grown orange trees are [[plant propagation|propagated]] [[asexual reproduction|asexually]] by [[grafting]] a mature [[cultivar]] onto a suitable [[seedling]] [[rootstock]] to ensure the same [[Crop yield|yield]], identical fruit characteristics, and resistance to diseases throughout the years. Propagation involves two stages: first, a rootstock is grown from seed. Then, when it is approximately one year old, the leafy top is cut off and a [[bud]] taken from a specific [[scion (grafting)|scion]] variety, is grafted into its bark. The scion is what determines the variety of orange, while the rootstock makes the tree resistant to pests and diseases and adaptable to specific [[Soil type|soil]] and climatic conditions. Thus, rootstocks influence the rate of growth and have an effect on fruit yield and quality.<ref name="Lacey">{{cite web |last=Lacey |first=Kevin |title=Citrus rootstocks for WA |url=http://www.agric.wa.gov.au/objtwr/imported_assets/content/hort/fn/cp/citrusfruits/ag%20dept%20fn539%20lores.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131112025544/http://www.agric.wa.gov.au/objtwr/imported_assets/content/hort/fn/cp/citrusfruits/ag%20dept%20fn539%20lores.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-date=2013-11-12 |publisher=Government of WA. Department of Agriculture and Food |access-date=30 November 2012 |date=July 2012}}</ref> Rootstocks must be compatible with the variety inserted into them because otherwise, the tree may decline, be less productive, or die.<ref name="Lacey"/> Among the advantages to grafting are that trees mature uniformly and begin to bear fruit earlier than those reproduced by seeds (3 to 4 years in contrast with 6 to 7 years),<ref name="Citrus">{{cite web |last=Price |first=Martin |title=Citrus Propagation and Rootstocks |url=http://www.ultimatecitrus.com/pdf/tncitrus.htm |publisher=ultimatecitrus.com |access-date=30 November 2012 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180406084607/http://www.ultimatecitrus.com/pdf/tncitrus.htm |archive-date=6 April 2018 |url-status=dead }}</ref> and that farmers can combine the best attributes of a scion with those of a rootstock.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ars-grin.gov/ars/SoAtlantic/fp/hb/bowman/citrus.html |title=Citrus Propagation. Research Program on Citrus Rootstock Breeding and Genetics |website=ars-grin.gov |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100528003825/http://www.ars-grin.gov/ars/SoAtlantic/fp/hb/bowman/citrus.html |archive-date=2010-05-28 }}</ref> |
|||
=== Harvest === |
|||
Canopy-shaking mechanical harvesters are being used increasingly in Florida to harvest oranges. Current canopy shaker machines use a series of six-to-seven-foot-long tines to shake the tree canopy at a relatively constant <!--shaking--> stroke and frequency.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Bora |first1=G. |last2=Hebel |first2=M. |last3=Lee |first3=K. |date=2007-12-01 |title=In-situ measurement of the detachment force of individual oranges harvested by a canopy shaker harvesting machine |url=http://www.fshs.org/Meetings/2007/FSHS_2007_abstracts.pdf |journal=Abstracts for the 2007 Joint Annual Meeting of the Florida State Horticulture Society. |s2cid=113761794 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110726020405/http://www.fshs.org/Meetings/2007/FSHS_2007_abstracts.pdf |archive-date=2011-07-26 }}</ref> Oranges are picked once they are pale orange.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://freshcitrusdirect.wordpress.com/tag/riverland/ |title=Fresh Citrus Direct |publisher=freshcitrusdirect.wordpress.com |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150110071334/https://freshcitrusdirect.wordpress.com/tag/riverland/ |archive-date=2015-01-10}}</ref> |
|||
=== Degreening === |
|||
Oranges must be mature when harvested. In the United States, laws forbid harvesting immature fruit for human consumption in Texas, Arizona, California and Florida.<ref name="Wagner">{{cite web |title=Harvesting and Pre-pack Handling |url=http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/citrus/l2294.htm |publisher=The Texas A&M University System |access-date=29 November 2012 |last1=Wagner, Alfred B. |last2=Sauls, Julian W. |archive-date=4 January 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130104041656/http://aggie-horticulture.tamu.edu/citrus/l2294.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> Ripe oranges, however, often have some green or yellow-green color in the skin. [[Ethylene]] gas is used to turn green skin to orange. This process is known as "degreening", "gassing", "sweating", or "curing".<ref name="Wagner"/> Oranges are non-[[Climacteric (botany)|climacteric]] fruits and cannot ripen internally in response to ethylene gas after harvesting, though they will de-green externally.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://postharvest.ucdavis.edu/PFfruits/Orange/ |title=Orange: Recommendations for Maintaining Postharvest Quality |last1=Arpaia, Mary Lu |last2=Kader, Adel A. |publisher=[[UCDavis]] Postharvest Technology Center |access-date=2013-12-12 |archive-date=2013-12-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131206115013/http://postharvest.ucdavis.edu/PFfruits/Orange/ |url-status=dead}}</ref> |
|||
=== Storage === |
|||
Commercially, oranges can be stored by refrigeration in controlled-atmosphere chambers for up to twelve weeks after harvest. Storage life ultimately depends on cultivar, maturity, pre-harvest conditions, and handling.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Ritenour, M.A. |url=http://www.ba.ars.usda.gov/hb66/100orange.pdf |title=Orange. The Commercial Storage of Fruits, Vegetables, and Florist and Nursery Stocks |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120127220523/http://www.ba.ars.usda.gov/hb66/100orange.pdf |archive-date=2012-01-27 |website=USDA |date=2004}}</ref> At home, oranges have a shelf life of about one month, and are best stored loose.<ref name=cpma>{{cite web |url=http://www.cpma.ca/Files/CPMA.HomeStorageGuide.English.pdf |title=Home Storage Guide for Fresh Fruits & Vegetables. Canadian Produce Marketing Association |website=cpma.ca |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130512161442/http://www.cpma.ca/Files/CPMA.HomeStorageGuide.English.pdf |archive-date=2013-05-12}}</ref> |
|||
<gallery mode=packed heights=155> |
|||
File:CSIRO ScienceImage 4314 Spraying oranges in an orchard at Griffith NSW 2002.jpg|Spraying oranges in an orchard in Australia |
|||
File:California Orange Grove2.jpg|Orange grove in [[California]] |
|||
100521 picking oranges in moshav zimrat PikiWiki Israel.jpg|Picking oranges, Israel |
|||
File:100535 picking oranges in moshav zimrat PikiWiki Israel.jpg|Harvest, Israel |
|||
File:2010-12-14 Maroc Agadir Soukh local market.jpg|Market stall, Morocco |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
== Pests and diseases == |
|||
=== Pests === |
|||
[[File:Icerya purchasi 1435060.jpg|thumb|[[Cottony cushion scale]] insects devastated orange groves across California in the 19th century, and were the first pest to be subject to successful [[biological control]].<ref name=coit/>]] |
|||
The first major pest that attacked orange trees in the United States was the cottony cushion scale (''[[Icerya purchasi]]''), imported from Australia to California in 1868. Within 20 years, it wiped out the citrus orchards around Los Angeles, and limited orange growth throughout California. In 1888, the USDA sent Alfred Koebele to Australia to study this [[scale insect]] in its native habitat. He brought back with him specimens of an Australian [[Coccinellidae|ladybird]], ''[[Novius cardinalis]]'' (the Vedalia beetle), and within a decade the pest was controlled. This was one of the first successful applications of [[biological pest control]] on any crop.<ref name=coit/> The [[orange dog]] caterpillar of the giant swallowtail butterfly, ''Papilio cresphontes'', is a pest of citrus plantations in North America, where it eats new foliage and can defoliate young trees.<ref name="Giant Swallowtail">{{cite journal |last=Mcauslane |first=Heather |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237833636 |title=Giant Swallowtail, Orangedog, Papilio cresphontes Cramer (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Papilionidae) |journal=Edis |publisher=[[University of Florida]] |date=May 2009 |issue=4 |access-date=14 March 2024 |doi=10.32473/edis-in134-2009 |archive-date=16 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240316051937/https://www.researchgate.net/publication/237833636_Giant_Swallowtail_Orangedog_Papilio_cresphontes_Cramer_Insecta_Lepidoptera_Papilionidae1 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
=== Diseases === |
|||
{{Further|List of citrus diseases}} |
|||
[[File:Asian Citrus Psyllid adult.jpg|thumb|The Asian citrus psyllid, ''[[Diaphorina citri]]'', is a major [[Disease vector|vector]] of [[citrus greening disease]].<ref name="Killiny Nehela 2021"/> ]] |
|||
[[Citrus greening disease]], caused by the bacterium ''[[Liberobacter asiaticum]]'', has been the most serious threat to orange production since 2010. It is characterized by streaks of different shades on the leaves, and deformed, poorly colored, unsavory fruit. In areas where the disease is endemic, citrus trees live for only five to eight years and never bear fruit suitable for consumption.<ref name=halbert/> In the western hemisphere, the disease was discovered in Florida in 1998, where it has attacked nearly all the trees ever since. It was reported in Brazil by Fundecitrus Brasil in 2004.<ref name="halbert">{{Cite journal |last1=Halbert |first1=Susan E. |last2=Manjunath |first2=Keremane L. |date=September 2004 |title=Asian citrus psyllids (Sternorrhyncha: Psyllidae) and greening disease of citrus: A literature review and assessment of risk in Florida |journal=[[The Florida Entomologist]] |volume=87 |issue=3 |pages=330–353 |doi=10.1653/0015-4040(2004)087[0330:ACPSPA]2.0.CO;2 |s2cid=56161727 |issn=0015-4040 |doi-access=free }}</ref> As from 2009, 0.87% of the trees in Brazil's main orange growing areas (São Paulo and Minas Gerais) showed symptoms of greening, an increase of 49% over 2008.<ref name=gainbr9006>{{Cite web |url=http://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%20GAIN%20Publications/Commodity%20Report_CITRUS%20SEMI-ANNUAL_Sao%20Paulo%20ATO_Brazil_6-18-2009.pdf |title=GAIN Report Number: BR9006 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110513205206/http://gain.fas.usda.gov/Recent%20GAIN%20Publications/Commodity%20Report_CITRUS%20SEMI-ANNUAL_Sao%20Paulo%20ATO_Brazil_6-18-2009.pdf |archive-date=2011-05-13 |publisher=USDA Foreign Agricultural Service |date=18 June 2009}}</ref> |
|||
The disease is spread primarily by [[psyllid]] plant lice such as the Asian citrus psyllid (''[[Diaphorina citri]]'' Kuwayama), an efficient [[Vector (epidemiology)|vector]] of the bacterium.<ref name="Killiny Nehela 2021">{{cite journal |last1=Killiny |first1=Nabil |last2=Nehela |first2=Yasser |last3=George |first3=Justin |last4=Rashidi |first4=Mahnaz |last5=Stelinski |first5=Lukasz L. |last6=Lapointe |first6=Stephen L. |date=2021-07-01 |title=Phytoene desaturase-silenced citrus as a trap crop with multiple cues to attract Diaphorina citri, the vector of Huanglongbing |journal=[[Plant Science (journal)|Plant Science]] |volume=308 |pages=110930 |doi=10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110930 |pmid=34034878 |s2cid=235203508 |issn=0168-9452|doi-access=free }}</ref> Foliar insecticides reduce psyllid populations for a short time, but also suppress beneficial predatory ladybird beetles. Soil application of [[aldicarb]] provided limited control of Asian citrus psyllid, while drenches of [[imidacloprid]] to young trees were effective for two months or more.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Qureshi |first1=J. |last2=Stansly |first2=P. |date=2007-12-01 |title=Integrated approaches for managing the Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in Florida |url=https://swfrec.ifas.ufl.edu/docs/pdf/entomology/publications/Stansly_Non_Qureshi07.pdf |journal=Proceedings of the Florida State Horticultural Society |volume=120 |pages=110–115 |s2cid=55798062 |access-date=2023-11-17 |archive-date=2023-11-17 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231117152819/https://swfrec.ifas.ufl.edu/docs/pdf/entomology/publications/Stansly_Non_Qureshi07.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Management of citrus greening disease requires an integrated approach that includes use of clean stock, elimination of inoculum via voluntary and regulatory means, use of pesticides to control psyllid vectors in the citrus crop, and biological control of the vectors in non-crop reservoirs.<ref name=halbert/> |
|||
Greasy spot, a [[Fungal infection in plants|fungal disease]] caused by the ascomycete ''[[Mycosphaerella citri]]'', produces leaf spots and premature defoliation, thus reducing the tree's vigour and yield. [[Ascospore]]s of ''M. citri'' are generated in [[Ascocarp|pseudothecia]] in decomposing fallen leaves.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Mondal |first1=S.N. |first2=K.T. |last2=Morgan |first3=L.W. |last3=Timme |date=June 2007 |title=Effect of Water Management and Soil Application of Nitrogen Fertilizers, Petroleum Oils, and Lime on Inoculum Production by Mycosphaerella citri, the Cause of Citrus Greasy Spot |url=http://www.fshs.org/Meetings/2007/FSHS_2007_abstracts.pdf |journal=Abstracts for the 2007 Joint Annual Meeting of the Florida State Horticulture Society. |s2cid=113761794 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110726020405/http://www.fshs.org/Meetings/2007/FSHS_2007_abstracts.pdf |archive-date=2011-07-26 }}</ref> |
|||
== Production == |
== Production == |
||
{{Out of date|section}} |
|||
{|class="wikitable floatright" style="width:15em; text-align:center;" |
|||
{{main|Citrus production}} |
|||
! colspan=2 |Production of oranges – 2022 |
|||
[[File:2005orange.PNG|thumb|550px|Orange output in 2005]] |
|||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! style="background:#ddf; width:75%;" |Country |
|||
|Top Orange Producers — 2005<br />(million tonnes) |
|||
! style="background:#ddf; width:25%;" |<small>Production (millions of [[tonne]]s)</small> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|{{BRA}} ||16.9 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|{{IND}} ||10.2 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|{{CHN}} ||7.6 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|{{MEX}} ||4.8 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|{{EGY}} ||3.4 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
|{{USA}} ||3.1 |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|'''World''' ||'''76.4''' |
|||
| {{ITA}} || align="right" | 2.2 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|colspan=2 |<small>Source: [[FAOSTAT]] of the [[United Nations]]<ref name="faostat">{{cite web |title=Orange production in 2022, Crops/Regions/World list/Production Quantity/Year (pick lists)|date=2024|publisher=UN Food and Agriculture Organization, Corporate Statistical Database |access-date=15 March 2024 |url=https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL |archive-date=12 November 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161112130804/https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL |url-status=live}}</ref></small> |
|||
| {{IRN}} || align="right" | 1.9 |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{EGY}} || align="right" | 1.8 |
|||
|- |
|||
| {{PAK}} || align="right" | 1.6 |
|||
|- |
|||
||'''World Total''' || align="right" | '''61.7''' |
|||
|- |
|||
|colspan=2|''Source: <br />[[UN Food & Agriculture Organisation]] (FAO)''<ref>[http://www.fao.org/es/ess/top/commodity.html?lang=en&item=490&year=2005 FAO Statistics] Statistics for 2005. Retrieved on 2009-06-19.</ref> |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
Oranges grown for commercial production are generally grown in groves and are produced throughout the world. The top three orange-producing countries are [[Brazil]], the [[United States]], and [[Mexico]]. Oranges are sensitive to [[frost]], and a common treatment to prevent frost damage when sub-freezing temperatures are expected, is to spray the trees with water, since as long as unfrozen water is turning to ice on the trees' branches, the ice that has formed stays just ''at'' the freezing point, giving protection even if air temperatures have dropped far lower.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.newton.dep.anl.gov/askasci/gen01/gen01243.htm |title=How Cold Can Water Get? |publisher=Newton.dep.anl.gov |date=2002-09-08 |accessdate=2009-04-16}}</ref> |
|||
{{Agriculture country lists|state=collapsed}} |
|||
{{Main|Citrus production}} |
|||
== Etymology == |
|||
{{main|Orange (word)}} |
|||
<!-- Please go to the above main article, [[Orange (word)]] if you wish to add further examples from any additional languages. --> |
|||
The word ''orange'' is derived from [[Sanskrit]] ''{{unicode|nāraṅgaḥ}}'' "orange tree."<ref>{{cite web | url = http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/orange | title = Orange | publisher = [[Reference.com]] | accessdate = 2008-01-31 | date = 2008 }}</ref> and in [[Telugu]] "Naringa". The Sanskrit word was borrowed into European languages through [[Persian language|Persian]] ''nārang'', [[Armenian language|Armenian]] ''nārinj'', [[Arabic language|Arabic]] ''nāranj'', ([[Spanish (language)|Spanish]] ''naranja'' and [[Portuguese (language)|Portuguese]] ''laranja''), [[Late Latin]] ''arangia'', [[Italian (language)|Italian]] ''arancia'' or ''arancio'', and [[Old French]] ''orenge'', in chronological order. The first appearance in English dates from the 14th century. The forms starting with n- are older; this initial n- may have been mistaken as part of the indefinite article, in languages with articles ending with an -n sound (e.g., in French ''une norenge'' may have been taken as ''une orenge''). The name of the colour is derived from the fruit, first appearing in this sense in 1542. |
|||
In 2022, world production of oranges was 76 million [[tonne]]s, led by [[Brazil]] with 22% of the total, followed by India, China, and Mexico.<ref name=faostat/> |
|||
Some languages have different words for the bitter and the sweet orange, such as Modern Greek ''nerantzi'' and ''portokali'', respectively. Or in Persian, the words are ''narang'' and ''porteghal'' (Portugal), in the same order. The reason is that the sweet orange was brought from China or India to Europe during the 15th century by the [[Portuguese people|Portuguese]]. For the same reason, some languages refer to it as ''Applesin'' (or variants), which means "Apple from China," while the bitter orange was introduced through Persia. |
|||
The [[United States Department of Agriculture]] has established [[food grading|grades]] for Florida oranges, primarily for oranges sold as fresh fruit.<ref name=usda_fla>{{Cite web |url=http://www.ams.usda.gov/AMSv1.0/getfile?dDocName=STELPRDC5050382 |title=United States Standards for Grades of Florida Oranges and Tangelos |publisher=USDA |date=February 1997 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110726100358/http://www.ams.usda.gov/AMSv1.0/getfile?dDocName=STELPRDC5050382 |archive-date=2011-07-26 }}</ref> In the United States, groves are located mainly in [[Florida]], [[California]], and [[Texas]].<ref>{{cite web |title=Oranges: Production Map by State |url=https://www.nass.usda.gov/Charts_and_Maps/Citrus_Fruits/orgmap.php |publisher=[[United States Department of Agriculture]] |access-date=1 April 2017 |date=1 March 2017 |archive-date=31 October 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211031021526/https://www.nass.usda.gov/Charts_and_Maps/Citrus_Fruits/orgmap.php |url-status=live }}</ref> The majority of California's crop is sold as fresh fruit, whereas Florida's oranges are destined to juice products. The [[Indian River (Florida)|Indian River]] area of Florida produces high quality juice, which is often sold fresh and blended with juice from other regions, because Indian River trees yield sweet oranges but in relatively small quantities.<ref>{{cite web |title=History of the Indian River Citrus District |url=http://ircitrusleague.org/history/ |publisher=Indian River Citrus League |access-date=27 November 2012 |archive-date=1 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211101165048/http://ircitrusleague.org/history/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
== |
== Culinary use == |
||
[[File:Oranges and orange juice.jpg|thumb|upright|Oranges and [[orange juice]]]] |
|||
Oranges are widely grown in warm climates worldwide, and the flavours of oranges vary from [[sweet]] to [[sour]]. The fruit is commonly peeled and eaten fresh, or squeezed for its juice. It has a thick bitter [[Peel (fruit)|rind]] that is usually discarded, but can be processed into animal feed by removing [[water]], using [[pressure]] and [[heat]]. It is also used in certain recipes as flavouring or a [[Garnish (food)|garnish]]. The outer-most layer of the rind can be grated or thinly veneered with a tool called a [[zester]], to produce orange [[zest (ingredient)|zest]]. Zest is popular in cooking because it contains the oil glands and has a strong flavour similar to the fleshy inner part of the orange. The white part of the rind, called the ''[[pericarp]]'' or ''albedo'' and including the [[pith]], is a source of [[pectin]] and has nearly the same amount of vitamin C as the flesh. |
|||
=== |
=== Dessert fruit and juice === |
||
* [[Orange juice]] is one of the commodities traded on the [[New York Board of Trade]]. Brazil is the largest producer of orange juice in the world, followed by the USA. It is made by squeezing the fruit on a special instrument called a "''juicer''" or a "''squeezer''." The juice is collected in a small tray underneath. This is mainly done in the home, and in industry is done on a much larger scale. |
|||
* Frozen orange juice concentrate is made from freshly squeezed and filtered orange juice.<ref>{{cite web|author=Posted on Nov 6th 2008 1:30PM by Kelly Wilson |url=http://members.aol.com/citrusweb/oj_story.html |title=The Story of Florida Orange Juice: From the Grove to Your Glass |publisher=Members.aol.com |date=2008-11-06 |accessdate=2009-04-16}}</ref> |
|||
* Sweet [[orange oil]] is a [[by-product]] of the juice industry produced by pressing the peel. It is used as a [[flavouring]] of food and drink and for its [[fragrance]] in [[perfume]] and [[aromatherapy]]. Sweet orange oil consists of about 90% [[Limonene|d-Limonene]], a [[solvent]] used in various household chemicals, such as to condition [[wood]]en [[furniture]], and along with other citrus oils in [[Petroleum|grease]] removal and as a [[hand]]-cleansing agent. It is an efficient cleaning agent which is promoted as being environmentally friendly and preferable to [[petroleum]] distillates. However, [[Limonene|d-Limonene]] is classified as toxic or very toxic in several countries{{Fact|date=April 2008}}. Its smell is considered more pleasant by some than those of other cleaning agents. Although once thought to cause [[Renal cell carcinoma|renal cancer]] in rats, limonene now is known as a significant [[chemoprophylaxis|chemopreventive]] agent<ref>Crowell PL. Prevention and therapy of cancer by dietary monoterpenes. J Nutr. 1999 Mar;129(3):775S-778S.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10082788]</ref> with potential value as a dietary anti-cancer tool in humans.<ref>Tsuda H, Ohshima Y, Nomoto H, Fujita K, Matsuda E, Iigo M, Takasuka N, Moore MA. Cancer prevention by natural compounds. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2004 Aug;19(4):245-63.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15499193]</ref> There is no evidence for [[carcinogen]]icity or [[genotoxic]]ity in humans. The [[International Agency for Research on Cancer|IARC]] classifies ''d''-limonene under Class 3: ''not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans''.{{Fact|date=May 2008}} |
|||
* The orange [[blossom]], which is the [[List of U.S. state flowers|state flower]] of Florida, is highly fragrant and traditionally associated with good fortune. It has long been popular in bridal bouquets and head wreaths for [[wedding]]s. |
|||
* Orange blossom essence is an important component in the making of [[perfume]]. |
|||
* The [[petal]]s of orange blossom can also be made into a delicately citrus-scented version of [[rosewater]]; orange blossom water (aka orange flower water) is a common part of both French and Middle Eastern cuisines, most often as an ingredient in desserts and baked goods. |
|||
* The orange blossom gives its touristic nickname to the ''[[Costa del Azahar]]'' ("Orange-blossom [[wiktionary:Costa|coast]]"), the [[Castellon (province)|Castellon]] seaboard. |
|||
* In Spain, fallen blossoms are dried and then used to make tea. |
|||
* Orange blossom [[honey]], or actually citrus honey, is produced by putting [[beehives]] in the citrus groves during bloom, which also [[pollination|pollinates]] seeded citrus varieties. Orange blossom honey is highly prized, and tastes much like orange. |
|||
* [[Marmalade]], a conserve usually made with [[Seville orange]]s. All parts of the orange are used to make marmalade: the pith and pips are separated, and typically placed in a muslin bag where they are boiled in the juice (and sliced peel) to extract their pectin, aiding the setting process. |
|||
* Orange peel is used by gardeners as a [[slug]] repellent. |
|||
* Orange leaves can be boiled to make tea. |
|||
* Orange wood sticks{{anchor|orange wood}} (also spelt orangewood) are used as [[cuticle pusher]]s in manicures and pedicures, and as [[spudger]]s for manipulating slender electronic wires |
|||
{{further|Orange juice}} |
|||
== Gallery == |
|||
<gallery perrow="5"> |
|||
Oranges, whose flavor may vary from [[sweet]] to [[sour]], are commonly peeled and eaten fresh raw as a dessert. [[Orange juice]] is obtained by squeezing the fruit on a special tool (a ''juicer'' or ''squeezer'') and collecting the juice in a tray or tank underneath. This can be made at home or, on a much larger scale, industrially.<ref name="juice">{{cite web |title=How orange juice is made |url=https://www.discoveryuk.com/how-its-made/how-orange-juice-is-made/ |publisher=Discovery Networks International |access-date=16 March 2024 |date=20 September 2022 |archive-date=24 September 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230924024259/https://www.discoveryuk.com/how-its-made/how-orange-juice-is-made/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Orange juice is a traded commodity on the [[Intercontinental Exchange]].<ref name="lawson">{{cite news |last1=Lawson |first1=Alex |title=The great orange juice trading rally – and why a big squeeze could lie ahead |url=https://www.theguardian.com/business/2023/oct/27/orange-juice-trading-rally |access-date=16 March 2024 |work=[[The Guardian]] |date=27 October 2023 |archive-date=22 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231122041214/https://www.theguardian.com/business/2023/oct/27/orange-juice-trading-rally |url-status=live }}</ref> Frozen orange juice concentrate is made from freshly squeezed and filtered juice.<ref>{{cite web |last=Townsend |first=Chet |url=http://www.ultimatecitrus.com/Story/oj_story.html |title=The Story of Florida Orange Juice: From the Grove to Your Glass |date=2012 |access-date=14 March 2024 |archive-date=18 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210418111255/http://www.ultimatecitrus.com/Story/oj_story.html |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
Image:Ambersweet oranges.jpg|These varieties are called 'Ambersweet' oranges. |
|||
Image:Orangeseeds.jpg|orange seeds (pips) |
|||
=== Marmalade === |
|||
Image:Florida navel orange 1.jpg|Navel oranges from Florida are the most commonly sold in US grocery stores. |
|||
Image:2007-12-25-IMG 0451.JPG|Satsuma Oranges picked on Christmas day 2007 in [[Gainesville, Florida]] |
|||
{{main|Marmalade}} |
|||
Image:orangetrees.jpg|Orange trees on a street in [[Morocco]]. |
|||
Image:OrangeGrov.jpg|An orange grove photographed from the air. |
|||
Oranges are made into [[Fruit preserves|jam]] in many countries; in Britain, bitter [[Seville orange]]s are used to make [[marmalade]]. Almost the whole Spanish production is exported to Britain for this purpose. The entire fruit is cut up and boiled with sugar; the pith contributes [[pectin]], which helps the marmalade to set. The first recipe was by an Englishwoman, [[Mary Kettilby]], in 1714. Pieces of peel were first added by [[Janet Keiller]] of [[Dundee]] in the 1790s, contributing a distinctively bitter taste.<ref name="Bateman 1993">{{cite news |last=Bateman |first=Michael |title=Hail marmalade, great chieftain o' the jammy race: Mrs Keiller of Dundee added chunks in the 1790s, thus finally defining a uniquely British gift to gastronomy |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/arts-entertainment/food-drink-hail-marmalade-great-chieftain-o-the-jammy-race-mrs-keiller-of-dundee-added-chunks-in-the-1476300.html |agency=[[The Independent]] |date=3 January 1993 |access-date=15 March 2024 |archive-date=23 February 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160223120454/http://www.independent.co.uk/arts-entertainment/food-drink-hail-marmalade-great-chieftain-o-the-jammy-race-mrs-keiller-of-dundee-added-chunks-in-the-1476300.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Orange peel contains the bitter substances [[limonene]] and [[naringin]].<ref>{{cite journal |journal=Food Chemistry |year=2012 |volume=134 |issue=4 |pages=1892–8 |doi=10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.090 |title=Antioxidant capacity and mineral content of pulp and peel from commercial cultivars of citrus from Brazil |last1=Barros |first1=H.R. |last2=Ferreira |first2=T.A. |last3=Genovese |first3=M.I. |pmid=23442635}}</ref><ref name="Hasegawa Berhow Fong 1996">{{cite book |last1=Hasegawa |first1=S. |last2=Berhow |first2=M. A. |last3=Fong |first3=C. H. |title=Fruit Analysis |chapter=Analysis of Bitter Principles in Citrus |publisher=[[Springer Science+Business Media|Springer]] |publication-place=Berlin, Heidelberg |volume=18 |date=1996 |isbn=978-3-642-79662-3 |doi=10.1007/978-3-642-79660-9_4 |pages=59–80}}</ref> |
|||
Image:Navel orange1.jpg|Navel orange fruit. |
|||
File:Orange Harvest.jpg|An unusual orange harvest after a flood, [[California]], 1941. |
|||
=== Extracts === |
|||
File:Orange1900ppx.jpg|Orange fruit |
|||
Image:Orangedelivery.jpg|Delivering oranges in Tulum, Mexico |
|||
{{further|Limonene}} |
|||
[[Zest (ingredient)|Zest]] is scraped from the [[flavedo|coloured outer part of the peel]], and used as a flavoring and garnish in desserts and [[cocktail]]s.<ref>{{cite book |last=Bender |first=David |author-link=David A. Bender |title=Oxford Dictionary of Food and Nutrition |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |year=2009 |isbn=978-0-19-923487-5 |page=[https://archive.org/details/dictionaryoffood00bend/page/215 215] |edition=third |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/dictionaryoffood00bend/page/215}}</ref> |
|||
Sweet [[orange oil]] is a [[by-product]] of the juice industry produced by pressing the peel. It is used for flavoring food and drinks; it is employed in the perfume industry and in [[aromatherapy]] for its [[fragrance]]. The oil consists of approximately 90% <small>D</small>-limonene, a [[solvent]] used in household chemicals such as wood conditioners for furniture and—along with other citrus oils—detergents and hand cleansers. It is an efficient cleaning agent with a pleasant smell, promoted for being environmentally friendly and therefore preferable to petrochemicals. It is, however, irritating to the skin and toxic to aquatic life.<ref>{{cite web |date=April 2005 |title=D-Limonene |publisher=[[International Programme on Chemical Safety]] |url=http://www.inchem.org/documents/icsc/icsc/eics0918.htm |access-date=2010-03-06 |archive-date=2021-11-04 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211104220433/https://inchem.org/documents/icsc/icsc/eics0918.htm |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=January 2019 |title=(±)-1-methyl-4-(1-methylvinyl)cyclohexene |publisher=[[ECHA]] |url=https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/103051 |access-date=2019-01-22 |archive-date=2020-10-29 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201029092926/https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database/-/discli/details/103051 |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
<gallery class=center mode=nolines widths=200 heights=200> |
|||
File:Oranges and orange juice.jpg|Fruit and [[Orange juice|juice]] |
|||
File:Zesting an orange.jpg|[[Zest (ingredient)|Zesting]] an orange |
|||
File:Sevilleorangemarmalade.jpg|Homemade [[marmalade]], England</gallery> |
|||
== In human culture == |
|||
Oranges have featured in human culture since ancient times. The earliest mention of the sweet orange in [[Chinese literature]] dates from 314 BC.<ref name=fullgenome/> Larissa Pham, in ''[[The Paris Review]]'', notes that sweet oranges were available in China much earlier than in the West. She writes that Zhao Lingrang's fan painting ''Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines'' pays attention not to the fruit's colour but the shape of the fruit-laden trees, and that Su Shi's poem on the same subject runs "You must remember, / the best scenery of the year, / Is exactly now, / when oranges turn yellow and tangerines green."<ref name="Pham 2019"/> |
|||
The scholar Cristina Mazzoni has examined the multiple uses of the fruit in Italian art and literature, from [[Catherine of Siena]]'s sending of candied oranges to [[Pope Urban V|Pope Urban]], to [[Sandro Botticelli]]'s setting of his painting ''[[Primavera (Botticelli)|Primavera]]'' in an orange grove. She notes that oranges symbolised desire and wealth on the one hand, and deformity on the other, while in the fairy-stories of Sicily, they have magical properties.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Freedman |first=Paul |title=Review of Golden Fruit: A Cultural History of Oranges in Italy, by Cristina Mazzoni |journal=Journal of Interdisciplinary History |volume=50 |issue=1 |year=2019 |pages=129–130 |publisher=Project MUSE |url=https://muse.jhu.edu/article/726018}}</ref> Pham comments that the ''[[Arnolfini Portrait]]'' by [[Jan van Eyck]] contains in a small detail one of the first representations of oranges in Western art, the costly fruit perhaps traded by the merchant Arnolfini himself.<ref name="Pham 2019">{{cite web |last1=Pham |first1=Larissa |title=For the Love of Orange |url=https://www.theparisreview.org/blog/2019/08/13/for-the-love-of-orange/ |publisher=[[The Paris Review]] |access-date=14 March 2024 |date=13 August 2019 |archive-date=14 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240314150503/https://www.theparisreview.org/blog/2019/08/13/for-the-love-of-orange/ |url-status=live }}</ref> By the 17th century, [[Orangery|orangeries]] were added to great houses in Europe, both to enable the fruit to be grown locally and for prestige, as seen in the [[Versailles Orangerie]] completed in 1686.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Thacker |first1=Christopher |last2=[[Louis XIV]] |date=1972 |title="La Manière de montrer les jardins de Versailles," by Louis XIV and Others |journal=Garden History |volume=1 |issue=1 |pages=49–69 |doi=10.2307/1586442 |issn=0307-1243 |jstor=1586442}}</ref> |
|||
The Dutch [[Post-Impressionist]] artist [[Vincent van Gogh]] portrayed oranges in paintings such as his 1889 ''Still Life of Oranges and Lemons with Blue Gloves'' and his 1890 ''A Child with Orange'', both works late in his life. The American artist of the [[Ashcan School]], [[John Sloan]], made a 1935 painting ''Blond Nude with Orange, Blue Couch'', while [[Henri Matisse]]'s last painting was his 1951 ''Nude with Oranges''; after that he only made cut-outs.<ref name="Michalska 2023">{{cite web |last1=Michalska |first1=Magda |title=The Scent of Orange in the Air: Paintings with Oranges |url=https://www.dailyartmagazine.com/portraits-with-oranges/ |publisher=Daily Art Magazine |access-date=14 March 2024 |date=23 December 2023 |archive-date=14 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240314153633/https://www.dailyartmagazine.com/portraits-with-oranges/ |url-status=live }}</ref> |
|||
<gallery mode=packed heights=175px> |
|||
File:Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines (橙黃橘綠) by Zhao Lingrang (趙令穰).jpg|''Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines'' by Zhao Lingrang, Chinese fan painting from the [[Song dynasty]], c. 1070–1100 |
|||
File:Jan van Eyck 002.jpg|Detail of the ''[[Arnolfini Portrait]]'' by [[Jan van Eyck]], 1434 |
|||
File:Primavera (Botticelli) (detail).jpg|Detail of ''[[Primavera (Botticelli)|Primavera]]'' by [[Sandro Botticelli]], 1482, set in an orange grove |
|||
File:Måleri, stilleben. Frukt - Skoklosters slott - 88970.tif|Still life with oranges on a plate. Possibly [[Jacques Linard]] or [[Louise Moillon]], 1640 |
|||
File:Orangerie du château de Versailles le 11 septembre 2015 - 78.jpg|The [[Versailles Orangerie]], 1686 |
|||
File:OUDRY Orange Tree.jpg|[[Jean-Baptiste Oudry]], ''The Orange Tree'', 1740 |
|||
File:Vincent van Gogh, Still Life of Oranges and Lemons with Blue Gloves, 1889, NGA 164923.jpg|'' Still Life of Oranges and Lemons with Blue Gloves'' by [[Vincent van Gogh]], 1889 |
|||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
* [[Cam sành]] (terra-cotta orange) |
|||
* [[Mandarin orange]] |
|||
* [[Orange production in Brazil]] |
|||
* [[Banana]] – another fruit exported and consumed in large quantities |
|||
== Footnotes == |
|||
* [[List of citrus fruits]] |
|||
{{reflist|2}} |
|||
* [[List of culinary fruits]] |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
* McPhee, John. ''Oranges'' (1966) - focuses on Florida groves. |
|||
{{reflist|30em}} |
|||
* Sackman, Douglas Cazaux. ''Orange Empire: California and the Fruits of Eden'' (2005) comprehensive, multidimensional history of citrus industry in California |
|||
* Train, John. ''Oranges'' (2006) |
|||
* [http://culturesheet.org/rutaceae:citrus Culture & Care for the genus Citrus] on CultureSheet.org |
|||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{Commons|Citrus sinensis}} |
|||
* [http://sun.ars-grin.gov:8080/npgspub/xsql/duke/plantdisp.xsql?taxon=282 ''Citrus sinensis'' List of Chemicals (Dr. Duke's Databases)] |
|||
* [http://www.360cities.net/image/raanana-city-orange-sculpture Orange sculpture - Virtual Tour 360] |
|||
{{Wikiquote|Oranges}} |
|||
[[Category:Citrus]] |
|||
{{Wiktionary|orange}} |
|||
[[Category:Tropical agriculture]] |
|||
[[Category:Symbols of Florida]] |
|||
[[Category:Symbols of California]] |
|||
[[Category:Riverside, California]] |
|||
* {{Commons-inline|Citrus sinensis}} |
|||
[[am:ብርቱካን (ፍሬ)]] |
|||
* {{Wikispecies-inline|Citrus sinensis}} |
|||
[[ar:برتقال]] |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20041118125823/http://sun.ars-grin.gov:8080/npgspub/xsql/duke/plantdisp.xsql?taxon=282 ''Citrus sinensis'' List of Chemicals (Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases)], [[USDA]], Agricultural Research Service. |
|||
[[an:Narancha (fruita)]] |
|||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20140524030656/http://anrcatalog.ucdavis.edu/Details.aspx?itemNo=8199 Oranges: Safe Methods to Store, Preserve, and Enjoy]. (2006). University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources. Accessed May 23, 2014. |
|||
[[ast:Naranxa (frutu)]] |
|||
[[az:Portağal]] |
|||
{{Citrus|state=collapsed}} |
|||
[[bn:কমলা (ফল)]] |
|||
{{US state flowers}} |
|||
[[zh-min-nan:Liú-teng]] |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[be:Апельсін]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Апэльсін]] |
|||
[[Category:Oranges (fruit)|Oranges (fruit)]] |
|||
[[bo:ཚ་ལུ་མ།]] |
|||
[[Category:Articles containing video clips]] |
|||
[[bs:Narandža]] |
|||
[[Category:Cocktail garnishes]] |
|||
[[br:Aouraval]] |
|||
[[Category:Crops originating from China]] |
|||
[[ca:Taronja]] |
|||
[[Category:Fruits originating in Asia]] |
|||
[[cs:Pomeranč]] |
|||
[[Category:Symbols of California]] |
|||
[[cy:Oren (ffrwyth)]] |
|||
[[Category:Symbols of Florida]] |
|||
[[da:Appelsin]] |
|||
[[Category:Tropical agriculture]] |
|||
[[de:Orange (Frucht)]] |
|||
[[nv:Chʼil łitsxooí]] |
|||
[[et:Apelsinipuu]] |
|||
[[el:Πορτοκαλιά]] |
|||
[[es:Naranja (fruta)]] |
|||
[[eo:Oranĝo (frukto)]] |
|||
[[eu:Laranja]] |
|||
[[fa:پرتقال]] |
|||
[[fr:Orange (fruit)]] |
|||
[[gl:Laranxa (froita)]] |
|||
[[gu:સંતરુ (ફળ)]] |
|||
[[ko:오렌지]] |
|||
[[hi:संतरा (फल)]] |
|||
[[hr:Naranča]] |
|||
[[id:Jeruk manis]] |
|||
[[is:Appelsína]] |
|||
[[it:Citrus × sinensis]] |
|||
[[he:תפוז]] |
|||
[[jv:Jeruk]] |
|||
[[kk:Апельсин]] |
|||
[[sw:Chungwa]] |
|||
[[ht:Zoranj]] |
|||
[[la:Citrus sinensis]] |
|||
[[lv:Apelsīns]] |
|||
[[lt:Apelsinas]] |
|||
[[ln:Lilála]] |
|||
[[hu:Narancs]] |
|||
[[ml:ഓറഞ്ച് (സസ്യം)]] |
|||
[[mr:संत्रे]] |
|||
[[mn:Жүрж]] |
|||
[[nah:Naranjaxocotl]] |
|||
[[nl:Sinaasappel]] |
|||
[[nds-nl:Appelsien]] |
|||
[[ja:オレンジ]] |
|||
[[nap:Pertegàll]] |
|||
[[no:Appelsin]] |
|||
[[nn:Appelsin]] |
|||
[[pms:Citrus sinensis]] |
|||
[[pl:Pomarańcza]] |
|||
[[pt:Laranjeira]] |
|||
[[qu:Chilina]] |
|||
[[ru:Апельсин]] |
|||
[[sco:Oranger]] |
|||
[[sq:Portokalli]] |
|||
[[scn:Arancia]] |
|||
[[simple:Orange (fruit)]] |
|||
[[sk:Pomaranč]] |
|||
[[sl:Pomaranča]] |
|||
[[szl:Apluzina]] |
|||
[[sr:Наранџа]] |
|||
[[fi:Appelsiini]] |
|||
[[sv:Apelsin]] |
|||
[[tl:Dalandan]] |
|||
[[ta:நரந்தம்பழம்]] |
|||
[[te:బత్తాయి]] |
|||
[[th:ส้ม (ผลไม้)]] |
|||
[[to:Moli]] |
|||
[[tr:Portakal]] |
|||
[[uk:Апельсин]] |
|||
[[ug:قىزغۇچ سېرىق]] |
|||
[[vi:Cam]] |
|||
[[yi:מאראנץ]] |
|||
[[yo:Ọsàn]] |
|||
[[zh-yue:橙]] |
|||
[[zh:橙]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 11:23, 16 November 2024

The orange, also called sweet orange to distinguish it from the bitter orange (Citrus × aurantium), is the fruit of a tree in the family Rutaceae. Botanically, this is the hybrid Citrus × sinensis, between the pomelo (Citrus maxima) and the mandarin orange (Citrus reticulata). The chloroplast genome, and therefore the maternal line, is that of pomelo. There are many related hybrids including of mandarins and sweet orange. The sweet orange has had its full genome sequenced.
The orange originated in a region encompassing Southern China, Northeast India, and Myanmar; the earliest mention of the sweet orange was in Chinese literature in 314 BC. Orange trees are widely grown in tropical and subtropical areas for their sweet fruit. The fruit of the orange tree can be eaten fresh or processed for its juice or fragrant peel. In 2022, 76 million tonnes of oranges were grown worldwide, with Brazil producing 22% of the total, followed by India and China.
Oranges, variously understood, have featured in human culture since ancient times. They first appear in Western art in the Arnolfini Portrait by Jan van Eyck, but they had been depicted in Chinese art centuries earlier, as in Zhao Lingrang's Song dynasty fan painting Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines. By the 17th century, an orangery had become an item of prestige in Europe, as seen at the Versailles Orangerie. More recently, artists such as Vincent van Gogh, John Sloan, and Henri Matisse included oranges in their paintings.
Description
The orange tree is a relatively small evergreen, flowering tree, with an average height of 9 to 10 m (30 to 33 ft), although some very old specimens can reach 15 m (49 ft).[1] Its oval leaves, which are alternately arranged, are 4 to 10 cm (1.6 to 3.9 in) long and have crenulate margins.[2] Sweet oranges grow in a range of different sizes, and shapes varying from spherical to oblong. Inside and attached to the rind is a porous white tissue, the white, bitter mesocarp or albedo (pith).[3] The orange contains a number of distinct carpels (segments or pigs, botanically the fruits) inside, typically about ten, each delimited by a membrane and containing many juice-filled vesicles and usually a few pips. When unripe, the fruit is green. The grainy irregular rind of the ripe fruit can range from bright orange to yellow-orange, but frequently retains green patches or, under warm climate conditions, remains entirely green. Like all other citrus fruits, the sweet orange is non-climacteric, not ripening off the tree. The Citrus sinensis group is subdivided into four classes with distinct characteristics: common oranges, blood or pigmented oranges, navel oranges, and acidless oranges.[4][5][6] The fruit is a hesperidium, a modified berry; it is covered by a rind formed by a rugged thickening of the ovary wall.[7][8]
-
Flowers
-
Fruit starting to develop
-
Flowers and fruit simultaneously
-
Mature tree in Galicia, Spain, fruiting in November
-
Structure of the botanical hesperidium
History
Hybrid origins
Citrus trees are angiosperms, and most species are almost entirely interfertile. This includes grapefruits, lemons, limes, oranges, and many citrus hybrids. As the interfertility of oranges and other citrus has produced numerous hybrids and cultivars, and bud mutations have also been selected, citrus taxonomy has proven difficult.[9]
The sweet orange, Citrus x sinensis,[10] is not a wild fruit, but arose in domestication in East Asia. It originated in a region encompassing Southern China, Northeast India,[11] and Myanmar.[12] The fruit was created as a cross between a non-pure mandarin orange and a hybrid pomelo that had a substantial mandarin component.[13][14] Since its chloroplast DNA is that of pomelo, it was likely the hybrid pomelo, perhaps a pomelo BC1 backcross, that was the maternal parent of the first orange.[15][16] Based on genomic analysis, the relative proportions of the ancestral species in the sweet orange are approximately 42% pomelo and 58% mandarin.[17] All varieties of the sweet orange descend from this prototype cross, differing only by mutations selected for during agricultural propagation.[16] Sweet oranges have a distinct origin from the bitter orange, which arose independently, perhaps in the wild, from a cross between pure mandarin and pomelo parents.[16]
Sweet oranges have in turn given rise to many further hybrids including the grapefruit, which arose from a sweet orange x pomelo backcross. Spontaneous and engineered backcrosses between the sweet orange and mandarin oranges or tangerines have produced the clementine and murcott. The ambersweet is a complex sweet orange x (Orlando tangelo x clementine) hybrid.[17][18] The citranges are a group of sweet orange x trifoliate orange (Citrus trifoliata) hybrids.[19]

Arab Agricultural Revolution

In Europe, the Moors introduced citrus fruits including the bitter orange, lemon, and lime to Al-Andalus in the Iberian Peninsula during the Arab Agricultural Revolution.[20] Large-scale cultivation started in the 10th century, as evidenced by complex irrigation techniques specifically adapted to support orange orchards.[21][20] Citrus fruits—among them the bitter orange—were introduced to Sicily in the 9th century during the period of the Emirate of Sicily, but the sweet orange was unknown there until the late 15th century or the beginnings of the 16th century, when Italian and Portuguese merchants brought orange trees into the Mediterranean area.[11]
Spread across Europe
Shortly afterward, the sweet orange quickly was adopted as an edible fruit. It was considered a luxury food grown by wealthy people in private conservatories, called orangeries. By 1646, the sweet orange was well known throughout Europe; it went on to become the most often cultivated of all fruit trees.[11] Louis XIV of France had a great love of orange trees and built the grandest of all royal Orangeries at the Palace of Versailles.[22] At Versailles, potted orange trees in solid silver tubs were placed throughout the rooms of the palace, while the Orangerie allowed year-round cultivation of the fruit to supply the court. When Louis condemned his finance minister, Nicolas Fouquet, in 1664, part of the treasures that he confiscated were over 1,000 orange trees from Fouquet's estate at Vaux-le-Vicomte.[23]
To the Americas
Spanish travelers introduced the sweet orange to the American continent. On his second voyage in 1493, Christopher Columbus may have planted the fruit on Hispaniola.[6] Subsequent expeditions in the mid-1500s brought sweet oranges to South America and Mexico, and to Florida in 1565, when Pedro Menéndez de Avilés founded St Augustine. Spanish missionaries brought orange trees to Arizona between 1707 and 1710, while the Franciscans did the same in San Diego, California, in 1769.[11] Archibald Menzies, the botanist on the Vancouver Expedition, collected orange seeds in South Africa, raised the seedlings on board, and gave them to several Hawaiian chiefs in 1792. The sweet orange came to be grown across the Hawaiian Islands, but its cultivation stopped after the arrival of the Mediterranean fruit fly in the early 1900s.[11][24] Florida farmers obtained seeds from New Orleans around 1872, after which orange groves were established by grafting the sweet orange on to sour orange rootstocks.[11]
Etymology
The word "orange" derives ultimately from Proto-Dravidian or Tamil நாரம் (nāram). From there the word entered Sanskrit नारङ्ग (nāraṅga), meaning 'orange tree'. The Sanskrit word reached European languages through Persian نارنگ (nārang) and its Arabic derivative نارنج (nāranj).[25]
The word entered Late Middle English in the 14th century via Old French pomme d'orenge.[26] Other forms include Old Provençal auranja,[27] Italian arancia, formerly narancia.[25] In several languages, the initial n present in earlier forms of the word dropped off because it may have been mistaken as part of an indefinite article ending in an n sound. In French, for example, une norenge may have been heard as une orenge. This linguistic change is called juncture loss. The color was named after the fruit,[28] with the first recorded use of orange as a color name in English in 1512.[29][30]

Composition
Nutrition
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 197 kJ (47 kcal) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
11.75 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sugars | 9.35 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dietary fiber | 2.4 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.12 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.94 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other constituents | Quantity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Water | 86.75 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults,[31] except for potassium, which is estimated based on expert recommendation from the National Academies.[32] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Orange flesh is 87% water, 12% carbohydrates, 1% protein, and contains negligible fat (see table). As a 100-gram reference amount, orange flesh provides 47 calories, and is a rich source of vitamin C, providing 64% of the Daily Value. No other micronutrients are present in significant amounts (see table).
Phytochemicals
Oranges contain diverse phytochemicals, including carotenoids (beta-carotene, lutein and beta-cryptoxanthin), flavonoids (e.g. naringenin)[33] and numerous volatile organic compounds producing orange aroma, including aldehydes, esters, terpenes, alcohols, and ketones.[34] Orange juice contains only about one-fifth the citric acid of lime or lemon juice (which contain about 47 g/L).[35]
Taste
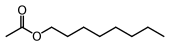
The taste of oranges is determined mainly by the ratio of sugars to acids, whereas orange aroma derives from volatile organic compounds, including alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, terpenes, and esters.[36][37] Bitter limonoid compounds, such as limonin, decrease gradually during development, whereas volatile aroma compounds tend to peak in mid- to late-season development.[38] Taste quality tends to improve later in harvests when there is a higher sugar/acid ratio with less bitterness.[38] As a citrus fruit, the orange is acidic, with pH levels ranging from 2.9[39] to 4.0.[39][40] Taste and aroma vary according to genetic background, environmental conditions during development, ripeness at harvest, postharvest conditions, and storage duration.[36][37]
Cultivars
Common
Common oranges (also called "white", "round", or "blond" oranges) constitute about two-thirds of all orange production. The majority of this crop is used for juice.[4][6]
Valencia
The Valencia orange is a late-season fruit; it is popular when navel oranges are out of season. Thomas Rivers, an English nurseryman, imported this variety from the Azores and catalogued it in 1865 under the name Excelsior. Around 1870, he provided trees to S. B. Parsons, a Long Island nurseryman, who in turn sold them to E. H. Hart of Federal Point, Florida.[41]
Navel
Navel oranges have a characteristic second fruit at the apex, which protrudes slightly like a human navel. They are mainly an eating fruit, as their thicker skin makes them easy to peel, they are less juicy and their bitterness makes them less suitable for juice.[4] The parent variety was probably the Portuguese navel orange or Umbigo.[42] The cultivar rapidly spread to other countries, but being seedless it had to be propagated by cutting and grafting.[43]
The Cara cara orange is a type of navel orange grown mainly in Venezuela, South Africa and California's San Joaquin Valley. It is sweet and low in acid,[44] with distinctively pinkish red flesh. It was discovered at the Hacienda Cara Cara in Valencia, Venezuela, in 1976.[45]
Blood
Blood oranges, with an intense red coloration inside, are widely grown around the Mediterranean; there are several cultivars.[11] The development of the red color requires cool nights.[46] The redness is mainly due to the anthocyanin pigment chrysanthemin (cyanidin 3-O-glucoside).[47]
Acidless
Acidless oranges are an early-season fruit with very low levels of acid. They also are called "sweet" oranges in the United States, with similar names in other countries: douce in France, sucrena in Spain, dolce or maltese in Italy, meski in North Africa and the Near East (where they are especially popular), succari in Egypt, and lima in Brazil.[4] The lack of acid, which protects orange juice against spoilage in other groups, renders them generally unfit for processing as juice, so they are primarily eaten. They remain profitable in areas of local consumption, but rapid spoilage renders them unsuitable for export to major population centres of Europe, Asia, or the United States.[4]
-
A grove of Valencia oranges in Florida
Cultivation
Climate
Like most citrus plants, oranges do well under moderate temperatures—between 15.5 and 29 °C (59.9 and 84.2 °F)—and require considerable amounts of sunshine and water. They are principally grown in tropical and subtropical regions.[6]
As oranges are sensitive to frost, farmers have developed methods to protect the trees from frost damage. A common process is to spray the trees with water so as to cover them with a thin layer of ice, insulating them even if air temperatures drop far lower. This practice, however, offers protection only for a very short time.[48] Another procedure involves burning fuel oil in smudge pots put between the trees. These burn with a great deal of particulate emission, so condensation of water vapor on the particulate soot prevents condensation on plants and raises the air temperature very slightly. Smudge pots were developed after a disastrous freeze in southern California in January 1913 destroyed a whole crop.[49]
Propagation
Commercially grown orange trees are propagated asexually by grafting a mature cultivar onto a suitable seedling rootstock to ensure the same yield, identical fruit characteristics, and resistance to diseases throughout the years. Propagation involves two stages: first, a rootstock is grown from seed. Then, when it is approximately one year old, the leafy top is cut off and a bud taken from a specific scion variety, is grafted into its bark. The scion is what determines the variety of orange, while the rootstock makes the tree resistant to pests and diseases and adaptable to specific soil and climatic conditions. Thus, rootstocks influence the rate of growth and have an effect on fruit yield and quality.[50] Rootstocks must be compatible with the variety inserted into them because otherwise, the tree may decline, be less productive, or die.[50] Among the advantages to grafting are that trees mature uniformly and begin to bear fruit earlier than those reproduced by seeds (3 to 4 years in contrast with 6 to 7 years),[51] and that farmers can combine the best attributes of a scion with those of a rootstock.[52]
Harvest
Canopy-shaking mechanical harvesters are being used increasingly in Florida to harvest oranges. Current canopy shaker machines use a series of six-to-seven-foot-long tines to shake the tree canopy at a relatively constant stroke and frequency.[53] Oranges are picked once they are pale orange.[54]
Degreening
Oranges must be mature when harvested. In the United States, laws forbid harvesting immature fruit for human consumption in Texas, Arizona, California and Florida.[55] Ripe oranges, however, often have some green or yellow-green color in the skin. Ethylene gas is used to turn green skin to orange. This process is known as "degreening", "gassing", "sweating", or "curing".[55] Oranges are non-climacteric fruits and cannot ripen internally in response to ethylene gas after harvesting, though they will de-green externally.[56]
Storage
Commercially, oranges can be stored by refrigeration in controlled-atmosphere chambers for up to twelve weeks after harvest. Storage life ultimately depends on cultivar, maturity, pre-harvest conditions, and handling.[57] At home, oranges have a shelf life of about one month, and are best stored loose.[58]
-
Spraying oranges in an orchard in Australia
-
Orange grove in California
-
Picking oranges, Israel
-
Harvest, Israel
-
Market stall, Morocco
Pests and diseases
Pests

The first major pest that attacked orange trees in the United States was the cottony cushion scale (Icerya purchasi), imported from Australia to California in 1868. Within 20 years, it wiped out the citrus orchards around Los Angeles, and limited orange growth throughout California. In 1888, the USDA sent Alfred Koebele to Australia to study this scale insect in its native habitat. He brought back with him specimens of an Australian ladybird, Novius cardinalis (the Vedalia beetle), and within a decade the pest was controlled. This was one of the first successful applications of biological pest control on any crop.[41] The orange dog caterpillar of the giant swallowtail butterfly, Papilio cresphontes, is a pest of citrus plantations in North America, where it eats new foliage and can defoliate young trees.[59]
Diseases

Citrus greening disease, caused by the bacterium Liberobacter asiaticum, has been the most serious threat to orange production since 2010. It is characterized by streaks of different shades on the leaves, and deformed, poorly colored, unsavory fruit. In areas where the disease is endemic, citrus trees live for only five to eight years and never bear fruit suitable for consumption.[61] In the western hemisphere, the disease was discovered in Florida in 1998, where it has attacked nearly all the trees ever since. It was reported in Brazil by Fundecitrus Brasil in 2004.[61] As from 2009, 0.87% of the trees in Brazil's main orange growing areas (São Paulo and Minas Gerais) showed symptoms of greening, an increase of 49% over 2008.[62] The disease is spread primarily by psyllid plant lice such as the Asian citrus psyllid (Diaphorina citri Kuwayama), an efficient vector of the bacterium.[60] Foliar insecticides reduce psyllid populations for a short time, but also suppress beneficial predatory ladybird beetles. Soil application of aldicarb provided limited control of Asian citrus psyllid, while drenches of imidacloprid to young trees were effective for two months or more.[63] Management of citrus greening disease requires an integrated approach that includes use of clean stock, elimination of inoculum via voluntary and regulatory means, use of pesticides to control psyllid vectors in the citrus crop, and biological control of the vectors in non-crop reservoirs.[61]
Greasy spot, a fungal disease caused by the ascomycete Mycosphaerella citri, produces leaf spots and premature defoliation, thus reducing the tree's vigour and yield. Ascospores of M. citri are generated in pseudothecia in decomposing fallen leaves.[64]
Production
| Production of oranges – 2022 | |
|---|---|
| Country | Production (millions of tonnes) |
| 16.9 | |
| 10.2 | |
| 7.6 | |
| 4.8 | |
| 3.4 | |
| 3.1 | |
| World | 76.4 |
| Source: FAOSTAT of the United Nations[65] | |
In 2022, world production of oranges was 76 million tonnes, led by Brazil with 22% of the total, followed by India, China, and Mexico.[65] The United States Department of Agriculture has established grades for Florida oranges, primarily for oranges sold as fresh fruit.[66] In the United States, groves are located mainly in Florida, California, and Texas.[67] The majority of California's crop is sold as fresh fruit, whereas Florida's oranges are destined to juice products. The Indian River area of Florida produces high quality juice, which is often sold fresh and blended with juice from other regions, because Indian River trees yield sweet oranges but in relatively small quantities.[68]
Culinary use
Dessert fruit and juice
Oranges, whose flavor may vary from sweet to sour, are commonly peeled and eaten fresh raw as a dessert. Orange juice is obtained by squeezing the fruit on a special tool (a juicer or squeezer) and collecting the juice in a tray or tank underneath. This can be made at home or, on a much larger scale, industrially.[69] Orange juice is a traded commodity on the Intercontinental Exchange.[70] Frozen orange juice concentrate is made from freshly squeezed and filtered juice.[71]
Marmalade
Oranges are made into jam in many countries; in Britain, bitter Seville oranges are used to make marmalade. Almost the whole Spanish production is exported to Britain for this purpose. The entire fruit is cut up and boiled with sugar; the pith contributes pectin, which helps the marmalade to set. The first recipe was by an Englishwoman, Mary Kettilby, in 1714. Pieces of peel were first added by Janet Keiller of Dundee in the 1790s, contributing a distinctively bitter taste.[72] Orange peel contains the bitter substances limonene and naringin.[73][74]
Extracts
Zest is scraped from the coloured outer part of the peel, and used as a flavoring and garnish in desserts and cocktails.[75]
Sweet orange oil is a by-product of the juice industry produced by pressing the peel. It is used for flavoring food and drinks; it is employed in the perfume industry and in aromatherapy for its fragrance. The oil consists of approximately 90% D-limonene, a solvent used in household chemicals such as wood conditioners for furniture and—along with other citrus oils—detergents and hand cleansers. It is an efficient cleaning agent with a pleasant smell, promoted for being environmentally friendly and therefore preferable to petrochemicals. It is, however, irritating to the skin and toxic to aquatic life.[76][77]
In human culture
Oranges have featured in human culture since ancient times. The earliest mention of the sweet orange in Chinese literature dates from 314 BC.[13] Larissa Pham, in The Paris Review, notes that sweet oranges were available in China much earlier than in the West. She writes that Zhao Lingrang's fan painting Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines pays attention not to the fruit's colour but the shape of the fruit-laden trees, and that Su Shi's poem on the same subject runs "You must remember, / the best scenery of the year, / Is exactly now, / when oranges turn yellow and tangerines green."[78]
The scholar Cristina Mazzoni has examined the multiple uses of the fruit in Italian art and literature, from Catherine of Siena's sending of candied oranges to Pope Urban, to Sandro Botticelli's setting of his painting Primavera in an orange grove. She notes that oranges symbolised desire and wealth on the one hand, and deformity on the other, while in the fairy-stories of Sicily, they have magical properties.[79] Pham comments that the Arnolfini Portrait by Jan van Eyck contains in a small detail one of the first representations of oranges in Western art, the costly fruit perhaps traded by the merchant Arnolfini himself.[78] By the 17th century, orangeries were added to great houses in Europe, both to enable the fruit to be grown locally and for prestige, as seen in the Versailles Orangerie completed in 1686.[80]
The Dutch Post-Impressionist artist Vincent van Gogh portrayed oranges in paintings such as his 1889 Still Life of Oranges and Lemons with Blue Gloves and his 1890 A Child with Orange, both works late in his life. The American artist of the Ashcan School, John Sloan, made a 1935 painting Blond Nude with Orange, Blue Couch, while Henri Matisse's last painting was his 1951 Nude with Oranges; after that he only made cut-outs.[81]
-
Yellow Oranges and Green Tangerines by Zhao Lingrang, Chinese fan painting from the Song dynasty, c. 1070–1100
-
Detail of the Arnolfini Portrait by Jan van Eyck, 1434
-
Detail of Primavera by Sandro Botticelli, 1482, set in an orange grove
-
Still life with oranges on a plate. Possibly Jacques Linard or Louise Moillon, 1640
-
The Versailles Orangerie, 1686
-
Jean-Baptiste Oudry, The Orange Tree, 1740
-
Still Life of Oranges and Lemons with Blue Gloves by Vincent van Gogh, 1889
See also
- Banana – another fruit exported and consumed in large quantities
- List of citrus fruits
- List of culinary fruits
References
- ^ Hodgson, Willard (1967–1989) [1943]. "Chapter 4: Horticultural Varieties of Citrus". In Webber, Herbert John; rev Walter Reuther and Harry W. Lawton (eds.). The Citrus Industry. Riverside, California: University of California Division of Agricultural Sciences. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05.
- ^ "Sweet Orange – Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck (pro. sp.) – Overview – Encyclopedia of Life". Encyclopedia of Life. Archived from the original on 2010-12-04. Retrieved 2011-01-18.
- ^ "Pith dictionary definition – pith defined". www.yourdictionary.com. Archived from the original on 2011-05-12. Retrieved 2011-01-17.
- ^ a b c d e Kimball, Dan A. (June 30, 1999). Citrus processing: a complete guide (2d ed.). New York: Springer. p. 450. ISBN 978-0-8342-1258-9.
- ^ Webber, Herbert John; Reuther, Walter; Lawton, Harry W. (1967–1989) [1903]. "The Citrus Industry". Riverside, California: University of California Division of Agricultural Sciences. Archived from the original on 2004-06-04.
- ^ a b c d Sauls, Julian W. (December 1998). "Home Fruit Production – Oranges". Texas A&M University. Archived from the original on 10 May 2023. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ Bailey, H. and Bailey, E. (1976). Hortus Third. Cornell University MacMillan. N.Y. p. 275.
- ^ "Seed and Fruits". esu.edu. Archived from the original on 2010-11-14.
- ^ Nicolosi, E.; Deng, Z. N.; Gentile, A.; La Malfa, S.; Continella, G.; Tribulato, E. (2000). "Citrus phylogeny and genetic origin of important species as investigated by molecular markers". Theoretical and Applied Genetics. 100 (8): 1155–1166. doi:10.1007/s001220051419. S2CID 24057066.
- ^ "Citrus ×sinensis (L.) Osbeck (pro sp.) (maxima × reticulata) sweet orange". Plants.USDA.gov. Archived from the original on May 12, 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g Morton, Julia F. (1987). Fruits of Warm Climates. pp. 134–142. Archived from the original on 2019-05-26. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ^ Talon, Manuel; Caruso, Marco; Gmitter, Fred G. Jr. (2020). The Genus Citrus. Woodhead Publishing. p. 17. ISBN 978-0128122174. Archived from the original on 2024-03-16. Retrieved 2020-05-05.
- ^ a b Xu, Q.; Chen, L.L.; Ruan, X.; Chen, D.; Zhu, A.; Chen, C.; et al. (Jan 2013). "The draft genome of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis)". Nature Genetics. 45 (1): 59–66. doi:10.1038/ng.2472. PMID 23179022.
- ^ Andrés García Lor (2013). Organización de la diversidad genética de los cítricos (PDF) (Thesis). p. 79. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-02-25. Retrieved 2015-04-24.
- ^ Velasco, R.; Licciardello, C. (2014). "A genealogy of the citrus family". Nature Biotechnology. 32 (7): 640–642. doi:10.1038/nbt.2954. PMID 25004231. S2CID 9357494.
- ^ a b c Wu, G. Albert (2014). "Sequencing of diverse mandarin, pomelo and orange genomes reveals complex history of admixture during citrus domestication". Nature Biotechnology. 32 (7): 656–662. doi:10.1038/nbt.2906. PMC 4113729. PMID 24908277.
- ^ a b c Wu, Guohong Albert; Terol, Javier; Ibanez, Victoria; López-García, Antonio; Pérez-Román, Estela; Borredá, Carles; et al. (2018). "Genomics of the origin and evolution of Citrus". Nature. 554 (7692): 311–316. Bibcode:2018Natur.554..311W. doi:10.1038/nature25447. hdl:20.500.11939/5741. PMID 29414943. and Supplement
- ^ Bai, Jinhe; Baldwin, Elizabeth B.; Hearn, Jake; Driggers, Randy; Stover, Ed (2014). "Volatile Profile Comparison of USDA Sweet Orange-like Hybrids versus 'Hamlin' and 'Ambersweet'". HortScience. 49 (10): 1262–1267. doi:10.21273/HORTSCI.49.10.1262. Archived from the original on 2016-07-21. Retrieved 2018-03-18.
- ^ "Trifoliate hybrids". University of California at Riverside, Givaudan Citrus Variety Collection. Archived from the original on 20 January 2022. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ a b Watson, Andrew M. (1974). "The Arab Agricultural Revolution and Its Diffusion, 700–1100". The Journal of Economic History. 34 (1): 8–35. doi:10.1017/S0022050700079602. JSTOR 2116954. S2CID 154359726.
- ^ Trillo San José, Carmen (1 September 2003). "Water and landscape in Granada". University of Granada. Archived from the original on 8 March 2023. Retrieved 7 January 2017.
- ^ Leroux, Jean-Baptiste (2002). The Gardens of Versailles. Thames & Hudson. p. 368.
- ^ Mitford, Nancy (1966). The Sun King. Sphere Books. p. 11.
- ^ Mau, Ronald; Kessing, Jayma Martin (April 2007). "Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann)". University of Hawaii. Archived from the original on 18 July 2012. Retrieved 5 December 2012.
- ^ a b "orange (n.)". Online Etymology Dictionary. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ "Definition of orange". OED online (www.oxforddictionaries.com). Archived from the original on May 11, 2013.
- ^ "Definition of orange". Collins English Dictionary (collinsdictionary.com). Archived from the original on 2013-04-03. Retrieved 2012-12-05.
- ^ Paterson, Ian (2003). A Dictionary of Colour: A Lexicon of the Language of Colour (1st paperback ed.). London: Thorogood (published 2004). p. 280. ISBN 978-1-85418-375-0. OCLC 60411025.
- ^ "orange colour". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ Maerz, Aloys John; Morris, Rea Paul (1930), A Dictionary of Color, New York: McGraw-Hill, p. 200
- ^ United States Food and Drug Administration (2024). "Daily Value on the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels". FDA. Archived from the original on 2024-03-27. Retrieved 2024-03-28.
- ^ National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Food and Nutrition Board; Committee to Review the Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium (2019). "Chapter 4: Potassium: Dietary Reference Intakes for Adequacy". In Oria, Maria; Harrison, Meghan; Stallings, Virginia A. (eds.). Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (US). pp. 120–121. doi:10.17226/25353. ISBN 978-0-309-48834-1. PMID 30844154. Retrieved 2024-12-05.
- ^ Aschoff, Julian K.; Kaufmann, Sabrina; Kalkan, Onur; Neidhart, Sybille; Carle, Reinhold; Schweiggert, Ralf M. (2015-01-21). "In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Carotenoids, Flavonoids, and Vitamin C from Differently Processed Oranges and Orange Juices [ Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck]". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 63 (2): 578–587. doi:10.1021/jf505297t. ISSN 0021-8561.
- ^ Perez-Cacho, P.R.; Rouseff, R.L. (2008). "Fresh squeezed orange juice odor: a review". Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 48 (7): 681–95. doi:10.1080/10408390701638902. PMID 18663618. S2CID 32567584.
- ^ Penniston, Kristina L.; Nakada, Stephen Y.; Holmes, Ross P.; Assimos, Dean G. (2008). "Quantitative Assessment of Citric Acid in Lemon Juice, Lime Juice, and Commercially-Available Fruit Juice Products". Journal of Endourology. 22 (3): 567–570. doi:10.1089/end.2007.0304. ISSN 0892-7790. PMC 2637791. PMID 18290732.
- ^ a b Tietel, Z.; Plotto, A.; Fallik, E.; Lewinsohn, E.; Porat, R. (2011). "Taste and aroma of fresh and stored mandarins". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 91 (1): 14–23. Bibcode:2011JSFA...91...14T. doi:10.1002/jsfa.4146. PMID 20812381.
- ^ a b El Hadi, M. A.; Zhang, F. J.; Wu, F. F.; Zhou, C. H.; Tao, J (2013). "Advances in fruit aroma volatile research". Molecules. 18 (7): 8200–29. doi:10.3390/molecules18078200. PMC 6270112. PMID 23852166.
- ^ a b Bai, J.; Baldwin, E. A.; McCollum, G.; Plotto, A.; Manthey, J. A.; Widmer, W. W.; Luzio, G.; Cameron, R. (2016). "Changes in Volatile and Non-Volatile Flavor Chemicals of "Valencia" Orange Juice over the Harvest Seasons". Foods. 5 (1): 4. doi:10.3390/foods5010004. PMC 5224568. PMID 28231099.
- ^ a b Sinclair, Walton B.; Bartholomew, E.T.; Ramsey, R. C. (1945). "Analysis of the organic acids of orange juice" (PDF). Plant Physiology. 20 (1): 3–18. doi:10.1104/pp.20.1.3. PMC 437693. PMID 16653966.
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (July 16, 1999). "Outbreak of Salmonella Serotype Muenchen Infections Associated with Unpasteurized Orange Juice – United States and Canada, June 1999". Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 48 (27): 582–585. PMID 10428096. Archived from the original on November 1, 2021. Retrieved September 10, 2017.
- ^ a b c Coit, John Eliot (1915). Citrus fruits: an account of the citrus fruit industry, with special reference to California requirements and practices and similar conditions. Macmillan. Retrieved 2 October 2011.
- ^ "Washington". Citrus ID. Archived from the original on 14 March 2024. Retrieved 14 March 2024., citing amongst other sources Risso, A.; Poiteau, A. (1819–1822). Histoire Naturelle des Orangers. Paris: Audot. Archived from the original on 2023-12-10. Retrieved 2024-03-14.
- ^ "Commodity Fact Sheet: Citrus Fruits" (PDF). California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ "UBC Botanical Garden, Botany Photo of the Day". Archived from the original on 2010-01-24.
- ^ "Cara Cara navel orange". University of California, Riverside. Archived from the original on 2019-04-25. Retrieved 2011-01-20.
- ^ McGee, Harold (2004). On food and cooking: the science and lore of the kitchen. New York: Scribner. p. 376. ISBN 0-684-80001-2. Archived from the original on 2023-07-28. Retrieved 2024-03-15.
- ^ Felgines, C.; Texier, O.; Besson, C.; Vitaglione, P; Lamaison, J.-L.; Fogliano, V.; et al. (2008). "Influence of glucose on cyanidin 3-glucoside absorption in rats". Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 52 (8): 959–64. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200700377. PMID 18646002.
- ^ "How Cold Can Water Get?". Argonne National Laboratory. 2002-09-08. Archived from the original on 2015-02-26. Retrieved 2009-04-16.
- ^ Moore, Frank Ensor (1995). Redlands Astride the Freeway: The Development of Good Automobile Roads. Redlands, California: Moore Historical Foundation. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-914167-07-5.
- ^ a b Lacey, Kevin (July 2012). "Citrus rootstocks for WA" (PDF). Government of WA. Department of Agriculture and Food. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-11-12. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ Price, Martin. "Citrus Propagation and Rootstocks". ultimatecitrus.com. Archived from the original on 6 April 2018. Retrieved 30 November 2012.
- ^ "Citrus Propagation. Research Program on Citrus Rootstock Breeding and Genetics". ars-grin.gov. Archived from the original on 2010-05-28.
- ^ Bora, G.; Hebel, M.; Lee, K. (2007-12-01). "In-situ measurement of the detachment force of individual oranges harvested by a canopy shaker harvesting machine" (PDF). Abstracts for the 2007 Joint Annual Meeting of the Florida State Horticulture Society. S2CID 113761794. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-26.
- ^ "Fresh Citrus Direct". freshcitrusdirect.wordpress.com. Archived from the original on 2015-01-10.
- ^ a b Wagner, Alfred B.; Sauls, Julian W. "Harvesting and Pre-pack Handling". The Texas A&M University System. Archived from the original on 4 January 2013. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- ^ Arpaia, Mary Lu; Kader, Adel A. "Orange: Recommendations for Maintaining Postharvest Quality". UCDavis Postharvest Technology Center. Archived from the original on 2013-12-06. Retrieved 2013-12-12.
- ^ Ritenour, M.A. (2004). "Orange. The Commercial Storage of Fruits, Vegetables, and Florist and Nursery Stocks" (PDF). USDA. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-01-27.
- ^ "Home Storage Guide for Fresh Fruits & Vegetables. Canadian Produce Marketing Association" (PDF). cpma.ca. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-05-12.
- ^ Mcauslane, Heather (May 2009). "Giant Swallowtail, Orangedog, Papilio cresphontes Cramer (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Papilionidae)". Edis (4). University of Florida. doi:10.32473/edis-in134-2009. Archived from the original on 16 March 2024. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ a b Killiny, Nabil; Nehela, Yasser; George, Justin; Rashidi, Mahnaz; Stelinski, Lukasz L.; Lapointe, Stephen L. (2021-07-01). "Phytoene desaturase-silenced citrus as a trap crop with multiple cues to attract Diaphorina citri, the vector of Huanglongbing". Plant Science. 308: 110930. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110930. ISSN 0168-9452. PMID 34034878. S2CID 235203508.
- ^ a b c Halbert, Susan E.; Manjunath, Keremane L. (September 2004). "Asian citrus psyllids (Sternorrhyncha: Psyllidae) and greening disease of citrus: A literature review and assessment of risk in Florida". The Florida Entomologist. 87 (3): 330–353. doi:10.1653/0015-4040(2004)087[0330:ACPSPA]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0015-4040. S2CID 56161727.
- ^ "GAIN Report Number: BR9006" (PDF). USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. 18 June 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-05-13.
- ^ Qureshi, J.; Stansly, P. (2007-12-01). "Integrated approaches for managing the Asian citrus psyllid Diaphorina citri (Homoptera: Psyllidae) in Florida" (PDF). Proceedings of the Florida State Horticultural Society. 120: 110–115. S2CID 55798062. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-11-17. Retrieved 2023-11-17.
- ^ Mondal, S.N.; Morgan, K.T.; Timme, L.W. (June 2007). "Effect of Water Management and Soil Application of Nitrogen Fertilizers, Petroleum Oils, and Lime on Inoculum Production by Mycosphaerella citri, the Cause of Citrus Greasy Spot" (PDF). Abstracts for the 2007 Joint Annual Meeting of the Florida State Horticulture Society. S2CID 113761794. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-26.
- ^ a b "Orange production in 2022, Crops/Regions/World list/Production Quantity/Year (pick lists)". UN Food and Agriculture Organization, Corporate Statistical Database. 2024. Archived from the original on 12 November 2016. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ "United States Standards for Grades of Florida Oranges and Tangelos". USDA. February 1997. Archived from the original on 2011-07-26.
- ^ "Oranges: Production Map by State". United States Department of Agriculture. 1 March 2017. Archived from the original on 31 October 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2017.
- ^ "History of the Indian River Citrus District". Indian River Citrus League. Archived from the original on 1 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2012.
- ^ "How orange juice is made". Discovery Networks International. 20 September 2022. Archived from the original on 24 September 2023. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ Lawson, Alex (27 October 2023). "The great orange juice trading rally – and why a big squeeze could lie ahead". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 22 November 2023. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ Townsend, Chet (2012). "The Story of Florida Orange Juice: From the Grove to Your Glass". Archived from the original on 18 April 2021. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ Bateman, Michael (3 January 1993). "Hail marmalade, great chieftain o' the jammy race: Mrs Keiller of Dundee added chunks in the 1790s, thus finally defining a uniquely British gift to gastronomy". The Independent. Archived from the original on 23 February 2016. Retrieved 15 March 2024.
- ^ Barros, H.R.; Ferreira, T.A.; Genovese, M.I. (2012). "Antioxidant capacity and mineral content of pulp and peel from commercial cultivars of citrus from Brazil". Food Chemistry. 134 (4): 1892–8. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.03.090. PMID 23442635.
- ^ Hasegawa, S.; Berhow, M. A.; Fong, C. H. (1996). "Analysis of Bitter Principles in Citrus". Fruit Analysis. Vol. 18. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 59–80. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-79660-9_4. ISBN 978-3-642-79662-3.
- ^ Bender, David (2009). Oxford Dictionary of Food and Nutrition (third ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-19-923487-5.
- ^ "D-Limonene". International Programme on Chemical Safety. April 2005. Archived from the original on 2021-11-04. Retrieved 2010-03-06.
- ^ "(±)-1-methyl-4-(1-methylvinyl)cyclohexene". ECHA. January 2019. Archived from the original on 2020-10-29. Retrieved 2019-01-22.
- ^ a b Pham, Larissa (13 August 2019). "For the Love of Orange". The Paris Review. Archived from the original on 14 March 2024. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ Freedman, Paul (2019). "Review of Golden Fruit: A Cultural History of Oranges in Italy, by Cristina Mazzoni". Journal of Interdisciplinary History. 50 (1). Project MUSE: 129–130.
- ^ Thacker, Christopher; Louis XIV (1972). ""La Manière de montrer les jardins de Versailles," by Louis XIV and Others". Garden History. 1 (1): 49–69. doi:10.2307/1586442. ISSN 0307-1243. JSTOR 1586442.
- ^ Michalska, Magda (23 December 2023). "The Scent of Orange in the Air: Paintings with Oranges". Daily Art Magazine. Archived from the original on 14 March 2024. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
External links
 Media related to Citrus sinensis at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Citrus sinensis at Wikimedia Commons Data related to Citrus sinensis at Wikispecies
Data related to Citrus sinensis at Wikispecies- Citrus sinensis List of Chemicals (Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases), USDA, Agricultural Research Service.
- Oranges: Safe Methods to Store, Preserve, and Enjoy. (2006). University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources. Accessed May 23, 2014.























