Villa Jovis: Difference between revisions
m Robot - Moving category 27 in Europe to Category:27 per CFD at Wikipedia:Categories for discussion/Log/2017 July 29. |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 25 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Roman palace on Capri, Italy}} |
|||
{{Infobox ancient site |
{{Infobox ancient site |
||
|name = Villa |
|name = Villa jovis |
||
|native_name = |
|native_name = |
||
|alternate_name = |
|alternate_name = |
||
|image = Villa Jovis.jpg |
|image = [[File:Villa Jovis (Capri) (3).jpg|260px]] |
||
|alt = |
|alt = |
||
|caption = The remains of Villa Jovis |
|caption = The remains of Villa Jovis |
||
|map_type = Italy |
|map_type = Italy |
||
|map_alt = |
|map_alt = |
||
| Line 35: | Line 36: | ||
|notes = |
|notes = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:Villa Jovis GoPro walkthrough.webm|thumb|270px|Villa Jovis slave quarters walkthrough]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Villa Jovis is the largest of the twelve Tiberian villas on Capri mentioned by [[Tacitus]]. The entire complex, spanning several terraces and a difference in elevation of about 40 m, covers some {{convert|7000|m2|sqyd|abbr=off}}.<ref name="heid">{{cite web | url=http://www.zaw.uni-heidelberg.de/hps/klarch/institut/villa_jovis.htm | title=Archäologisches Institut Heidelberg - Villa Jovis | publisher=[[Heidelberg University]] | year=2003 | access-date=July 6, 2012}}</ref> While the remaining eight levels of walls and staircases only hint at the grandeur the building must have had in its time, recent reconstructions have shown the villa to be a remarkable testament to 1st-century Roman architecture. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==Location and description of the palace== |
==Location and description of the palace== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Villa Jovis is situated in the very northeast of the island atop |
Villa Jovis is situated in the very northeast of the island atop Monte Tiberio; its 334 m elevation makes it the second-highest peak of Capri, after [[Monte Solaro]] (589 m elevation) in [[Anacapri]].<ref>Krause (2003), p. 28</ref> |
||
The north wing of the building contained the living quarters, while the south wing saw administrative use.<ref>Krause (2003), p. 82–83</ref> The east wing was meant for receptions, whereas the west wing featured an open-walled hall (''ambulatio'') which offered a scenic view towards Anacapri.<ref name="Krause 2003, p. 83">Krause (2003), p. 83</ref> |
The north wing of the building contained the living quarters, while the south wing saw administrative use.<ref>Krause (2003), p. 82–83</ref> The east wing was meant for receptions, whereas the west wing featured an open-walled hall (''ambulatio'') which offered a scenic view towards Anacapri.<ref name="Krause 2003, p. 83">Krause (2003), p. 83</ref> |
||
As water was difficult to |
As water was difficult to obtain at the villa's location, Roman engineers constructed an intricate system for the collection of rainwater from the roofs and a large [[cistern]] that supplied the palace with fresh water.<ref name="Krause 2003, p. 83"/> |
||
South of the main building there are remains of a [[watch tower]] (''specula'') for the quick [[telegraph]]ic exchange of messages with the mainland, e.g. by fire or smoke.<ref>Krause (2003), p. 84</ref> |
South of the main building there are remains of a [[watch tower]] (''specula'') for the quick [[telegraph]]ic exchange of messages with the mainland, e.g. by fire or smoke.<ref>Krause (2003), p. 84</ref> |
||
Access to the complex is |
Access to the complex is possible only on foot, and involves an uphill walk of about two kilometres from [[Capri (town)|Capri]] town. |
||
==Tiberius and his life on Capri== |
==Tiberius and his life on Capri== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Apparently the main motivations for Tiberius's move from Rome to Capri were his wariness of the political manoeuvring in Rome and a lingering fear of [[assassination]]. The villa is situated at a very secluded spot on the island and Tiberius's quarters in the north and east of the palatial villa were particularly difficult to reach and heavily guarded. |
||
| ⚫ | Apparently, the main motivations for Tiberius's move from Rome to Capri were his wariness of the political manoeuvring in Rome and a lingering fear of [[assassination]]. The villa is situated at a very secluded spot on the island and Tiberius's quarters in the north and east of the palatial villa were particularly difficult to reach and heavily guarded. |
||
| ⚫ | The Villa Jovis is also, at least according to [[Lives of the Twelve Caesars|Suetonius]], the place where Tiberius engaged in wild debauchery.<ref name="suetonius-twelve-caesars-43">Suetonius, ''The Lives of Twelve Caesars'', Life of Tiberius [ |
||
| ⚫ | The Villa Jovis is also, at least according to [[Lives of the Twelve Caesars|Suetonius]], the place where Tiberius engaged in wild debauchery.<ref name="suetonius-twelve-caesars-43">Suetonius, ''The Lives of Twelve Caesars'', Life of Tiberius [https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/Tiberius*.html#43 43], [https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/Tiberius*.html#44 44], [https://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Suetonius/12Caesars/Tiberius*.html#45 45]</ref> Most modern historians regard these tales as sensationalized, but Suetonius's stories at least paint a picture of how Tiberius was perceived by the Roman people at the time.<ref>Wallace-Hadrill, Andrew (1984) ''Suetonius: The Scholar and His Caesars'', Yale University Press, {{ISBN|0-300-03000-2}}</ref> |
||
==Gallery== |
|||
<gallery widths="145px" heights="145px"> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
</gallery> |
|||
==Footnotes== |
==Footnotes== |
||
| Line 64: | Line 71: | ||
==References and further reading== |
==References and further reading== |
||
*J.M.Barnes, "Villa Iovis — A Sonnet Cycle." Tennyson Press, Reading MA. 2008. |
|||
*Clemens Krause, 2003. "Villa Jovis — Die Residenz des Tiberius auf Capri", ''Zaberns Bildbände zur Archäologie'' (Mainz am Rhein) |
*Clemens Krause, 2003. "Villa Jovis — Die Residenz des Tiberius auf Capri", ''Zaberns Bildbände zur Archäologie'' (Mainz am Rhein) |
||
*Clemens Krause, Villa Jovis. L'edificio residenziale, electa napoli 2006. |
*Clemens Krause, Villa Jovis. L'edificio residenziale, electa napoli 2006. |
||
| Line 71: | Line 77: | ||
{{Commons category|Villa Jovis (Capri)}} |
{{Commons category|Villa Jovis (Capri)}} |
||
*[http://www.capri.net/en/s/villa-jovis-mount-tiberio Capri Online: Villa Jovis - Mount Tiberio] |
*[http://www.capri.net/en/s/villa-jovis-mount-tiberio Capri Online: Villa Jovis - Mount Tiberio] |
||
*[http://www.ijkfoto.net/main.php?g2_itemId=17249 Photo Gallery from Capri Island] |
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20090629210047/http://www.ijkfoto.net/main.php?g2_itemId=17249 Photo Gallery from Capri Island] |
||
{{Archaeological sites in Campania}} |
{{Archaeological sites in Campania}} |
||
{{Capri topics}} |
{{Capri topics}} |
||
{{authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:27]] |
[[Category:27]] |
||
Latest revision as of 15:25, 22 November 2024
 The remains of Villa Jovis | |
| Location | Capri, Italy |
|---|---|
| Region | Campania |
| Coordinates | 40°33′30″N 14°15′44″E / 40.55833°N 14.26222°E |
| Type | Dwelling |
| History | |
| Periods | Roman Imperial |
| Cultures | Roman |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Ownership | Public |
| Public access | Yes |
| Website | cir |
Villa Jovis ("Villa of Jupiter") is a Roman palace on Capri, southern Italy, built by Emperor Tiberius and completed in 27 AD. Tiberius ruled mainly from there until his death in 37 AD.[1]
Villa Jovis is the largest of the twelve Tiberian villas on Capri mentioned by Tacitus. The entire complex, spanning several terraces and a difference in elevation of about 40 m, covers some 7,000 square metres (8,400 square yards).[1] While the remaining eight levels of walls and staircases only hint at the grandeur the building must have had in its time, recent reconstructions have shown the villa to be a remarkable testament to 1st-century Roman architecture.
Location and description of the palace
[edit]Villa Jovis is situated in the very northeast of the island atop Monte Tiberio; its 334 m elevation makes it the second-highest peak of Capri, after Monte Solaro (589 m elevation) in Anacapri.[2]
The north wing of the building contained the living quarters, while the south wing saw administrative use.[3] The east wing was meant for receptions, whereas the west wing featured an open-walled hall (ambulatio) which offered a scenic view towards Anacapri.[4]
As water was difficult to obtain at the villa's location, Roman engineers constructed an intricate system for the collection of rainwater from the roofs and a large cistern that supplied the palace with fresh water.[4]
South of the main building there are remains of a watch tower (specula) for the quick telegraphic exchange of messages with the mainland, e.g. by fire or smoke.[5]
Access to the complex is possible only on foot, and involves an uphill walk of about two kilometres from Capri town.
Tiberius and his life on Capri
[edit]Apparently, the main motivations for Tiberius's move from Rome to Capri were his wariness of the political manoeuvring in Rome and a lingering fear of assassination. The villa is situated at a very secluded spot on the island and Tiberius's quarters in the north and east of the palatial villa were particularly difficult to reach and heavily guarded.
The Villa Jovis is also, at least according to Suetonius, the place where Tiberius engaged in wild debauchery.[6] Most modern historians regard these tales as sensationalized, but Suetonius's stories at least paint a picture of how Tiberius was perceived by the Roman people at the time.[7]
Gallery
[edit]-
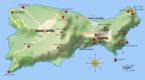
Map of Capri with Villa Jovis in the north-east corner of the island
-
Reconstruction by Weichardt (1900), view from the south-west
-
Reconstruction by Weichardt (1900), view from the east
-
Marble statue of Tiberius found on Capri
Footnotes
[edit]- ^ a b "Archäologisches Institut Heidelberg - Villa Jovis". Heidelberg University. 2003. Retrieved July 6, 2012.
- ^ Krause (2003), p. 28
- ^ Krause (2003), p. 82–83
- ^ a b Krause (2003), p. 83
- ^ Krause (2003), p. 84
- ^ Suetonius, The Lives of Twelve Caesars, Life of Tiberius 43, 44, 45
- ^ Wallace-Hadrill, Andrew (1984) Suetonius: The Scholar and His Caesars, Yale University Press, ISBN 0-300-03000-2
References and further reading
[edit]- Clemens Krause, 2003. "Villa Jovis — Die Residenz des Tiberius auf Capri", Zaberns Bildbände zur Archäologie (Mainz am Rhein)
- Clemens Krause, Villa Jovis. L'edificio residenziale, electa napoli 2006.