Central Thailand: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Undid revision 1257900638 by Moo1882 (talk) |
||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Region in Thailand}} |
|||
{{ |
{{more citations needed|date=January 2019}} |
||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
<!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> |
<!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> |
||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
|parts = {{nobold|21 Provinces <br> 1 Special administrative area }} |
|parts = {{nobold|21 Provinces <br> 1 Special administrative area }} |
||
| p1 = [[Bangkok]] |
| p1 = [[Bangkok]] |
||
| p2 = [[Nakhon Pathom |
| p2 = [[Nakhon Pathom province]] |
||
| p3 = [[Nonthaburi |
| p3 = [[Nonthaburi province]] |
||
| p4 = [[Pathum Thani |
| p4 = [[Pathum Thani province]] |
||
| p5 = [[Samut Prakan |
| p5 = [[Samut Prakan province]] |
||
| p6 = [[Samut Sakhon |
| p6 = [[Samut Sakhon province]] |
||
| p7 = [[Samut Songkhram |
| p7 = [[Samut Songkhram province]] |
||
| p8 = [[Kamphaeng Phet |
| p8 = [[Kamphaeng Phet province]] |
||
| p9 = [[Nakhon Sawan |
| p9 = [[Nakhon Sawan province]] |
||
| p10 = [[Phetchabun |
| p10 = [[Phetchabun province]] |
||
| p11 = [[Phichit |
| p11 = [[Phichit province]] |
||
| p12 = [[Phitsanulok |
| p12 = [[Phitsanulok province]] |
||
| p13 = [[Sukhothai |
| p13 = [[Sukhothai province]] |
||
| p14 = [[Uthai Thani |
| p14 = [[Uthai Thani province]] |
||
| p15 = [[Ang Thong |
| p15 = [[Ang Thong province]] |
||
| p16 = [[Ayutthaya |
| p16 = [[Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province]] |
||
| p17 = [[Chai Nat |
| p17 = [[Chai Nat province]] |
||
| p18 = [[Lopburi |
| p18 = [[Lopburi province]] |
||
| p19 = [[Nakhon Nayok |
| p19 = [[Nakhon Nayok province]] |
||
| p20 = [[Saraburi |
| p20 = [[Saraburi province]] |
||
| p21 = [[Sing Buri |
| p21 = [[Sing Buri province]] |
||
| p22 = [[Suphanburi |
| p22 = [[Suphanburi province]] |
||
| subdivision_type1 = Largest city |
| subdivision_type1 = Largest city |
||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Bangkok]] |
| subdivision_name1 = [[Bangkok]] |
||
| Line 64: | Line 65: | ||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
| population_density_km2 = auto |
||
| population_demonym = |
| population_demonym = |
||
<!-- GDP ---------------> |
|||
| demographics_type2 = GDP |
|||
| demographics2_footnotes = <ref name="NESDB-2017">{{cite journal|title=''Gross Regional and Provincial Product, 2019 Edition''|journal=<> |date=July 2019|url=https://www.nesdc.go.th/ewt_dl_link.php?nid=5628&filename=gross_regional|access-date=22 January 2020|publisher=Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC)|language=en|issn=1686-0799}}</ref> |
|||
|demographics2_title1 = Total |
|||
|demographics2_info1 = US$286.7 billion (2019) |
|||
|demographics2_title2 = Per capita |
|||
|demographics2_info2 = |
|||
| blank1_name_sec2 = {{nowrap|[[Language]]}} |
| blank1_name_sec2 = {{nowrap|[[Language]]}} |
||
| blank1_info_sec2 = [[Thai language|Thai]] • ''others'' |
| blank1_info_sec2 = [[Thai language|Thai]] • ''others'' |
||
| timezone1 = [[Time in Thailand|ICT]] |
|||
| utc_offset1 = +07:00 |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Central Thailand''' (Central |
'''Central Thailand''' (Central Plain) (historically also known as '''Siam''' or '''[[Dvaravati]]''') is one of the [[regions of Thailand]], covering the broad [[alluvial plain]] of the [[Chao Phraya River]]. It is separated from northeast Thailand ([[Isan]]) by the [[Phetchabun Mountains|Phetchabun mountain range]]. The [[Tenasserim Hills]] separate it from [[Myanmar]] to the west. In the north it is bounded by the [[Phi Pan Nam Range]], one of the hilly systems of [[northern Thailand]]. The area was the heartland of the [[Ayutthaya Kingdom]] (at times referred to as [[Siam]]) and is still the dominant area of [[Thailand]] since it contains the world's most [[primate city#Examples|primate city]], [[Bangkok]]. |
||
==Definition== |
==Definition== |
||
The grouping of Thai provinces into regions follow two major systems |
The grouping of Thai provinces into regions follow two major systems in which Thailand is divided into either [[Regions of Thailand|four or six regions]]. In the six-region system, commonly used in geographical studies, central Thailand extends from [[Sukhothai Province|Sukhothai]] and [[Phitsanulok Province|Phitsanulok]] Provinces in the north to the provinces bordering the [[Gulf of Thailand]] in the south, excluding the mountainous provinces bordering Myanmar to the west and the coastal provinces of the east. The four-region system includes provinces only as far north as [[Chai Nat]], [[Sing Buri]] and [[Lopburi]] and extends west and east to the borders of Myanmar and Cambodia.<br> |
||
The central region, as defined by [[Royal Forest Department]] in 2019, consists of 18 provinces (7 provinces of Greater Bangkok, 8 provinces of South Central Thailand and 3 provinces of Western Thailand). The total area of this central region is {{convert|67,473|km²|abbr=on}}, while the total forest area is {{convert|22,374|km²|abbr=on}} or 33.2 percent of this regional area.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.forest.go.th |title=ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562 |year=2019 |department=Royal Forest Department |language= |
The central region, as defined by [[Royal Forest Department]] in 2019, consists of 18 provinces (7 provinces of Greater Bangkok, 8 provinces of South Central Thailand and 3 provinces of Western Thailand). The total area of this central region is {{convert|67,473|km²|abbr=on}}, while the total forest area is {{convert|22,374|km²|abbr=on}} or 33.2 percent of this regional area.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.forest.go.th |title=ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562 |year=2019 |department=Royal Forest Department |language=th |trans-title=Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019 |access-date=6 April 2021 |postscript=, information, Forest statistics Year 2019}}</ref> |
||
==Administrative divisions== |
==Administrative divisions== |
||
There are [[Regions of Thailand|several different systems]] of dividing modern Thailand into different regions, which gives slightly different boundaries for Central Thailand. In the geographic six-region system, the central region includes the following 22 provinces, divided into three groups: |
|||
The central region is divided into 22 [[Provinces of Thailand|provinces]], which includes the following: |
|||
*[[Bangkok Metropolitan Area|Greater Bangkok]]: [[Bangkok]], [[Nakhon Pathom Province|Nakhon Pathom]], [[Nonthaburi Province|Nonthaburi]], [[Pathum Thani Province|Pathum Thani]], [[Samut Prakan Province|Samut Prakan]], [[Samut Sakhon Province|Samut Sakhon]], [[Samut Songkhram Province|Samut Songkhram]] |
*[[Bangkok Metropolitan Area|Greater Bangkok]]: [[Bangkok]], [[Nakhon Pathom Province|Nakhon Pathom]], [[Nonthaburi Province|Nonthaburi]], [[Pathum Thani Province|Pathum Thani]], [[Samut Prakan Province|Samut Prakan]], [[Samut Sakhon Province|Samut Sakhon]], [[Samut Songkhram Province|Samut Songkhram]] |
||
*North Central Thailand region: [[Kamphaeng Phet Province|Kamphaeng Phet]], [[Nakhon Sawan Province|Nakhon Sawan]], [[Phetchabun Province|Phetchabun]], [[Phichit Province|Phichit]], [[Phitsanulok Province|Phitsanulok]], [[Sukhothai Province|Sukhothai]], [[Uthai Thani Province|Uthai Thani]] |
*North Central Thailand region: [[Kamphaeng Phet Province|Kamphaeng Phet]], [[Nakhon Sawan Province|Nakhon Sawan]], [[Phetchabun Province|Phetchabun]], [[Phichit Province|Phichit]], [[Phitsanulok Province|Phitsanulok]], [[Sukhothai Province|Sukhothai]], [[Uthai Thani Province|Uthai Thani]] |
||
*South Central Thailand region: [[Ang Thong Province|Ang Thong]], [[Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Province|Ayutthaya]], [[Chai Nat Province|Chainat]], [[Lopburi Province|Lopburi]], [[Nakhon Nayok Province|Nakhon Nayok]], [[Saraburi Province|Saraburi]], [[Sing Buri Province|Sing Buri]]; [[Suphan Buri Province|Suphanburi]] |
*South Central Thailand region: [[Ang Thong Province|Ang Thong]], [[Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya Province|Ayutthaya]], [[Chai Nat Province|Chainat]], [[Lopburi Province|Lopburi]], [[Nakhon Nayok Province|Nakhon Nayok]], [[Saraburi Province|Saraburi]], [[Sing Buri Province|Sing Buri]]; [[Suphan Buri Province|Suphanburi]] |
||
The four-region system includes 26 [[Provinces of Thailand|provinces]] in its definition of Central Thailand. Especially for statistical purposes, they are divided into four groups:<ref>List according to Wolf Donner, ''Thailand'', {{ISBN|3-534-02779-5}}</ref> |
|||
*Greater Bangkok: [[Bangkok]], [[Nakhon Pathom Province|Nakhon Pathom]], [[Nonthaburi Province|Nonthaburi]], [[Pathum Thani Province|Pathum Thani]], [[Samut Prakan Province|Samut Prakan]], [[Samut Sakhon Province|Samut Sakhon]] |
*Greater Bangkok: [[Bangkok]], [[Nakhon Pathom Province|Nakhon Pathom]], [[Nonthaburi Province|Nonthaburi]], [[Pathum Thani Province|Pathum Thani]], [[Samut Prakan Province|Samut Prakan]], [[Samut Sakhon Province|Samut Sakhon]] |
||
| Line 90: | Line 98: | ||
*[[Eastern Thailand]] region: [[Chachoengsao Province|Chachoengsao]], [[Chanthaburi Province|Chanthaburi]], [[Chonburi Province|Chonburi]], [[Prachinburi Province|Prachinburi]], [[Rayong Province|Rayong]], [[Sa Kaeo Province|Sa Kaeo]], [[Trat Province|Trat]] |
*[[Eastern Thailand]] region: [[Chachoengsao Province|Chachoengsao]], [[Chanthaburi Province|Chanthaburi]], [[Chonburi Province|Chonburi]], [[Prachinburi Province|Prachinburi]], [[Rayong Province|Rayong]], [[Sa Kaeo Province|Sa Kaeo]], [[Trat Province|Trat]] |
||
The eastern region is sometimes listed as a separate region distinct from |
The eastern region is sometimes listed as a separate region distinct from Central Thailand: sometimes only the four coastal provincesand sometimes the above list excluding Nakhon Nayok. None of those regions are political subdivisions; they are only geographical or statistical groupings. |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
==Economy== |
==Economy== |
||
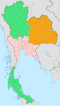
[[File:Thailand Central provinces.png|right|200px]] |
[[File:Thailand Central provinces.png|right|200px]] |
||
For economic statistics of |
For economic statistics of Central Thailand by [[National Statistical Office]] (NSO) the following six provinces are listed: 1.Ang Thong 2.Ayutthaya 3.Chai Nat 4.Lopburi 5.Saraburi 6.Sing Buri<br> |
||
However Nakhon Nayok province is listed by eastern Thailand.<br> |
However Nakhon Nayok province is listed by eastern Thailand.<br> |
||
For FY 2018, Central Region had a combined economic output of 863.328 billion baht (US$27.85 billion), or 5.3 percent of Thailand's GDP. Ayutthaya province had an economic output of 412.701 billion baht (US$13.3 billion). This amounts to GPP per capita of 454,953 baht (US$14,676), 40 percent more than Saraburi province, next in the ranking and three times more than for all subsequent provinces in the ranking.<ref>{{cite report |title=Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Report 2562-2019: Economic Statistics - National Accounts |department=Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Office |publication-date=2020 |issn=1905-8314 |publisher=National Statistical Office (NSO) |page=93}}</ref> |
For FY 2018, Central Region had a combined economic output of 863.328 billion baht (US$27.85 billion), or 5.3 percent of Thailand's GDP. Ayutthaya province had an economic output of 412.701 billion baht (US$13.3 billion). This amounts to GPP per capita of 454,953 baht (US$14,676), 40 percent more than Saraburi province, next in the ranking and three times more than for all subsequent provinces in the ranking.<ref>{{cite report |title=Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Report 2562-2019: Economic Statistics - National Accounts |department=Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Office |publication-date=2020 |issn=1905-8314 |publisher=National Statistical Office (NSO) |page=93}}</ref> |
||
| Line 140: | Line 148: | ||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{ |
{{commons category|Central Thailand}} |
||
*{{Wikivoyage |
*{{Wikivoyage inline|Central (Thailand)}} |
||
{{Regions of Thailand}} |
{{Regions of Thailand}} |
||
| Line 147: | Line 155: | ||
{{coord|15|N|100|E|display=title|scale:3000000}} |
{{coord|15|N|100|E|display=title|scale:3000000}} |
||
[[Category:Central Region (Thailand)| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Regions of Thailand]] |
[[Category:Regions of Thailand]] |
||
{{Thailand-geo-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 02:54, 23 November 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2019) |
Central Region
ภาคกลาง | |
|---|---|
|
From upper-left to lower-right: Lumphini Park; Wat Chaiwatthanaram; Fishing, Bueng Boraphet; Wat Mahathat Sukhothai Historical Park; Khao Kho National Park | |
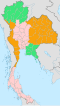
 Central Region in Thailand | |
| Largest city | Bangkok |
| Provinces | 21 Provinces 1 Special administrative area
|
| Area | |
• Total | 91,798.64 km2 (35,443.65 sq mi) |
| Population (2015) | |
• Total | 20,183,134 |
| • Density | 220/km2 (570/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | US$286.7 billion (2019) |
| Time zone | UTC+07:00 (ICT) |
| Language | Thai • others |
Central Thailand (Central Plain) (historically also known as Siam or Dvaravati) is one of the regions of Thailand, covering the broad alluvial plain of the Chao Phraya River. It is separated from northeast Thailand (Isan) by the Phetchabun mountain range. The Tenasserim Hills separate it from Myanmar to the west. In the north it is bounded by the Phi Pan Nam Range, one of the hilly systems of northern Thailand. The area was the heartland of the Ayutthaya Kingdom (at times referred to as Siam) and is still the dominant area of Thailand since it contains the world's most primate city, Bangkok.
Definition
[edit]The grouping of Thai provinces into regions follow two major systems in which Thailand is divided into either four or six regions. In the six-region system, commonly used in geographical studies, central Thailand extends from Sukhothai and Phitsanulok Provinces in the north to the provinces bordering the Gulf of Thailand in the south, excluding the mountainous provinces bordering Myanmar to the west and the coastal provinces of the east. The four-region system includes provinces only as far north as Chai Nat, Sing Buri and Lopburi and extends west and east to the borders of Myanmar and Cambodia.
The central region, as defined by Royal Forest Department in 2019, consists of 18 provinces (7 provinces of Greater Bangkok, 8 provinces of South Central Thailand and 3 provinces of Western Thailand). The total area of this central region is 67,473 km2 (26,051 sq mi), while the total forest area is 22,374 km2 (8,639 sq mi) or 33.2 percent of this regional area.[2]
Administrative divisions
[edit]There are several different systems of dividing modern Thailand into different regions, which gives slightly different boundaries for Central Thailand. In the geographic six-region system, the central region includes the following 22 provinces, divided into three groups:
- Greater Bangkok: Bangkok, Nakhon Pathom, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram
- North Central Thailand region: Kamphaeng Phet, Nakhon Sawan, Phetchabun, Phichit, Phitsanulok, Sukhothai, Uthai Thani
- South Central Thailand region: Ang Thong, Ayutthaya, Chainat, Lopburi, Nakhon Nayok, Saraburi, Sing Buri; Suphanburi
The four-region system includes 26 provinces in its definition of Central Thailand. Especially for statistical purposes, they are divided into four groups:[3]
- Greater Bangkok: Bangkok, Nakhon Pathom, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon
- Sub-Central Thailand region: Ang Thong, Ayutthaya, Chainat, Lopburi, Nakhon Nayok, Saraburi, Sing Buri
- Western Thailand region: Kanchanaburi, Phetchaburi, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ratchaburi, Samut Songkhram, Suphanburi
- Eastern Thailand region: Chachoengsao, Chanthaburi, Chonburi, Prachinburi, Rayong, Sa Kaeo, Trat
The eastern region is sometimes listed as a separate region distinct from Central Thailand: sometimes only the four coastal provincesand sometimes the above list excluding Nakhon Nayok. None of those regions are political subdivisions; they are only geographical or statistical groupings.
Economy
[edit]
For economic statistics of Central Thailand by National Statistical Office (NSO) the following six provinces are listed: 1.Ang Thong 2.Ayutthaya 3.Chai Nat 4.Lopburi 5.Saraburi 6.Sing Buri
However Nakhon Nayok province is listed by eastern Thailand.
For FY 2018, Central Region had a combined economic output of 863.328 billion baht (US$27.85 billion), or 5.3 percent of Thailand's GDP. Ayutthaya province had an economic output of 412.701 billion baht (US$13.3 billion). This amounts to GPP per capita of 454,953 baht (US$14,676), 40 percent more than Saraburi province, next in the ranking and three times more than for all subsequent provinces in the ranking.[4]
| Rank | Province | GPP (million baht) |
Population (x 1000) |
GPP per capita (baht) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ayutthaya | 412,701 | 907 | 454,953 |
| 2 | Saraburi | 246,063 | 758 | 324,820 |
| 3 | Sing Buri | 27,783 | 190 | 145,899 |
| 4 | Lopburi | 110,962 | 777 | 142,741 |
| 5 | Ang Thong | 30,539 | 250 | 122,159 |
| 6 | Chai Nat | 35,280 | 294 | 119,850 |
| Central region | 863,328 | 3,177 | 271,759 |
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. There is more info on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
References
[edit]- ^ "Gross Regional and Provincial Product, 2019 Edition". <>. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). July 2019. ISSN 1686-0799. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ^ "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ List according to Wolf Donner, Thailand, ISBN 3-534-02779-5
- ^ Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Report 2562-2019: Economic Statistics - National Accounts. Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Office (Report). National Statistical Office (NSO). 2020. p. 93. ISSN 1905-8314.
External links
[edit] Central (Thailand) travel guide from Wikivoyage
Central (Thailand) travel guide from Wikivoyage