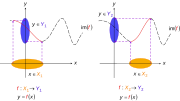Injective function: Difference between revisions
m v2.04b - Bot T12 CW#548 - Fix errors for CW project (Punctuation in link - Title linked in text - Link equal to linktext) |
Alsosaid1987 (talk | contribs) Added info on specialized arrows for injective function to match analogous information in the corresponding surjective function article. |
||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 19 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Function that preserves distinctness}} |
{{Short description|Function that preserves distinctness}} |
||
{{Redirect|Injective| |
{{Redirect|Injective|other uses|Injective module|and|Injective object}} |
||
{{Functions}} |
{{Functions}} |
||
| ⚫ | In [[mathematics]], an '''injective function''' (also known as '''injection''', or '''one-to-one function'''<ref>Sometimes ''one-one function'', in Indian mathematical education. {{Cite web |title=Chapter 1:Relations and functions |url=https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/lemh101.pdf |via=NCERT |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231226194119/https://ncert.nic.in/ncerts/l/lemh101.pdf |archive-date= Dec 26, 2023 }}</ref> ) is a [[function (mathematics)|function]] {{math|''f''}} that maps [[Distinct (mathematics)|distinct]] elements of its domain to distinct elements of its codomain; that is, {{math|1=''x''<sub>1</sub> ≠ ''x''<sub>2</sub>}} implies {{math|''f''(''x''<sub>1</sub>) {{≠}} ''f''(''x''<sub>2</sub>)}} (equivalently by [[contraposition]], {{math|''f''(''x''<sub>1</sub>) {{=}} ''f''(''x''<sub>2</sub>)}} implies {{math|1=''x''<sub>1</sub> = ''x''<sub>2</sub>}}). In other words, every element of the function's [[codomain]] is the [[Image (mathematics)|image]] of {{em|at most}} one element of its [[Domain of a function|domain]].<ref name=":0">{{Cite web|url=https://www.mathsisfun.com/sets/injective-surjective-bijective.html|title=Injective, Surjective and Bijective|website=Math is Fun |access-date=2019-12-07}}</ref> The term {{em|one-to-one function}} must not be confused with {{em|one-to-one correspondence}} that refers to [[bijective function]]s, which are functions such that each element in the codomain is an image of exactly one element in the domain. |
||
{{hatnote|For visual examples, as well as [[mathematical intuition]], readers are directed to the [[#Gallery|gallery section.]]}} |
|||
| ⚫ | A [[homomorphism]] between [[algebraic structure]]s is a function that is compatible with the operations of the structures. For all common algebraic structures, and, in particular for [[vector space]]s, an {{em|injective homomorphism}} is also called a {{em|[[monomorphism]]}}. However, in the more general context of [[category theory]], the definition of a monomorphism differs from that of an injective homomorphism.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://stacks.math.columbia.edu/tag/00V5|title=Section 7.3 (00V5): Injective and surjective maps of presheaves |website=The Stacks project |access-date=2019-12-07}}</ref> This is thus a theorem that they are equivalent for algebraic structures; see {{slink|Homomorphism|Monomorphism}} for more details. |
||
| ⚫ | In [[mathematics]], an '''injective function''' (also known as '''injection''', or '''one-to-one function''') is a [[function (mathematics)|function]] {{math|''f''}} that maps [[Distinct (mathematics)|distinct]] elements to distinct elements; that is, {{math| |
||
| ⚫ | A [[homomorphism]] between [[algebraic structure]]s is a function that is compatible with the operations of the structures. For all common algebraic structures, and, in particular for [[vector space]]s, an {{em|injective homomorphism}} is also called a {{em|[[monomorphism]]}}. However, in the more general context of [[category theory]], the definition of a monomorphism differs from that of an injective homomorphism.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://stacks.math.columbia.edu/tag/00V5|title=Section 7.3 (00V5): Injective and surjective maps of |
||
A function <math>f</math> that is not injective is sometimes called many-to-one.<ref name=":0" /> |
A function <math>f</math> that is not injective is sometimes called many-to-one.<ref name=":0" /> |
||
== Definition == |
== Definition == |
||
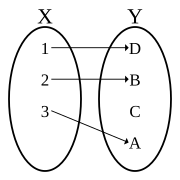
[[file:Injection.svg|thumb|An injective function, which is not also [[Surjective function|surjective]].]] |
|||
{{Further|topic=notation|Function (mathematics)#Notation}} |
{{Further|topic=notation|Function (mathematics)#Notation}} |
||
Let <math>f</math> be a function whose domain is a set <math>X.</math> The function <math>f</math> is said to be '''injective''' provided that for all <math>a</math> and <math>b</math> in <math>X,</math> if <math>f(a) = f(b),</math> then <math>a = b</math>; that is, <math>f(a) = f(b)</math> implies <math>a=b.</math> Equivalently, if <math>a \neq b,</math> then <math>f(a) \neq f(b)</math> in the [[Contraposition|contrapositive]] statement. |
Let <math>f</math> be a function whose domain is a set <math>X.</math> The function <math>f</math> is said to be '''injective''' provided that for all <math>a</math> and <math>b</math> in <math>X,</math> if <math>f(a) = f(b),</math> then <math>a = b</math>; that is, <math>f(a) = f(b)</math> implies <math>a=b.</math> Equivalently, if <math>a \neq b,</math> then <math>f(a) \neq f(b)</math> in the [[Contraposition|contrapositive]] statement. |
||
Symbolically,<math display="block">\forall a,b \in X, \;\; f(a)=f(b) \Rightarrow a=b,</math> |
Symbolically,<math display="block">\forall a,b \in X, \;\; f(a)=f(b) \Rightarrow a=b,</math> |
||
which is logically equivalent to the [[Contraposition|contrapositive]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.math.umaine.edu/~farlow/sec42.pdf|title=Injections, Surjections, and Bijections|last=Farlow|first=S. J.|author-link= Stanley Farlow |website= |
which is logically equivalent to the [[Contraposition|contrapositive]],<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.math.umaine.edu/~farlow/sec42.pdf|title=Section 4.2 Injections, Surjections, and Bijections |last=Farlow|first=S. J.|author-link= Stanley Farlow |website=Mathematics & Statistics - University of Maine |access-date=2019-12-06 |url-status=dead |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20191207035302/http://www.math.umaine.edu/~farlow/sec42.pdf |archive-date= Dec 7, 2019 }}</ref><math display="block">\forall a, b \in X, \;\; a \neq b \Rightarrow f(a) \neq f(b).</math>An injective function (or, more generally, a monomorphism) is often denoted by using the specialized arrows ↣ or ↪ (for example, <math>f:A\rightarrowtail B</math> or <math>f:A\hookrightarrow B</math>), although some authors specifically reserve ↪ for an [[inclusion map]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=What are usual notations for surjective, injective and bijective functions? |url=https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/46678/what-are-usual-notations-for-surjective-injective-and-bijective-functions |access-date=2024-11-24 |website=Mathematics Stack Exchange |language=en}}</ref> |
||
== Examples == |
== Examples == |
||
''For visual examples, readers are directed to the [[# |
''For visual examples, readers are directed to the [[#Gallery|gallery section.]]'' |
||
* For any set <math>X</math> and any subset <math>S \subseteq X,</math> the [[inclusion map]] <math>S \to X</math> (which sends any element <math>s \in S</math> to itself) is injective. In particular, the [[identity function]] <math>X \to X</math> is always injective (and in fact bijective). |
* For any set <math>X</math> and any subset <math>S \subseteq X,</math> the [[inclusion map]] <math>S \to X</math> (which sends any element <math>s \in S</math> to itself) is injective. In particular, the [[identity function]] <math>X \to X</math> is always injective (and in fact bijective). |
||
* If the domain of a function is the [[empty set]], then the function is the [[empty function]], which is injective. |
* If the domain of a function is the [[empty set]], then the function is the [[empty function]], which is injective. |
||
| Line 35: | Line 32: | ||
== Injections can be undone == |
== Injections can be undone == |
||
Functions with [[Inverse function#Left and right inverses|left inverses]] are always injections. That is, given <math>f : X \to Y,</math> if there is a function <math>g : Y \to X</math> such that for every <math>x \in X |
Functions with [[Inverse function#Left and right inverses|left inverses]] are always injections. That is, given <math>f : X \to Y,</math> if there is a function <math>g : Y \to X</math> such that for every <math>x \in X</math>, <math>g(f(x)) = x</math>, then <math>f</math> is injective. In this case, <math>g</math> is called a [[Retract (category theory)|retraction]] of <math>f.</math> Conversely, <math>f</math> is called a [[Retract (category theory)|section]] of <math>g.</math> |
||
Conversely, every injection <math>f</math> with non-empty domain has a left inverse <math>g |
Conversely, every injection <math>f</math> with a non-empty domain has a left inverse <math>g</math>. It can be defined by choosing an element <math>a</math> in the domain of <math>f</math> and setting <math>g(y)</math> to the unique element of the pre-image <math>f^{-1}[y]</math> (if it is non-empty) or to <math>a</math> (otherwise).{{refn|Unlike the corresponding statement that every surjective function has a right inverse, this does not require the [[axiom of choice]], as the existence of <math>a</math> is implied by the non-emptiness of the domain. However, this statement may fail in less conventional mathematics such as [[constructive mathematics]]. In constructive mathematics, the inclusion <math>\{ 0, 1 \} \to \R</math> of the two-element set in the reals cannot have a left inverse, as it would violate [[Indecomposability (constructive mathematics)|indecomposability]], by giving a [[Retract (category theory)|retraction]] of the real line to the set {0,1}.}} |
||
The left inverse <math>g</math> is not necessarily an [[Inverse function|inverse]] of <math>f,</math> because the composition in the other order, <math>f \circ g,</math> may differ from the identity on <math>Y.</math> In other words, an injective function can be "reversed" by a left inverse, but is not necessarily [[Inverse function|invertible]], which requires that the function is bijective. |
The left inverse <math>g</math> is not necessarily an [[Inverse function|inverse]] of <math>f,</math> because the composition in the other order, <math>f \circ g,</math> may differ from the identity on <math>Y.</math> In other words, an injective function can be "reversed" by a left inverse, but is not necessarily [[Inverse function|invertible]], which requires that the function is bijective. |
||
| Line 43: | Line 40: | ||
== Injections may be made invertible == |
== Injections may be made invertible == |
||
In fact, to turn an injective function <math>f : X \to Y</math> into a bijective (hence invertible) function, it suffices to replace its codomain <math>Y</math> by its actual |
In fact, to turn an injective function <math>f : X \to Y</math> into a bijective (hence invertible) function, it suffices to replace its codomain <math>Y</math> by its actual image <math>J = f(X).</math> That is, let <math>g : X \to J</math> such that <math>g(x) = f(x)</math> for all <math>x \in X</math>; then <math>g</math> is bijective. Indeed, <math>f</math> can be factored as <math>\operatorname{In}_{J,Y} \circ g,</math> where <math>\operatorname{In}_{J,Y}</math> is the [[inclusion function]] from <math>J</math> into <math>Y.</math> |
||
More generally, injective [[partial function]]s are called [[partial bijection]]s. |
More generally, injective [[partial function]]s are called [[partial bijection]]s. |
||
== Other properties == |
== Other properties == |
||
{{See also|List of set identities and relations#Functions and sets}}[[Image:Injective composition2.svg|thumb|300px|The composition of two injective functions is injective.]] |
{{See also|List of set identities and relations#Functions and sets}} |
||
[[Image:Injective composition2.svg|thumb|300px|The composition of two injective functions is injective.]] |
|||
* If <math>f</math> and <math>g</math> are both injective then <math>f \circ g</math> is injective. |
* If <math>f</math> and <math>g</math> are both injective then <math>f \circ g</math> is injective. |
||
* If <math>g \circ f</math> is injective, then <math>f</math> is injective (but <math>g</math> need not be). |
* If <math>g \circ f</math> is injective, then <math>f</math> is injective (but <math>g</math> need not be). |
||
* <math>f : X \to Y</math> is injective if and only if, given any functions <math>g,</math> <math>h : W \to X</math> whenever <math>f \circ g = f \circ h,</math> then <math>g = h.</math> In other words, injective functions are precisely the [[monomorphism]]s in the [[category theory|category]] '''[[Category of sets|Set]]''' of sets. |
* <math>f : X \to Y</math> is injective if and only if, given any functions <math>g,</math> <math>h : W \to X</math> whenever <math>f \circ g = f \circ h,</math> then <math>g = h.</math> In other words, injective functions are precisely the [[monomorphism]]s in the [[category theory|category]] '''[[Category of sets|Set]]''' of sets. |
||
| Line 65: | Line 62: | ||
A proof that a function <math>f</math> is injective depends on how the function is presented and what properties the function holds. |
A proof that a function <math>f</math> is injective depends on how the function is presented and what properties the function holds. |
||
For functions that are given by some formula there is a basic idea. |
For functions that are given by some formula there is a basic idea. |
||
We use the definition of injectivity, namely that if <math>f(x) = f(y),</math> then <math>x = y.</math><ref>{{cite web|last=Williams|first=Peter|title=Proving Functions One-to-One|url=http://www.math.csusb.edu/notes/proofs/bpf/node4.html|archive-date= 4 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170604162511/http://www.math.csusb.edu/notes/proofs/bpf/node4.html}}</ref> |
We use the definition of injectivity, namely that if <math>f(x) = f(y),</math> then <math>x = y.</math><ref>{{cite web|last=Williams|first=Peter|title=Proving Functions One-to-One|url=http://www.math.csusb.edu/notes/proofs/bpf/node4.html |date=Aug 21, 1996 |website=Department of Mathematics at CSU San Bernardino Reference Notes Page |archive-date= 4 June 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170604162511/http://www.math.csusb.edu/notes/proofs/bpf/node4.html}}</ref> |
||
Here is an example: |
Here is an example: |
||
| Line 78: | Line 75: | ||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
{{Gallery |
{{Gallery |
||
| |
|perrow=4 |
||
|align=center |
|align=center |
||
|Image:Injection.svg|An '''injective''' non-surjective function (injection, not a bijection) |
|Image:Injection.svg|An '''injective''' non-surjective function (injection, not a bijection) |
||
| Line 87: | Line 84: | ||
{{Gallery |
{{Gallery |
||
| |
|perrow=3 |
||
|align=center |
|align=center |
||
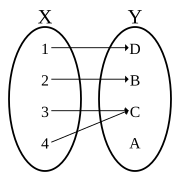
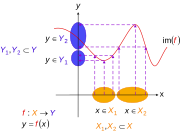
| ⚫ | |Image:Non-injective function2.svg|Making functions injective. The previous function <math>f : X \to Y</math> can be reduced to one or more injective functions (say) <math>f : X_1 \to Y_1</math> and <math>f : X_2 \to Y_2,</math> shown by solid curves (long-dash parts of initial curve are not mapped to anymore). Notice how the rule <math>f</math> has not changed – only the domain and range. <math>X_1</math> and <math>X_2</math> are subsets of <math>X, Y_1</math> and <math>Y_2</math> are subsets of <math>Y</math>: for two regions where the initial function can be made injective so that one domain element can map to a single range element. That is, only one <math>x</math> in <math>X</math> maps to one <math>y</math> in <math>Y.</math> |
||
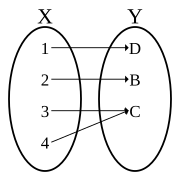
|Image:Non-injective function1.svg|Not an injective function. Here <math>X_1</math> and <math>X_2</math> are subsets of <math>X, Y_1</math> and <math>Y_2</math> are subsets of <math>Y</math>: for two regions where the function is not injective because more than one domain [[Element (mathematics)|element]] can map to a single range element. That is, it is possible for {{em|more than one}} <math>x</math> in <math>X</math> to map to the {{em|same}} <math>y</math> in <math>Y.</math> |
|Image:Non-injective function1.svg|Not an injective function. Here <math>X_1</math> and <math>X_2</math> are subsets of <math>X, Y_1</math> and <math>Y_2</math> are subsets of <math>Y</math>: for two regions where the function is not injective because more than one domain [[Element (mathematics)|element]] can map to a single range element. That is, it is possible for {{em|more than one}} <math>x</math> in <math>X</math> to map to the {{em|same}} <math>y</math> in <math>Y.</math> |
||
| ⚫ | |Image:Non-injective function2.svg|Making functions injective. The previous function <math>f : X \to Y</math> can be reduced to one or more injective functions (say) <math>f : X_1 \to Y_1</math> and <math>f : X_2 \to Y_2,</math> shown by solid curves (long-dash parts of initial curve are not mapped to anymore). Notice how the rule <math>f</math> has not changed – only the domain and range. <math>X_1</math> and <math>X_2</math> are subsets of <math>X, Y_1</math> and <math>Y_2</math> are subsets of <math>Y</math>: for two regions where the initial function can be made injective so that one domain element can map to a single range element. That is, only one <math>x</math> in <math>X</math> maps to one <math>y</math> in <math>Y.</math> |
||
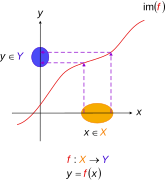
|Image:Injective function.svg|Injective functions. Diagramatic interpretation in the [[Cartesian plane]], defined by the [[Map (mathematics)|mapping]] <math>f : X \to Y,</math> where <math>y = f(x),</math> {{nowrap|<math>X =</math> domain of function}}, {{nowrap|<math>Y = </math> [[range of a function|range of function]]}}, and <math>\operatorname{im}(f)</math> denotes image of <math>f.</math> Every one <math>x</math> in <math>X</math> maps to exactly one unique <math>y</math> in <math>Y.</math> The circled parts of the axes represent domain and range sets— in accordance with the standard diagrams above |
|Image:Injective function.svg|Injective functions. Diagramatic interpretation in the [[Cartesian plane]], defined by the [[Map (mathematics)|mapping]] <math>f : X \to Y,</math> where <math>y = f(x),</math> {{nowrap|<math>X =</math> domain of function}}, {{nowrap|<math>Y = </math> [[range of a function|range of function]]}}, and <math>\operatorname{im}(f)</math> denotes image of <math>f.</math> Every one <math>x</math> in <math>X</math> maps to exactly one unique <math>y</math> in <math>Y.</math> The circled parts of the axes represent domain and range sets— in accordance with the standard diagrams above |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 117: | Line 114: | ||
* [http://jeff560.tripod.com/i.html Earliest Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics: entry on Injection, Surjection and Bijection has the history of Injection and related terms.] |
* [http://jeff560.tripod.com/i.html Earliest Uses of Some of the Words of Mathematics: entry on Injection, Surjection and Bijection has the history of Injection and related terms.] |
||
* [http://www.khanacademy.org/math/linear-algebra/v/surjective--onto--and-injective--one-to-one--functions Khan Academy – Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions: Introduction to surjective and injective functions] |
* [http://www.khanacademy.org/math/linear-algebra/v/surjective--onto--and-injective--one-to-one--functions Khan Academy – Surjective (onto) and Injective (one-to-one) functions: Introduction to surjective and injective functions] |
||
{{Mathematical logic}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
Latest revision as of 00:04, 24 November 2024
| Function |
|---|
| x ↦ f (x) |
| History of the function concept |
| Types by domain and codomain |
| Classes/properties |
| Constructions |
| Generalizations |
| List of specific functions |
In mathematics, an injective function (also known as injection, or one-to-one function[1] ) is a function f that maps distinct elements of its domain to distinct elements of its codomain; that is, x1 ≠ x2 implies f(x1) ≠ f(x2) (equivalently by contraposition, f(x1) = f(x2) implies x1 = x2). In other words, every element of the function's codomain is the image of at most one element of its domain.[2] The term one-to-one function must not be confused with one-to-one correspondence that refers to bijective functions, which are functions such that each element in the codomain is an image of exactly one element in the domain.
A homomorphism between algebraic structures is a function that is compatible with the operations of the structures. For all common algebraic structures, and, in particular for vector spaces, an injective homomorphism is also called a monomorphism. However, in the more general context of category theory, the definition of a monomorphism differs from that of an injective homomorphism.[3] This is thus a theorem that they are equivalent for algebraic structures; see Homomorphism § Monomorphism for more details.
A function that is not injective is sometimes called many-to-one.[2]
Definition
[edit]
Let be a function whose domain is a set The function is said to be injective provided that for all and in if then ; that is, implies Equivalently, if then in the contrapositive statement.
Symbolically, which is logically equivalent to the contrapositive,[4]An injective function (or, more generally, a monomorphism) is often denoted by using the specialized arrows ↣ or ↪ (for example, or ), although some authors specifically reserve ↪ for an inclusion map.[5]
Examples
[edit]For visual examples, readers are directed to the gallery section.
- For any set and any subset the inclusion map (which sends any element to itself) is injective. In particular, the identity function is always injective (and in fact bijective).
- If the domain of a function is the empty set, then the function is the empty function, which is injective.
- If the domain of a function has one element (that is, it is a singleton set), then the function is always injective.
- The function defined by is injective.
- The function defined by is not injective, because (for example) However, if is redefined so that its domain is the non-negative real numbers [0,+∞), then is injective.
- The exponential function defined by is injective (but not surjective, as no real value maps to a negative number).
- The natural logarithm function defined by is injective.
- The function defined by is not injective, since, for example,
More generally, when and are both the real line then an injective function is one whose graph is never intersected by any horizontal line more than once. This principle is referred to as the horizontal line test.[2]
Injections can be undone
[edit]Functions with left inverses are always injections. That is, given if there is a function such that for every , , then is injective. In this case, is called a retraction of Conversely, is called a section of
Conversely, every injection with a non-empty domain has a left inverse . It can be defined by choosing an element in the domain of and setting to the unique element of the pre-image (if it is non-empty) or to (otherwise).[6]
The left inverse is not necessarily an inverse of because the composition in the other order, may differ from the identity on In other words, an injective function can be "reversed" by a left inverse, but is not necessarily invertible, which requires that the function is bijective.
Injections may be made invertible
[edit]In fact, to turn an injective function into a bijective (hence invertible) function, it suffices to replace its codomain by its actual image That is, let such that for all ; then is bijective. Indeed, can be factored as where is the inclusion function from into
More generally, injective partial functions are called partial bijections.
Other properties
[edit]
- If and are both injective then is injective.
- If is injective, then is injective (but need not be).
- is injective if and only if, given any functions whenever then In other words, injective functions are precisely the monomorphisms in the category Set of sets.
- If is injective and is a subset of then Thus, can be recovered from its image
- If is injective and and are both subsets of then
- Every function can be decomposed as for a suitable injection and surjection This decomposition is unique up to isomorphism, and may be thought of as the inclusion function of the range of as a subset of the codomain of
- If is an injective function, then has at least as many elements as in the sense of cardinal numbers. In particular, if, in addition, there is an injection from to then and have the same cardinal number. (This is known as the Cantor–Bernstein–Schroeder theorem.)
- If both and are finite with the same number of elements, then is injective if and only if is surjective (in which case is bijective).
- An injective function which is a homomorphism between two algebraic structures is an embedding.
- Unlike surjectivity, which is a relation between the graph of a function and its codomain, injectivity is a property of the graph of the function alone; that is, whether a function is injective can be decided by only considering the graph (and not the codomain) of
Proving that functions are injective
[edit]A proof that a function is injective depends on how the function is presented and what properties the function holds. For functions that are given by some formula there is a basic idea. We use the definition of injectivity, namely that if then [7]
Here is an example:
Proof: Let Suppose So implies which implies Therefore, it follows from the definition that is injective.
There are multiple other methods of proving that a function is injective. For example, in calculus if is a differentiable function defined on some interval, then it is sufficient to show that the derivative is always positive or always negative on that interval. In linear algebra, if is a linear transformation it is sufficient to show that the kernel of contains only the zero vector. If is a function with finite domain it is sufficient to look through the list of images of each domain element and check that no image occurs twice on the list.
A graphical approach for a real-valued function of a real variable is the horizontal line test. If every horizontal line intersects the curve of in at most one point, then is injective or one-to-one.
Gallery
[edit]-
Not an injective function. Here and are subsets of and are subsets of : for two regions where the function is not injective because more than one domain element can map to a single range element. That is, it is possible for more than one in to map to the same in
-
Making functions injective. The previous function can be reduced to one or more injective functions (say) and shown by solid curves (long-dash parts of initial curve are not mapped to anymore). Notice how the rule has not changed – only the domain and range. and are subsets of and are subsets of : for two regions where the initial function can be made injective so that one domain element can map to a single range element. That is, only one in maps to one in
-
Injective functions. Diagramatic interpretation in the Cartesian plane, defined by the mapping where domain of function, range of function, and denotes image of Every one in maps to exactly one unique in The circled parts of the axes represent domain and range sets— in accordance with the standard diagrams above
See also
[edit]- Bijection, injection and surjection – Properties of mathematical functions
- Injective metric space – Type of metric space
- Monotonic function – Order-preserving mathematical function
- Univalent function – Mathematical concept
Notes
[edit]- ^ Sometimes one-one function, in Indian mathematical education. "Chapter 1:Relations and functions" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on Dec 26, 2023 – via NCERT.
- ^ a b c "Injective, Surjective and Bijective". Math is Fun. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
- ^ "Section 7.3 (00V5): Injective and surjective maps of presheaves". The Stacks project. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
- ^ Farlow, S. J. "Section 4.2 Injections, Surjections, and Bijections" (PDF). Mathematics & Statistics - University of Maine. Archived from the original (PDF) on Dec 7, 2019. Retrieved 2019-12-06.
- ^ "What are usual notations for surjective, injective and bijective functions?". Mathematics Stack Exchange. Retrieved 2024-11-24.
- ^ Unlike the corresponding statement that every surjective function has a right inverse, this does not require the axiom of choice, as the existence of is implied by the non-emptiness of the domain. However, this statement may fail in less conventional mathematics such as constructive mathematics. In constructive mathematics, the inclusion of the two-element set in the reals cannot have a left inverse, as it would violate indecomposability, by giving a retraction of the real line to the set {0,1}.
- ^ Williams, Peter (Aug 21, 1996). "Proving Functions One-to-One". Department of Mathematics at CSU San Bernardino Reference Notes Page. Archived from the original on 4 June 2017.
References
[edit]- Bartle, Robert G. (1976), The Elements of Real Analysis (2nd ed.), New York: John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-471-05464-1, p. 17 ff.
- Halmos, Paul R. (1974), Naive Set Theory, New York: Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-90092-6, p. 38 ff.










































![{\displaystyle f^{-1}[y]}](https://wikimedia.org/enwiki/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c5ffa43f26ddc0c27fedee54ea4051661d56fa21)