Colaba: Difference between revisions
→History: relative image sizing |
Sandcat555 (talk | contribs) direct link to 2008 Mumbai attacks |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 26 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Use dmy dates|date=May 2018}} |
{{Use dmy dates|date=May 2018}} |
||
{{Use Indian English|date=May 2018}} |
{{Use Indian English|date=May 2018}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
| name = Colaba |
| name = Colaba |
||
| native_name = |
| native_name = |
||
| native_name_lang = |
| native_name_lang = |
||
| other_name = |
| other_name = Kolābā |
||
| settlement_type = Neighbourhood |
| settlement_type = Neighbourhood |
||
| image_skyline = |
| image_skyline = |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
| named_for = |
| named_for = |
||
| government_type = [[Municipal Corporation]] |
| government_type = [[Municipal Corporation]] |
||
| governing_body = [[Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation]] ( |
| governing_body = [[Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation]] (BMC) |
||
| unit_pref = Metric |
| unit_pref = Metric |
||
| area_footnotes = |
| area_footnotes = |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
| utc_offset1 = +5:30 |
| utc_offset1 = +5:30 |
||
| postal_code_type = [[Postal Index Number|PIN]] |
| postal_code_type = [[Postal Index Number|PIN]] |
||
| postal_code = 400005<ref name="pcode">{{cite web|url=https:// |
| postal_code = 400005<ref name="pcode">{{cite web|url=https://indiapincodes.net/Maharashtra/Mumbai/Colaba/|title=Pin code : Colaba, Mumbai |
||
| |
|access-date=9 February 2015|publisher=indiapincodes.net}}</ref> |
||
| area_code = 022 |
| area_code = 022 |
||
| area_code_type = |
| area_code_type = |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Colaba''' ({{IPA-mr|koˈlaːbaː|}} |
'''Colaba''' ({{IPA-mr|koˈlaːbaː|}}; or [[ISO 15919|ISO]]: '''Kolābā)''' is a part of the city of [[Mumbai]], India. It is one of the four peninsulas of Mumbai while the other three are [[Worli]], [[Bandra]] and [[Malabar Hill]]. During Portuguese rule in the 16th century, the island was known as Kolbhat. After the British took over the island in the late 17th century, it was known as Kolio.{{cn|date=August 2022}} |
||
[[File:Marine Drive.JPG|thumb|right|Marine Drive, looking at Nariman Point and Colaba]] |
|||
==History== |
==History== |
||
[[File:Sevenislandsofbombay.png|left|upright=0.6|thumb|[[Seven Islands of Bombay]], before reclamation]] |
[[File:Sevenislandsofbombay.png|left|upright=0.6|thumb|[[Seven Islands of Bombay|Seven Islands of Mumbai]], before reclamation]] |
||
The name Colaba comes from ''Kolabhat'', a word in the language of [[Kolis]], the indigenous inhabitants of the islands, before the arrival of the Portuguese.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://bbs.keyhole.com/ubb/printthread.php/Cat/0/Board/modEarthTourism/main/1067868/type/thread|title=Google Groups|website=bbs.keyhole.com| |
The name Colaba comes from ''Kolabhat'', a word in the language of [[Kolis]], the indigenous inhabitants of the islands, before the arrival of the Portuguese.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://bbs.keyhole.com/ubb/printthread.php/Cat/0/Board/modEarthTourism/main/1067868/type/thread|title=Google Groups|website=bbs.keyhole.com|access-date=18 August 2017}}{{Dead link|date=December 2023 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> The area that is now Colaba was originally a region consisting of two islands: Colaba and Little Colaba (or [[Old Woman's Island]]). The island of Colaba was one of the [[Seven Islands of Bombay|Seven Islands of Mumbai]] ruled by the [[Portuguese India|Portuguese]]. |
||
The Portuguese had acquired these lands from the [[Sultanate of Cambay]] by the [[Treaty of Bassein (1534)]]. The group of islands was given by |
The Portuguese had acquired these lands from the [[Cambay State|Sultanate of Cambay]] by the [[Treaty of Bassein (1534)|Treaty of Vasai (1534)]]. The group of islands was given by Portugal to [[Charles II of England]] as a dowry when he married [[Catherine of Braganza]] in 1661. The cession of Mumbai and dependencies was strongly resented by Portuguese officials in [[Goa]] and Mumbai, who resisted transfer of possession for several years, while the English representatives were confined to the island of [[Anjediva]] while negotiations continued. Angered by the back-tracking, Charles II leased these lands to the [[British East India Company]] for a nominal annual rent. [[Gerald Aungier]], second Governor (1672), and the president of the English settlement of [[Surat]], took possession of Colaba and [[Old Woman's Island]] on behalf of the Company in 1675. |
||
Portugal continued to hold Little Colaba island for several decades more before ceding it to the English in about 1762, subject to the retention of Portuguese ownership of a house on the island, that is now the Blessed Sacrament Chapel in Middle Colaba. This was leased by the Portuguese Government of Goa to the [[Bishop of Damao]], the head of the [[Padroado]] party in |
Portugal continued to hold Little Colaba island for several decades more before ceding it to the English in about 1762, subject to the retention of Portuguese ownership of a house on the island, that is now the Blessed Sacrament Chapel in Middle Colaba. This was leased by the Portuguese Government of Goa to the [[Bishop of Damao]], the head of the [[Padroado]] party in Mumbai, as his residence. After an attempt by the [[Propaganda Fide]] party to seize the chapel, a court ruled that the house remained the property of the Government of Portugal and evicted the Propaganda Fide party. |
||
[[File:Bombay 1909.jpg|left|upright=0.6|thumb|[[Old |
[[File:Bombay 1909.jpg|left|upright=0.6|thumb|[[South Mumbai|Old Mumbai]], 1909]][[File:BombayReclamation 1911.jpg|left|140px|thumb|Ambitious reclamation plans from 1912 have been only partly realised.]] |
||
[[File:Colaba Chapel, Bombay (Clutterbuck, p. 173) - Copy.jpg|thumb|upright|Colaba Chapel, |
[[File:Colaba Chapel, Bombay (Clutterbuck, p. 173) - Copy.jpg|thumb|upright|Colaba Chapel, Mumbai (Clutterbuck, 1889, p. 173)<ref name=Clutterbuck>{{cite journal|last1=Clutterbuck|first1=G W|title=A Sketch of the Mission in Bombay|journal=Wesleyan-Methodist Magazine|date=1889|page=[https://archive.org/details/wesleyanmethodi00unkngoog/page/n558 199]|url=https://archive.org/details/wesleyanmethodi00unkngoog|access-date=3 November 2015}}</ref>]] |
||
In 1743, British Colaba was leased to [[Richard Broughton (Colaba)|Richard Broughton]] at Rs. 200 yearly, and the lease was renewed in 1764.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://theory.tifr.res.in/bombay/physical/geo/colaba.html|title=Colaba, Cuffe Parade and Navy Nagar: Mumbai/Bombay pages|first=Sourendu|last=Gupta|date=28 October 1999|website=theory.tifr.res.in| |
In 1743, British Colaba was leased to [[Richard Broughton (Colaba)|Richard Broughton]] at Rs. 200 yearly, and the lease was renewed in 1764.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://theory.tifr.res.in/bombay/physical/geo/colaba.html|title=Colaba, Cuffe Parade and Navy Nagar: Mumbai/Bombay pages|first=Sourendu|last=Gupta|date=28 October 1999|website=theory.tifr.res.in|access-date=18 August 2017}}</ref> By 1796, Colaba had become a cantonment. Colaba was known for the variety of fishes – the [[bombil]] ([[Bombay duck]]), [[Eleutheronema tetradactylum|rawas]], [[Black pomfret|halwa]], turtles, crabs, prawns and lobsters. |
||
A [[Colaba Observatory]], a [[Meteorology|meteorological]] [[observatory]] was established in 1826 in the part that was called Upper Colaba. The [[Colaba Causeway]] was completed in 1838, and thus, the remaining two islands were joined to the others. Gradually, Colaba became a commercial center, after the Cotton Exchange was opened at [[Cotton Green]] in 1844. The real estate prices in the area went up. The Colaba Causeway was widened in 1861 and 1863. |
A [[Colaba Observatory]], a [[Meteorology|meteorological]] [[observatory]] was established in 1826 in the part that was called Upper Colaba. The [[Colaba Causeway]] was completed in 1838, and thus, the remaining two islands were joined to the others. Gradually, Colaba became a commercial center, after the Cotton Exchange was opened at [[Cotton Green]] in 1844. The real estate prices in the area went up. The Colaba Causeway was widened in 1861 and 1863. |
||
[[File:Colaba.jpg|thumb| One of the Colonial-era buildings opposite [[Regal Cinema]]]] |
[[File:Colaba.jpg|thumb| One of the Colonial-era buildings opposite [[Regal Cinema]]]] |
||
Colaba became a separate municipality ward in 1872. The Sick Bungalows (now known as INHS |
Colaba became a separate municipality ward in 1872. The Sick Bungalows (now known as INHS Asvini) were built in the 19th century. The construction of the [[Afghan Church]] after the [[First Afghan War]] of 1838) began in 1847. The Church was consecrated in 1858, with the work on the [[steeple (architecture)|steeple]] being concluded in 1865. |
||
The horse-drawn tram-cars were introduced in 1873 by [[Stearns and Kitteredge]], who had their offices on the west side of the Causeway, where the Electric House now stands. |
The horse-drawn tram-cars were introduced in 1873 by [[Stearns and Kitteredge]], who had their offices on the west side of the Causeway, where the Electric House now stands. |
||
The Prong's lighthouse was constructed at the southern tip of the island in 1875. The eponymous [[Sassoon Docks]] were built by [[David Sassoon]] on reclaimed land in the same year. The BB&CI Railways established the [[Colaba railway station]] or [[Terminal station|terminus]], the site of which is now occupied by the [[Badhwar Park]] layout. The development of Colaba pushed the native [[kolis]] to the edges of the island. |
The Prong's lighthouse was constructed at the southern tip of the island in 1875. The eponymous [[Sassoon Docks]] were built by [[David Solomon Sassoon]] on reclaimed land in the same year. The BB&CI Railways established the [[Colaba railway station]] or [[Terminal station|terminus]], the site of which is now occupied by the [[Badhwar Park]] layout. The development of Colaba pushed the native [[kolis]] to the edges of the island. |
||
The [[Bombay City Improvement Trust]] reclaimed around {{convert|90000|yd2|m2}} on the western shore of Colaba. Eminent citizens of Mumbai, such as Sir [[Pherozeshah Mehta]], opposed the work, fearing that the reclamation would depress prices of land. However, the reclamation work continued and was completed in 1905. There was no fall in the land prices. In 1906, a seafront road with a raised sea-side promenade was completed, and named as "[[Cuffe Parade]]" after T. W. Cuffe of the Trust. |
The [[Bombay City Improvement Trust|Mumbai City Improvement Trust]] reclaimed around {{convert|90000|yd2|m2}} on the western shore of Colaba. Eminent citizens of Mumbai, such as Sir [[Pherozeshah Mehta]], opposed the work, fearing that the reclamation would depress prices of land. However, the reclamation work continued and was completed in 1905. There was no fall in the land prices. In 1906, a seafront road with a raised sea-side promenade was completed, and named as "[[Cuffe Parade]]" after T. W. Cuffe of the Trust. |
||
== Present == |
== Present day == |
||
The [[Gateway of India]], the [[art deco]] style Regal Theatre, the cafes ([[Café Mondegar]], Cafe Royal and [[Leopold Cafe]]), and the [[Taj Mahal Palace & Tower]], [[Royal Bombay Yacht Club]], Bademiya Restaurant and Bagdadi restaurant, as well as a number of modern pubs, restaurants and clubs all add to the atmosphere. The southern tip is occupied by a military cantonment, including the large [[Navy Nagar]] layout built on reclaimed land known as Holiday Camp. The older parts of the cantonment retains its large, wooded spaces and is the only bit of green left in this otherwise congested area. In the midst of Navy Nagar lies the [[Tata Institute of Fundamental Research]] (TIFR), one of India's leading scientific institutions. Colaba is renowned for high-end boutiques and imitation consumer goods, and is popular with tourists. Notable residents include [[Ratan Tata]], [[Anil Ambani]], and [[Ravi Shastri]]. Colaba Causeway, or just "Causeway" as it is known in Mumbai, offers everything from bracelets to perfumes to clothes to watches, clocks, DVDs and CDs. It has an old English charm and a very modern feel as well. Colaba is also the art center of Mumbai, with all the major galleries and museums located in and around this area.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/Colaba|title=Colaba: Latest News, Videos and Photos - Times of India|website=The Times of India| |
The [[Gateway of India]], the [[art deco]] style Regal Theatre, the cafes ([[Café Mondegar]], Cafe Royal and [[Leopold Cafe]]), and the [[Taj Mahal Palace & Tower]], [[Royal Bombay Yacht Club]], Bademiya Restaurant and Bagdadi restaurant, as well as a number of modern pubs, restaurants and clubs all add to the atmosphere. The southern tip is occupied by a military cantonment, including the large [[Navy Nagar]] layout built on reclaimed land known as Holiday Camp. The older parts of the cantonment retains its large, wooded spaces and is the only bit of green left in this otherwise congested area. In the midst of Navy Nagar lies the [[Tata Institute of Fundamental Research]] (TIFR), one of India's leading scientific institutions. Colaba is renowned for high-end boutiques and imitation consumer goods, and is popular with tourists. Notable residents include [[Ratan Tata]], [[Anil Ambani]], and [[Ravi Shastri]]. Colaba Causeway, or just "Causeway" as it is known in Mumbai, offers everything from bracelets to perfumes to clothes to watches, clocks, DVDs and CDs. It has an old English charm and a very modern feel as well. Colaba is also the art center of Mumbai, with all the major galleries and museums located in and around this area.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/topic/Colaba|title=Colaba: Latest News, Videos and Photos - Times of India|website=The Times of India|access-date=18 August 2017}}</ref> Even today, in 2020, the government has managed to preserve most of its colonial-era architectures. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Colaba is home to the [[Cooperage Ground|Cooperage Football Ground]]. |
Colaba is home to the [[Cooperage Ground|Cooperage Football Ground]]. |
||
=== Transport === |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Nearest railway stations: |
Nearest railway stations: |
||
* [[Churchgate]] |
* [[Churchgate]] |
||
* [[Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus]] (" |
* [[Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus]] ("CSMT", Victoria Terminus) |
||
===Visitor attractions=== |
===Visitor attractions=== |
||
| Line 126: | Line 129: | ||
==Terrorist attack in November 2008== |
==Terrorist attack in November 2008== |
||
{{main| |
{{main|2008 Mumbai attacks}} |
||
On 26 November 2008, terrorist strikes occurred at various places in Colaba, notably the [[Taj Mahal Palace & Tower]], [[Leopold Cafe|Leopold Café]] and [[Mumbai Chabad House]]. The attacks resulted in over 100 deaths and significant damages. |
On 26 November 2008, terrorist strikes occurred at various places in and near Colaba, notably the [[Taj Mahal Palace & Tower]], [[Leopold Cafe|Leopold Café]], [[Marine Drive, Mumbai|Marine Drive]] and [[Mumbai Chabad House]]. The attacks resulted in over 100 deaths and significant damages. |
||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
{{portal|Islands}} |
|||
* [[Colaba Woods]] |
* [[Colaba Woods]] |
||
* Other business districts in and around Mumbai: [[Fort (Mumbai precinct)|Fort]], [[Nariman Point]], [[Vashi]], [[CBD Belapur]], [[Worli]], [[Bandra Kurla Complex]], [[Andheri]], [[Lower Parel]] |
* Other business districts in and around Mumbai: [[Fort (Mumbai precinct)|Fort]], [[Nariman Point]], [[Vashi]], [[CBD Belapur]], [[Worli]], [[Bandra Kurla Complex]], [[Andheri]], [[Lower Parel]] |
||
| Line 146: | Line 149: | ||
[[Category:Neighbourhoods in Mumbai]] |
[[Category:Neighbourhoods in Mumbai]] |
||
[[Category:Islands of India]] |
|||
[[Category:Populated places in India]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 19:32, 26 November 2024
Colaba
Kolābā | |
|---|---|
Neighbourhood | |
| Coordinates: 18°55′N 72°49′E / 18.91°N 72.81°E | |
| Country | India |
| State | Maharashtra |
| District | Mumbai City |
| City | Mumbai |
| Zone | 1 |
| Ward | A |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal Corporation |
| • Body | Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) |
| Elevation | 4 m (13 ft) |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Marathi |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN | 400005[1] |
| Area code | 022 |
| Vehicle registration | MH 01 |
| Lok Sabha Constituency | Mumbai South |
| Vidhan Sabha Constituency | Colaba |
| Civic agency | BMC |
Colaba ([koˈlaːbaː]; or ISO: Kolābā) is a part of the city of Mumbai, India. It is one of the four peninsulas of Mumbai while the other three are Worli, Bandra and Malabar Hill. During Portuguese rule in the 16th century, the island was known as Kolbhat. After the British took over the island in the late 17th century, it was known as Kolio.[citation needed]

History
[edit]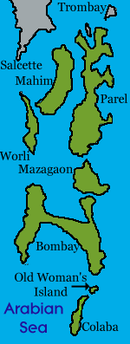
The name Colaba comes from Kolabhat, a word in the language of Kolis, the indigenous inhabitants of the islands, before the arrival of the Portuguese.[2] The area that is now Colaba was originally a region consisting of two islands: Colaba and Little Colaba (or Old Woman's Island). The island of Colaba was one of the Seven Islands of Mumbai ruled by the Portuguese.
The Portuguese had acquired these lands from the Sultanate of Cambay by the Treaty of Vasai (1534). The group of islands was given by Portugal to Charles II of England as a dowry when he married Catherine of Braganza in 1661. The cession of Mumbai and dependencies was strongly resented by Portuguese officials in Goa and Mumbai, who resisted transfer of possession for several years, while the English representatives were confined to the island of Anjediva while negotiations continued. Angered by the back-tracking, Charles II leased these lands to the British East India Company for a nominal annual rent. Gerald Aungier, second Governor (1672), and the president of the English settlement of Surat, took possession of Colaba and Old Woman's Island on behalf of the Company in 1675.
Portugal continued to hold Little Colaba island for several decades more before ceding it to the English in about 1762, subject to the retention of Portuguese ownership of a house on the island, that is now the Blessed Sacrament Chapel in Middle Colaba. This was leased by the Portuguese Government of Goa to the Bishop of Damao, the head of the Padroado party in Mumbai, as his residence. After an attempt by the Propaganda Fide party to seize the chapel, a court ruled that the house remained the property of the Government of Portugal and evicted the Propaganda Fide party.



In 1743, British Colaba was leased to Richard Broughton at Rs. 200 yearly, and the lease was renewed in 1764.[4] By 1796, Colaba had become a cantonment. Colaba was known for the variety of fishes – the bombil (Bombay duck), rawas, halwa, turtles, crabs, prawns and lobsters.
A Colaba Observatory, a meteorological observatory was established in 1826 in the part that was called Upper Colaba. The Colaba Causeway was completed in 1838, and thus, the remaining two islands were joined to the others. Gradually, Colaba became a commercial center, after the Cotton Exchange was opened at Cotton Green in 1844. The real estate prices in the area went up. The Colaba Causeway was widened in 1861 and 1863.

Colaba became a separate municipality ward in 1872. The Sick Bungalows (now known as INHS Asvini) were built in the 19th century. The construction of the Afghan Church after the First Afghan War of 1838) began in 1847. The Church was consecrated in 1858, with the work on the steeple being concluded in 1865.
The horse-drawn tram-cars were introduced in 1873 by Stearns and Kitteredge, who had their offices on the west side of the Causeway, where the Electric House now stands.
The Prong's lighthouse was constructed at the southern tip of the island in 1875. The eponymous Sassoon Docks were built by David Solomon Sassoon on reclaimed land in the same year. The BB&CI Railways established the Colaba railway station or terminus, the site of which is now occupied by the Badhwar Park layout. The development of Colaba pushed the native kolis to the edges of the island.
The Mumbai City Improvement Trust reclaimed around 90,000 square yards (75,000 m2) on the western shore of Colaba. Eminent citizens of Mumbai, such as Sir Pherozeshah Mehta, opposed the work, fearing that the reclamation would depress prices of land. However, the reclamation work continued and was completed in 1905. There was no fall in the land prices. In 1906, a seafront road with a raised sea-side promenade was completed, and named as "Cuffe Parade" after T. W. Cuffe of the Trust.
Present day
[edit]The Gateway of India, the art deco style Regal Theatre, the cafes (Café Mondegar, Cafe Royal and Leopold Cafe), and the Taj Mahal Palace & Tower, Royal Bombay Yacht Club, Bademiya Restaurant and Bagdadi restaurant, as well as a number of modern pubs, restaurants and clubs all add to the atmosphere. The southern tip is occupied by a military cantonment, including the large Navy Nagar layout built on reclaimed land known as Holiday Camp. The older parts of the cantonment retains its large, wooded spaces and is the only bit of green left in this otherwise congested area. In the midst of Navy Nagar lies the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), one of India's leading scientific institutions. Colaba is renowned for high-end boutiques and imitation consumer goods, and is popular with tourists. Notable residents include Ratan Tata, Anil Ambani, and Ravi Shastri. Colaba Causeway, or just "Causeway" as it is known in Mumbai, offers everything from bracelets to perfumes to clothes to watches, clocks, DVDs and CDs. It has an old English charm and a very modern feel as well. Colaba is also the art center of Mumbai, with all the major galleries and museums located in and around this area.[5] Even today, in 2020, the government has managed to preserve most of its colonial-era architectures.

Colaba is home to the Cooperage Football Ground.
Transport
[edit]Nearest railway stations:
- Churchgate
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus ("CSMT", Victoria Terminus)
Visitor attractions
[edit]- Colaba Causeway
- Colaba Observatory
- Cowasji Jehangir Hall
- Ballard Estate
- Cathedral of the Holy Name
- Prong's Lighthouse
- Gateway of India
- Sassoon Docks
- David Sassoon Library
Gallery
[edit]-
Cafe Mondegar on Colaba Causeway
-
Colaba Apartments
-
Colaba Causeway construction, view from Colaba island, 1826
Terrorist attack in November 2008
[edit]On 26 November 2008, terrorist strikes occurred at various places in and near Colaba, notably the Taj Mahal Palace & Tower, Leopold Café, Marine Drive and Mumbai Chabad House. The attacks resulted in over 100 deaths and significant damages.
See also
[edit]- Colaba Woods
- Other business districts in and around Mumbai: Fort, Nariman Point, Vashi, CBD Belapur, Worli, Bandra Kurla Complex, Andheri, Lower Parel
References
[edit]- ^ "Pin code : Colaba, Mumbai". indiapincodes.net. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Google Groups". bbs.keyhole.com. Retrieved 18 August 2017.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Clutterbuck, G W (1889). "A Sketch of the Mission in Bombay". Wesleyan-Methodist Magazine: 199. Retrieved 3 November 2015.
- ^ Gupta, Sourendu (28 October 1999). "Colaba, Cuffe Parade and Navy Nagar: Mumbai/Bombay pages". theory.tifr.res.in. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- ^ "Colaba: Latest News, Videos and Photos - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 18 August 2017.










