Picatinny rail: Difference between revisions
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by 37.4.225.216 to version by 2601:646:9500:4EF:1966:54A5:D28:E5BE. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (4114198) (Bot) |
P.koulloupas (talk | contribs) added a citation |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 32 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description| |
{{Short description|Rail interface for firearm accessories}} |
||
{{refimprove|date=July 2015}} |
{{refimprove|date=July 2015}} |
||
{{Lead too short|date=March 2021}} |
|||
}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
The '''1913 rail''' ('''MIL-STD-1913 rail)''' is an American [[rail integration system]] designed by Richard Swan<ref>{{Cite web |title=A.R.M.S. Inc. (Dick Swan) vs. Troy Industries (Steve Troy): ARMS/Swan Wins $1.8 Million |url=https://defensereview.com/arms-inc-dick-swan-vs-troy-industries-steve-troy-round-1-goes-to-armsswan/ |access-date=2024-02-08 |website=DefenseReview.com (DR): An online tactical technology and military defense technology magazine with particular focus on the latest and greatest tactical firearms news (tactical gun news), tactical gear news and tactical shooting news. |language=en-US}}</ref> that provides a mounting platform for [[firearm]] accessories. It forms part of the NATO standard [[Standardization agreement#Partial list|STANAG 2324 rail]]. It was originally used for [[scope mount|mounting]] of [[scope (rifle)|scope]]s atop the [[receiver (firearms)|receiver]]s of larger caliber [[rifle]]s. |
|||
The '''Picatinny rail''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|p|ɪ|k|ə|t|ɪ|n|i}} or {{IPAc-en|ˌ|p|ɪ|k|ə|ˈ|t|ɪ|n|i}}), or '''Pic rail''' for short, also known as a '''MIL-STD-1913 rail''' or '''[[STANAG]] 2324 rail''' (cancelled), is a [[United States Military Standard|military standard]] [[Rail Integration System|rail interface system]] that provides a mounting platform for [[firearm]] accessories. It was originally used for [[scope mount|mounting]] of [[scope (rifle)|scope]]s atop the [[receiver (firearms)|receiver]]s of larger caliber [[rifle]]s. Once established, its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: [[iron sights]], [[tactical light]]s, [[laser aiming module]]s, [[night vision device]]s, [[reflex sight]]s, [[Holographic weapon sight|holographic sight]]s, [[foregrip]]s, [[bipod]]s, [[sling (firearms)|sling]]s and [[bayonet]]s. |
|||
Once established as [[United States Military Standard]], its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: [[iron sights]], [[tactical light]]s, [[laser aiming module]]s, [[night vision device]]s, [[reflex sight]]s, [[Holographic weapon sight|holographic sight]]s, [[foregrip]]s, [[bipod]]s, [[sling (firearms)|sling]]s and [[bayonet]]s. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
== Significance == |
|||
| ⚫ | Because of their many uses, |
||
| ⚫ | |||
== History == |
== History == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | Attempts to standardize the [[Weaver rail]] designs date back to the early 1980s from work by the A.R.M.S. company and |
||
| ⚫ | Attempts to standardize the [[Weaver rail]] designs date back to the early 1980s from work by the A.R.M.S. company and Richard Swanson.{{Citation needed|date=November 2012}} Specifications for the [[M16 rifle|M16A2E4 rifle]] and the [[M4 carbine|M4E1 carbine]] received type classification generic in December 1994.{{Citation needed|date=November 2012}} These were the M16A2<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/systems/ground/m16-variants-a2.htm|title=M16 5.56mm Rifle|last=Pike|first=John|website=www.globalsecurity.org|access-date=2016-05-30}}</ref> and the M4<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/systems/ground/m4.htm|title=M4 / M4A1 5.56mm Carbine|last=Pike|first=John|website=www.globalsecurity.org|access-date=2016-05-30}}</ref> modified with new upper receivers where rails replaced hand guards. {{verification needed|date=July 2018}} |
||
The rail itself is named after the [[Picatinny Arsenal]] in [[New Jersey]], which was named "after the [[Lenape]]-named peak overlooking the old forge, loosely translated to mean 'rugged cliff by water' or 'water by the hills'."<ref>{{Cite web|title=Picatinny Peak|url=https://njskylands.com/history-picatinny_arsenal|access-date=2020-09-27|website=njskylands.com}}</ref> The Picatinny Arsenal was tasked in 1992 to develop a standardized mounting system after the [[U.S. Army]] was dissatisfied with the contemporary products on the market. The Picatinny team was headed by mechanical designer Gary Houtsma (who was awarded the [[Order of Saint Maurice (United States)|Order of Saint Maurice Award]] in 2014 for this contribution<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.army.mil/article/137761/picatinny_engineer_recognized_for_developing_venerable_picatinny_rail|title=Picatinny engineer recognized for developing venerable Picatinny Rail|publisher=U.S. Army|date=2014-11-06}}</ref>), who took the measurements from 20 or so different Weaver rail products from weapons bunkers at Picatinny (and even local [[sporting goods]] stores) and came up with an average set of numbers set on a 45-degree angled surface. Houtsma then took the [[specification (technical standard)|specification]]s over to the production facility and requested they design a dimensioning style so the rail could be easily produced and inspected. The factory recognized the similarity of the purposed rail interface to the existing rail design on [[105 mm]] [[howitzer]]s, so they chose to scale down the howitzer rail design and co-opted the production and inspection procedures. The team then sent the finished [[prototype]] over to [[Rock Island Arsenal]] for review and trial, and then to the technical data section to determine if it should be a standard or a specification. After it was determined that the new rail should be a standard, not a specification, it was adopted and fielded in 1995<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.shootingtimes.com/optics/optics_st_railcrazy_200907/|title=Rail Crazy: Picatinny Rail Basics|last=Guthrie|first=J.|publisher=Shooting Times|date=2010-09-23}}</ref> with the designation ''MIL-STD-1913'', dated February 3, 1995.<ref name="Military Standard 1913">{{ cite web | url = http://www.quarterbore.com/library/pdf_files/mil-std-1913.pdf | title = Dimensioning of accessory mounting rail for small arms weapons | url-status = dead | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20101126233329/http://quarterbore.com/library/pdf_files/mil-std-1913.pdf | archive-date = 2010-11-26 }}</ref> |
|||
The MIL-STD-1913 rail is at times called the 'Picatinny Rail', in reference to the [[Picatinny Arsenal]] in [[New Jersey]]. Picatinny Arsenal works as a contracting office for small arms design (they contracted engineers to work on the M4<ref>{{Cite web |last=Danrit |first=C. P. T. |date=2020-07-10 |title=US Army Develops New Fluted Barrel for M4 Carbine |url=https://www.firearmsnews.com/editorial/us-army-develops-new-fluted-barrel-for-m4-carbine/378850 |access-date=2024-02-08 |website=Firearms News |language=en}}</ref>). |
|||
| ⚫ | A [[metric system|metric]]-upgraded version of the |
||
Picatinny Arsenal requested Swan's help in developing the rail, but did not draft blueprints or request paperwork for a patent. That credit goes to ARMS Inc's Richard Swanson, who conducted Research and Development ''and'' achieved a patent for the rail in 1995.<ref>{{Cite web |title=HOME > ARMS |url=https://armsmounts.com/ |access-date=2024-02-08 |website=ARMS}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Swan has visited civil court against Colt and Troy industries regarding patent infringement. The courts found that Troy had developed rifles with rail mounting systems nearly identical to the MIL-STD-1913 rail.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Johnson |first=Steve |date=2009-08-03 |title=A.R.M.S. Inc. Wins Trade Secret Lawsuit against Troy Industries |url=https://www.thefirearmblog.com/blog/2009/08/03/a-r-m-s-inc-wins-trade-secret-lawsuit-against-troy-industries/ |access-date=2024-11-29 |website=thefirearmblog.com |language=en}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | A [[metric system|metric]]-upgraded version of the 1913 rail, the [[Standardization Agreement|STANAG 4694]] [[NATO Accessory Rail]], was designed in conjunction with weapon manufacturers like [[Aimpoint]], [[Beretta]], [[Colt Firearms|Colt]], [[FN Herstal]] and [[Heckler & Koch]], and was approved by the NATO Army Armaments Group (NAAG), Land Capability Group 1 Dismounted Soldier (LCG1-DS) on May 8, 2009. |
||
| ⚫ | Many firearm manufacturers include a MIL-STD-1913 rail system from factory, such as the [[Ruger Mini-14|Ruger Mini-14 Ranch Rifle]].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Ruger® Mini-14® Ranch Rifle Autoloading Rifle Model 5801|url=https://ruger.com/products/mini14RanchRifle/specSheets/5801.html|access-date=2020-09-17|website=ruger.com}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:Picatinny.svg|thumb|right|Metric dimensions of a Picatinny rail]] |
|||
The [[rail system (firearms)|rail]] consists of a strip undercut to form a "flattened T" with a hexagonal top [[Cross section (geometry)|cross-section]], with cross slots interspersed with flats that allow accessories to be slid into place from the end of the rail and then locked in place. It is similar in concept to the earlier commercial [[Weaver rail mount]] used to mount [[telescopic sights]], but is taller and has wider slots at regular intervals along the entire length. |
The [[rail system (firearms)|rail]] consists of a strip undercut to form a "flattened T" with a hexagonal top [[Cross section (geometry)|cross-section]], with cross slots interspersed with flats that allow accessories to be slid into place from the end of the rail and then locked in place. It is similar in concept to the earlier commercial [[Weaver rail mount]] used to mount [[telescopic sights]], but is taller and has wider slots at regular intervals along the entire length. |
||
The |
The MIL-STD-1913 locking slot width is {{cvt|0.206|in|mm|2}}. The spacing of slot centres is {{cvt|0.394|in|mm|2}} and the slot depth is {{cvt|0.118|in|mm|2}}.<ref name="Military Standard 1913">{{cite web |title=Dimensioning of accessory mounting rail for small arms weapons |url=http://www.quarterbore.com/library/pdf_files/mil-std-1913.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101126233329/http://quarterbore.com/library/pdf_files/mil-std-1913.pdf |archive-date=2010-11-26}}</ref> |
||
== Comparison to Weaver rail == |
== Comparison to Weaver rail == |
||
{{unreferenced|section|date=July 2018}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
The only significant difference between the |
The only significant difference between the MIL-STD-1913 rail and the similar [[Weaver rail]] are the size and shapes of the slots. Whereas the earlier Weaver rail is modified from a low, wide [[dovetail rail]] and has rounded slots, the 1913 rail has a more pronounced angular section and square-bottomed slots. This means that an accessory designed for a Weaver rail will fit onto a MIL-STD-1913 rail whereas the opposite might not be possible (unless the slots in the Weaver rail are modified to have square bottoms).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Weaver Vs. Picatinny Style Bases |url=https://warnescopemounts.com/blog/weaver-vs-picatinny-style-bases/#:~:text=The%20two%20major%20areas%20where,wider,%20and%20slightly%20deeper%20slot. |access-date=2024-11-29 |website=Warne Scope Mounts |language=en}}</ref> |
||
While some accessories are designed to fit on both Weaver and 1913 rails, most 1913 compatible devices will not fit on Weaver rails. From May 2012, most mounting rails are cut to MIL-STD-1913 standards.{{Citation needed|date=July 2018}} Many accessories can be secured to a rail with a single spring-loaded retaining pin. |
|||
| ⚫ | Designed to mount heavy sights of various kinds, a great variety of accessories and attachments are now available and the rails are no longer confined to the rear upper surface ([[Receiver (firearms)|receiver]]) of long arms but are either fitted to or [[Milling (machining)|machine milled]] into the upper, side or lower surfaces of all manner of weapons from crossbows to [[Handgun|pistols]] and long arms up to and including [[anti-materiel rifle]]s. |
||
== Impact == |
|||
| ⚫ | Because of their many uses, 1913 rails and accessories have replaced [[iron sights]] in the design of many firearms and are available as aftermarket add-on parts for most actions that do not have them integrated, and they are also on the undersides of [[semi-automatic pistol]] frames and grips.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://gunbelts.com/blog/accessory-rail-for-ccw-gun/|title=Does a Concealed Carry Gun Need an Accessory Rail? {{!}} Gun Belts Blog|website=Bigfoot Gun Belts|language=en|access-date=2018-12-19}}</ref> |
||
Their usefulness has led to them being used in [[paintball]], [[gel blasters]] and [[airsoft]].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.tippmann.com/p/magfed-tcr?pp=24&mobile=0|title=Magfed TCR|website=Tippmann Sports|language=en-US|access-date=2018-12-19|archive-date=December 20, 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181220230743/https://www.tippmann.com/p/magfed-tcr?pp=24&mobile=0|url-status=dead}}</ref><!-- Preceding source is for purchase of railed paintball, a discussion about rails on paintball guns would work much better --> |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
* [[NATO Accessory Rail]] |
|||
* [[Warsaw Pact rail]], is a rail mount system to connect telescopic sights to rifles |
|||
* [[Rail System (firearms)|Rail Systems]] |
|||
* [[Zeiss rail]], a ringless scope mounting standard |
|||
* [[Third Arm Weapon Interface System]] |
* [[Third Arm Weapon Interface System]] |
||
* [[Warsaw Pact rail]] |
|||
* [[Zeiss rail]] |
|||
== References == |
== References == |
||
{{reflist}} |
|||
{{refs}} |
|||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{commonscat}} |
|||
{{commons category}} |
|||
* [http://www.biggerhammer.net/picatinny Picatinny Rail Specifications] |
* [http://www.biggerhammer.net/picatinny Picatinny Rail Specifications] |
||
{{Firearm accessories mounting standards}} |
{{Firearm accessories mounting standards}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Firearm components]] |
[[Category:Firearm components]] |
||
[[Category:Mechanical standards]] |
[[Category:Mechanical standards]] |
||
Latest revision as of 12:09, 29 November 2024
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2015) |
The 1913 rail (MIL-STD-1913 rail) is an American rail integration system designed by Richard Swan[1] that provides a mounting platform for firearm accessories. It forms part of the NATO standard STANAG 2324 rail. It was originally used for mounting of scopes atop the receivers of larger caliber rifles.
Once established as United States Military Standard, its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: iron sights, tactical lights, laser aiming modules, night vision devices, reflex sights, holographic sights, foregrips, bipods, slings and bayonets.
An updated version of the rail is adopted as a NATO standard as the STANAG 4694 NATO Accessory Rail.

History
[edit]
Attempts to standardize the Weaver rail designs date back to the early 1980s from work by the A.R.M.S. company and Richard Swanson.[citation needed] Specifications for the M16A2E4 rifle and the M4E1 carbine received type classification generic in December 1994.[citation needed] These were the M16A2[2] and the M4[3] modified with new upper receivers where rails replaced hand guards. [verification needed]
The MIL-STD-1913 rail is at times called the 'Picatinny Rail', in reference to the Picatinny Arsenal in New Jersey. Picatinny Arsenal works as a contracting office for small arms design (they contracted engineers to work on the M4[4]).
Picatinny Arsenal requested Swan's help in developing the rail, but did not draft blueprints or request paperwork for a patent. That credit goes to ARMS Inc's Richard Swanson, who conducted Research and Development and achieved a patent for the rail in 1995.[5]
Swan has visited civil court against Colt and Troy industries regarding patent infringement. The courts found that Troy had developed rifles with rail mounting systems nearly identical to the MIL-STD-1913 rail.[6]
A metric-upgraded version of the 1913 rail, the STANAG 4694 NATO Accessory Rail, was designed in conjunction with weapon manufacturers like Aimpoint, Beretta, Colt, FN Herstal and Heckler & Koch, and was approved by the NATO Army Armaments Group (NAAG), Land Capability Group 1 Dismounted Soldier (LCG1-DS) on May 8, 2009.
Many firearm manufacturers include a MIL-STD-1913 rail system from factory, such as the Ruger Mini-14 Ranch Rifle.[7]
Design
[edit]The rail consists of a strip undercut to form a "flattened T" with a hexagonal top cross-section, with cross slots interspersed with flats that allow accessories to be slid into place from the end of the rail and then locked in place. It is similar in concept to the earlier commercial Weaver rail mount used to mount telescopic sights, but is taller and has wider slots at regular intervals along the entire length.
The MIL-STD-1913 locking slot width is 0.206 in (5.23 mm). The spacing of slot centres is 0.394 in (10.01 mm) and the slot depth is 0.118 in (3.00 mm).[8]
Comparison to Weaver rail
[edit]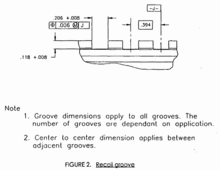
The only significant difference between the MIL-STD-1913 rail and the similar Weaver rail are the size and shapes of the slots. Whereas the earlier Weaver rail is modified from a low, wide dovetail rail and has rounded slots, the 1913 rail has a more pronounced angular section and square-bottomed slots. This means that an accessory designed for a Weaver rail will fit onto a MIL-STD-1913 rail whereas the opposite might not be possible (unless the slots in the Weaver rail are modified to have square bottoms).[9]
While some accessories are designed to fit on both Weaver and 1913 rails, most 1913 compatible devices will not fit on Weaver rails. From May 2012, most mounting rails are cut to MIL-STD-1913 standards.[citation needed] Many accessories can be secured to a rail with a single spring-loaded retaining pin.
Designed to mount heavy sights of various kinds, a great variety of accessories and attachments are now available and the rails are no longer confined to the rear upper surface (receiver) of long arms but are either fitted to or machine milled into the upper, side or lower surfaces of all manner of weapons from crossbows to pistols and long arms up to and including anti-materiel rifles.
Impact
[edit]Because of their many uses, 1913 rails and accessories have replaced iron sights in the design of many firearms and are available as aftermarket add-on parts for most actions that do not have them integrated, and they are also on the undersides of semi-automatic pistol frames and grips.[10]
Their usefulness has led to them being used in paintball, gel blasters and airsoft.[11]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "A.R.M.S. Inc. (Dick Swan) vs. Troy Industries (Steve Troy): ARMS/Swan Wins $1.8 Million". DefenseReview.com (DR): An online tactical technology and military defense technology magazine with particular focus on the latest and greatest tactical firearms news (tactical gun news), tactical gear news and tactical shooting news. Retrieved February 8, 2024.
- ^ Pike, John. "M16 5.56mm Rifle". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ^ Pike, John. "M4 / M4A1 5.56mm Carbine". www.globalsecurity.org. Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ^ Danrit, C. P. T. (July 10, 2020). "US Army Develops New Fluted Barrel for M4 Carbine". Firearms News. Retrieved February 8, 2024.
- ^ "HOME > ARMS". ARMS. Retrieved February 8, 2024.
- ^ Johnson, Steve (August 3, 2009). "A.R.M.S. Inc. Wins Trade Secret Lawsuit against Troy Industries". thefirearmblog.com. Retrieved November 29, 2024.
- ^ "Ruger® Mini-14® Ranch Rifle Autoloading Rifle Model 5801". ruger.com. Retrieved September 17, 2020.
- ^ "Dimensioning of accessory mounting rail for small arms weapons" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on November 26, 2010.
- ^ "Weaver Vs. Picatinny Style Bases". Warne Scope Mounts. Retrieved November 29, 2024.
- ^ "Does a Concealed Carry Gun Need an Accessory Rail? | Gun Belts Blog". Bigfoot Gun Belts. Retrieved December 19, 2018.
- ^ "Magfed TCR". Tippmann Sports. Archived from the original on December 20, 2018. Retrieved December 19, 2018.
External links
[edit]
