Veldenz: Difference between revisions
m r2.7.2+) (Robot: Adding uz:Veldenz |
m use wikitable |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 19 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox German |
{{Infobox German place |
||
|image_photo = |
|image_photo = Veldenz 2019.jpg |
||
|image_caption = The village of Veldenz as seen from [[Schloss Veldenz|Veldenz Castle]] |
|||
|Wappen = Wappen Veldenz.svg |
|||
| |
|image_coa = Wappen Veldenz.svg |
||
|coordinates = {{coord|49|53|26|N|7|1|33|E|format=dms|display=inline,title}} |
|||
|lon_deg = 7 |lon_min = 1 |lon_sec = 33 |
|||
| |
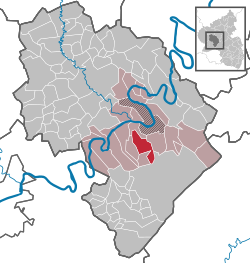
|image_plan = Veldenz in WIL.svg |
||
| |
|state = Rheinland-Pfalz |
||
| |
|district = Bernkastel-Wittlich |
||
|Verbandsgemeinde = Bernkastel-Kues |
|Verbandsgemeinde = Bernkastel-Kues |
||
| |
|elevation = 170 |
||
| |
|area = 14.41 |
||
| |
|postal_code = 54472 |
||
| |
|area_code = 06534 |
||
| |
|licence = WIL |
||
|Vorwahl = 06534 |
|||
|Kfz = WIL |
|||
|Gemeindeschlüssel = 07 2 31 126 |
|Gemeindeschlüssel = 07 2 31 126 |
||
| |
|divisions = 2 |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|Adresse-Verband = Gestade 18<br>54470 Bernkastel-Kues |
|||
|mayor = Norbert Sproß<ref>[https://www.wahlen.rlp.de/de/kw/wahlen/kd/gebiete/2310000000000.html Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Bernkastel-Wittlich], Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 6 August 2021.</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|leader_term = 2019–24 |
|||
|Bürgermeister = Norbert Sproß |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File: |
[[File:Veldenz 2007.jpg|thumb|upright=1.3|Veldenz valley is a dry fallen [[meander]] of the river [[Moselle]]. The village to the left and [[Geisberg (Middle Moselle)|Geisberg]] mountain to the right.]] |
||
'''Veldenz''' is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a [[Municipalities of Germany|municipality]] belonging to a ''[[Verbandsgemeinde]]'', a kind of collective municipality – in the [[Bernkastel-Wittlich]] [[Districts of Germany|district]] in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]], [[Germany]]. It is the former main seat of the [[County of Veldenz]], once a prominent principality to which belonged 120 villages and towns now in Rhineland-Palatinate and northern [[Alsace]]. |
'''Veldenz''' is an ''Ortsgemeinde'' – a [[Municipalities of Germany|municipality]] belonging to a ''[[Verbandsgemeinde]]'', a kind of collective municipality – in the [[Bernkastel-Wittlich]] [[Districts of Germany|district]] in [[Rhineland-Palatinate]], [[Germany]]. It is the former main seat of the [[County of Veldenz]], once a prominent principality to which belonged 120 villages and towns now in Rhineland-Palatinate and northern [[Alsace]] and [[Lorraine]]. |
||
== Geography == |
== Geography == |
||
=== Location === |
=== Location === |
||
The municipality lies in the [[Mittelmosel|Middle Moselle]] region of valley country marked by even slopes and former oxbows of the [[Moselle (river)|Moselle]]. Veldenz is found on the |
The municipality lies in the [[Mittelmosel|Middle Moselle]] region of valley country marked by even slopes and former oxbows of the [[Moselle (river)|Moselle]]. Veldenz is found on the Moselle's right bank, but does not lie right at the water's edge, but rather some two kilometres back from the river, under the outermost forests of the [[Hunsrück]]. Roughly 850 ha of the 1 441 ha municipal area is wooded. About 130 ha is given over to [[winegrowing]]. |
||
Veldenz belongs to the [[Bernkastel-Kues (Verbandsgemeinde)|''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Bernkastel-Kues]], whose seat is in the [[Bernkastel-Kues|like-named town]]. |
Veldenz belongs to the [[Bernkastel-Kues (Verbandsgemeinde)|''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Bernkastel-Kues]], whose seat is in the [[Bernkastel-Kues|like-named town]]. |
||
| Line 34: | Line 33: | ||
=== Constituent communities === |
=== Constituent communities === |
||
Veldenz's ''[[Ortsteil]]e'' are Veldenz and Thalveldenz. |
|||
=== Climate === |
=== Climate === |
||
| Line 40: | Line 39: | ||
== History == |
== History == |
||
As early as 500 BC, the [[Treveri]], a people of mixed [[Celts|Celtic]] and [[Germanic peoples|Germanic]] stock, from whom the [[Latin]] name for the city of [[Trier]], ''[[History of Trier|Augusta Treverorum]]'', is also derived, settled in |
As early as 500 BC, the [[Treveri]], a people of mixed [[Celts|Celtic]] and [[Germanic peoples|Germanic]] stock, from whom the [[Latin]] name for the city of [[Trier]], ''[[History of Trier|Augusta Treverorum]]'', is also derived, settled in Veldenz's fertile valley. After them, from about 50 BC to AD 500 came the [[Ancient Rome|Romans]]. Possibly about the year 1129, Gerlach I built a castle, today's [[Schloss Veldenz]]. In 1286, [[Rudolph I of Germany|Rudolph of Habsburg]] granted Veldenz town and market rights. By 1444, the castle and its environs had passed to [[Stephen, Count Palatine of Simmern-Zweibrücken]], or between 1543 and 1694 the Principality of [[County of Veldenz#Palantine Veldenz Line|Palatinate-Veldenz]]. In 1752, in [[Burgen, Bernkastel-Wittlich|Burgen]] near Veldenz, the widely known robber, [[Johann Peter Petri]], also known as ''Schwarzer Peter'' (“Black Peter”), was born. From 1777 to 1797, Veldenz belonged to [[Bavaria]]. After French rule as part of [[Sarre (department)|Sarre]] department, it was annexed to [[Prussia]] in 1815. In 1835 the Veldenz Lion was adopted as the Bavarian Lion in that kingdom's coat of arms. Even today, many examples of comital building undertakings from the 18th century can be found, among them the town hall. |
||
== Politics == |
== Politics == |
||
<!--[[File:Bevoelkerung Veldenz.png|thumb|Population development of the ''Ortsgemeinde'' of Veldenz]]--> |
<!--[[File:Bevoelkerung Veldenz.png|thumb|Population development of the ''Ortsgemeinde'' of Veldenz]]--> |
||
=== Municipal council === |
=== Municipal council === |
||
The council is made up of 12 council members, who were elected at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009. The mayor is Norbert Sproß. |
The council is made up of 12 council members, who were elected at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009. The mayor is Norbert Sproß. |
||
[[File:Bayerisches Staatswappen 1835.png|thumb|180px|right|Bavarian coat of arms from 1835 with the Lion of Veldenz. It also |
[[File:Bayerisches Staatswappen 1835.png|thumb|180px|right|Bavarian coat of arms from 1835 with the Lion of Veldenz. It also depicts: the [[Palatine Lion]], the Franconian Rake and the Margraviate of Burgau as well as the Bavarian lozenges in the inescutcheon. These arms held their place until the end of the monarchy.]] |
||
The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results: |
The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results: |
||
{| |
{| class="wikitable" width="400" |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|- bgcolor="#eeeeee" align="center" |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|- align="center" |
|- align="center" |
||
| 2009 || 7 || 5 || 12 seats |
| 2009 || 7 || 5 || 12 seats |
||
| Line 58: | Line 57: | ||
=== Coat of arms === |
=== Coat of arms === |
||
[[File:Wappen Veldenz.svg|left|70px|Coat of arms of Veldenz]] |
[[File:Wappen Veldenz.svg|left|70px|Coat of arms of Veldenz]] |
||
The |
The municipality's [[Coat of arms|arms]] might be described thus: Bendy lozengy argent and azure, in dexter chief an inescutcheon of the first charged with a lion rampant of the second armed and langued gules. |
||
The lion in the [[inescutcheon]] is the heraldic [[charge (heraldry)|charge]] once borne by the [[County of Veldenz|Counts of Veldenz]], and the “bendy lozengy” pattern seen on the field is the [[House of Wittelsbach|Wittelsbach |
The lion in the [[inescutcheon]] is the heraldic [[charge (heraldry)|charge]] once borne by the [[County of Veldenz|Counts of Veldenz]], and the “bendy lozengy” pattern seen on the field is the [[House of Wittelsbach|Wittelsbach dynasty's]] armorial bearing. In 1835, this lion was adopted by [[Ludwig I of Bavaria|Ludwig I, King of Bavaria]] into that kingdom's state coat of arms, where it remained as a charge until the end of the [[First World War]] when the last Bavarian king, [[Ludwig III of Bavaria|Ludwig III]] was forced to abdicate as a result of the [[German Revolution of 1918–19|November Revolution]]. |
||
== Culture and sightseeing == |
== Culture and sightseeing == |
||
=== Village culture === |
=== Village culture === |
||
In 1993 and 1995, Veldenz won the silver medal of the Federal Republic in the contest ''Unser Dorf soll schöner werden'' (“Our village should become lovelier”); in 2006, the villagers managed to triumph once again in the district and regional contest. In the vineyard locations of Elisenberg, Kirchberg, Mühlberg, Grafschafter Sonnenberg and Carlsberg, there is [[winegrowing]]. There still exist today in the municipality about a dozen wineries; [[Riesling]] is the customary variety. |
In 1993 and 1995, Veldenz won the silver medal of the Federal Republic in the contest ''Unser Dorf soll schöner werden'' (“Our village should become lovelier”); in 2006, the villagers managed to triumph once again in the district and regional contest. In the vineyard locations of Elisenberg, Kirchberg, Mühlberg, Grafschafter Sonnenberg and Carlsberg, there is [[winegrowing]]. There still exist today in the municipality about a dozen wineries; [[Riesling]] is the customary variety. |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
=== Sightseeing === |
=== Sightseeing === |
||
[[File:Schloss-veldenz-okt-2007.jpg|thumb|Schloss Veldenz 2007]] |
[[File:Schloss-veldenz-okt-2007.jpg|thumb|Schloss Veldenz 2007]] |
||
Well known points of interest are the ''Villa Romana'' and [[Schloss Veldenz]]. There are other monumental buildings, such as the town hall, a signal tower from the 12th century, a mint, a Celtic wall and museums with various exhibits. Further points of interest are an historical market (''Krammarkt''), a |
Well known points of interest are the ''Villa Romana'' and [[Schloss Veldenz]]. There are other monumental buildings, such as the town hall, a signal tower from the 12th century, a mint, a Celtic wall and museums with various exhibits. Further points of interest are an historical market (''Krammarkt''), a farmer's garden (''Bauerngarten''), a wild garden, the ''Josefinenhöhe'' (heights), the ''Pionierfelsen'' (cliff), many ore and slate mines, the ''Roter Bohles'' leisure complex and many imposing cliff formations. |
||
== Economy and infrastructure == |
== Economy and infrastructure == |
||
[[Winegrowing]] and [[tourism]] play a prominent rôle. In Veldenz there are two village squares, three community houses, a village hall, several barbecue pits, educational paths dealing with both wine and the forest, a memorial, a graveyard, two churches and a sporting ground. Furthermore, Veldenz also has its own [[primary school]], a [[kindergarten]], a youth centre, a [[Association football|football]] field and four |
[[Winegrowing]] and [[tourism]] play a prominent rôle. In Veldenz there are two village squares, three community houses, a village hall, several barbecue pits, educational paths dealing with both wine and the forest, a memorial, a graveyard, two churches and a sporting ground. Furthermore, Veldenz also has its own [[primary school]], a [[kindergarten]], a youth centre, a [[Association football|football]] field and four children's playgrounds. In the village is also a regional children's and youth home. Roughly 45 km of hiking trails lead around the village. Public transport in Veldenz is integrated into the ''Verkehrsverbund Region Trier'' (VRT), whose fares therefore apply. |
||
== Further reading == |
== Further reading == |
||
* Ernst Probst: ''Der Schwarze Peter. Ein Räuber im Hunsrück und Odenwald.'' Probst, Mainz-Kostheim 2005, ISBN |
* Ernst Probst: ''Der Schwarze Peter. Ein Räuber im Hunsrück und Odenwald.'' Probst, Mainz-Kostheim 2005, {{ISBN|3-936326-39-8}} |
||
* Theodor Gümbel: ''Geschichte des Fürstentums Pfalz-Veldenz.'' E. Grusius, Kaiserslautern 1900. |
* Theodor Gümbel: ''Geschichte des Fürstentums Pfalz-Veldenz.'' E. Grusius, Kaiserslautern 1900. |
||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
{{ |
{{commons category|Veldenz}} |
||
* [http://www.veldenz.de |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20070526161253/http://www.veldenz.de/tools/internet/view.php?rID=2&TabellenName=katalog1&SpracheChange=1 Municipality’s official webpage] |
||
* [http://www.schlossveldenz.com/ Schloss Veldenz] |
* [http://www.schlossveldenz.com/ Schloss Veldenz] |
||
* [http://www.sv-veldenz.de/ Sportverein Veldenz] (sport club) |
* [http://www.sv-veldenz.de/ Sportverein Veldenz] (sport club) |
||
{{de}} |
|||
{{Cities and towns in Bernkastel-Wittlich (district)}} |
{{Cities and towns in Bernkastel-Wittlich (district)}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[de:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[eo:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[Category:Bernkastel-Wittlich]] |
|||
[[fr:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[it:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[kk:Фельденц]] |
|||
[[nl:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[uz:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[pl:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[pt:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[ro:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[ru:Фельденц]] |
|||
[[sr:Фелденц]] |
|||
[[vi:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[vo:Veldenz]] |
|||
[[war:Veldenz]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 08:50, 30 November 2024
Veldenz | |
|---|---|
 The village of Veldenz as seen from Veldenz Castle | |
| Coordinates: 49°53′26″N 7°1′33″E / 49.89056°N 7.02583°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | Bernkastel-Wittlich |
| Municipal assoc. | Bernkastel-Kues |
| Subdivisions | 2 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–24) | Norbert Sproß[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 14.41 km2 (5.56 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 170 m (560 ft) |
| Population (2022-12-31)[2] | |
• Total | 956 |
| • Density | 66/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 54472 |
| Dialling codes | 06534 |
| Vehicle registration | WIL |
| Website | www.veldenz.de |

Veldenz is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bernkastel-Wittlich district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is the former main seat of the County of Veldenz, once a prominent principality to which belonged 120 villages and towns now in Rhineland-Palatinate and northern Alsace and Lorraine.
Geography
[edit]Location
[edit]The municipality lies in the Middle Moselle region of valley country marked by even slopes and former oxbows of the Moselle. Veldenz is found on the Moselle's right bank, but does not lie right at the water's edge, but rather some two kilometres back from the river, under the outermost forests of the Hunsrück. Roughly 850 ha of the 1 441 ha municipal area is wooded. About 130 ha is given over to winegrowing.
Veldenz belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Bernkastel-Kues, whose seat is in the like-named town.
Nearby municipalities
[edit]Neighbouring municipalities are, among others, Burgen and Mülheim. The nearest middle centres are Bernkastel-Kues, some 10 km away, and Wittlich, some 17 km away. Trier lies some 45 km away.
Constituent communities
[edit]Veldenz's Ortsteile are Veldenz and Thalveldenz.
Climate
[edit]Veldenz lies within the temperate zone; compared to other regions in Germany, a very warm and sunny climate prevails here. In neighbouring Brauneberg on 11 August 1998, a record temperature of 41.2 °C in the shade, the highest ever air temperature recorded in the Federal Republic, was confirmed. Because of its location alee of the Eifel, precipitation from northwest weather systems is often kept away. Ongoing evaporation of water from the Moselle regularly leads to high humidity, which, especially in summer, makes at times for heavy and muggy weather, and which also brings many storms along with it.
History
[edit]As early as 500 BC, the Treveri, a people of mixed Celtic and Germanic stock, from whom the Latin name for the city of Trier, Augusta Treverorum, is also derived, settled in Veldenz's fertile valley. After them, from about 50 BC to AD 500 came the Romans. Possibly about the year 1129, Gerlach I built a castle, today's Schloss Veldenz. In 1286, Rudolph of Habsburg granted Veldenz town and market rights. By 1444, the castle and its environs had passed to Stephen, Count Palatine of Simmern-Zweibrücken, or between 1543 and 1694 the Principality of Palatinate-Veldenz. In 1752, in Burgen near Veldenz, the widely known robber, Johann Peter Petri, also known as Schwarzer Peter (“Black Peter”), was born. From 1777 to 1797, Veldenz belonged to Bavaria. After French rule as part of Sarre department, it was annexed to Prussia in 1815. In 1835 the Veldenz Lion was adopted as the Bavarian Lion in that kingdom's coat of arms. Even today, many examples of comital building undertakings from the 18th century can be found, among them the town hall.
Politics
[edit]Municipal council
[edit]The council is made up of 12 council members, who were elected at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009. The mayor is Norbert Sproß.

The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results:
| Year | Freie Wählergruppe Veldenz e.V. | Freie Wählergruppe Bauer | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 7 | 5 | 12 seats |
Coat of arms
[edit]
The municipality's arms might be described thus: Bendy lozengy argent and azure, in dexter chief an inescutcheon of the first charged with a lion rampant of the second armed and langued gules.
The lion in the inescutcheon is the heraldic charge once borne by the Counts of Veldenz, and the “bendy lozengy” pattern seen on the field is the Wittelsbach dynasty's armorial bearing. In 1835, this lion was adopted by Ludwig I, King of Bavaria into that kingdom's state coat of arms, where it remained as a charge until the end of the First World War when the last Bavarian king, Ludwig III was forced to abdicate as a result of the November Revolution.
Culture and sightseeing
[edit]Village culture
[edit]In 1993 and 1995, Veldenz won the silver medal of the Federal Republic in the contest Unser Dorf soll schöner werden (“Our village should become lovelier”); in 2006, the villagers managed to triumph once again in the district and regional contest. In the vineyard locations of Elisenberg, Kirchberg, Mühlberg, Grafschafter Sonnenberg and Carlsberg, there is winegrowing. There still exist today in the municipality about a dozen wineries; Riesling is the customary variety.
Sightseeing
[edit]
Well known points of interest are the Villa Romana and Schloss Veldenz. There are other monumental buildings, such as the town hall, a signal tower from the 12th century, a mint, a Celtic wall and museums with various exhibits. Further points of interest are an historical market (Krammarkt), a farmer's garden (Bauerngarten), a wild garden, the Josefinenhöhe (heights), the Pionierfelsen (cliff), many ore and slate mines, the Roter Bohles leisure complex and many imposing cliff formations.
Economy and infrastructure
[edit]Winegrowing and tourism play a prominent rôle. In Veldenz there are two village squares, three community houses, a village hall, several barbecue pits, educational paths dealing with both wine and the forest, a memorial, a graveyard, two churches and a sporting ground. Furthermore, Veldenz also has its own primary school, a kindergarten, a youth centre, a football field and four children's playgrounds. In the village is also a regional children's and youth home. Roughly 45 km of hiking trails lead around the village. Public transport in Veldenz is integrated into the Verkehrsverbund Region Trier (VRT), whose fares therefore apply.
Further reading
[edit]- Ernst Probst: Der Schwarze Peter. Ein Räuber im Hunsrück und Odenwald. Probst, Mainz-Kostheim 2005, ISBN 3-936326-39-8
- Theodor Gümbel: Geschichte des Fürstentums Pfalz-Veldenz. E. Grusius, Kaiserslautern 1900.
References
[edit]- ^ Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Bernkastel-Wittlich, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 6 August 2021.
- ^ "Bevölkerungsstand 2022, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden" (PDF) (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz. 2023.