Southern France: Difference between revisions
Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
m hatnote |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description| |
{{short description|Geographical area of France}} |
||
{{redirect|South of France|the Future song|South of France (song)}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
|name = Southern France |
|name = Southern France |
||
| Line 6: | Line 7: | ||
|native_name_lang = |
|native_name_lang = |
||
|settlement_type = |
|settlement_type = |
||
|image_skyline = |
|image_skyline = En-Vau calanque 4.jpg |
||
|imagesize = |
|imagesize = |
||
|image_alt = |
|image_alt = |
||
| Line 111: | Line 112: | ||
|footnotes = |
|footnotes = |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Southern France''', also known as the ''' |
'''Southern France''', also known as the '''south of France''' or colloquially in [[French language|French]] as '''{{lang|fr|le Midi}}''',<ref>{{cite book |title=Cycling guide to the Canal du Midi, Languedoc, France, Europe |first=Declan |last=Lyons |isbn=978-1-85284-559-9 |date=18 February 2009 |publisher=Midpoint Trade Books }}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=International French–English and English–French dictionary |first=Paul |last=Passy |isbn=<!-- too early to have one --> |publisher=Hinds, Noble & Eldredge |year=1904 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yKBiAAAAMAAJ&pg=PA388}}</ref> is a defined geographical area consisting of the [[regions of France]] that border the [[Atlantic Ocean]] south of the [[Marais Poitevin]],<ref name=a>Louis Papy, ''Le midi atlantique'', Atlas et géographie de la France moderne, Flammarion, Paris, 1984.</ref> [[Spain]], the [[Mediterranean Sea]] and [[Italy]]. It includes southern [[Nouvelle-Aquitaine]] in the west, [[Occitania (administrative region)|Occitanie]] in the centre, the southern parts of [[Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes]] in the northeast, [[Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur]] in the southeast, as well as the island of [[Corsica]] in the southeast. Southern France is generally considered part of [[southern Europe]] because of its association with the Mediterranean Sea. |
||
The term {{lang|fr|Midi}} derives from {{lang|fro|mi}} ('middle') and {{lang|fro|di}} ('day') in [[Old French]], comparable to the term {{lang|it|[[Southern Italy|Mezzogiorno]]}} to indicate |
The term {{lang|fr|Midi}} derives from {{lang|fro|mi}} ('middle') and {{lang|fro|di}} ('day') in [[Old French]], comparable to the term {{lang|it|[[Southern Italy|Mezzogiorno]]}} to indicate southern Italy, {{lang|ro|Miazăzi}} which is a synonym for south in [[Romanian language|Romanian]], or {{lang|es|meridional}} which is a synonym for the south direction in [[Spanish language|Spanish]]. The time of midday was synonymous with south because in France, as in the rest of the [[Northern Hemisphere]] north of the [[Tropic of Cancer]], the sun is in the south at noon. The [[synonymy]] has existed since [[Middle French]] as well; {{lang|frm|meridien}} could refer to both ''midday'' and ''south''. The Midi is considered to start at [[Valence, Drôme|Valence]], hence the saying {{lang|fr|à Valence le Midi commence}} ("At Valence the Midi starts"). |
||
| ⚫ | |||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
The area corresponds in large part to [[Occitania]] (''Occitanie'') in [[southern Europe]], the historical and cultural region in which [[Occitan language|Occitan]] ({{ |
The area corresponds in large part to [[Occitania]] (''Occitanie'') in [[southern Europe]], the historical and cultural region in which [[Occitan language|Occitan]] ({{langx|fr|langue d'oc}}), as distinct from the {{lang|fr|[[langues d'oïl]]}} of northern [[France]], was the predominant language. Despite being part of Occitania, the regions of [[Auvergne (region)|Auvergne]] and [[Limousin]] are not normally considered part of southern France. The largest cities of southern France are [[Marseille]], [[Toulouse]], [[Bordeaux]], [[Nice]] and [[Montpellier]]. The [[Pyrenees]] and [[French Alps]] are also located in the area, in respectively its southwestern and eastern parts. [[Corsica]], which is south of [[Continental France]] and just north of [[Sardinia]], [[Italy]], may also be included. |
||
==Tourism== |
==Tourism== |
||
Notable touristic landmarks include the Roman-era [[Pont du Gard]] and [[Arena of Nîmes]] |
Notable touristic landmarks include the [[Roman Empire|Roman]]-era [[Pont du Gard]] and the [[Arena of Nîmes]]; the [[Verdon Gorge]], in [[Alpes-de-Haute-Provence]]; the [[Canal du Midi]], linking Toulouse by to the [[Mediterranean Sea]]; and the natural regions of [[Larzac]], [[Luberon]] and [[Camargue]]. The [[French Riviera]] is in southern France's southeastern quadrant. Several towns in southern France are renowned for their architecture and surroundings, such as [[Roussillon, Vaucluse|Roussillon]], [[Ménerbes]], [[Cordes-sur-Ciel]], [[Gordes]], [[Rocamadour]], [[Rennes-le-Château]], [[Les Baux-de-Provence]], [[Lourmarin]], [[Gassin]], [[Saint-Paul-de-Vence]], [[L'Isle-sur-la-Sorgue]], [[Seillans]], [[Crillon-le-Brave]] and [[Saint-Rémy-de-Provence]]. |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery mode="packed" heights="140px"> |
||
Nizza-overview-4070938-PanoPS.jpg|[[Nice]] is often considered to be |
Nizza-overview-4070938-PanoPS.jpg|[[Nice]] is often considered abroad to be southern France's best-known city although [[Marseille]] is the largest. |
||
Road-view at Sainte-Maxim with very old pinetrees. Lovely - panoramio.jpg|Coastal road near [[Sainte-Maxime]] |
Road-view at Sainte-Maxim with very old pinetrees. Lovely - panoramio.jpg|Coastal road near [[Sainte-Maxime]] |
||
Champ de lavande,France.jpg|Lavender fields |
Champ de lavande,France.jpg|Lavender fields, a well-known feature of southern France, are mainly in [[Provence]]. |
||
Pont du Gard 001.jpg|[[Pont du Gard]], a [[UNESCO]] World Heritage Site |
Pont du Gard 001.jpg|[[Pont du Gard]], a [[UNESCO]] World Heritage Site |
||
Terroir Vacqueyras.jpg| |
Terroir Vacqueyras.jpg|View of [[Vaucluse]] vineyards producing [[Provence wine]] |
||
LescunVueVersPasDAzuns.jpg|Traditional landscape of the historical province of [[Béarn]], in |
LescunVueVersPasDAzuns.jpg|Traditional landscape of the historical province of [[Béarn]], in [[Pyrénées-Atlantiques]] |
||
Fontaine de Vaucluse 03.jpg|Village of [[Fontaine-de-Vaucluse]] near [[Avignon]] |
Fontaine de Vaucluse 03.jpg|Village of [[Fontaine-de-Vaucluse]], near [[Avignon]] |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
==Cuisine== |
==Cuisine== |
||
Southern France |
Southern France has a cuisine that is different from those of northern France and other Mediterranean countries. The major difference from the rest of France is in the use of olive oil, instead of butter. Local agriculture supplies the olives for consumption as well as cooking, the ducks and geese to make [[foie gras]], [[haricot beans]] that are used in [[cassoulet]], the sheep whose milk produces [[Roquefort]] cheese, tomatoes and melons. To accompany the richer food, the area also supplies much stronger wines, from [[Bordeaux wine regions|Bordeaux]], [[Cahors wine|Cahors]], [[Madiran wine|Madiran]], and [[Languedoc-Roussillon wine|Languedoc]], all of which are washed down with [[brandy]] from [[Armagnac]].<ref>{{cite book|first=Colin Duncan|last=Taylor|title=Menu from the Midi: A Gastronomic Journey through the South of France|year=2021|publisher=Matador |language=English| isbn= 978-1800464964}}</ref> |
||
==Films== |
==Films== |
||
The following films are set in |
The following films are set in southern France: |
||
{{ |
{{Columns-list|colwidth=17em| |
||
* ''[[To Catch a Thief]]'' (1955) |
* ''[[To Catch a Thief]]'' (1955) |
||
* ''[[Summer Holiday (1963 film)|Summer Holiday]]'' (1963) |
* ''[[Summer Holiday (1963 film)|Summer Holiday]]'' (1963) |
||
| Line 159: | Line 160: | ||
* ''[[Amer (film)|Amer]]'' (2009) |
* ''[[Amer (film)|Amer]]'' (2009) |
||
* ''[[Magic in the Moonlight]]'' (2014) |
* ''[[Magic in the Moonlight]]'' (2014) |
||
* ''[[Johnny English Strikes Again]]'' (2018) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
{{Div col|colwidth=15em}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*[[ |
* [[Béarn]] |
||
*[[ |
* [[Corsica]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[French Riviera]] |
||
* [[Gascony]] |
|||
* [[Mediterranean Sea]] |
* [[Mediterranean Sea]] |
||
* [[Northern Basque Country]] |
|||
* [[Northern Catalonia]] |
* [[Northern Catalonia]] |
||
* [[Novempopulania]] |
* [[Novempopulania]] |
||
* [[ |
* [[Occitania]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Southern Europe]] |
* [[Southern Europe]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
* [[Vichy France]] |
* [[Vichy France]] |
||
{{Div col end}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 179: | Line 184: | ||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
[[Category:Southern France| ]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[Category:Geography of France]] |
[[Category:Geography of France]] |
||
[[Category:Geography of |
[[Category:Geography of Europe]] |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Latest revision as of 20:48, 30 November 2024
Southern France
| |
|---|---|
 | |
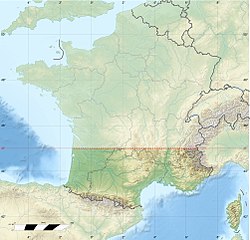 Southern France, based on a split along the 45th parallel | |
| Country | France |
Southern France, also known as the south of France or colloquially in French as le Midi,[1][2] is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,[3] Spain, the Mediterranean Sea and Italy. It includes southern Nouvelle-Aquitaine in the west, Occitanie in the centre, the southern parts of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes in the northeast, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur in the southeast, as well as the island of Corsica in the southeast. Southern France is generally considered part of southern Europe because of its association with the Mediterranean Sea.
The term Midi derives from mi ('middle') and di ('day') in Old French, comparable to the term Mezzogiorno to indicate southern Italy, Miazăzi which is a synonym for south in Romanian, or meridional which is a synonym for the south direction in Spanish. The time of midday was synonymous with south because in France, as in the rest of the Northern Hemisphere north of the Tropic of Cancer, the sun is in the south at noon. The synonymy has existed since Middle French as well; meridien could refer to both midday and south. The Midi is considered to start at Valence, hence the saying à Valence le Midi commence ("At Valence the Midi starts").
Geography
[edit]The area corresponds in large part to Occitania (Occitanie) in southern Europe, the historical and cultural region in which Occitan (French: langue d'oc), as distinct from the langues d'oïl of northern France, was the predominant language. Despite being part of Occitania, the regions of Auvergne and Limousin are not normally considered part of southern France. The largest cities of southern France are Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Nice and Montpellier. The Pyrenees and French Alps are also located in the area, in respectively its southwestern and eastern parts. Corsica, which is south of Continental France and just north of Sardinia, Italy, may also be included.
Tourism
[edit]Notable touristic landmarks include the Roman-era Pont du Gard and the Arena of Nîmes; the Verdon Gorge, in Alpes-de-Haute-Provence; the Canal du Midi, linking Toulouse by to the Mediterranean Sea; and the natural regions of Larzac, Luberon and Camargue. The French Riviera is in southern France's southeastern quadrant. Several towns in southern France are renowned for their architecture and surroundings, such as Roussillon, Ménerbes, Cordes-sur-Ciel, Gordes, Rocamadour, Rennes-le-Château, Les Baux-de-Provence, Lourmarin, Gassin, Saint-Paul-de-Vence, L'Isle-sur-la-Sorgue, Seillans, Crillon-le-Brave and Saint-Rémy-de-Provence.
-
Coastal road near Sainte-Maxime
-
Lavender fields, a well-known feature of southern France, are mainly in Provence.
-
Pont du Gard, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
-
View of Vaucluse vineyards producing Provence wine
-
Traditional landscape of the historical province of Béarn, in Pyrénées-Atlantiques
-
Village of Fontaine-de-Vaucluse, near Avignon
Cuisine
[edit]Southern France has a cuisine that is different from those of northern France and other Mediterranean countries. The major difference from the rest of France is in the use of olive oil, instead of butter. Local agriculture supplies the olives for consumption as well as cooking, the ducks and geese to make foie gras, haricot beans that are used in cassoulet, the sheep whose milk produces Roquefort cheese, tomatoes and melons. To accompany the richer food, the area also supplies much stronger wines, from Bordeaux, Cahors, Madiran, and Languedoc, all of which are washed down with brandy from Armagnac.[4]
Films
[edit]The following films are set in southern France:
- To Catch a Thief (1955)
- Summer Holiday (1963)
- Pierrot le Fou (1965)
- Lacombe, Lucien (1974)
- French Connection II (1975)
- Never Say Never Again (1983)
- Under the Cherry Moon (1986)
- Jean de Florette (1986)
- Manon des Sources (1986)
- Dirty Rotten Scoundrels (1988)
- Happiness Is in the Field (1995)
- Taxi (1998)
- Chocolat (2000)
- The Transporter (2002)
- Swimming Pool (2003)
- Le Grand Voyage (2004)
- Priceless (2006)
- The Grocer's Son (2007)
- Mr. Bean's Holiday (2007)
- Amer (2009)
- Magic in the Moonlight (2014)
- Johnny English Strikes Again (2018)
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Lyons, Declan (18 February 2009). Cycling guide to the Canal du Midi, Languedoc, France, Europe. Midpoint Trade Books. ISBN 978-1-85284-559-9.
- ^ Passy, Paul (1904). International French–English and English–French dictionary. Hinds, Noble & Eldredge.
- ^ Louis Papy, Le midi atlantique, Atlas et géographie de la France moderne, Flammarion, Paris, 1984.
- ^ Taylor, Colin Duncan (2021). Menu from the Midi: A Gastronomic Journey through the South of France. Matador. ISBN 978-1800464964.







