Islam in American Samoa: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
Hydrangeans (talk | contribs) Added navigation box per bidirectionality guideline |
||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox dependency |
|||
{{Islam by country}} |
|||
| name = American Samoa |
|||
| native_name = ''Amerika Sāmoa'' |
|||
| settlement_type = [[Unincorporated territories of the United States|Unincorporated and unorganized U.S. territory]] |
|||
| image_flag = Flag of American Samoa.svg |
|||
| flag_size = 125px |
|||
| flag_link = Flag of American Samoa |
|||
| image_seal = Seal of American Samoa.svg |
|||
| seal_size = 85px |
|||
| seal_type = Seal |
|||
| seal_link = Seal of American Samoa |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Infobox demographics |
{{Infobox demographics |
||
| type = Religious population of American Samoa |
| type = Religious population of American Samoa |
||
| group1 = Islam |
| group1 = Islam |
||
| percent1 = |
| percent1 = 1.3% |
||
| group2 = Christianity |
| group2 = Christianity |
||
| percent2 = |
| percent2 = 96.9% |
||
| group3 = - Protestant |
| group3 = - Protestant |
||
| percent3 = |
| percent3 = 41.7% |
||
| group4 = - Catholic |
| group4 = - Catholic |
||
| percent4 = 27.3% |
| percent4 = 27.3% |
||
| Line 18: | Line 29: | ||
| group8 = Other |
| group8 = Other |
||
| percent8 = 1.17%% |
| percent8 = 1.17%% |
||
| source = <ref |
| source = <ref name="Association of Religion Data Archives">{{cite web |author1=Association of Religion Data Archives |title=American Samoa |url=https://www.thearda.com/internationalData/countries/Country_5_1.asp |date=2020}}</ref> |
||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:NPS american-samoa-map.pdf|thumb|American Samoa map]] |
|||
'''[[American Samoa]]''' is an unincorporated [[Territories of the United States|territory of the United States]], located [[Oceania|South East of Samoa]] and consisting of seven main islands.<ref name="South Pacific">{{cite book |last1=Stanley |first1=David |title=South Pacific |date=2004 |publisher=Moon Handbooks}}</ref> American Samoa is a predominantly [[Christianity|Christian]] nation, identifying as a region founded by God, however, has become more religiously diverse since the mid-20th century.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Bouma, G |author2=Ling, R |author3=Pratt, D |title=Samoa |journal=Religious Diversity in Southeast Asia and the Pacific |date=2010 |doi=10.1007/978-90-481-3389-5_23 |publisher=Springer Netherlands}}</ref> The religion of [[Islam]] was first brought to American Samoa in the mid-1980s by [[Muslims|Muslim]] expatriate workers from government programs.<ref name="History of Islam in Samoa">{{cite web |last1=Terdiman |first1=Moshe |title=History of Islam in Samoa |url=https://www.samoaobserver.ws/category/article/21695 |date=2011}}</ref> The region received their first native convert in 1985, although Muslim adherents still remain a minority in American Samoan society today.<ref name="History of Islam in Samoa"/> While the population is small, the spread of Islam has been a significant part of the Island’s history. |
|||
Claiming that as result of increased terrorist activities globally in the early 2000s, specifically [[2002 Bali bombings|the Bali bombing]], the government imposed a strict ban on residents of 23 nations from entering their territory without explicit permission from the island’s attorney general’s office.<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald">{{cite web |author1=Sydney Morning Herald |title=American Samoa bans nations from 23 countries |url=https://www.smh.com.au/world/american-samoa-bans-nationals-from-23-countries-20021224-gdg0hq.html |date=2002}}</ref> Most of the countries banned were either located in the [[Middle East]] and identified as Muslim nations, or were home to a large number of Muslim adherents.<ref name="South Pacific" /> The ban has received opposition from human rights groups along with those on the list as well as neighboring islands, mainly over issues of religious freedom.<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald"/> |
|||
The religion still influences life in American Samoa, with the establishment of public education and health groups as well as a range of community activities by native converts and Muslim organizations with the aim of teaching the natives about Islam.<ref name="Syd morning herald" /> |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
Ofu Beach American Samoa US National Park Service.jpg|Ofu Beach in American Samoa |
|||
NPS american-samoa-map.pdf|American Samoa map |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
==American Samoan religious background== |
==American Samoan religious background== |
||
[[File:PopulationAmericanSamoa.jpg|thumb|Religious population of American Samos 2015<ref name="Association of Religion Data Archives"/>]] |
|||
A large majority of pacific islanders are Christians as the Christian belief was welcomed in the mid 20th century and has been deeply entrenched in the Pacific since. <ref> Barker, J. (1996). Winds of Change: Rapidly Growing Religious Groups in the Pacific Islands (Book Review) [Review of Winds of Change: Rapidly Growing Religious Groups in the Pacific Islands (Book Review)]. The Contemporary Pacific, 8(1), 234–236. Centre for Pacific Islands studies & University of HawaI’I press.</ref> |
|||
The [[Assemblies of God]], [[Pentecostalism|Pentecostal]] a group of the [[Protestantism|protestant church]] who first arrived in American Samoa in 1926. <ref> Encyclopedia.com (2020, November 21). Oceanic Religions: Missionary Movement. Retrieved from https://www.encyclopedia.com/ </ref> |
|||
The majority of Christians in American Samoa remain Protestants, with 42.7% of the population, however there is a large [[Catholic Church|Catholic]] population with 22.6%. <ref> Association of Religion Data Archives, 2020. American Samoa. Retrieved from https://www.thearda.com/internationalData/countries/Country_5_1.asp</ref> |
|||
The spread of Christianity to the South Pacific brought about a number of social programs including the acquisition of literacy to many communities and has had a substantial intellectual impact on the South Pacific. <ref> Encyclopedia.com (2020, November 21). Oceanic Religions: Missionary Movement. Retrieved from https://www.encyclopedia.com/ </ref> |
|||
Although Islam was brought to the region more recently, it has similarly impacted the social and cultural lives of much of the South Pacific. [[Islamic missionary activity|Muslim missionary work]] has been conducted in the South Pacific since the 1970s and has resulted in a “small but steady stream of local converts”. <ref> Esposito, J. (2003). Pacific Region, Islam in. In The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-1802 </ref> The first convert to Islam, was in 1985 in the neighbouring [[Samoa|Western Samoa ]], a result of Muslim expats from overseas sharing their beliefs with the local people. <ref> Terdiman, M. (2011, November). History of Islam in Samoa. Retrieved from https://www.samoaobserver.ws/ </ref> It is believed that this religious influence spread to American Samoa as the territory recorded a dozen adherents a decade later in the 1990s. <ref> Kettani, H. (2010). Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301613_Muslim_Population_in_Oceania_1950_-_2020 </ref> |
|||
===Background as a Christian nation=== |
|||
In a number of the larger South Pacific states, Muslims are supported by regional bodies and organisations including the [[Fiji Muslim League]] and the Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific (RISEAP), which formed in 1980 and aimed to coordinate their Islamic missionary activities, “training individuals for Islamic social work” and establishing mosques and Islamic centres around the South Pacific. <ref> Esposito, J. (2003). Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific. In The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-1997 </ref> |
|||
A large majority of pacific islanders are Christians as the Christian belief was welcomed into the region in the mid 20th century and has been deeply entrenched in the Pacific since.<ref>Barker, J. (1996). Winds of Change: Rapidly Growing Religious Groups in the Pacific Islands (Book Review) [Review of Winds of Change: Rapidly Growing Religious Groups in the Pacific Islands (Book Review)]. The Contemporary Pacific, 8(1), 234–236. Centre for Pacific Islands studies & University of HawaI’I press.</ref> The [[Assemblies of God]], a [[Pentecostalism|Pentecostal]] community within the [[Protestantism|Protestant tradition]], are an example of this early influence, having first arrived in American Samoa in 1926.<ref name="Missonary Movement">{{cite web |author1=Encyclopedia.com |title=Oceanic Religions: Missionary Movement |url=https://www.encyclopedia.com/environment/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/oceanic-religions-missionary-movements |date=2002}}</ref> The majority of Christians in American Samoa remain Protestants, encompassing 42.7% of the total population, however there is also large [[Catholic Church|Catholic]] population with 22.6%.<ref name="Association of Religion Data Archives"/> The spread of Christianity to the South Pacific brought about a number of social programs including the acquisition of literacy to many communities and has had a substantial intellectual impact on the South Pacific.<ref name="Missonary Movement"/> |
|||
American Samoa is not presently a member of the RISEAP, however the organisation partners with neighbouring countries such as [[Islam in Fiji|Fiji]] and [[Religion in Samoa|Samoa]]. <ref> Esposito, J. (2003). Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific. In The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-1997 </ref> |
|||
==The |
===The spread of Islam=== |
||
Although Islam arrived in the region more recently, it has similarly impacted the social and cultural lives of many people in the South Pacific. [[Dawah]] is an [[Arabic]] word traditionally meaning to invite individuals and communities to come "back to God", however in the 20th century it has become the foundation for a number of social, political and cultural activities worldwide.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Oxford Islamic Studies Online |title=Dawah |journal=The Oxford Dictionary of Islam |date=2020 |url=http://www.oxfordislamicstudies.com/article/opr/t125/e511|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131204162659/http://www.oxfordislamicstudies.com/article/opr/t125/e511|url-status=dead|archive-date=December 4, 2013}}</ref> The growing globalisation of the world has also “facilitated interest in religious alternatives” such as Islam in many South Pacific nations including American Samoa.<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Scott Flower |title=Conversion to Islam in Papua New Guinea: Preserving Traditional Culture against Modernity’s Cargo-Cult Mentality |journal=The Journal of Alternative and Emergent Religions |date=2015 |volume=18 |pages=55–82 |publisher=University of California Press}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:PopulationAmericanSamoa.jpg|thumb|Religious population of American Samos 2015<ref>Association of Religion Data Archives, 2020. American Samoa. Retrieved from https://www.thearda.com/internationalData/countries/Country_5_1.asp</ref>]] |
|||
[[Islamic missionary activity]] has been conducted in the South Pacific since the 1970s and has resulted in a “small but steady stream of local converts” due to the conditions of an increasingly globalised world.<ref name="Islam in Pacific Region">{{cite journal |last1=Esposito |first1=John |title=Pacific Region, Islam in |journal=The Oxford Dictionary of Islam |date=2003 |url=http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-1802 |publisher=Oxford University Press}}</ref> The first convert joined Islam in 1985 in neighboring [[Samoa|Western Samoa]], as a result of Muslim immigrants from abroad sharing their beliefs with the local people.<ref name="History of Islam in Samoa" /> It is believed that this religious influence spread to American Samoa as the territory recorded a dozen adherents a decade later in the 1990s.<ref name="Muslim population in Oceania">{{cite web |last1=Kettani |first1=Houssain |title=Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020 |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301613_Muslim_Population_in_Oceania_1950_-_2020 |date=2010}}</ref> |
|||
[[File:Total Muslim adherents.png|thumb|Total Muslim adherents in American Samoa 1990-2020<ref>Kettani, H. (2010). Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301613_Muslim_Population_in_Oceania_1950_-_2020</ref>]] |
|||
In a number of the larger South Pacific states, Muslims are supported by regional bodies and organisations including the [[Fiji Muslim League]] and the Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific (RISEAP), which formed in 1980 and aimed to coordinate their Islamic missionary activities, “training individuals for Islamic social work” and establishing mosques and Islamic centres around the South Pacific.<ref name="RISEAP">{{cite journal |last1=Esposito |first1=John |title=Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific |journal=The Oxford Dictionary of Islam |date=2003 |url=http://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195125580.001.0001/acref-9780195125580-e-1997 |publisher=Oxford University Press}}</ref> American Samoa is not presently a member of the RISEAP, however the organisation partners with neighbouring countries such as [[Islam in Fiji|Fiji]] and [[Religion in Samoa|Samoa]].<ref name="RISEAP" /> The first President of RISEAP, Tunku Abdul Rahman, stated their mission to encourage Muslims to continue their religious pursuits in the Pacific nations where they are minorities.<ref>{{cite web |title=RISEAP |url=https://riseap.org/ |website=RISEAP |date=2020}}</ref> The Pacific Island countries are traditionally “collectivity-oriented” and have similar customs and practices to some religious groupings.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Yabaki |first1=Rev Akulia |title=The Impact of Tradition and Religion on Women’s Lives in the South Pacific |journal=Pacific Women's Bureau |date=2004}}</ref> Muslims in the South Pacific have been involved in educating activities, engaging with the communities and instructing people in Islam.<ref name="Syd morning herald">{{cite web |author1=Sydney Morning Herald |title=Heeding the call to prayer in a region that reveres the pig |url=https://www.smh.com.au/world/heeding-the-call-to-prayer-in-a-region-that-reveres-the-pig-20070908-gdr29k.html |date=2007}}</ref> This influence has seen the creation of the Islamic Institute of the South Pacific in Fiji. Islam is also often associated with the establishment of social and public health organisations in the region.<ref name="Syd morning herald" /> |
|||
It is estimated that there are about half a million Muslims in Oceania, equating to about 1.4% of the total population of the continent. .<ref>Kettani, H. (2010). Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301613_Muslim_Population_in_Oceania_1950_-_2020</ref> Within the Asia-Pacific Muslim population, it is estimated that about 12-15% of adherents are [[Shia Islam|Shia]], the majority instead adhering to the [[Sunni Islam|Sunni]] denomination of Islam.<ref>Pew Research Centre (2009, October 7). Mapping the global Muslim population. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/</ref> The islands are dominated by the Christian faith, with 98.3% of the population being Christian adherents.<ref>Kettani, H. (2010). Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301613_Muslim_Population_in_Oceania_1950_-_2020</ref> However, it is estimated that 0.03% of the American Samoan population are Muslim adherents, the population almost doubling between the years 1990 to 2020 from 12 to 23 adherents. <ref>Kettani, H. (2010). Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271301613_Muslim_Population_in_Oceania_1950_-_2020</ref> |
|||
==The Muslim population== |
|||
A study of where American Samoan residents were born showed that 6.3% of the population migrated from the United States, a nation with over 3.45 million Muslims in 2017. <ref>Mohamed, B. (2018, January 3). New estimates show U.S. Muslim population continues to grow. Retrieved from https://www.pewresearch.org/</ref> The religious diversity of this nation is an influencing factor on the American Samoan Muslim population. <ref> American Samoa Department of Commerce & the Office of Insular Affairs, U. S. Department of the Interior. (2006, January). Population and housing in American Samoa. Retrieved from https://pacificweb.org/DOCS/amsamoa/ASMonograph/2006ASMono.pdf</ref> |
|||
[[File:Total Muslim adherents.png|thumb|Total Muslim adherents in American Samoa 1990-2020 <ref name="Muslim population in Oceania"/>]] |
|||
It is estimated that there are about half a million Muslims in Oceania, equating to about 1.4% of the total population of the continent.<ref name="Muslim population in Oceania"/> Within the Asia-Pacific Muslim population, it is estimated that about 12-15% of adherents are [[Shia Islam|Shia]], the majority instead adhering to the [[Sunni Islam|Sunni]] denomination of Islam.<ref name="Mapping the global">{{cite web |author1=Pew Research Centre |title=Mapping the global Muslim population |url=https://www.pewforum.org/2009/10/07/mapping-the-global-muslim-population/ |date=2009}}</ref> The islands are dominated by the Christian faith, with 98.3% of the population being Christian adherents.<ref name="Muslim population in Oceania"/> However, it is estimated that 0.03% of the American Samoan population are Muslim adherents, the population almost doubling between the years 1990 to 2020 from 12 to 23 adherents.<ref name="Muslim population in Oceania"/> |
|||
A study of where American Samoan residents were born showed that 6.3% of the population [[Islam in the United States|migrated from the United States]], a nation with over 3.45 million Muslims in 2017.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Mohamed |first1=Besheer |title=New estimates show U.S. Muslim population continues to grow |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2018/01/03/new-estimates-show-u-s-muslim-population-continues-to-grow/ |date=2018}}</ref> The religious diversity of this nation is an influencing factor on the American Samoan Muslim population.<ref>{{cite web |author1=American Samoa Department of Commerce |author2=U. S. Department of the Interior |title=Population and housing in American Samoa |url=https://pacificweb.org/DOCS/amsamoa/ASMonograph/2006ASMono.pdf |date=2006}}</ref> |
|||
==The 2002 ban== |
==The 2002 ban== |
||
[[File:GovSunia.jpg|thumb|Tauese Fiti Sunia - 56th Governor of American Samoa (1997-2003)]] |
|||
In December 2002, action was taken to ban nationals from 23 countries from entering American Samoa without explicit approval from Fiti Sunia, the territory’s attorney general’s office.<ref>Sydney Moring Herald (2002, December 24). American Samoa bans nations from 23 countries. Retrieved from https://www.smh.com.au/</ref> Those banned from American Samoa were mainly Arab nations, including a number in the middle east.<ref>Sydney Moring Herald (2002, December 24). American Samoa bans nations from 23 countries. Retrieved from https://www.smh.com.au/</ref> As a part of this regulation, any visitor to the islands with a Middle Eastern appearance or Muslim sounding name received thorough examination before arrival and could be refused entry altogether.<ref>Stanley, D. (2004). Moon Handbooks South Pacific (8th Edition). Retrieved from https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_EDGapfBX-CAC/mode/2up</ref> |
|||
[[File:AmericanSamoaLegislatureBuilding.jpg|thumb|American Samoa Legislature Building]] |
|||
In December 2002, action was taken to ban nationals from 23 countries from entering American Samoa without explicit approval from Fiti Sunia, the territory’s attorney general’s office.<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald"/> Those banned from American Samoa were mainly Arab nations, including a number in the [[Middle East]].<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald" /> As a part of this regulation, any visitor to the islands with a Middle Eastern appearance or Muslim sounding name received thorough examination before arrival and could be refused entry altogether. |
|||
<ref name="South Pacific"/> |
|||
This decision was |
This decision was enforced after Governor Tauese Sunia claimed that a credible security threat was made, speculating that American Samoa could be targeted for terrorist activities because of its status as a US territory.<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald"/> The action to ban these nations was put in place because officials claimed they did not have the supplies to manage and enforce “anything less sweeping and make it effective”.<ref>{{cite web |publisher=Pacific Business News |title=American Samoa, banning Muslims, bans Fijians |url=https://www.bizjournals.com/pacific/stories/2002/12/23/daily7.html |date=23 December 2002 |access-date=8 February 2023}}</ref> |
||
It is widely believed that this sweeping action by American Samoan officials was prompted by the Bali bombing, an explosion which killed 202 people, |
It is widely believed that this sweeping action by American Samoan officials was prompted by the Bali bombing, an explosion which killed 202 people, organized and carried out by a terrorist organisation named Jemaah Islamiya and occurring two months prior to the decision in October 2002.<ref>{{cite web |author1=National Museum Australia |title=Bali bombings |url=https://www.nma.gov.au/defining-moments/resources/bali-bombings |date=2002}}</ref> According to members who coordinated the attack, Bali was chosen because it was often frequented by American citizens, thus it was believed that the American Samoan status as a US territory linked the nation to further retaliation from extremists.<ref>{{cite web |author1=BBC |title=The 12 October 2002 Bali bombing plot |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-19881138#:~:text=Two%20bombs%20ripped%20through%20the,38%20Indonesians%20and%2028%20Britons. |date=2012}}</ref> The widespread ban of several Muslim nations was therefore claimed to have been implemented for the safety of the citizens.<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald" /> However, the scale of the ban has led to some drawing comparisons to US President [[Donald Trump]]’s threat to impose bans on Muslims entering the United States at an election rally in December 2015.<ref name="Want to ban Islam">{{cite web |last1=Samuels |first1=Gabriel |title=The Pacific islanders who want to ban Islam |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/australasia/church-leader-calls-islam-ban-samoa-constitution-review-gathers-pace-a7046366.html |date=2016}}</ref> |
||
Furthermore, members of the [[Islamic Human Rights Commission]] |
Furthermore, members of the [[Islamic Human Rights Commission]] have claimed that the closing of the island’s American consulate was prompted by a terrorist alert, in which two “unidentified men of ‘middle eastern appearance’” were taking photos of the consulate, although these claims have not been officially confirmed.<ref name="IHRC">{{cite web |author1=Islamic Human Rights Commission |title=Bannings and Deportations in the Pacific: racial and religious profiling in Fiji and American Samoa |url=https://www.ihrc.org.uk/publications/briefings/7221-briefing-bannings-and-deportations-in-the-pacific-racial-and-religious-profiling-in-fiji-and-american-samoa/ |date=2003}}</ref><ref name="South Pacific"/> |
||
===The countries banned=== |
===The countries banned=== |
||
{{columns-list |colwidth=15em| |
|||
{{Columns |
|||
* {{flag|Afghanistan}} |
|||
|col1= |
|||
* {{flag|Algeria}} |
|||
*Afghanistan |
|||
* {{flag|Bahrain}} |
|||
*Algeria |
|||
* {{flag|Cuba}} |
|||
*Bahrain |
|||
* {{flag|Fiji}} (until 2003) |
|||
*Cuba |
|||
* {{flag|Indonesia}} |
|||
*Fiji |
|||
* {{flag|Iran}} |
|||
*Indonesia |
|||
* {{flag|Iraq}} |
|||
*Iran |
|||
*Iraq |
|||
* {{flag|Libya}} |
|||
|col2= |
|||
* {{flag|Morocco}} |
|||
*Lebanon |
|||
* {{flag|North Korea}} |
|||
*Libya |
|||
* {{flag|Oman}} |
|||
*Morocco |
|||
* {{flag|Pakistan}} |
|||
*North Korea |
|||
* {{flag|Philippines}} |
|||
*Oman |
|||
* {{flag|Qatar}} |
|||
*Pakistan |
|||
* {{flag|Saudi Arabia}} |
|||
*Philippines |
|||
* {{flag|Somalia}} |
|||
*Qatar |
|||
* {{flag|Sudan}} |
|||
|col3= |
|||
* {{flag|Syria}} |
|||
*Saudi Arabia |
|||
* {{flag|Tunisia}} |
|||
*Somalia |
|||
* {{flag|United Arab Emirates}} |
|||
*Sudan |
|||
* {{flag|Yemen}}<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald"/> |
|||
*Syria |
|||
*Tunisia |
|||
*United Arab Emirates |
|||
*Yemen<ref>Sydney Moring Herald (2002, December 24). American Samoa bans nations from 23 countries. Retrieved from https://www.smh.com.au/</ref> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The ban included the island of [[Islam in Fiji|Fiji]], the only other |
The ban included the island of [[Islam in Fiji|Fiji]], the only other Pacific Island on the list. Their addition was linked to the nation's large Muslim population, with approximately 80,000 adherents on the island.<ref name="Sydney Morning Herald" /> The extension of the ban to other South Pacific nations was justified as some Fijian Muslim adherents have travelled to and studied at Islamic institutions in typically Muslim countries.<ref name="IHRC"/> However, after strong protest from Fijians as well as oppositional media coverage across the territory, the island was removed from the list in early 2003.<ref name="South Pacific"/> |
||
==Reaction to the 2002 ban== |
==Reaction to the 2002 ban== |
||
===Support for the ban=== |
===Support for the ban=== |
||
In the early 2000s, there was a fear of a spread of [[Islamic extremism|radical Islam]] to American Samoa, and the potential for an outbreak of religious wars globally.<ref |
In the early 2000s, there was a fear of a spread of [[Islamic extremism|radical Islam]] to American Samoa, and the potential for an outbreak of religious wars globally.<ref name="Samoa Officially Becomes a Christian State">{{cite web |last1=Wyeth |first1=Grant |title=Samoa Officially Becomes a Christian State |url=https://thediplomat.com/2017/06/samoa-officially-becomes-a-christian-state/ |date=2016}}</ref> |
||
The risk of terrorism has remained a concern of the South Pacific, the regional body, the [[Pacific Islands Forum]], holding a conference to examine legislative reform, directly targeting terrorism in 2003. |
The risk of terrorism has remained a concern of the South Pacific, the regional body, the [[Pacific Islands Forum]], holding a conference to examine legislative reform, directly targeting terrorism in 2003.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Panichi |first1=James |title=Muslim cleric expelled from Fiji |url=https://www.abc.net.au/worldtoday/stories/s793452.htm |date=2003}}</ref> After the terrorist attacks in Bali, the [[Australian Strategic Policy Institute]] released a policy review identifying the increased threat of terrorism in South Pacific nations such as American Samoa.<ref name="Security Challenges">{{cite web |author1=Foreign Affairs, Defence and Trade References Committee |title=Security challenges facing Papua New Guinea and the island states of the southwest Pacific |url=https://www.aph.gov.au/Parliamentary_Business/Committees/Senate/Foreign%20Affairs%20Defence%20and%20Trade/Completed%20inquiries/2008-10/swpacific/report2/index |date=2010}}</ref> |
||
The review suggested a number of states were susceptible to terrorist activities and could be “potential havens for terrorist groups” and Islamic extremism, particularly due to their close proximity to Australia and connection as a territory of the United States. |
The review suggested a number of states were susceptible to terrorist activities and could be “potential havens for terrorist groups” and Islamic extremism, particularly due to their close proximity to Australia and connection as a territory of the United States.<ref name="Security Challenges"/> However, the threat level posed in the Pacific is still “recognised as low”.<ref name="Security Challenges"/> |
||
Samoan Prime Minister Tuilaepa Malielegaoi advocated the duty of the government in legislating to avoid such religious tensions through means such as the ban instated by American Samoan officials. |
Samoan Prime Minister Tuilaepa Malielegaoi advocated the duty of the government in legislating to avoid such religious tensions through means such as the ban instated by American Samoan officials.<ref name="Samoa Officially Becomes a Christian State"/> Furthermore, Mohammed Daniel Stanley, an American Samoan convert to Islam, came out in support of Sunia’s decision.<ref name="History of Islam in Samoa" /> |
||
This ban was also supported by a number of neighbouring South Pacific actors including the secretary general of the Samoa Council of Churches, who called for the nation of Samoa to “bring in a blanket ban on Islam”.<ref |
This ban was also supported by a number of neighbouring South Pacific actors including the secretary general of the Samoa Council of Churches, who called for the nation of Samoa to “bring in a blanket ban on Islam”.<ref name="Want to ban Islam"/> Samoan Reverend Motu similarly claimed that Islam posed a threat to the future of his country, pressing the Samoan government to entirely prohibit the religion on the island.<ref name="Want to ban Islam"/> |
||
===Opposition to the ban=== |
===Opposition to the ban=== |
||
The actions of American Samoa were officially condemned by the Islamic Human Rights Commission, claiming the ban violates international law and calling for the government to rescind the ban and issue a formal apology to individuals affected.<ref |
The actions of American Samoa were officially condemned by the Islamic Human Rights Commission, claiming the ban violates international law and calling for the government to rescind the ban and issue a formal apology to individuals affected.<ref name="IHRC"/> No known action has been made toward rescinding the bans as of November 2020. |
||
==Restrictions on religious freedom== |
==Restrictions on religious freedom== |
||
Particularly after the 2002 ban of a number of Muslim nations from American Samoa, a number of sources started questioning issues to do with [[freedom of religion|religious freedom]]. |
Particularly after the 2002 ban of a number of Muslim nations from American Samoa, a number of sources started questioning issues to do with [[freedom of religion|religious freedom]].<ref>{{cite web |author1=[[RNZ]] |title=American Samoa restates freedom of religion amid scientology campaign |url=https://www.rnz.co.nz/international/pacific-news/175945/american-samoa-restates-freedom-of-religion-amid-scientology-campaign#:~:text=American%20Samoa%20restates%20freedom%20of%20religion%20amid%20scientology%20campaign,-3%3A26%20pm&text=The%20American%20Samoan%20governor%2C%20Togiola,display%20of%20Scientology%20Church%20billboards.&text=He%20said%20this%20is%20the,movie%20the%20Da%20Vinci%20Code%20. |date=2008}}</ref> In the South Pacific countries, the average scores of laws and policies used to restrict religious freedom as well as government favouritism shown towards religious groups increased over 20% in the decade between 2007 and 2017.<ref name="A closer look">{{cite web |author1=Pew Research Centre |title=A closer look at how religious restrictions have arisen around the world |url=https://www.pewforum.org/2019/07/15/a-closer-look-at-how-religious-restrictions-have-risen-around-the-world/ |date=2019}}</ref> The region is relatively high in this category, measuring 5.0 compared with the global average of 4.7.<ref name="A closer look"/> It was also reported that 86% of countries in the Asia-Pacific region in 2017 reported events of “harassment or intimidation of religious groups by governments” and over half the countries in the region have experienced some type of “communal tension” between religious groupings.<ref name="A closer look"/> |
||
Several Christian groups have also attempted to influence the government and the populace in general to support restricting the practice of Islam in the territory or even ban it outright.<ref name="Want to ban Islam" /> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 109: | Line 121: | ||
* [[Islam in Fiji]] |
* [[Islam in Fiji]] |
||
* [[Territories of the United States]] |
* [[Territories of the United States]] |
||
* [[Islam in Samoa]] |
|||
* [[2002 Bali bombings]] |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
| Line 114: | Line 128: | ||
{{American Samoa}} |
{{American Samoa}} |
||
{{Oceania topic|Islam in}} |
{{Oceania topic|Islam in}}{{Islam in the United States by state/city}} |
||
[[Category:Politics of American Samoa]] |
[[Category:Politics of American Samoa]] |
||
[[Category:Islam in Oceania|American Samoa]] |
[[Category:Islam in Oceania|American Samoa]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Anti-Islam sentiment in Oceania]] |
||
[[Category:2002 in American law]] |
[[Category:2002 in American law]] |
||
[[Category:Fiji–United States relations]] |
[[Category:Fiji–United States relations]] |
||
[[Category:Islam |
[[Category:Islam in insular areas of the United States|American Samoa]] |
||
[[Category:Religion in American Samoa]] |
|||
{{islam-country-stub}} |
|||
{{oceania-stub}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 00:03, 2 December 2024
American Samoa Amerika Sāmoa | |
|---|---|
| Religious population of American Samoa | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Islam | 1.3% | ||
| Christianity | 96.9% | ||
| - Protestant | 41.7% | ||
| - Catholic | 27.3% | ||
| - Pentecostal | 5.3% | ||
| - Other Christian | 22.6% | ||
| Non-religious | 0.9% | ||
| Source: [1] | |||
American Samoa is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located South East of Samoa and consisting of seven main islands.[2] American Samoa is a predominantly Christian nation, identifying as a region founded by God, however, has become more religiously diverse since the mid-20th century.[3] The religion of Islam was first brought to American Samoa in the mid-1980s by Muslim expatriate workers from government programs.[4] The region received their first native convert in 1985, although Muslim adherents still remain a minority in American Samoan society today.[4] While the population is small, the spread of Islam has been a significant part of the Island’s history.
Claiming that as result of increased terrorist activities globally in the early 2000s, specifically the Bali bombing, the government imposed a strict ban on residents of 23 nations from entering their territory without explicit permission from the island’s attorney general’s office.[5] Most of the countries banned were either located in the Middle East and identified as Muslim nations, or were home to a large number of Muslim adherents.[2] The ban has received opposition from human rights groups along with those on the list as well as neighboring islands, mainly over issues of religious freedom.[5]
The religion still influences life in American Samoa, with the establishment of public education and health groups as well as a range of community activities by native converts and Muslim organizations with the aim of teaching the natives about Islam.[6]
American Samoan religious background
[edit]
Background as a Christian nation
[edit]A large majority of pacific islanders are Christians as the Christian belief was welcomed into the region in the mid 20th century and has been deeply entrenched in the Pacific since.[7] The Assemblies of God, a Pentecostal community within the Protestant tradition, are an example of this early influence, having first arrived in American Samoa in 1926.[8] The majority of Christians in American Samoa remain Protestants, encompassing 42.7% of the total population, however there is also large Catholic population with 22.6%.[1] The spread of Christianity to the South Pacific brought about a number of social programs including the acquisition of literacy to many communities and has had a substantial intellectual impact on the South Pacific.[8]
The spread of Islam
[edit]Although Islam arrived in the region more recently, it has similarly impacted the social and cultural lives of many people in the South Pacific. Dawah is an Arabic word traditionally meaning to invite individuals and communities to come "back to God", however in the 20th century it has become the foundation for a number of social, political and cultural activities worldwide.[9] The growing globalisation of the world has also “facilitated interest in religious alternatives” such as Islam in many South Pacific nations including American Samoa.[10]
Islamic missionary activity has been conducted in the South Pacific since the 1970s and has resulted in a “small but steady stream of local converts” due to the conditions of an increasingly globalised world.[11] The first convert joined Islam in 1985 in neighboring Western Samoa, as a result of Muslim immigrants from abroad sharing their beliefs with the local people.[4] It is believed that this religious influence spread to American Samoa as the territory recorded a dozen adherents a decade later in the 1990s.[12]
In a number of the larger South Pacific states, Muslims are supported by regional bodies and organisations including the Fiji Muslim League and the Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific (RISEAP), which formed in 1980 and aimed to coordinate their Islamic missionary activities, “training individuals for Islamic social work” and establishing mosques and Islamic centres around the South Pacific.[13] American Samoa is not presently a member of the RISEAP, however the organisation partners with neighbouring countries such as Fiji and Samoa.[13] The first President of RISEAP, Tunku Abdul Rahman, stated their mission to encourage Muslims to continue their religious pursuits in the Pacific nations where they are minorities.[14] The Pacific Island countries are traditionally “collectivity-oriented” and have similar customs and practices to some religious groupings.[15] Muslims in the South Pacific have been involved in educating activities, engaging with the communities and instructing people in Islam.[6] This influence has seen the creation of the Islamic Institute of the South Pacific in Fiji. Islam is also often associated with the establishment of social and public health organisations in the region.[6]
The Muslim population
[edit]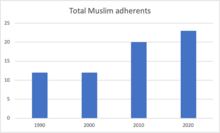
It is estimated that there are about half a million Muslims in Oceania, equating to about 1.4% of the total population of the continent.[12] Within the Asia-Pacific Muslim population, it is estimated that about 12-15% of adherents are Shia, the majority instead adhering to the Sunni denomination of Islam.[16] The islands are dominated by the Christian faith, with 98.3% of the population being Christian adherents.[12] However, it is estimated that 0.03% of the American Samoan population are Muslim adherents, the population almost doubling between the years 1990 to 2020 from 12 to 23 adherents.[12]
A study of where American Samoan residents were born showed that 6.3% of the population migrated from the United States, a nation with over 3.45 million Muslims in 2017.[17] The religious diversity of this nation is an influencing factor on the American Samoan Muslim population.[18]
The 2002 ban
[edit]

In December 2002, action was taken to ban nationals from 23 countries from entering American Samoa without explicit approval from Fiti Sunia, the territory’s attorney general’s office.[5] Those banned from American Samoa were mainly Arab nations, including a number in the Middle East.[5] As a part of this regulation, any visitor to the islands with a Middle Eastern appearance or Muslim sounding name received thorough examination before arrival and could be refused entry altogether. [2]
This decision was enforced after Governor Tauese Sunia claimed that a credible security threat was made, speculating that American Samoa could be targeted for terrorist activities because of its status as a US territory.[5] The action to ban these nations was put in place because officials claimed they did not have the supplies to manage and enforce “anything less sweeping and make it effective”.[19]
It is widely believed that this sweeping action by American Samoan officials was prompted by the Bali bombing, an explosion which killed 202 people, organized and carried out by a terrorist organisation named Jemaah Islamiya and occurring two months prior to the decision in October 2002.[20] According to members who coordinated the attack, Bali was chosen because it was often frequented by American citizens, thus it was believed that the American Samoan status as a US territory linked the nation to further retaliation from extremists.[21] The widespread ban of several Muslim nations was therefore claimed to have been implemented for the safety of the citizens.[5] However, the scale of the ban has led to some drawing comparisons to US President Donald Trump’s threat to impose bans on Muslims entering the United States at an election rally in December 2015.[22]
Furthermore, members of the Islamic Human Rights Commission have claimed that the closing of the island’s American consulate was prompted by a terrorist alert, in which two “unidentified men of ‘middle eastern appearance’” were taking photos of the consulate, although these claims have not been officially confirmed.[23][2]
The countries banned
[edit]The ban included the island of Fiji, the only other Pacific Island on the list. Their addition was linked to the nation's large Muslim population, with approximately 80,000 adherents on the island.[5] The extension of the ban to other South Pacific nations was justified as some Fijian Muslim adherents have travelled to and studied at Islamic institutions in typically Muslim countries.[23] However, after strong protest from Fijians as well as oppositional media coverage across the territory, the island was removed from the list in early 2003.[2]
Reaction to the 2002 ban
[edit]Support for the ban
[edit]In the early 2000s, there was a fear of a spread of radical Islam to American Samoa, and the potential for an outbreak of religious wars globally.[24] The risk of terrorism has remained a concern of the South Pacific, the regional body, the Pacific Islands Forum, holding a conference to examine legislative reform, directly targeting terrorism in 2003.[25] After the terrorist attacks in Bali, the Australian Strategic Policy Institute released a policy review identifying the increased threat of terrorism in South Pacific nations such as American Samoa.[26] The review suggested a number of states were susceptible to terrorist activities and could be “potential havens for terrorist groups” and Islamic extremism, particularly due to their close proximity to Australia and connection as a territory of the United States.[26] However, the threat level posed in the Pacific is still “recognised as low”.[26]
Samoan Prime Minister Tuilaepa Malielegaoi advocated the duty of the government in legislating to avoid such religious tensions through means such as the ban instated by American Samoan officials.[24] Furthermore, Mohammed Daniel Stanley, an American Samoan convert to Islam, came out in support of Sunia’s decision.[4]
This ban was also supported by a number of neighbouring South Pacific actors including the secretary general of the Samoa Council of Churches, who called for the nation of Samoa to “bring in a blanket ban on Islam”.[22] Samoan Reverend Motu similarly claimed that Islam posed a threat to the future of his country, pressing the Samoan government to entirely prohibit the religion on the island.[22]
Opposition to the ban
[edit]The actions of American Samoa were officially condemned by the Islamic Human Rights Commission, claiming the ban violates international law and calling for the government to rescind the ban and issue a formal apology to individuals affected.[23] No known action has been made toward rescinding the bans as of November 2020.
Restrictions on religious freedom
[edit]Particularly after the 2002 ban of a number of Muslim nations from American Samoa, a number of sources started questioning issues to do with religious freedom.[27] In the South Pacific countries, the average scores of laws and policies used to restrict religious freedom as well as government favouritism shown towards religious groups increased over 20% in the decade between 2007 and 2017.[28] The region is relatively high in this category, measuring 5.0 compared with the global average of 4.7.[28] It was also reported that 86% of countries in the Asia-Pacific region in 2017 reported events of “harassment or intimidation of religious groups by governments” and over half the countries in the region have experienced some type of “communal tension” between religious groupings.[28]
Several Christian groups have also attempted to influence the government and the populace in general to support restricting the practice of Islam in the territory or even ban it outright.[22]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Association of Religion Data Archives (2020). "American Samoa".
- ^ a b c d e Stanley, David (2004). South Pacific. Moon Handbooks.
- ^ Bouma, G; Ling, R; Pratt, D (2010). "Samoa". Religious Diversity in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. Springer Netherlands. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-3389-5_23.
- ^ a b c d Terdiman, Moshe (2011). "History of Islam in Samoa".
- ^ a b c d e f g h Sydney Morning Herald (2002). "American Samoa bans nations from 23 countries".
- ^ a b c Sydney Morning Herald (2007). "Heeding the call to prayer in a region that reveres the pig".
- ^ Barker, J. (1996). Winds of Change: Rapidly Growing Religious Groups in the Pacific Islands (Book Review) [Review of Winds of Change: Rapidly Growing Religious Groups in the Pacific Islands (Book Review)]. The Contemporary Pacific, 8(1), 234–236. Centre for Pacific Islands studies & University of HawaI’I press.
- ^ a b Encyclopedia.com (2002). "Oceanic Religions: Missionary Movement".
- ^ Oxford Islamic Studies Online (2020). "Dawah". The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Archived from the original on December 4, 2013.
- ^ Scott Flower (2015). "Conversion to Islam in Papua New Guinea: Preserving Traditional Culture against Modernity's Cargo-Cult Mentality". The Journal of Alternative and Emergent Religions. 18. University of California Press: 55–82.
- ^ Esposito, John (2003). "Pacific Region, Islam in". The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press.
- ^ a b c d e Kettani, Houssain (2010). "Muslim population in Oceania: 1950-2020".
- ^ a b Esposito, John (2003). "Regional Islamic Dawah Council of Southeast Asia and the Pacific". The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press.
- ^ "RISEAP". RISEAP. 2020.
- ^ Yabaki, Rev Akulia (2004). "The Impact of Tradition and Religion on Women's Lives in the South Pacific". Pacific Women's Bureau.
- ^ Pew Research Centre (2009). "Mapping the global Muslim population".
- ^ Mohamed, Besheer (2018). "New estimates show U.S. Muslim population continues to grow".
- ^ American Samoa Department of Commerce; U. S. Department of the Interior (2006). "Population and housing in American Samoa" (PDF).
- ^ "American Samoa, banning Muslims, bans Fijians". Pacific Business News. 23 December 2002. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- ^ National Museum Australia (2002). "Bali bombings".
- ^ BBC (2012). "The 12 October 2002 Bali bombing plot".
- ^ a b c d Samuels, Gabriel (2016). "The Pacific islanders who want to ban Islam".
- ^ a b c Islamic Human Rights Commission (2003). "Bannings and Deportations in the Pacific: racial and religious profiling in Fiji and American Samoa".
- ^ a b Wyeth, Grant (2016). "Samoa Officially Becomes a Christian State".
- ^ Panichi, James (2003). "Muslim cleric expelled from Fiji".
- ^ a b c Foreign Affairs, Defence and Trade References Committee (2010). "Security challenges facing Papua New Guinea and the island states of the southwest Pacific".
- ^ RNZ (2008). "American Samoa restates freedom of religion amid scientology campaign".
- ^ a b c Pew Research Centre (2019). "A closer look at how religious restrictions have arisen around the world".


