Nizhyn: Difference between revisions
Citation bot (talk | contribs) Altered title. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Dominic3203 | Category:Articles with dead external links from May 2022 | #UCB_Category 485/951 |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
{{For|the air base|Nizhyn (air base)}} |
{{For|the air base|Nizhyn (air base)}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date=July 2014}} |
{{Use dmy dates|date=July 2014}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Infobox settlement |
{{Infobox settlement |
||
| settlement_type |
| settlement_type = [[List of cities in Ukraine|City]] |
||
| name |
| name = Nizhyn |
||
| native_name |
| native_name = {{lang|uk|Ніжин}} |
||
| other_name |
| other_name = |
||
| image_skyline |
| image_skyline = {{Photomontage|position=center |
||
| photo1a = Миколаївський собор.jpg |
| photo1a = Миколаївський собор.jpg |
||
| photo2a = 74-104-5004 Grafsky park SAM 0511.jpg |
| photo2a = 74-104-5004 Grafsky park SAM 0511.jpg |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| border = 0 |
| border = 0 |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| image_shield |
| image_shield = Nizhyn gerb.png |
||
| image_caption = {{hlist|Clockwise from top: [[St. Nicholas Cathedral, Nizhyn|St. Nicholas Cathedral]]|[[Nizhyn Gogol State University]]|Intercession Church|Nizhyn Agrotechnical College|{{nowrap|St. Michael's}} Church|Count's Park}} |
|||
| image_flag = Nizhyn prapor.png |
|||
| |
| image_flag = Nizhyn prapor.png |
||
| subdivision_type = [[List of sovereign states|Country]] |
|||
| subdivision_name |
| subdivision_name = {{UKR}} |
||
| subdivision_type1 = [[Oblasts of Ukraine|Oblast]] |
|||
| |
| subdivision_type1 = [[Oblasts of Ukraine|Oblast]] |
||
| subdivision_name1 = [[Chernihiv Oblast]] |
|||
| subdivision_type2 |
| subdivision_type2 = [[Raions of Ukraine|Raion]] |
||
| subdivision_name2 |
| subdivision_name2 = [[Nizhyn Raion]] |
||
| population_total = 65830 |
|||
| |
| population_total = 65830 |
||
| |
| population_as_of = 2022 |
||
| |
| area_total_km2 = 43.2 |
||
| established_date = 1625 |
|||
| established_title |
| established_title = [[Magdeburg rights]] |
||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| |
| elevation_m = |
||
| pushpin_map = Ukraine Chernihiv Oblast#Ukraine |
|||
| pushpin_label_position |
| pushpin_label_position = |
||
| pushpin_map_caption |
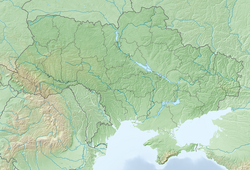
| pushpin_map_caption = Location of Nizhyn in [[Chernihiv Oblast]] |
||
| pushpin_mapsize |
| pushpin_mapsize = |
||
| coordinates |
| coordinates = {{coord|51|02|17|N|31|53|10|E|region:UA|display=inline,title}} |
||
| website |
| website = http://www.nizhynrada.org |
||
| image_map |
| image_map = |
||
| map_caption |
| map_caption = Location of Nizhyn in [[Ukraine]] |
||
| pushpin_relief |
| pushpin_relief = y |
||
| module |
| module = {{Infobox mapframe |wikidata=yes |zoom=12|height= |width= | stroke-width=1 |coord={{WikidataCoord|display=i}}}} |
||
| subdivision_type3 = [[Hromada]] |
|||
| subdivision_name3 = [[Nizhyn urban hromada]] |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
[[File:План Ніжина. 1773.jpg|thumb|1773 map of the Nizhyn fortress and its citadel]] |
[[File:План Ніжина. 1773.jpg|thumb|1773 map of the Nizhyn fortress and its citadel]] |
||
'''Nizhyn''' ({{ |
'''Nizhyn''' ({{langx|uk|Ніжин}}, {{IPA|uk|ˈn⁽ʲ⁾iʒɪn|pron|LL-Q8798 (ukr)-Gzhegozh-Ніжин.wav}}; {{langx|ru|Нежин}}) is a city located in [[Chernihiv Oblast]] of northern [[Ukraine]] along the [[Oster River]]. The city is located {{convert|116|km|mi|0|abbr=on}} north-east of the national capital [[Kyiv]]. Nizhyn serves as the [[capital city|administrative center]] of [[Nizhyn Raion]]. It hosts the administration of [[Nizhyn urban hromada]] which is one of the [[hromada]]s of Ukraine<ref name="admreform_2020_nizhyn">{{cite web |title=Нежинская городская громада |url=https://gromada.info/ru/obschina/nizhyn/ |publisher=Портал об'єднаних громад України |language=ru}}</ref> and was once a major city of the [[Chernigov Governorate]]. Nizhyn has a population of {{Ua-pop-est2022|65,830|.}} |
||
== History == |
== History == |
||
The earliest known references to the location go back to 1147, when it was briefly mentioned as '''Unenezh'''.<ref>Нежин // Украинская Советская Энциклопедия. том 7. Киев, «Украинская Советская энциклопедия», 1982. стр.223</ref> |
The earliest known references to the location go back to 1147, when it was briefly mentioned as '''Unenezh'''.<ref>Нежин // Украинская Советская Энциклопедия. том 7. Киев, «Украинская Советская энциклопедия», 1982. стр.223</ref> |
||
In the times of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]], Nizhyn was granted [[Magdeburg rights]] (1625) as a self-governing town. In 1663 Nizhyn was the place of the [[Chorna rada of 1663|Black Council]] of [[Ukrainian Cossacks]], which elected [[Ivan Briukhovetsky|Bryukhovetsky]] as the new [[Hetman of Zaporizhian Host|Hetman]] of the [[Zaporizhian Host]] thus conditionally dividing Ukraine ([[Cossack Hetmanate]]) into [[left-bank Ukraine]] and [[right-bank Ukraine]]. It was also the seat of a major [[Cossack]] regiment (until 1782). |
In the times of the [[Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth]], Nizhyn was granted [[Magdeburg rights]] (1625) as a self-governing town. In 1663, Nizhyn was the place of the [[Chorna rada of 1663|Black Council]] of [[Ukrainian Cossacks]], which elected [[Ivan Briukhovetsky|Bryukhovetsky]] as the new [[Hetman of Zaporizhian Host|Hetman]] of the [[Zaporizhian Host]] thus conditionally dividing Ukraine ([[Cossack Hetmanate]]) into [[left-bank Ukraine]] and [[right-bank Ukraine]]. It was also the seat of a major [[Cossack]] regiment (until 1782). |
||
In the Cossack Hetmanate, Nizhyn had six [[voivode]]s (a Muscovite military position) from 1665 to 1697. The voivodes of the city were Ivan Rzhevskiy (1665–1672),<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Lesyk |first=Lyudmyla |date=2016 |title=The Report of Nizhyn Voivodes in the «Acts of South Western Russia» |url=http://mics.org.ua/journal/index.php/mics/article/view/9 |journal=City History, Culture, Society |language=en |issue=1 |pages=163–170 |doi=10.15407/mics2016.01.163 |issn=2616-4280 |doi-access=free}}</ref> Stepan Khruscheov (1672–1673), Prince Vladimir Volkonskiy (1673–1675), Prince Semeon Zvenigorodskiy (1673–1675), Avraam Khitrovo (1689–1692), and Ivan Saveolov Junior (1692–1697).{{Citation needed|date=May 2024}} |
|||
Nizhyn was once a major center of [[Hasidic Judaism]] and is the site of the ''[[Ohel (Chabad)|Ohel]]'' (tomb) of the [[Rebbe|Hasidic master]], Rabbi [[Dovber Schneuri]] of [[Chabad-Lubavitch]]. The city also housed the thriving Greek community,{{Citation needed|date=January 2008}} which enjoyed a number of privileges granted by [[Bohdan Khmelnytsky]]. |
Nizhyn was once a major center of [[Hasidic Judaism]] and is the site of the ''[[Ohel (Chabad)|Ohel]]'' (tomb) of the [[Rebbe|Hasidic master]], Rabbi [[Dovber Schneuri]] of [[Chabad-Lubavitch]]. The city also housed the thriving Greek community,{{Citation needed|date=January 2008}} which enjoyed a number of privileges granted by [[Bohdan Khmelnytsky]]. |
||
| Line 60: | Line 65: | ||
===Jewish population=== |
===Jewish population=== |
||
Jews first settled in Nizhyn at the beginning of the 19th century after the [[Partitions of Poland|partition]] of [[Poland]]. The town grew to become a center for the [[Chabad]] [[Hasidic Judaism|Hasidim]] of Ukraine. [[Dovber Schneuri]], the second Chabad rebbe, is buried here. |
Jews first settled in Nizhyn at the beginning of the 19th century after the [[Partitions of Poland|partition]] of [[Poland]]. The town grew to become a center for the [[Chabad]] [[Hasidic Judaism|Hasidim]] of Ukraine. [[Dovber Schneuri]], the second Chabad rebbe, is buried here. By 1847, 1,299 Jews had registered as residents. In 1897, 24% of the population, or 7,361 residents, were Jewish. |
||
A wave of [[pogrom]]s severely affected the Jewish population in 1881 and 1905. One group of emigrants settled in Philadelphia and founded the [[Neziner Congregation]] in 1896. |
A wave of [[pogrom]]s severely affected the Jewish population in 1881 and 1905. One group of emigrants settled in Philadelphia and founded the [[Neziner Congregation]] in 1896. |
||
| Line 72: | Line 77: | ||
===Modern times=== |
===Modern times=== |
||
The city of Nizhyn is one of the ancient cities of Ukraine. The architectural complex of the city forms an expressive ensemble of an ancient trade city. The experts' estimates distinguish more than 300 ancient buildings, where 70 are of a great cultural and historical value. The expressive 200 years ensemble of Post Station (the only one preserved in Ukraine) deserves special mention. Nizhyn is a city of students (each fifth inhabitant of Nizhyn is a student). The following educational establishments operate in Nizhyn – State University named after Gogol; Agro-technical College, faculty of Kremenchyk Institute of Economy and New Technologies, College of Culture and Arts named after Zankovetska, Medical College, Nizhyn Professional Lyceum of Services, Nizhyn Agrarian Lyceum, vocational college, Lyceum at the |
The city of Nizhyn is one of the ancient cities of Ukraine. The architectural complex of the city forms an expressive ensemble of an ancient trade city. The experts' estimates distinguish more than 300 ancient buildings, where 70 are of a great cultural and historical value. The expressive 200 years ensemble of Post Station (the only one preserved in Ukraine) deserves special mention. Nizhyn is a city of students (each fifth inhabitant of Nizhyn is a student). The following educational establishments operate in Nizhyn – State University named after Gogol; Agro-technical College, faculty of Kremenchyk Institute of Economy and New Technologies, College of Culture and Arts named after Zankovetska, Medical College, Nizhyn Professional Lyceum of Services, Nizhyn Agrarian Lyceum, vocational college, Lyceum at the university. There are four club institutions, the Drama Theater named after Kotsiubynskyi, the Choreographic school and park landscapes in the city. |
||
The city boasts 38 libraries with the total fund of 17,365 thousand books, which caters for 44,429 readers, more than a dozen of museums, including Nizhyn Regional museum with the following sections: art, history, Nizhyn Post Station, with about 31 thousand of exhibits of the main fund, the Museum of the History of School No.3, the Museum of the History of School No.7 with a room of M.V.Nechkina, the Korolyov Museum in School No.14, the Glory Museum of Agrarian and Technical Institute, the Museum-Chemists shop named after M.Ligda. The following institutions function at Nizhyn State Pedagogical Institute named after Gogol: The Museum of Gogol, Art Gallery, the Museum “Rare book”, zoological museum, and botanical museum. |
The city boasts 38 libraries with the total fund of 17,365 thousand books, which caters for 44,429 readers, more than a dozen of museums, including Nizhyn Regional museum with the following sections: art, history, Nizhyn Post Station, with about 31 thousand of exhibits of the main fund, the Museum of the History of School No.3, the Museum of the History of School No.7 with a room of M. V. Nechkina, the Korolyov Museum in School No.14, the Glory Museum of Agrarian and Technical Institute, the Museum-Chemists shop named after M. Ligda. The following institutions function at Nizhyn State Pedagogical Institute named after Gogol: The Museum of [[Nikolai Gogol|Gogol]], Art Gallery, the Museum “Rare book”, zoological museum, and botanical museum. |
||
Nizhyn is a well-known industrial center, where 16 industrial enterprises, which belong to 8 branches, operate. Nizhyn is also an attractive tourist city. It is included into the tour “Necklace of Slavutych”. |
Nizhyn is a well-known industrial center, where 16 industrial enterprises, which belong to 8 branches, operate. Nizhyn is also an attractive tourist city. It is included into the tour “Necklace of Slavutych”. |
||
| Line 177: | Line 182: | ||
== Attractions == |
== Attractions == |
||
[[File:Nizhyn Church Ioanna Bogoslova.jpg|thumb|200px|John the Apostle Church in Nizhyn |
[[File:Nizhyn Church Ioanna Bogoslova.jpg|thumb|200px|John the Apostle Church in Nizhyn]] |
||
Architecturally Nizhyn was shaped in the 18th century. Foremost among its buildings must be mentioned its seven [[Baroque architecture|Baroque]] churches: Annunciation Cathedral (1702–16, modernised 1814), Presentation Cathedral (1788), St. Michael's Church of the Greek community (1719–29), St John's Church (1752, ''illustrated, to the right''), Saviour's Transfiguration Church (1757), Intercession Church (1765), and the so-called Cossack Cathedral of St. Nicholas (1658, restored 1980s), a rare survival from the days of Nizhyn's Cossack glory, noted for its octagonal vaults and drums crowned by archetypal pear-shaped domes.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://sobory.ru/photo/index.html?photo=17063|title=Photo|website=sobory.ru}}</ref> Other notable buildings include the Trinity Church (1733, rebuilt a century later), the Greek magistrate (1785), and the Neoclassical complex of the [[Nizhyn Lyceum]] (designed by [[Luigi Rusca]], built in 1805–17, expanded in 1876–79). |
Architecturally Nizhyn was shaped in the 18th century. Foremost among its buildings must be mentioned its seven [[Baroque architecture|Baroque]] churches: Annunciation Cathedral (1702–16, modernised 1814), Presentation Cathedral (1788), St. Michael's Church of the Greek community (1719–29), St John's Church (1752, ''illustrated, to the right''), Saviour's Transfiguration Church (1757), Intercession Church (1765), and the so-called Cossack [[St. Nicholas Cathedral, Nizhyn|Cathedral of St. Nicholas]] (1658, restored 1980s), a rare survival from the days of Nizhyn's Cossack glory, noted for its octagonal vaults and drums crowned by archetypal pear-shaped domes.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://sobory.ru/photo/index.html?photo=17063|title=Photo|website=sobory.ru}}</ref> Other notable buildings include the Trinity Church (1733, rebuilt a century later), the Greek magistrate (1785), and the Neoclassical complex of the [[Nizhyn Lyceum]] (designed by [[Luigi Rusca]], built in 1805–17, expanded in 1876–79). |
||
There is the memorial museum of Russian naval officer and explorer [[Yuri Lisyansky]] in {{ill|Yuri Lisyanky birthplace house|lt=his family house|uk|Будинок, де народився Юрій Лисянський}} in Nizhyn and a monument by the house.<ref>[https://web.archive.org/web/20220228215532/http://nizhyn-travel.com.ua/uk/pages/208-memorialnyj_budynok-muzej_yuriya_lysyanskogo Меморіальний будинок-музей Юрія Лисянського]</ref> |
|||
== Industry == |
== Industry == |
||
Modern Nizhyn is a major industrial center. The city has 16 companies and firms from eight industries: |
Modern Nizhyn is a major industrial center. The city has 16 companies and firms from eight industries:{{Citation needed|date=July 2024}} |
||
* ''Engineering'': |
* ''Engineering'': |
||
** NEC "Progress" – the production of photographic supplies, hunting scopes, medical equipment, household goods; |
** NEC "Progress" – the production of photographic supplies, hunting scopes, medical equipment, household goods; |
||
** JSC "Mechanical Plant" – manufacture of machinery for agriculture; |
** JSC "Mechanical Plant" – manufacture of machinery for agriculture; |
||
** Plant "Nezhinselmash" – poultry equipment, motorcycles, bicycles, spare parts, fittings for gas and vodogonov; |
** Plant "Nezhinselmash" – poultry equipment, motorcycles, bicycles, spare parts, fittings for gas and vodogonov; |
||
** |
** Nizhynske Training and Production Enterprise "UTOS" – covers of metal for home canning, switches, electric sockets, nails, clips, extension cords. |
||
* ''Food'': |
* ''Food'': |
||
** |
** Nizhynskyi cannery – the leading state-owned enterprise for the production of canned vegetables; |
||
** JSC "Nizhyn bread" – the production of bakery, confectionery and pasta; |
** JSC "Nizhyn bread" – the production of bakery, confectionery and pasta; |
||
** |
** JSC "Nizhyn brewery" (stopped in the summer of 2008) – the production of beer; |
||
** JSC "Nizhyn zhirkombinat" – manufacture and sale of varnishes, lacquers, oils, makukha. |
** JSC "Nizhyn zhirkombinat" – manufacture and sale of varnishes, lacquers, oils, makukha. |
||
* ''Medicine'': |
* ''Medicine'': |
||
| Line 207: | Line 214: | ||
* "Printing": |
* "Printing": |
||
** LLC "Aspect". |
** LLC "Aspect". |
||
Starting in 1915, the city was served by a tram [[public transportation]] system. The tram system had a [[track gauge]] of {{Track gauge|1524mm|lk=on}} and first began as [[Horse trams|horse-pulled trams]] at its opening in 1915. The system became defunct in the mid-1920s and never recovered. Information on the number of lines that existed is not available. |
|||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
<gallery> |
<gallery> |
||
File:Church of All Saints in Nizhyn (Ukraine).jpg|All Saints' Church |
File:Church of All Saints in Nizhyn (Ukraine).jpg|All Saints' Church |
||
File:NSH Nizhyn Mykolayivs'kiy sobor 001.JPG|St. Nicholas Cathedral |
File:NSH Nizhyn Mykolayivs'kiy sobor 001.JPG|[[St. Nicholas Cathedral, Nizhyn|St. Nicholas Cathedral]] |
||
File:NSH Nizhyn Pokrovs'ka Tserkva 001.JPG| |
File:NSH Nizhyn Pokrovs'ka Tserkva 001.JPG|Intercession Church |
||
File:Nizhyn Epiphany Church.jpg|Epiphany Church |
File:Nizhyn Epiphany Church.jpg|Epiphany Church |
||
File:Ніжин — Василівська церква.jpg|St. Basil Church |
File:Ніжин — Василівська церква.jpg|St. Basil Church |
||
| Line 224: | Line 232: | ||
File:NSH Nizhyn Pamyatnyk Gogolyu.JPG|[[Nikolai Gogol]] monument |
File:NSH Nizhyn Pamyatnyk Gogolyu.JPG|[[Nikolai Gogol]] monument |
||
File:Аптека Лігди Ніжин.jpg|Old drugstore in Nizhyn |
File:Аптека Лігди Ніжин.jpg|Old drugstore in Nizhyn |
||
File:Будинок А.Ф.Кушакевича та міський комерційний банк, вул. Гоголя, 15.JPG|Old buildings |
File:Будинок А.Ф.Кушакевича та міський комерційний банк, вул. Гоголя, 15.JPG|Old buildings on Hohol Street |
||
File:Вул. Гоголя, 2-а.JPG|Soviet architecture in |
File:Вул. Гоголя, 2-а.JPG|Soviet architecture in the main square |
||
File:Будинок дітей та юнацтва. Дом пионеров.JPG|House of youth and children (former telegraph station) |
File:Будинок дітей та юнацтва. Дом пионеров.JPG|House of youth and children (former telegraph station) |
||
File:Вот он Нежинский огурец - panoramio.jpg|Monument to Nizhyn cucumber |
File:Вот он Нежинский огурец - panoramio.jpg|{{ill|Monument to the Nizhyn cucumber|uk|Пам'ятник ніжинському огірку}}|alt=Monument to Nizhyn cucumber [uk] |
||
File:Grave of Rabbi Dovber Schneuri.jpg|Grave of Rabbi Dovber Schneuri |
File:Grave of Rabbi Dovber Schneuri.jpg|Grave of Rabbi Dovber Schneuri |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
| Line 245: | Line 253: | ||
* [[Jacob Pavlovitch Adler]], [[Jewish]] actor. |
* [[Jacob Pavlovitch Adler]], [[Jewish]] actor. |
||
* [[Sonya Adler]], one of the first women to perform in Yiddish theater in Imperial Russia. |
* [[Sonya Adler]], one of the first women to perform in Yiddish theater in Imperial Russia. |
||
* [[Antoni Andrzejowski]], Polish botanist, teacher of the Nizhyn Lyceum |
* [[Antoni Andrzejowski]], Polish botanist, teacher of the Nizhyn Lyceum (1839–1856), author of the diary ''Wspomnienia starego detiuka''. |
||
* [[Abraham Berline]], artist. |
* [[Abraham Berline]], artist. |
||
* [[Mark Bernes]], a Soviet actor and singer of Jewish ancestry. |
* [[Mark Bernes]], a Soviet actor and singer of Jewish ancestry. |
||
| Line 255: | Line 263: | ||
* [[Nestor Kukolnik]], a Russian playwright and [[prose]] writer. |
* [[Nestor Kukolnik]], a Russian playwright and [[prose]] writer. |
||
* [[Yuri Lisyansky]], headed the [[first Russian circumnavigation]] of the globe. |
* [[Yuri Lisyansky]], headed the [[first Russian circumnavigation]] of the globe. |
||
* [[Oleksandr Matsievskyi]], [[Ukrainian Ground Forces]] member and captive executed by [[Russian Ground Forces|Russian soldiers]] during the [[Battle of Bakhmut]] in the [[Russian invasion of Ukraine (2022–present)|Russian invasion of Ukraine]].<ref>{{cite web|date=25 November 2023|access-date=25 November 2023|title=Ukraine unveils monument to soldier shot dead on video|url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/ukraine-unveils-monument-soldier-shot-dead-widely-shared-video-2023-11-25/|website=[[Reuters]]| |
* [[Oleksandr Matsievskyi]], [[Ukrainian Ground Forces]] member and captive executed by [[Russian Ground Forces|Russian soldiers]] during the [[Battle of Bakhmut]] in the [[Russian invasion of Ukraine (2022–present)|Russian invasion of Ukraine]].<ref>{{cite web|date=25 November 2023|access-date=25 November 2023|title=Ukraine unveils monument to soldier shot dead on video|url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/ukraine-unveils-monument-soldier-shot-dead-widely-shared-video-2023-11-25/|website=[[Reuters]]|language=English}}</ref> |
||
* [[Kateryna Pavlenko]], lead singer of the Ukrainian electro-folk band [[Go_A]]. |
* [[Kateryna Pavlenko]], lead singer of the Ukrainian electro-folk band [[Go_A]]. |
||
* [[Zhanna Pintusevich-Block]], a world champion [[Sprint (running)|sprinter]]. |
* [[Zhanna Pintusevich-Block]], a world champion [[Sprint (running)|sprinter]]. |
||
| Line 267: | Line 275: | ||
== External links == |
== External links == |
||
* {{ |
* {{Commons category-inline}} |
||
* {{in lang|ru|uk}} ''"A city, glorious and tender, loved by all"'', in |
* {{in lang|ru|uk}} ''"A city, glorious and tender, loved by all"'', in [[Zerkalo Nedeli]] (''the Mirror Weekly''), July 2005. [http://www.zerkalo-nedeli.com/ie/show/555/50609/ in Russian]{{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}, [http://www.zn.kiev.ua/ie/show/555/50609/ in Ukrainian]{{dead link|date=December 2017 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }} |
||
* {{in lang|en}} [http://www.encyclopediaofukraine.com/display.asp?linkpath=pages%5CU%5CN%5CUnionfortheLiberationofUkraineSVU.htm\N\I\Nizhen.htm Nizhen/Nizhyn]{{dead link|date=May 2022|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}} in the [http://www.encyclopediaofukraine.com Encyclopedia of Ukraine] |
* {{in lang|en}} [http://www.encyclopediaofukraine.com/display.asp?linkpath=pages%5CU%5CN%5CUnionfortheLiberationofUkraineSVU.htm\N\I\Nizhen.htm Nizhen/Nizhyn]{{dead link|date=May 2022|bot=medic}}{{cbignore|bot=medic}} in the [http://www.encyclopediaofukraine.com Encyclopedia of Ukraine] |
||
* {{in lang|ru}} [http://pacovan.io.com.ua/story.php?ids=5727 History of Nizhyn] |
* {{in lang|ru}} [http://pacovan.io.com.ua/story.php?ids=5727 History of Nizhyn] |
||
| Line 274: | Line 282: | ||
* [http://www.radozamok.com.ua/en/ The Official Site of Radomysl Castle] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200814134402/http://www.radozamok.com.ua/en/ |date=14 August 2020 }} |
* [http://www.radozamok.com.ua/en/ The Official Site of Radomysl Castle] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200814134402/http://www.radozamok.com.ua/en/ |date=14 August 2020 }} |
||
* [http://www.yadvashem.org/untoldstories/database/index.asp?cid=340 The murder of the Jews of Nizhyn] during [[World War II]], at [[Yad Vashem]] website. |
* [http://www.yadvashem.org/untoldstories/database/index.asp?cid=340 The murder of the Jews of Nizhyn] during [[World War II]], at [[Yad Vashem]] website. |
||
* {{cite web |title=Parovoz |url=http://transit.parovoz.com/masstransit/index.php?ID=189 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://archive.today/20130427155323/http://transit.parovoz.com/masstransit/index.php?ID=189 |archivedate=2013-04-27 |language=Russian}} |
|||
{{Nizhyn Raion}} |
|||
{{Chernihiv Oblast}} |
{{Chernihiv Oblast}} |
||
{{Authority control}} |
{{Authority control}} |
||
| Line 280: | Line 290: | ||
[[Category:Nizhyn| ]] |
[[Category:Nizhyn| ]] |
||
[[Category:Cities in Chernihiv Oblast]] |
[[Category:Cities in Chernihiv Oblast]] |
||
[[Category:Nezhinsky Uezd]] |
|||
[[Category:Kiev Voivodeship]] |
|||
[[Category:Cossack Hetmanate]] |
|||
[[Category:Historic Jewish communities in Ukraine]] |
[[Category:Historic Jewish communities in Ukraine]] |
||
[[Category:Magdeburg rights]] |
[[Category:Magdeburg rights]] |
||
Latest revision as of 18:28, 2 December 2024
Nizhyn
Ніжин | |
|---|---|
| |
Location of Nizhyn in Chernihiv Oblast | |
| Coordinates: 51°02′17″N 31°53′10″E / 51.03806°N 31.88611°E | |
| Country | |
| Oblast | Chernihiv Oblast |
| Raion | Nizhyn Raion |
| Hromada | Nizhyn urban hromada |
| Magdeburg rights | 1625 |
| Area | |
• Total | 43.2 km2 (16.7 sq mi) |
| Population (2022) | |
• Total | 65,830 |
| Website | http://www.nizhynrada.org |
 | |

Nizhyn (Ukrainian: Ніжин, pronounced [ˈn⁽ʲ⁾iʒɪn] ⓘ; Russian: Нежин) is a city located in Chernihiv Oblast of northern Ukraine along the Oster River. The city is located 116 km (72 mi) north-east of the national capital Kyiv. Nizhyn serves as the administrative center of Nizhyn Raion. It hosts the administration of Nizhyn urban hromada which is one of the hromadas of Ukraine[1] and was once a major city of the Chernigov Governorate. Nizhyn has a population of 65,830 (2022 estimate).[2]
History
[edit]The earliest known references to the location go back to 1147, when it was briefly mentioned as Unenezh.[3]
In the times of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Nizhyn was granted Magdeburg rights (1625) as a self-governing town. In 1663, Nizhyn was the place of the Black Council of Ukrainian Cossacks, which elected Bryukhovetsky as the new Hetman of the Zaporizhian Host thus conditionally dividing Ukraine (Cossack Hetmanate) into left-bank Ukraine and right-bank Ukraine. It was also the seat of a major Cossack regiment (until 1782).
In the Cossack Hetmanate, Nizhyn had six voivodes (a Muscovite military position) from 1665 to 1697. The voivodes of the city were Ivan Rzhevskiy (1665–1672),[4] Stepan Khruscheov (1672–1673), Prince Vladimir Volkonskiy (1673–1675), Prince Semeon Zvenigorodskiy (1673–1675), Avraam Khitrovo (1689–1692), and Ivan Saveolov Junior (1692–1697).[citation needed]
Nizhyn was once a major center of Hasidic Judaism and is the site of the Ohel (tomb) of the Hasidic master, Rabbi Dovber Schneuri of Chabad-Lubavitch. The city also housed the thriving Greek community,[citation needed] which enjoyed a number of privileges granted by Bohdan Khmelnytsky.
In the 19th century Nizhyn became an uyezd capital of the Chernihiv Governorate and the biggest city in the guberniya. In 1805, the Bezborodko Lyceum was established there (today — Nizhyn Gogol State University); its graduates include Nikolai Gogol whose statue graces one of city streets as well as Yevhen Hrebinka among other graduates. Nizhyn has also long been noted for its famous cucumbers.[5][6]
During World War II, Nizhyn was occupied by the German Army from 13 September 1941 to 15 September 1943.
Jewish population
[edit]Jews first settled in Nizhyn at the beginning of the 19th century after the partition of Poland. The town grew to become a center for the Chabad Hasidim of Ukraine. Dovber Schneuri, the second Chabad rebbe, is buried here. By 1847, 1,299 Jews had registered as residents. In 1897, 24% of the population, or 7,361 residents, were Jewish.
A wave of pogroms severely affected the Jewish population in 1881 and 1905. One group of emigrants settled in Philadelphia and founded the Neziner Congregation in 1896.
During their retreat from the Germans in the spring of 1918, the Red Army carried out additional pogroms. During World War II, the region was occupied by Germany, who murdered all Jews in the area. Only those who escaped survived.
In 1959, 1,400 Jews lived in Nizhyn, about 3% of the town's population. In 2005, Nizhyn population reached 80,000. Only about 300 Jewish families lived in the city.[7]
Aircraft crash
[edit]In July 1969 two Tupolev Tu-22 aircraft from the nearby air base collided in mid-air. The crew ejected and the plane flew on unpiloted for 52 minutes, threatening the city of Nizhyn before crashing 0.5 km from the city's railway station.[8]
Modern times
[edit]The city of Nizhyn is one of the ancient cities of Ukraine. The architectural complex of the city forms an expressive ensemble of an ancient trade city. The experts' estimates distinguish more than 300 ancient buildings, where 70 are of a great cultural and historical value. The expressive 200 years ensemble of Post Station (the only one preserved in Ukraine) deserves special mention. Nizhyn is a city of students (each fifth inhabitant of Nizhyn is a student). The following educational establishments operate in Nizhyn – State University named after Gogol; Agro-technical College, faculty of Kremenchyk Institute of Economy and New Technologies, College of Culture and Arts named after Zankovetska, Medical College, Nizhyn Professional Lyceum of Services, Nizhyn Agrarian Lyceum, vocational college, Lyceum at the university. There are four club institutions, the Drama Theater named after Kotsiubynskyi, the Choreographic school and park landscapes in the city.
The city boasts 38 libraries with the total fund of 17,365 thousand books, which caters for 44,429 readers, more than a dozen of museums, including Nizhyn Regional museum with the following sections: art, history, Nizhyn Post Station, with about 31 thousand of exhibits of the main fund, the Museum of the History of School No.3, the Museum of the History of School No.7 with a room of M. V. Nechkina, the Korolyov Museum in School No.14, the Glory Museum of Agrarian and Technical Institute, the Museum-Chemists shop named after M. Ligda. The following institutions function at Nizhyn State Pedagogical Institute named after Gogol: The Museum of Gogol, Art Gallery, the Museum “Rare book”, zoological museum, and botanical museum. Nizhyn is a well-known industrial center, where 16 industrial enterprises, which belong to 8 branches, operate. Nizhyn is also an attractive tourist city. It is included into the tour “Necklace of Slavutych”.
A postage stamp featuring the coat of arms of Nizhyn was released by Ukraine in 2017.
Until 18 July 2020, Nizhyn was designated as a city of oblast significance and did not belong to Nizhyn Raion even though it was the center of the raion. As part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Chernihiv Oblast to four, the city was merged into Nizhyn Raion.[9][10]
Geography
[edit]Climate
[edit]| Climate data for Nizhyn (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −1.6 (29.1) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
4.9 (40.8) |
13.9 (57.0) |
20.9 (69.6) |
23.8 (74.8) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.0 (77.0) |
18.9 (66.0) |
12.1 (53.8) |
3.9 (39.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −4.3 (24.3) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
0.8 (33.4) |
8.5 (47.3) |
14.8 (58.6) |
18.0 (64.4) |
19.8 (67.6) |
18.6 (65.5) |
13.1 (55.6) |
7.3 (45.1) |
1.0 (33.8) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −7.0 (19.4) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
3.6 (38.5) |
8.7 (47.7) |
12.5 (54.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
12.9 (55.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
3.3 (37.9) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
3.3 (37.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 36.1 (1.42) |
38.0 (1.50) |
32.7 (1.29) |
45.3 (1.78) |
57.0 (2.24) |
73.3 (2.89) |
80.9 (3.19) |
57.8 (2.28) |
61.1 (2.41) |
42.9 (1.69) |
47.3 (1.86) |
44.0 (1.73) |
616.4 (24.27) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 8.7 | 9.1 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 8.4 | 9.2 | 8.9 | 6.5 | 7.6 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 9.3 | 98.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 85.4 | 82.6 | 78.2 | 70.3 | 67.5 | 72.0 | 72.9 | 73.2 | 78.5 | 81.8 | 87.4 | 87.5 | 78.1 |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization[11] | |||||||||||||
Attractions
[edit]
Architecturally Nizhyn was shaped in the 18th century. Foremost among its buildings must be mentioned its seven Baroque churches: Annunciation Cathedral (1702–16, modernised 1814), Presentation Cathedral (1788), St. Michael's Church of the Greek community (1719–29), St John's Church (1752, illustrated, to the right), Saviour's Transfiguration Church (1757), Intercession Church (1765), and the so-called Cossack Cathedral of St. Nicholas (1658, restored 1980s), a rare survival from the days of Nizhyn's Cossack glory, noted for its octagonal vaults and drums crowned by archetypal pear-shaped domes.[12] Other notable buildings include the Trinity Church (1733, rebuilt a century later), the Greek magistrate (1785), and the Neoclassical complex of the Nizhyn Lyceum (designed by Luigi Rusca, built in 1805–17, expanded in 1876–79).
There is the memorial museum of Russian naval officer and explorer Yuri Lisyansky in his family house in Nizhyn and a monument by the house.[13]
Industry
[edit]Modern Nizhyn is a major industrial center. The city has 16 companies and firms from eight industries:[citation needed]
- Engineering:
- NEC "Progress" – the production of photographic supplies, hunting scopes, medical equipment, household goods;
- JSC "Mechanical Plant" – manufacture of machinery for agriculture;
- Plant "Nezhinselmash" – poultry equipment, motorcycles, bicycles, spare parts, fittings for gas and vodogonov;
- Nizhynske Training and Production Enterprise "UTOS" – covers of metal for home canning, switches, electric sockets, nails, clips, extension cords.
- Food:
- Nizhynskyi cannery – the leading state-owned enterprise for the production of canned vegetables;
- JSC "Nizhyn bread" – the production of bakery, confectionery and pasta;
- JSC "Nizhyn brewery" (stopped in the summer of 2008) – the production of beer;
- JSC "Nizhyn zhirkombinat" – manufacture and sale of varnishes, lacquers, oils, makukha.
- Medicine:
- LLC "Lab scanning devices" – the production of medical equipment, optical and electronic devices, rubber means;
- LLC RDC "Metecol" – the production of medical products using and training simulators.
- Light:
- JSC "DiSi Nezhinka" – design and manufacture of clothing;
- Dry:
- JSC "Nifar" – the production and supply of paints, detergents, toothpastes, plant protection products;
- Timber:
- Of "Furniture Factory"
PVKF ** "Courier";
- Building:
- JSC "Plant management of construction materials";
- "Printing":
- LLC "Aspect".
Starting in 1915, the city was served by a tram public transportation system. The tram system had a track gauge of 1,524 mm (5 ft) and first began as horse-pulled trams at its opening in 1915. The system became defunct in the mid-1920s and never recovered. Information on the number of lines that existed is not available.
Gallery
[edit]-
All Saints' Church
-
Intercession Church
-
Epiphany Church
-
St. Basil Church
-
Ascension Church
-
Nizhyn Railway Station
-
Bank building on Zankovetska Street
-
Nizhyn shopping street
-
Old power station
-
Former Jewish hotel building
-
Merchant Assembly building
-
Nikolai Gogol monument
-
Old drugstore in Nizhyn
-
Old buildings on Hohol Street
-
Soviet architecture in the main square
-
House of youth and children (former telegraph station)
-
Grave of Rabbi Dovber Schneuri
International relations
[edit]Twin towns – sister cities
[edit]Nizhyn is twinned with:
Notable people
[edit]- Jacob Pavlovitch Adler, Jewish actor.
- Sonya Adler, one of the first women to perform in Yiddish theater in Imperial Russia.
- Antoni Andrzejowski, Polish botanist, teacher of the Nizhyn Lyceum (1839–1856), author of the diary Wspomnienia starego detiuka.
- Abraham Berline, artist.
- Mark Bernes, a Soviet actor and singer of Jewish ancestry.
- Elina Bystritskaya, a Soviet film actress, People's Artist of the USSR.
- Semyon Desnitsky, a disciple of Adam Smith who introduced his ideas to the Russian public.
- Timofei Dokshizer, principal trumpeter and trumpet soloist of the Bolshoi Theater, of Jewish ancestry.[16]
- Olga Khokhlova, Pablo Picasso's wife.
- Sergey Korolyov, the father of the Soviet space program.
- Nestor Kukolnik, a Russian playwright and prose writer.
- Yuri Lisyansky, headed the first Russian circumnavigation of the globe.
- Oleksandr Matsievskyi, Ukrainian Ground Forces member and captive executed by Russian soldiers during the Battle of Bakhmut in the Russian invasion of Ukraine.[17]
- Kateryna Pavlenko, lead singer of the Ukrainian electro-folk band Go_A.
- Zhanna Pintusevich-Block, a world champion sprinter.
- Israel Rosenberg, founded the first Yiddish theater troupe in Imperial Russia.
- Ihor Sholin, former professional Ukrainian football player.
- Maria Zankovetska, a Ukrainian theater actress, the very first recipient of People's Artist of Ukraine.
References
[edit]- ^ "Нежинская городская громада" (in Russian). Портал об'єднаних громад України.
- ^ Чисельність наявного населення України на 1 січня 2022 [Number of Present Population of Ukraine, as of January 1, 2022] (PDF) (in Ukrainian and English). Kyiv: State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 July 2022.
- ^ Нежин // Украинская Советская Энциклопедия. том 7. Киев, «Украинская Советская энциклопедия», 1982. стр.223
- ^ Lesyk, Lyudmyla (2016). "The Report of Nizhyn Voivodes in the «Acts of South Western Russia»". City History, Culture, Society (1): 163–170. doi:10.15407/mics2016.01.163. ISSN 2616-4280.
- ^ "газета Kyiv Weekly". 22 April 2009. Archived from the original on 22 April 2009. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ "Його Величнiсть нiжинський огiрок - Всеукраїнський незалежний медійний простір "Сіверщина"". siver.com.ua. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ "Nezhin in the 1800s". Retrieved 12 October 2009.
- ^ Gordon, Yefim (1999). Tupolev Tu-22 'Blinder' Tu-22M 'Backfire'. Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-065-6.
- ^ "Про утворення та ліквідацію районів. Постанова Верховної Ради України № 807-ІХ". Голос України (in Ukrainian). 18 July 2020. Retrieved 3 October 2020.
- ^ "Нові райони: карти + склад" (in Ukrainian). Міністерство розвитку громад та територій України.
- ^ "World Meteorological Organization Climate Normals for 1981–2010". World Meteorological Organization. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- ^ "Photo". sobory.ru.
- ^ Меморіальний будинок-музей Юрія Лисянського
- ^ "Από τη Δομπόλη και τη Ζωσιμαία ως τη Νίζνα". 11 March 2022.
- ^ "Ψηφιακό Αρχείο Πρακτικών Συνεδριάσεων Δημοτικού Συμβουλίου και Δημαρχιακής Επιτροπής Ιωαννίνων".
- ^ Anatoly Selianin. "Timofei Dokshizer, Russian Trumpet Virtuoso [Rare Documentary]". YouTube. Archived from the original on 21 December 2021. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- ^ "Ukraine unveils monument to soldier shot dead on video". Reuters. 25 November 2023. Retrieved 25 November 2023.
External links
[edit] Media related to Nizhyn at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Nizhyn at Wikimedia Commons- (in Russian and Ukrainian) "A city, glorious and tender, loved by all", in Zerkalo Nedeli (the Mirror Weekly), July 2005. in Russian[permanent dead link], in Ukrainian[permanent dead link]
- (in English) Nizhen/Nizhyn[dead link] in the Encyclopedia of Ukraine
- (in Russian) History of Nizhyn
- History of Jewish Community in Nezhin
- The Official Site of Radomysl Castle Archived 14 August 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- The murder of the Jews of Nizhyn during World War II, at Yad Vashem website.
- "Parovoz" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 27 April 2013.



























![Monument to Nizhyn cucumber [uk]](/upwiki/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b5/%D0%92%D0%BE%D1%82_%D0%BE%D0%BD_%D0%9D%D0%B5%D0%B6%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B9_%D0%BE%D0%B3%D1%83%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%86_-_panoramio.jpg/120px-%D0%92%D0%BE%D1%82_%D0%BE%D0%BD_%D0%9D%D0%B5%D0%B6%D0%B8%D0%BD%D1%81%D0%BA%D0%B8%D0%B9_%D0%BE%D0%B3%D1%83%D1%80%D0%B5%D1%86_-_panoramio.jpg)

