Condyloid process: Difference between revisions
Tag: shouting |
Unrulyevil5 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Part of the jawbone which hinges it to the skull}} |
|||
{{Infobox |
{{Infobox bone |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| Name = Condyloid process |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
GraySubject = 44 | |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
GrayPage = 174 | |
|||
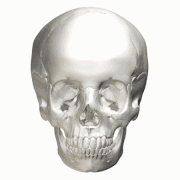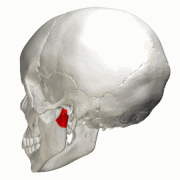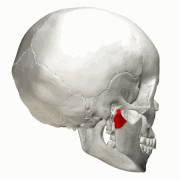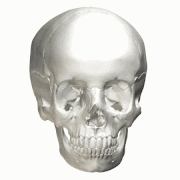
| Caption = Position of condyloid process (shown in red). |
|||
Image = Processuscondylarismandibulae.PNG | |
|||
| Image2 = Condyloid process - close-up - superior view2.png |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| Caption2 = [[Human mandible|Mandible]]. Condyloid processes are shown in red. |
|||
Image2 = | |
|||
Caption2 = | |
|||
Precursor = | |
|||
System = | |
|||
Artery = | |
|||
Vein = | |
|||
Nerve = | |
|||
Lymph = | |
|||
MeshName = | |
|||
MeshNumber = | |
|||
DorlandsPre = p_34 | |
|||
DorlandsSuf = 12667389 | |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''condyloid process''' is |
The '''condyloid process''' or '''condylar process''' is the [[process (anatomy)|process]] on the human and other [[mammalia]]n species' [[mandible]]s that ends in a [[condyle (anatomy)|condyle]], the '''mandibular condyle'''. It is thicker than the [[coronoid process of the mandible]] and consists of two portions: the condyle and the constricted portion which supports it, the neck. |
||
==Condyle == |
==Condyle == |
||
The condyle presents an articular surface for articulation |
The most superior part of the mandible, the condyle presents an articular surface for articulation with the [[articular disk of the temporomandibular joint|articular disk]] of the [[temporomandibular joint]];<ref name=":1">{{Citation|last=Breeland|first=Grant|title=Anatomy, Head and Neck, Mandible|date=2021|url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532292/|work=StatPearls|place=Treasure Island (FL)|publisher=StatPearls Publishing|pmid=30335325|access-date=2021-07-08|last2=Aktar|first2=Aylin|last3=Patel|first3=Bhupendra C.}}</ref> it is convex from before backward and from side to side, and extends further on the posterior than on the anterior surface. |
||
Its long axis is directed medialward and slightly backward, and if prolonged to the middle line will meet that of the opposite condyle near the anterior margin of the foramen magnum. |
Its long axis is directed medialward and slightly backward, and if prolonged to the middle line will meet that of the opposite condyle near the anterior margin of the [[foramen magnum]]. |
||
At the lateral extremity of the condyle is a small tubercle for the attachment of the [[temporomandibular ligament]]. |
At the lateral extremity of the condyle is a small tubercle for the attachment of the [[temporomandibular ligament]]. |
||
The articular surface of the condyle is covered by fibrous tissue, and interfaces with an articular disk (or meniscus) of avascular, non-innervated fibrous tissue (collagen, fibroblasts). |
The articular surface of the condyle is covered by fibrous tissue, and interfaces with an articular disk (or meniscus) of avascular, non-innervated fibrous tissue (collagen, fibroblasts). When the mouth is closed the meniscus is bordered medially and superiorly by the glenoid fossa of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. When the mouth is opened maximally, the meniscus is distracted anteriorly and inferiorly along the slope of the inferior portion of the temporal bone towards the tubercle, or articular eminence, in order to remain interposed between the condyle and the temporal bone in all jaw positions. |
||
==Neck== |
==Neck== |
||
The neck is flattened from before backward, and strengthened by ridges which descend from the forepart and sides of the condyle. |
The neck of the process rises from the posterior of the [[ramus mandibulae]].<ref name=":1" /> It is flattened from before backward, and strengthened by ridges which descend from the forepart and sides of the condyle. |
||
Its posterior surface is convex; its anterior |
Its posterior surface is convex; its anterior surface has a depression for the attachment of the [[lateral pterygoid muscle]].<ref name=":1" /> |
||
CRAIG ARNOT LOVES VAG |
|||
==Fractures== |
|||
Since the articular disk prevents the mandible from moving posteriorly, the condylar neck is often subject to fracturing when the jaw suffers a blow.<ref name=":1" /> |
|||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
{{Gallery|File:Condyloid process - animation.gif|Position of condyloid process (shown in red) |
|||
<gallery> |
|||
|File:Condyloid process - close-up - animation2.gif|Mandible. Position of condyloid process is shown in red. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
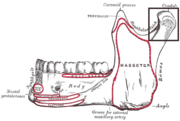
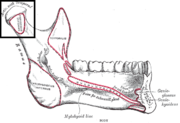
|File:Gray177 - Condyloid process.png|Inner surface of mandible. Condyloid process is at upper left. |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
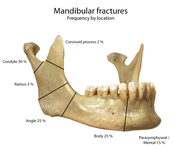
|File:Mandbular fractures.png|Frequency of mandibular fractures by location. |
|||
}} |
|||
== |
==References== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
|||
* [[Ramus mandibulae]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
{{Commons category|Condyloid process}} |
|||
* {{NormanAnatomy|lesson1}} |
* {{NormanAnatomy|lesson1}} |
||
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|22|os|10|01}} - "Osteology of the Skull: Mandible of Intact Skull" |
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|22|os|10|01}} - "Osteology of the Skull: Mandible of Intact Skull" |
||
* {{MeshName|Mandibular+condyle}} |
* {{MeshName|Mandibular+condyle}} |
||
* {{cite web|url=http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34256.000-2.html|title=Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-2|work=Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator|publisher=Elsevier|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140101000000/http://www.tk.de/rochelexikon/pics/s34256.000-2.html|archivedate=2014-01-01|url-status=dead}} |
|||
* {{RocheLexicon|34256.000-2}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Facial bones}} |
{{Facial bones}} |
||
{{Portal bar|Anatomy}} |
|||
{{Authority control}} |
|||
[[Category:Bones of the head and neck]] |
[[Category:Bones of the head and neck]] |
||
{{musculoskeletal-stub}} |
|||
[[it:Condilo mandibolare]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[pt:Côndilo]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 04:27, 6 December 2024
| Condyloid process | |
|---|---|
 Position of condyloid process (shown in red). | |
 Mandible. Condyloid processes are shown in red. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus condylaris mandibulae |
| MeSH | D008335 |
| TA98 | A02.1.15.035 |
| TA2 | 872 |
| FMA | 52836 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The condyloid process or condylar process is the process on the human and other mammalian species' mandibles that ends in a condyle, the mandibular condyle. It is thicker than the coronoid process of the mandible and consists of two portions: the condyle and the constricted portion which supports it, the neck.
Condyle
[edit]The most superior part of the mandible, the condyle presents an articular surface for articulation with the articular disk of the temporomandibular joint;[1] it is convex from before backward and from side to side, and extends further on the posterior than on the anterior surface.
Its long axis is directed medialward and slightly backward, and if prolonged to the middle line will meet that of the opposite condyle near the anterior margin of the foramen magnum.
At the lateral extremity of the condyle is a small tubercle for the attachment of the temporomandibular ligament.
The articular surface of the condyle is covered by fibrous tissue, and interfaces with an articular disk (or meniscus) of avascular, non-innervated fibrous tissue (collagen, fibroblasts). When the mouth is closed the meniscus is bordered medially and superiorly by the glenoid fossa of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. When the mouth is opened maximally, the meniscus is distracted anteriorly and inferiorly along the slope of the inferior portion of the temporal bone towards the tubercle, or articular eminence, in order to remain interposed between the condyle and the temporal bone in all jaw positions.
Neck
[edit]The neck of the process rises from the posterior of the ramus mandibulae.[1] It is flattened from before backward, and strengthened by ridges which descend from the forepart and sides of the condyle.
Its posterior surface is convex; its anterior surface has a depression for the attachment of the lateral pterygoid muscle.[1]
Fractures
[edit]Since the articular disk prevents the mandible from moving posteriorly, the condylar neck is often subject to fracturing when the jaw suffers a blow.[1]
Additional images
[edit]-
Position of condyloid process (shown in red)
-
Mandible. Position of condyloid process is shown in red.
-
Mandible. Outer surface. Side view. (Condyle and neck labeled at upper right.)
-
Inner surface of mandible. Condyloid process is at upper left.
-
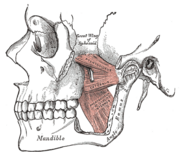
The Pterygoidei; the zygomatic arch and a portion of the ramus of the mandible have been removed.
-
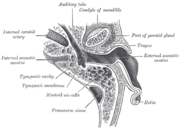
Horizontal section through left ear; upper half of section.
-
Frequency of mandibular fractures by location.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 174 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 174 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
[edit]- lesson1 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Anatomy photo:22:os-1001 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Osteology of the Skull: Mandible of Intact Skull"
- Mandibular+condyle at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.