Fort Loyal: Difference between revisions
Hantsheroes (talk | contribs) |
m Removed erroneous space |
||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 13 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox military installation |
|||
'''Fort Loyal''' was a [[United Kingdom|British]] [[Colonialism|colonial]] outpost built during the [[King William's War]] at Falmouth (present-day [[Portland, Maine]]) in [[Casco Bay]]. It was later replaced by the New Casco Fort. |
|||
|name = Fort Loyal |
|||
|location = Portland, Maine |
|||
|image = Fort Loyal 1763.jpg |
|||
|caption = Fort Falmouth on Falmouth Neck; map by Henry Barnsley, 1763 |
|||
|type = Fort |
|||
|built = 1678 |
|||
|materials = log palisade |
|||
|used = 1678-1690, 1742-1763, 1775-1783 |
|||
|controlledby = [[Great Britain]] |
|||
|garrison= 15 |
|||
|past_commanders = [[Edward Tyng (military officer)|Edward Tyng]], George Lockhart, Sylvanus Davis, Moses Fowler, Abner Lowell |
|||
|battles = [[Battle of Fort Loyal]] |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Fort Loyal''' was a British settler refuge and [[Colonialism|colonial]] outpost built in 1678 at Falmouth (present-day [[Portland, Maine]]) in [[Casco Bay]]. It was destroyed in 1690 by [[Abenaki]] and [[Kingdom of France|French]] forces at the [[Battle of Falmouth (1690)|Battle of Fort Loyal]]. The fort was rebuilt in 1742 and renamed '''Falmouth Fort''' before [[King George's War]] and rearmed again in 1755 for the [[French and Indian War]]. The fort was rebuilt a final time in 1775 for the [[American Revolutionary War|American Revolution]].<ref>Robert B. Roberts, Encyclopedia of Historic Forts: The Military, Pioneer, and Trading Posts of the United States, Macmillan: New York, 1988, 10th printing, {{ISBN|0-02-926880-X}}, page 367</ref> |
|||
The |
The peninsula was first colonized by the English in 1632 as a fishing and trading village named '''Casco'''. When the [[Massachusetts Bay Colony]] absorbed the [[Province of Maine]] in 1658, the town's name changed to '''Falmouth'''. In 1676, the village was destroyed by the [[Abenaki]] during [[King Philip's War]]. English colonists returned two years later when peace resumed. |
||
Fort Loyal was built in 1678 in the center of Portland at the foot of present-day India Street. |
Fort Loyal was built in 1678 in the center of Portland at the foot of present-day India Street to protect the town from future attacks. In 1690 Fort Loyal consisted of four wooden blockhouses and eight guns. During [[King William's War]], a raiding party of French and Native allies destroyed the English settlement and massacred its inhabitants in the [[Battle of Fort Loyal]] (1690). At the end of the conflict Massachusetts did not rebuild the fort, instead building [[Fort Casco]] in [[Falmouth, Maine|Falmouth]]. |
||
The fort was rebuilt in 1742 and renamed "Falmouth Fort" before [[King George's War]] and then rearmed during the [[French and Indian War]] in 1755.<ref>William Willis, History of Portland, 431.</ref> |
|||
During [[King William's War]], a raiding party of French and Native allies attacked and largely destroyed it again in the [[Battle of Fort Loyal]] (1690). |
|||
Reverend Thomas Smith described the 1759 celebration at the fort in Falmouth upon the arrival of news that [[Battle of the Plains of Abraham|Quebec had fallen]]: "The cannon were fired at the fort yesterday and today. Mr. Mayhew's house was illuminated, and small arms fired in the evening, upon further and more authentic news of the victory at Quebec."<ref>The last mention of the fort I could find: W.M. Willis, Journals of the Rev. Thomas Smith and the Rev. Samuel Deane(Portland: 1849), 74.</ref> |
|||
== Fort New Casco == |
|||
With the ruin of Fort Loyal, a [[palisade]]d fort was built in [[Falmouth, Maine]] on [[Casco Bay]], built in 1698 after the conclusion of [[King William's War]]. This fort was the largest on the east coast.<ref>[http://books.google.ca/books?id=UXMFAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q=fort&f=false William Willis. History of Portland, p. 313]</ref> Fort New Casco's site today lies opposite Pine Grove Cemetery on Route 88. Fort New Casco lay at the boundary between Massachusetts and the Abenaki in 1700. Massachusetts built the fort at the behest of local Abenaki who desired a convenient place to trade and sharpen tools. A 1701 meeting between local Abenaki-Pigwackets and Massachusetts officials cemented an alliance between the two. A pair of stone cairns were then erected to symbolize the new partnership. The nearby Two Brothers Islands later received their name from this now long-forgotten monument.<ref>http://w3.salemstate.edu/~ebaker/earthfast/earthfastpaper.html</ref> |
|||
Earthworks were constructed on the Fort Loyal site in 1775 as part of harbor defenses during the [[American Revolutionary War|American Revolution]] and known as the "Lower Battery." Elements from earlier iterations of the fort, such as the guard house, were still in use. The bluff on which the fort had been located was leveled off during the construction of the [[Grand Trunk Railway]] in the 1850s. Today the fort's location is memorialized by a plaque on the Grand Trunk Office Building at the corner of India and Thames Streets in Portland.<ref>Nathan Goold, "Falmouth Neck in the Revolution" in Collections and Proceedings of the Maine Historical Society, second series, vol. III (Portland, 1897), 85.</ref> |
|||
Unfortunately this peace would last less than three years, with the inauguration of [[Queen Anne's War]] in 1702. Governor [[Joseph Dudley]] held a [[Treaty of Casco (1703)|conference]] at New Casco with representatives of the [[Abenaki]] tribes on June 20, 1703, trying to convince them not to ally with the French. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
His efforts were unsuccessful, as the fort was besieged only two months later by Abenaki chiefs Moxus, Wanungonet, Assacombuit and their [[Kingdom of France|French]] Allies in the [[Northeast Coast Campaign (1703)]]. [[John March]] was the commander of the fort.<ref>[http://books.google.ca/books?id=UXMFAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q=fort&f=false William Willis. History of Portland, p. 313]</ref> vastly outnumbered English were relieved by the armed vessel "Province Galley", which dispersed the Abenaki and the some 500 French with its guns. The natives killed 25 English and took many others prisoner.<ref>[http://books.google.ca/books?id=UXMFAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover&source=gbs_ge_summary_r&cad=0#v=onepage&q=fort&f=false William Willis. History of Portland, p. 312]</ref> |
|||
In January 1707, at Casco (specifically Black Point, Maine, near present-day [[Portland, Maine|Portland]]), [[Winthrop Hilton]] ambushed 18 natives as they slept and massacred all but one. Later that year, Hilton also participated in the [[Siege of Port Royal (1707)|Siege of Port Royal]]. |
|||
Major [[Samuel Moody]] became the commander of the fort in 1707.<ref>William Willis, p. 317</ref> |
|||
Peace returned in 1713 with the [[Treaty of Portsmouth (1713)|Treaty of Portsmouth]]. When the resettlement of present-day Portland began in 1716, the [[Province of Massachusetts Bay|Province of Massachusetts]] ordered that the fort at New Casco be demolished rather than maintain it. The vision that built Fort New Casco in 1700, that of a partnership between the English and Native Americans, was dead.<ref>{{Citation |
|||
| last = Varney |
|||
| first = George J. |
|||
| title = Gazetteer of the state of Maine. Falmouth |
|||
| place = Boston |
|||
| publisher = Russell |
|||
| year = 1886 |
|||
| url = http://history.rays-place.com/me/falmouth-me.htm }} |
|||
</ref> |
|||
The [[Fort Loyal|New Casco Fort]] was used throughout [[KIng Georges War]] and then repaired during the [[French and Indian War]] in 1755.<ref>[https://archive.org/stream/historyofportlan1865will#page/431/mode/1up p.431]</ref>New Casco could not be safely settled by the English until the [[Battle of the Plains of Abraham|fall of Quebec]] in 1759 permanently removed the threat of French and Indian attack. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
{{Coord|43.6590|-70.2481|display=title}} |
|||
{{coord missing|Maine}} |
|||
[[Category:Military history of Acadia]] |
[[Category:Military history of Acadia]] |
||
[[Category:Colonial forts in Maine|Loyal]] |
[[Category:Colonial forts in Maine|Loyal]] |
||
[[Category: |
[[Category:Military in Portland, Maine]] |
||
[[Category:1678 establishments in the Thirteen Colonies]] |
|||
[[Category:17th-century establishments in Maine]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 18:10, 7 December 2024
| Fort Loyal | |
|---|---|
| Portland, Maine | |
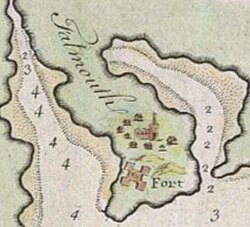 Fort Falmouth on Falmouth Neck; map by Henry Barnsley, 1763 | |
| Type | Fort |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by | Great Britain |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1678 |
| In use | 1678-1690, 1742-1763, 1775-1783 |
| Materials | log palisade |
| Battles/wars | Battle of Fort Loyal |
| Garrison information | |
| Past commanders | Edward Tyng, George Lockhart, Sylvanus Davis, Moses Fowler, Abner Lowell |
| Garrison | 15 |
Fort Loyal was a British settler refuge and colonial outpost built in 1678 at Falmouth (present-day Portland, Maine) in Casco Bay. It was destroyed in 1690 by Abenaki and French forces at the Battle of Fort Loyal. The fort was rebuilt in 1742 and renamed Falmouth Fort before King George's War and rearmed again in 1755 for the French and Indian War. The fort was rebuilt a final time in 1775 for the American Revolution.[1]
The peninsula was first colonized by the English in 1632 as a fishing and trading village named Casco. When the Massachusetts Bay Colony absorbed the Province of Maine in 1658, the town's name changed to Falmouth. In 1676, the village was destroyed by the Abenaki during King Philip's War. English colonists returned two years later when peace resumed.
Fort Loyal was built in 1678 in the center of Portland at the foot of present-day India Street to protect the town from future attacks. In 1690 Fort Loyal consisted of four wooden blockhouses and eight guns. During King William's War, a raiding party of French and Native allies destroyed the English settlement and massacred its inhabitants in the Battle of Fort Loyal (1690). At the end of the conflict Massachusetts did not rebuild the fort, instead building Fort Casco in Falmouth.
The fort was rebuilt in 1742 and renamed "Falmouth Fort" before King George's War and then rearmed during the French and Indian War in 1755.[2]
Reverend Thomas Smith described the 1759 celebration at the fort in Falmouth upon the arrival of news that Quebec had fallen: "The cannon were fired at the fort yesterday and today. Mr. Mayhew's house was illuminated, and small arms fired in the evening, upon further and more authentic news of the victory at Quebec."[3]
Earthworks were constructed on the Fort Loyal site in 1775 as part of harbor defenses during the American Revolution and known as the "Lower Battery." Elements from earlier iterations of the fort, such as the guard house, were still in use. The bluff on which the fort had been located was leveled off during the construction of the Grand Trunk Railway in the 1850s. Today the fort's location is memorialized by a plaque on the Grand Trunk Office Building at the corner of India and Thames Streets in Portland.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Robert B. Roberts, Encyclopedia of Historic Forts: The Military, Pioneer, and Trading Posts of the United States, Macmillan: New York, 1988, 10th printing, ISBN 0-02-926880-X, page 367
- ^ William Willis, History of Portland, 431.
- ^ The last mention of the fort I could find: W.M. Willis, Journals of the Rev. Thomas Smith and the Rev. Samuel Deane(Portland: 1849), 74.
- ^ Nathan Goold, "Falmouth Neck in the Revolution" in Collections and Proceedings of the Maine Historical Society, second series, vol. III (Portland, 1897), 85.
